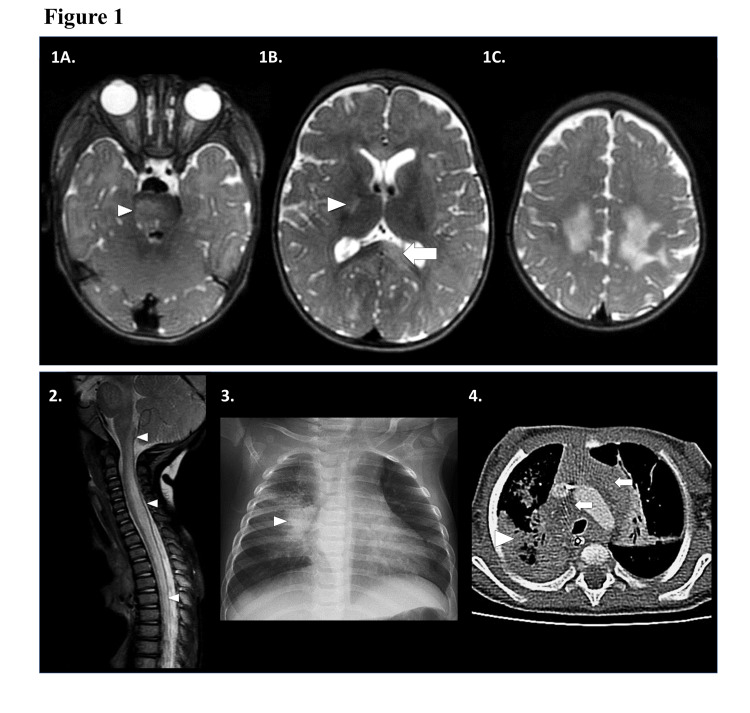
Figure 1. Neuroimaging and chest imaging.
1) MRI brain, transaxial T2-weighted images showing multifocal T2-hyperintense foci in the: (A) right pons [white arrowhead]; (B) posterior limb of the right internal capsule [white arrowhead] and left splenium of the corpus callosum [white arrow]; (C) bilateral centrum semiovale and frontoparietal subcortical white matter. Other MRI sequences not shown revealed no associated reduced diffusivity, blood products, or contrast enhancement. 2) MRI spine, sagittal T2-weighted image showing extensive bilateral intramedullary T2-hyperintense edema and swelling along the cervicomedullary junction and throughout the cervical, upper and visualized mid thoracic spinal cord. No associated contrast enhancement was present on other MRI sequences. 3) Frontal chest radiograph: right perihilar opacity and hilar lymphadenopathy [white arrowhead]. Additional right upper, and left lower pneumonia and left hilar lymphadenopathy present. 4) Transaxial contrast-enhanced CT chest: dense necrotic right lower lobe [white arrowhead] with additional right middle and left upper lobe pneumonia, and bilateral bulky mediastinal lymphadenopathy [white arrows]. There was no enhancement or reduced diffusion.