Supplemental Digital Content is available in the text.
Abstract
Background.
Hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion (HOPE) reduces ischemia-reperfusion injury of donor livers and is increasingly used in clinical transplantation. However, it remains unclear whether perfusion via the portal vein alone (HOPE) or via both the portal vein and hepatic artery (dual HOPE or DHOPE) is superior.
Methods.
Twelve porcine livers donated after circulatory death were randomized for 2 h of HOPE (n = 6) or DHOPE (n = 6), followed by 4 h of warm reperfusion with whole blood, to mimic transplantation. Hepatobiliary and endothelial cell function and injury markers were determined in perfusate and bile samples. Biopsies of bile ducts, hepatic arteries, and liver parenchyma were collected to assess histological damage and the expression of endothelial protective genes (KLF-2, eNOS, ET-1, CD31, VWF, VEGF-A).
Results.
There were no differences in hepatobiliary function and injury after warm reperfusion between the groups, apart from a 2-fold lower concentration of alanine aminotransferase in the perfusate (P = 0.045) and a lower peak lactate dehydrogenase in bile (P = 0.04) of livers preserved by DHOPE. Endothelial cell function and injury, as assessed by perfusate nitric oxide and von Willebrand factor antigen levels, as well as endothelial protective gene expressions, were similar between the groups. The hepatic arteries of both groups showed no microscopic evidence of injury.
Conclusions.
This study did not reveal major differences in hepatobiliary or endothelial function and injury after preservation by single or dual HOPE of porcine livers donated after circulatory death.
INTRODUCTION
End-ischemic ex situ hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion (HOPE) reduces ischemia-reperfusion injury of donor livers.1-3 Hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion is generally performed at 4–12°C and has been shown to resuscitate the mitochondria. This results in restoration of cellular ATP levels and a reduction of reactive oxygen species formation after subsequent warm reperfusion, thereby reducing injury of cholangiocytes, hepatocytes, and endothelial cells.1,3 Hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion can be performed via the portal vein alone (HOPE) or via both the portal vein and hepatic artery (dual HOPE or DHOPE). The clinical efficacy of both HOPE and DHOPE is currently being evaluated in multicenter, randomized clinical trials.4
Whether DHOPE has benefits over HOPE is still a matter of debate.5-7 DHOPE mimics the physiological situation better than HOPE, and this might be particularly beneficial for the bile ducts and cholangiocytes (epithelial cells lining the bile ducts), as these are mainly perfused via the hepatic artery. The hepatic artery drains into the peribiliary vascular plexus (PVP), which is the microvasculature that provides oxygen and nutrients to the bile ducts. It has previously been demonstrated that DHOPE prevents arteriolonecrosis of the PVP and thus reduces biliary injury.8,9 This, however, has not yet been studied for HOPE.
In addition, DHOPE may provide biomechanical stimulation of the arterial endothelium, which is lacking in HOPE. Several studies have described a positive effect of biomechanical stimulation on endothelial cells, as it enhances the expression of transcription factor Krüppel-like factor 2 (KLF-2), which in turn induces upregulation of cytoprotective genes, such as endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS).10-13 eNOS is responsible for the production of nitric oxide (NO), which stimulates vasodilatation. Furthermore, KLF-2 expression results in downregulation of endothelin-1 (ET-1), which is a vasoconstrictor.14-16 The combination of increased vasodilatation and reduced vasoconstriction leads to improved blood flow through the PVP and may thus provide better preservation of the bile ducts and biliary epithelial cells.
We, therefore, hypothesized that DHOPE is superior to HOPE in regards to preservation and protection of the hepatic endothelium and bile ducts due to biomechanical endothelial cell stimulation and better perfusion of the PVP. In this study, we compared HOPE and DHOPE by assessing endothelial and biliary epithelial cell function and injury in a porcine donation after circulatory death (DCD) ex situ warm reperfusion model.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study Groups
An established porcine DCD liver model was used for this study.17 Porcine livers were obtained from the local slaughterhouse. Before procurement, livers were randomized to undergo either end-ischemic HOPE or DHOPE. Randomization was performed by opening a sealed envelope containing information on the group assignment. Twelve livers were included in this study, and all underwent 2 h of hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion after a period of static cold storage; 6 of the livers were perfused via the portal vein alone (HOPE group) and the other 6 livers via both the portal vein and hepatic artery (DHOPE group). After (D)HOPE, all livers underwent 4 h of normothermic ex situ reperfusion using heparinized porcine whole blood to mimic transplantation.
Procurement of the Livers
Large white landrace pigs weighing between 100 and 120 kg were terminated in a standard manner by electrocution and exsanguination. Two liters of blood were collected in a beaker containing 25 000 IU of heparin (Heparin LEO 5000 IU/ml, LEO Pharmaceutical Products, Ballerup, Denmark) for ex situ reperfusion. Blood and liver were obtained from the same pig. The procedure mimicked a DCD procedure. Donor warm ischemia time, defined as the time from cardiac arrest until hepatic cold flush via the portal vein, was kept under 30 min.
All thoracic and abdominal organs were excised en-bloc, and the liver was removed during the back-table procedure. The portal vein was cannulated using a 24 Fr cannula (Organ Assist, Groningen, the Netherlands). Cold flush via the portal vein was performed by gravity with 1 L of cold (4°C) 0.9% NaCl with the addition of 25 000 IU of heparin, immediately followed by 2 L of cold Belzer University of Wisconsin (UW) Machine Perfusion Solution (Bridge-to-Life, Ltd, Northbrook, IL). After cold flush via the portal vein, the hepatic artery and aorta were dissected free for cannulation, and the side branches were clipped. After cannulation of the supratruncal abdominal aorta, cold flush of the hepatic artery was carried out using a syringe with Belzer UW Machine Perfusion Solution. The cystic duct was ligated, and the common bile duct was gently flushed using a syringe with preservation solution and cannulated with an 8 Fr Meredith silicon catheter for bile collection after warm reperfusion.
Hypothermic Machine Perfusion
Machine perfusion was performed using the Liver Assist (Organ Assist, Groningen, the Netherlands). The disposable perfusion circuit was primed with Belzer UW Machine Perfusion Solution for (D)HOPE. The temperature of the fluid was kept at 10°C, and portal perfusion pressure was set at 5 mm Hg. In the DHOPE group, arterial perfusion pressure was set at 25 mm Hg. In both groups, adequate oxygenation was achieved by 1 L/min of 100% oxygen using an inline membrane oxygenator. Perfusate gas analyses were carried out at hourly intervals by using a handheld i-STAT device (Abbott Point of Care, Princeton, NJ). Immediately after termination of (D)HOPE, the liver was flushed out by gravity with consecutively 1 L of cold 0.9% NaCl and 1 L of 0.9% NaCl at room temperature.
Ex Situ Warm Reperfusion
After (D)HOPE, livers underwent 4 h of ex situ warm reperfusion with porcine whole blood to mimic transplantation. During (D)HOPE, a second Liver Assist was primed with the 2 L of heparinized porcine whole blood.
The temperature was set at 37°C, and portal and arterial perfusion pressures were set at 11 and 75 mm Hg, respectively. Livers were oxygenated with 1 L/min of carbogen (95% oxygen/5% carbon dioxide). Blood gas analyses were performed at hourly intervals. If necessary, blood pH was corrected by the addition of bolus doses of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3–). Blood samples were collected every hour and following centrifugation at 1500 rcf for 10 min, plasma was obtained and stored in aliquots at –80°C until analysis.
Bile was collected in Eppendorf tubes under mineral oil to prevent gas exchange between the bile and ambient air. Biliary pH, bicarbonate, and glucose were determined every 30 min, using a handheld i-STAT device.
Biopsies of liver parenchyma and extrahepatic bile duct (EHBD) were collected after liver procurement, after (D)HOPE, and at the end of warm reperfusion. Hepatic artery biopsies were also collected at the end of warm reperfusion. Biopsies were snap-frozen and stored in 10% formalin and later embedded in paraffin. Paraffin-embedded tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin.
Hepatic Parenchymal Function and Injury
Hepatic parenchymal injury and function were assessed during warm reperfusion by determination of blood pH, lactate, and glucose concentrations, as well as serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), using routine biochemical analysis. ALT concentrations were corrected for baseline levels in porcine blood before connection of the liver.
Cholangiocellular Function and Bile Duct Injury
Histological signs of bile duct injury were assessed by an established scoring system, as described by op den Dries et al.9 In addition, immunohistochemistry for von Willebrand factor (VWF) was performed to determine peribiliary vascular density of both intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts. VWF antibody (Dako, Glostrup, Denmark) was applied to deparaffinized slides in a dilution of 1:250 according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Arterioles of the PVP that were positively stained for VWF were counted at a magnification of ×20, and the mean of 5 fields per slide was used to calculate the vascular density score. All histological assessments were performed by 2 independent investigators (YdV and IMAB), who were blinded for the perfusion group and supervised by an experienced hepato-pathologist (ASHG).
In addition, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) concentration in bile samples was determined as a marker of biliary epithelial cell death.18 Biliary pH, bicarbonate, and glucose were used as established biomarkers of biliary injury and function.19
Endothelial Cell Function and Injury
Endothelial cell function and injury were determined by a combination of biochemical and molecular biomarkers, as well as vascular histology.
Healthy endothelial cells produce NO. Total NO concentration in blood samples during reperfusion was determined using a Nitrate/Nitrite Colorimetric Assay Kit (Cayman Chemical, Ann Arbor, MI), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. NO concentrations were corrected for baseline values.
VWF antigen levels in perfusate were determined with an in-house ELISA as described previously.20 Perfusate samples that were obtained during warm reperfusion were diluted 1:500. VWF antigen levels were corrected for baseline. In addition, liver parenchyma biopsies were immunostained for VWF to determine the amount of VWF that was attached to the sinusoidal (sub)endothelium of the portal triads and sinusoids, as well as the septa. VWF antibody (Dako, Glostrup, Denmark) was applied to deparaffinized slides in a dilution of 1:250 according to the manufacturers’ instructions.
Biopsies of the hepatic artery, taken at the end of warm reperfusion, were used to determine ATP concentration, as described previously.21 Furthermore, immunohistochemistry staining was performed for the endothelial cell stress protein, erythroblast transformation specific-related gene (ERG) (Ventana Medical Systems, Oro Valley, AZ), using a machine (Ventana Benchmark, Roche, Bazel, Switzerland) for staining via a standardized protocol.
Gene Expression of Endothelial Proteins
Snap-frozen biopsies were used for the determination of biomechanical stress-induced gene expression of endothelial proteins (Table S1, SDC, http://links.lww.com/TXD/A346s). RNA was isolated from liver parenchyma and hepatic artery using TRIzol (Invitrogen Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA). Concentrations of RNA were measured spectrophotometrically (Nanodrop Technologies, Wilmington, DE). Subsequently, RNA was run by electrophoresis to verify RNA quality with UV-light (Bio-Rad Gel Doc EZ Imager). RNA was copied to cDNA, using M-MLV Reverse Transcriptase (Invitrogen, Basel, Switzerland). For quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR), primers were designed using Primer Express Software (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA), verified with Blast NCBI, and ordered at Invitrogen. GAPDH was used as a housekeeping gene. cDNA was amplified and detected with Quantstudio 7 Flex Real-Time PCR System (Thermo Fisher). Data were analyzed using Quant Studio Real-Time PCR Software v1.3 (Thermo Fisher).
Statistical Analyses
Continuous variables are presented as means with standard deviations. Categorical variables are presented as numbers and percentages. Continuous variables were analyzed using the T-test and categorical variables using the Chi-square test. For repeated measurements of continuous variables, the area under the curve (AUC) was calculated. AUCs between the groups were compared using the T-test. The paired T-test was used for paired data. Categorical variables were compared using the chi-square test. Analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics 23 and Graph Pad Prism 5. A P value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
There were no differences in baseline characteristics between HOPE and DHOPE. Donor warm ischemia time was 26 ± 5 min in the HOPE group and 24 ± 6 min in the DHOPE group (P = 0.48). Cold ischemia time was 140 ± 27 min in the HOPE group and 129 ± 28 min in the DHOPE group (P = 0.51).
Machine Perfusion Characteristics
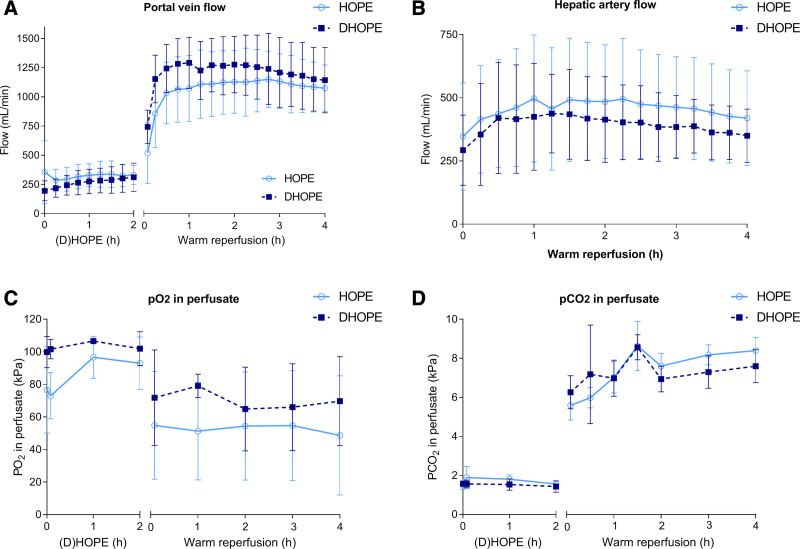
There were no significant differences in either portal vein flow or hepatic artery flow between the 2 groups (Figure 1A and B). Oxygen saturation of the perfusion fluid of both groups was between 97% and 100% during (D)HOPE and warm reperfusion. Perfusate arterial Po2 and Pco2 were not different between the groups during (D)HOPE and warm reperfusion (Figure 1C and D).
FIGURE 1.
Machine perfusion characteristics. (A) Portal vein flow and (B) hepatic artery flow were similar between HOPE and DHOPE during hypothermic machine perfusion and warm reperfusion. (C) Po2 and (D) Pco2 in the perfusate during (D) HOPE and warm reperfusion were similar between the 2 groups. DHOPE, dual hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion; HOPE, hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion.
Hepatic Parenchymal Function and Injury
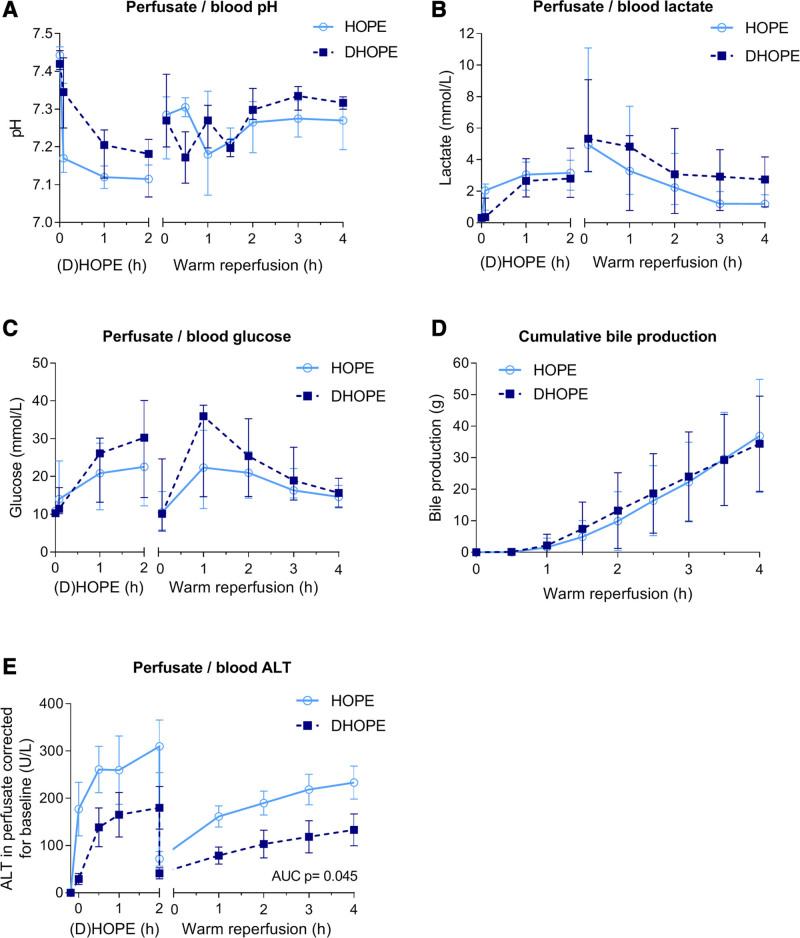
No significant differences in blood pH during warm reperfusion of HOPE or DHOPE-preserved livers were observed (Figure 2A). The total amount of NaHCO3– boluses required to correct a low pH (<7.35) was also not different between the 2 groups: 39 ± 17 mL in the HOPE group and 38 ± 13 mL in the DHOPE group (P = 0.93). There were no significant differences in blood lactate concentrations between the groups after warm reperfusion (Figure 2B). After 4 h of warm reperfusion, glucose concentrations were 15.1 ± 4.6 mmol/L and 15.8 ± 4.1 mmol/L in the HOPE and DHOPE group, respectively (P = 0.78) (Figure 2C). Cumulative bile production during warm reperfusion was similar in both groups, reaching 37 ± 18 mL in the HOPE group and 34 ± 15 mL in the DHOPE group (P = 0.80) (Figure 2D).
FIGURE 2.
Hepatocyte function and injury. (A) Perfusate and blood pH, (B) perfusate and blood lactate concentration, (C) perfusate and blood glucose concentration, (D) cumulative bile production during warm reperfusion. There were no significant differences between the groups in these parameters. (E) Perfusate and blood ALT levels; the AUC was significantly lower for DHOPE preserved livers. ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AUC, area under the curve; DHOPE, dual hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion; HOPE, hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion.
After the initial washout, perfusate ALT concentrations were stable during both HOPE and DHOPE. During warm reperfusion, ALT concentration slightly increased to 233 ± 86 U/L in the HOPE group and 133 ± 83 U/L in the DHOPE group (P = 0.07) (Figure 2E). The AUC including hourly ALT levels during 4 h reperfusion was significantly lower in the DHOPE group (P = 0.045).
Cholangiocellular Function and Bile Duct Injury
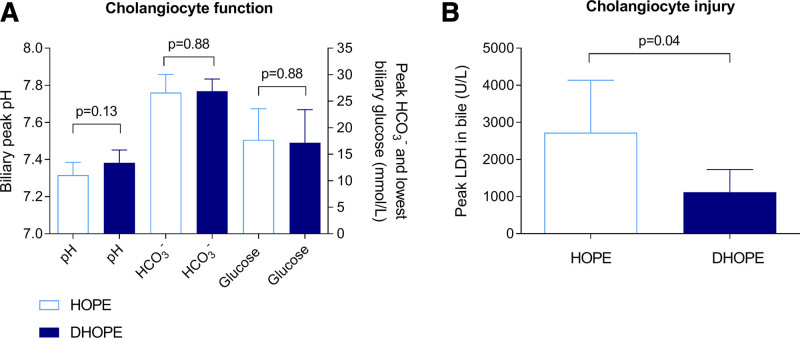
Peak pH of bile did not differ between the groups and was 7.31 ± 0.07 in the HOPE group and 7.38 ± 0.07 in the DHOPE group (P = 0.13) (Figure 3A). The peak biliary HCO3– concentration was not different between the groups (P = 0.88). The lowest glucose level in bile was 17.8 ± 5.6 mmol/L in the HOPE group versus 17.2 ± 6.3 mmol/L in the DHOPE group (P = 0.88). Peak LDH in bile, a marker of cholangiocyte injury, was significantly higher in HOPE-preserved livers, compared with DHOPE-preserved livers (2721 ± 1415 U/L versus 1117 ± 612 U/L; P = 0.04) (Figure 3B).
FIGURE 3.
Cholangiocyte function and injury. (A) Cholangiocyte function did not differ between the 2 groups, based on peak biliary pH, HCO3–, and lowest glucose in bile. (B) Cholangiocyte injury was determined by the LDH concentration in bile, which was significantly lower for DHOPE preserved livers. DHOPE, dual hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion; HCO3-, bicarbonate; HOPE, hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase.
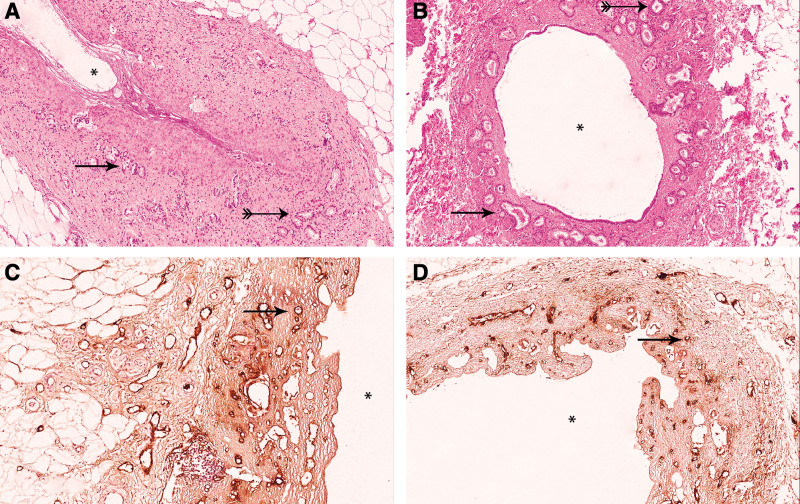
The epithelium lining the luminal side of the extrahepatic and intrahepatic bile ducts was absent in biopsies obtained after procurement, as well as at the end of warm reperfusion in both groups. Peribiliary glands (PBGs) were located either close to the lumen (periluminal PBGs) or at the junction of the stroma and fibromuscular layer of the bile duct wall (deep PBGs) (Figure 4A and B). Damage of the periluminal and deep PBGs of the EHBDs before the start of machine perfusion and at the end of machine perfusion was not different between the 2 groups (Table 1). Periluminal and deep PBG damage did not differ between the HOPE and DHOPE groups.
FIGURE 4.
Histological bile duct injury. (A) H&E stained extrahepatic bile duct. The periluminal PBGs, as indicated by a single arrowhead, were largely intact in both groups. The deep PBGs are indicated by double markings on the arrow and appeared intact in both groups, suggesting a well-preserved niche of progenitor cells. (B) H&E stained intrahepatic bile duct showing >50% of the luminal epithelium intact. The periluminal PBGs, as indicated by a single arrowhead, were largely intact. Deep PBG can be observed but are not always present in IHBD, and these showed almost no signs of histological injury (double marked arrow). (C) VWF stained extrahepatic bile duct (×20). (D) VWF stained IHBD (×10). Asterisks indicates the bile duct lumen. IHBD, intrahepatic bile duct; PBG, peribiliary gland; VWF, von Willebrand factor.
TABLE 1.
Injury of the periluminal and deep PBG of the extrahepatic bile duct after machine perfusion
| HOPE | P a | DHOPE | P b | HOPE vs DHOPE P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Periluminal PBG | |||||
| Grade 1 | 0 | c | 0 | c | c |
| ≤50% epithelial cell loss | |||||
| Grade 2 | 5 (83.3%)d | 6 (100%) | |||
| >50% epithelial cell loss | |||||
| Deep PBG | |||||
| Grade 0 | 0 | 0.14 | 1 (16.7%) | 0.43 | 0.52 |
| No epithelial cell loss | |||||
| Grade 1 | 4 (66.7%) | 4 (66.7%) | |||
| ≤50% epithelial cell loss | |||||
| Grade 2 | 1 (16.7%)d | 1 (16.7%) | |||
| >50% epithelial cell loss | |||||
aP value relative to baseline within the single perfusion group.
bP value relative to baseline within the dual perfusion group.
cP value for epithelial cell loss of the periluminal PBG could not be computed as all livers had >50% loss of epithelial cell lining.
dOne bile duct biopsy was missing. Injury of the PBGs was graded based on epithelial cell loss. Grade 0, no loss of the epithelial cell lining; grade 1, ≤50% loss of epithelial cell lining; grade 2, >50% loss of epithelial cell lining of the PBG. Values displayed in the table are injury scores at the end of normothermic reperfusion.
DHOPE, dual hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion; HOPE, hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion; PBG, peribiliary gland.
No difference in vascular density of the PVP of the EHBDs was found between HOPE and DHOPE. Furthermore, vascular density of the PVP of the intrahepatic bile ducts was similar between HOPE and DHOPE (8 ± 8 and 11 ± 7 counts per field, respectively) (Figure 4C and D).
Endothelial Cell Function and Injury
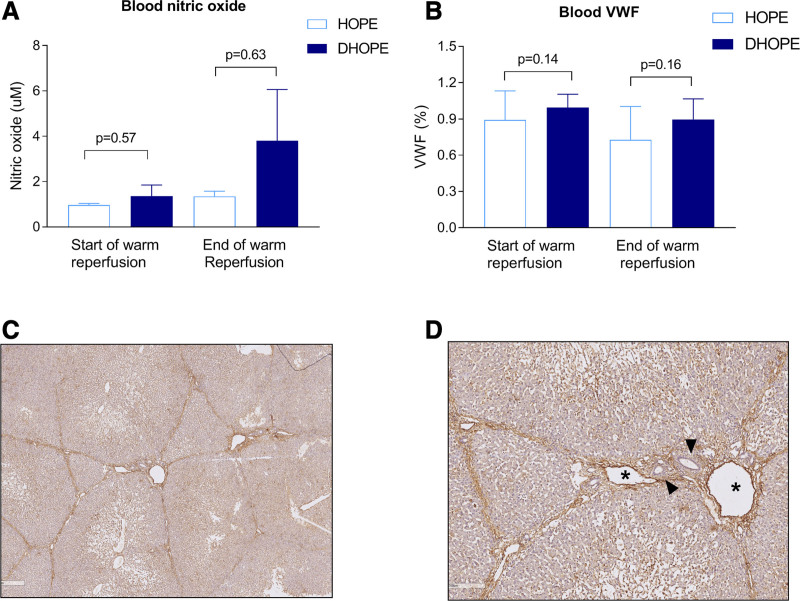
There were no differences in NO production during HOPE or DHOPE. After warm reperfusion, NO production in the DHOPE group was higher compared with the HOPE group, albeit not statistically significant (P = 0.63) (Figure 5A). VWF antigen levels in the perfusate only marginally increased during HOPE and DHOPE and did not change after warm reperfusion (Figure 5B). VWF staining of the liver parenchyma was similar between the groups (Figure 5C and D).
FIGURE 5.
Endothelial cell function and injury. (A) NO concentration corrected for baseline and (B) VWF antigen levels. There were no significant differences between the groups at the start of warm reperfusion and after 4 h. (C) VWF stained liver parenchyma (×10) and (D) VWF stained liver parenchyma (×40) showing a portal triad. Asterisks indicate central vein, and arrowheads indicate bile ducts. DHOPE, dual hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion; HOPE, hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion; NO, nitric oxide; VWF, von Willebrand factor.
Hepatic Artery Function and Injury
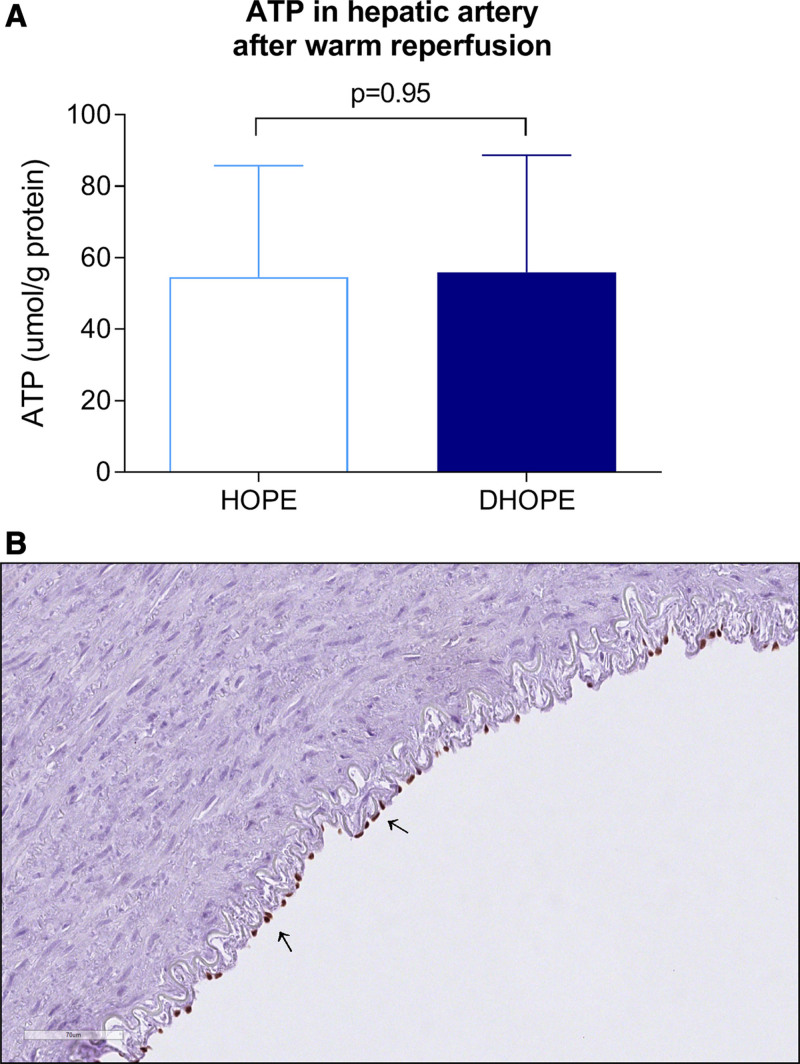
ATP concentration in hepatic artery biopsies was similar after HOPE and DHOPE treatment. After warm reperfusion, ATP concentration was 55 ± 31 µmol/g protein in the HOPE group versus 56 ± 33 µmol/g protein in the DHOPE group (P = 0.95) (Figure 6A).
FIGURE 6.
Hepatic artery function and injury. (A) ATP concentration in hepatic artery biopsies was similar between the groups at the end of warm reperfusion. (B) Representative image of ERG staining of a hepatic artery. At the luminal side of the hepatic artery, positively stained endothelial cells (suggestive for an intact endothelium) are indicated by the arrows. DHOPE, dual hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion; ERG, erythroblast transformation specific-related gene; HOPE, hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion.
Hepatic artery H&E slides of both the HOPE and DHOPE groups showed that all layers of the arterial wall, intima, media, and adventitia, were intact and well preserved. ERG staining revealed a similar amount of endothelial cells at the luminal side in all hepatic arteries in both the HOPE and DHOPE group (Figure 6B).
Gene Expression of Endothelial Proteins
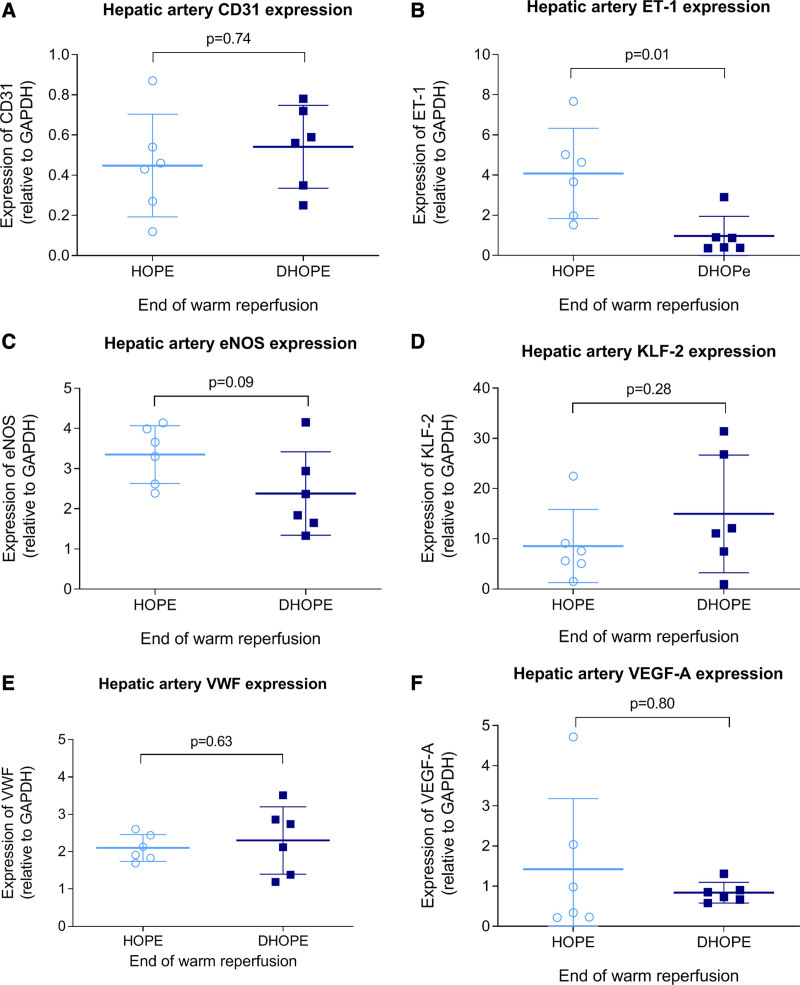
Gene expression of endothelial proteins (KLF-2, eNOS, CD31, VWF, VEGF-A) in hepatic arteries did not differ between HOPE and DHOPE, except for ET-1 expression, which was higher in the HOPE group (P = 0.01) (Figure 7). Gene expression of endothelial proteins (CD31, eNOS, KLF-2, VWF, VEGF-A, ET-1) in liver parenchyma was similar between HOPE and DHOPE.
FIGURE 7.
Gene expression of endothelial proteins in hepatic arteries at the end of warm reperfusion. (A) CD31, (B) ET-1, (C) eNOS, (D) KLF-2, (E) VWF, and (F) VEGF-A. Gene expression was similar between the groups, except for ET-1, which was significantly lower in the DHOPE group. DHOPE, dual hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; ET-1, endothelin-1; HOPE, hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion; KLF-2, Krüppel-like factor 2; VEGF-A, vascular endothelial growth factor A; VWF, von Willebrand factor.
DISCUSSION
This study was designed to investigate whether HOPE versus DHOPE results in differences in hepatobiliary or endothelial injury or function. We hypothesized that DHOPE, compared with HOPE, would provide additional benefits regarding preservation of the hepatic artery endothelium and bile ducts due to biomechanical endothelial cell stimulation and better perfusion of the PVP. Based on the results of this study, we have to refute that hypothesis. There were no differences in hepatobiliary function and injury between livers that were preserved by HOPE or DHOPE, except for a 2-fold lower ALT concentration and a 3-fold lower peak LDH in bile after reperfusion in the DHOPE group. Moreover, biomechanical stimulation of the arterial endothelium by DHOPE did not lead to differences between the 2 preservation techniques in terms of perfusate NO levels and gene expression of endothelial protective proteins. These findings are clinically relevant, as both HOPE and DHOPE are currently studied in multicenter, randomized clinical trials.21,22
It remains a discussion whether hypothermic machine perfusion should be performed through the portal vein alone or via both the portal vein and hepatic artery.5-7 In the physiological situation, the bile ducts, and thus the cholangiocytes, are mainly perfused by the hepatic artery and PVP. Moreover, the expression of cytoprotective genes in the endothelium of hepatic arteries and arterioles is stimulated by shear and pressure-induced stress. The latter can be expected during DHOPE, but to a lesser degree during HOPE. We, therefore, hypothesized that biliary preservation would be superior in livers preserved by DHOPE.
Schlegel et al previously found that perfusion via the portal vein alone (HOPE) results in perfusion of the extrahepatic and intrahepatic bile ducts despite the lack of direct arterial perfusion.5 However, the authors did not provide histological evidence of adequate preservation of the larger bile ducts and the PVP. In the current study, cholangiocyte function and bile duct injury were largely similar between HOPE and DHOPE. In line with other studies, the luminal biliary epithelium was absent after cold storage and before preservation by (D)HOPE, and this does, therefore, not give us information about cholangiocyte injury after machine perfusion from a histological perspective.9,23,24 Injury to the PBGs was not different between HOPE and DHOPE. Therefore, the lower LDH in bile in livers preserved by DHOPE cannot be substantiated from a histological perspective but seems a solitary finding.
It has been suggested that cannulation of the hepatic artery might cause mechanical damage to the endothelium. In the current study, no histological signs of damage to the hepatic artery were observed in either group. It must be noted that for DHOPE, the supratruncal aorta was cannulated instead of the hepatic artery, which is standard clinical practice nowadays. Many clinical trials are now focusing on ex situ rewarming or normothermic machine perfusion, and in these situations, cannulation and perfusion of the aorta or celiac artery are necessary.25-27 There is no evidence for a higher rate of arterial injury or arterial thrombosis posttransplantation after normothermic machine perfusion (own data). Cannulation and ex situ perfusion of donor livers via de hepatic artery should not be omitted for that reason.
Several studies have described a positive effect of biomechanical stimulation on the endothelium due to fluid pressure or shear stress.10-13 We assessed endothelial cell function by gene expression of protective endothelial proteins, such as KLF-2 and its downstream product eNOS. Expression of these genes did not differ between HOPE and DHOPE preserved livers. However, gene expression of ET-1, a protein causing vasoconstriction, was significantly higher in the HOPE group. This is an isolated finding, and we cannot explain why only gene expression of ET-1 was different, as both eNOS and ET-1 are downstream products of KLF-2. The similar gene expression profiles between the groups are in line with other findings of this study, including similar NO concentrations and VWF antigen levels. Altogether, the results from this study indicate that, in addition to portal perfusion, arterial perfusion of donor livers during hypothermic machine perfusion does not provide additional benefit via upregulation of cytoprotective genes/proteins due to biomechanical stimulation of the endothelium.
This study has some limitations. First, the use of relatively good quality DCD livers. Risk factors such as older donor age or hepatic steatosis were absent in our porcine model, which could have contributed to an underestimation of the effect on preservation injury. Furthermore, injury to the livers in the NMP reperfusion model used in the current study might not be as severe as in a transplantation model, where more mediators of ischemia-reperfusion mediated inflammation are present. On the other hand, reactive oxygen species, which are to a large extend responsible for ischemia-reperfusion injury after transplantation, will still be formed in a reperfusion model. Using blood from the same pig may also have mitigated immune responses and, therefore injury, although the impact of an alloimmune response in the pathogenesis of hepatobiliary ischemia-reperfusion injury is limited. Moreover, we did not test the long-term consequences in a transplantation model, such as the development of nonanastomotic biliary strictures, which are a known result of biliary ischemia-reperfusion injury. Last, because of the relatively small sample size we used, subtle significant differences between DHOPE and HOPE may have been missed
In conclusion, this study did not reveal major differences in hepatobiliary or endothelial function and injury after either single or dual HOPE preservation of porcine DCD livers.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to Organ Assist for allowing us to perform the experiments at their wet laboratory and for lending us the 2 Liver Assist machines. We thank Emma Offringa for her assistance with the experiments. We would also like to thank Martin Kuizenga for his advice and help during the procurement of the livers. Finally, we would like to thank the research technicians Susanne Veldhuis, Jelle Adelmeijer, and Janneke Wiersema-Buist for performing the laboratory analyses.
Supplementary Material
Footnotes
Published online 5 August, 2021.
The authors declare no funding or conflicts of interest.
The study was initiated and designed by Y.d.V. and R.J.P. Y.d.V., I.M.A.B., S.A.K., F.A.v.M., O.B.v.L., L.C.B., I.E.M.d.J., A.S.H.G., V.E.d.M., T.L., and R.J.P. contributed to the final study design. Y.d.V., I.M.A.B., S.A.K., F.A.v.M., O.B.v.L., I.E.M.d.J., and R.J.P. participated in the performance of the research. Y.d.V. and R.J.P. participated in data analysis. The article was drafted by Y.d.V., I.M.A.B., and R.J.P. Y.d.V., I.M.A.B., S.A.K., F.A.v.M., O.B.v.L., L.C.B., I.E.M.d.J., A.S.H.G., V.E.d.M., T.L., and R.J.P. edited the article and approved the final version of the article.
Supplemental digital content (SDC) is available for this article. Direct URL citations appear in the printed text, and links to the digital files are provided in the HTML text of this article on the journal’s Web site (www.transplantationdirect.com).
REFERENCES
- 1.van Rijn R, Karimian N, Matton APM, et al. Dual hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion in liver transplants donated after circulatory death. Br J Surg. 2017;104:907–917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schlegel A, Muller X, Kalisvaart M, et al. Outcomes of DCD liver transplantation using organs treated by hypothermic oxygenated perfusion before implantation. J Hepatol. 2019;70:50–57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schlegel A, de Rougemont O, Graf R, et al. Protective mechanisms of end-ischemic cold machine perfusion in DCD liver grafts. J Hepatol. 2013;58:278–286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dutkowski P, Guarrera JV, de Jonge J, et al. Evolving trends in machine perfusion for liver transplantation. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:1542–1547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Schlegel A, Kron P, De Oliveira ML, et al. Is single portal vein approach sufficient for hypothermic machine perfusion of DCD liver grafts? J Hepatol. 2016;64:239–241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Brüggenwirth IMA, Burlage LC, Porte RJ, et al. Is single portal vein perfusion the best approach for machine preservation of liver grafts? J Hepatol. 2016;64:1194–1195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Selten J, Schlegel A, de Jonge J, et al. Hypo- and normothermic perfusion of the liver: which way to go? Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2017;31:171–179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.op den Dries S, Sutton ME, Karimian N, et al. Hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion prevents arteriolonecrosis of the peribiliary plexus in pig livers donated after circulatory death. PLoS One. 2014;9:e88521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.op den Dries S, Westerkamp AC, Karimian N, et al. Injury to peribiliary glands and vascular plexus before liver transplantation predicts formation of non-anastomotic biliary strictures. J Hepatol. 2014;60:1172–1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Pahakis MY, Kosky JR, Dull RO, et al. The role of endothelial glycocalyx components in mechanotransduction of fluid shear stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;355:228–233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rehm M, Bruegger D, Christ F, et al. Shedding of the endothelial glycocalyx in patients undergoing major vascular surgery with global and regional ischemia. Circulation. 2007;116:1896–1906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Burlage LC, Karimian N, Westerkamp AC, et al. Oxygenated hypothermic machine perfusion after static cold storage improves endothelial function of extended criteria donor livers. HPB (Oxford). 2017;19:538–546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gallinat A, Efferz P, Paul A, et al. One or 4 h of “in-house” reconditioning by machine perfusion after cold storage improve reperfusion parameters in porcine kidneys. Transpl Int. 2014;27:1214–1219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dekker RJ, van Thienen JV, Rohlena J, et al. Endothelial KLF2 links local arterial shear stress levels to the expression of vascular tone-regulating genes. Am J Pathol. 2005;167:609–618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Dekker RJ, van Soest S, Fontijn RD, et al. Prolonged fluid shear stress induces a distinct set of endothelial cell genes, most specifically lung Krüppel-like factor (KLF2). Blood. 2002;100:1689–1698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Topper JN, Cai J, Falb D, et al. Identification of vascular endothelial genes differentially responsive to fluid mechanical stimuli: cyclooxygenase-2, manganese superoxide dismutase, and endothelial cell nitric oxide synthase are selectively up-regulated by steady laminar shear stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:10417–10422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Brüggenwirth IMA, van Leeuwen OB, de Vries Y, et al. Extended hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion enables ex situ preservation of porcine livers for up to 24 hours. JHEP Rep. 2020;2:100092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Liu Q, Nassar A, Farias K, et al. Sanguineous normothermic machine perfusion improves hemodynamics and biliary epithelial regeneration in donation after cardiac death porcine livers. Liver Transpl. 2014;20:987–999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Matton APM, de Vries Y, Burlage LC, et al. Biliary bicarbonate, pH, and glucose are suitable biomarkers of biliary viability during ex situ normothermic machine perfusion of human donor livers. Transplantation. 2019;103:1405–1413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Groeneveld DJ, Alkozai EM, Adelmeijer J, et al. Balance between von Willebrand factor and ADAMTS13 following major partial hepatectomy. Br J Surg. 2016;103:735–743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Czigany Z, Schöning W, Ulmer TF, et al. Hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion (HOPE) for orthotopic liver transplantation of human liver allografts from extended criteria donors (ECD) in donation after brain death (DBD): a prospective multicentre randomised controlled trial (HOPE ECD-DBD). BMJ Open. 2017;7:e017558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.van Rijn R, van den Berg AP, Erdmann JI, et al. Study protocol for a multicenter randomized controlled trial to compare the efficacy of end-ischemic dual hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion with static cold storage in preventing non-anastomotic biliary strictures after transplantation of liver grafts donated after circulatory death: DHOPE-DCD trial. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019;19:40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sutton ME, op den Dries S, Karimian N, et al. Criteria for viability assessment of discarded human donor livers during ex vivo normothermic machine perfusion. PLoS One. 2014;9:e110642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Brunner SM, Junger H, Ruemmele P, et al. Bile duct damage after cold storage of deceased donor livers predicts biliary complications after liver transplantation. J Hepatol. 2013;58:1133–1139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nasralla D, Coussios CC, Mergental H, et al. A randomized trial of normothermic preservation in liver transplantation. Nature. 2018;557:50–56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Watson CJE, Kosmoliaptsis V, Pley C, et al. Observations on the ex situ perfusion of livers for transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2018;18:2005–2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.de Vries Y, Matton APM, Nijsten MWN, et al. Pretransplant sequential hypo- and normothermic machine perfusion of suboptimal livers donated after circulatory death using a hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier perfusion solution. Am J Transplant. 2019;19:1202–1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.