Abstract
Mast cells (MCs) play a pathobiologic role in type 2 (T2) allergic inflammatory diseases of the airway, including asthma and chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis (CRSwNP). Distinct MC subsets infiltrate the airway mucosa in T2 disease, including subepithelial MCs expressing the proteases tryptase and chymase (MCTC) and epithelial MCs expressing tryptase without chymase (MCT). However, mechanisms underlying MC expansion and the transcriptional programs underlying their heterogeneity are poorly understood. Here we use flow cytometry and single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) to conduct a comprehensive analysis of human MC hyperplasia in CRSwNP, a T2 cytokine-mediated inflammatory disease. We link discrete cell surface phenotypes to the distinct transcriptomes of CRSwNP MCT and MCTC, which represent polarized ends of a transcriptional gradient of nasal polyp MCs. We discover a subepithelial population of CD38highCD117high MCs that is markedly expanded during T2 inflammation. These CD38highCD117high MCs exhibit an intermediate phenotype relative to the expanded MCT and MCTC subsets. CD38highCD117high MCs are distinct from circulating MC progenitors and are enriched for proliferation, which is markedly increased in CRSwNP patients with aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD), a severe disease subset characterized by increased MC burden and elevated MC activation. We observe that MCs expressing a polyp MCT-like effector program are also found within the lung during fibrotic diseases and asthma, and further identify marked differences between MCTC in nasal polyps and skin. These results indicate that MCs display distinct inflammation-associated effector programs and suggest in situ MC proliferation is a major component of MC hyperplasia in human T2 inflammation.
Keywords: Mast cell, type 2 inflammation, human immunology, nasal polyposis, scRNA-seq
Introduction
Mast cells (MCs) are found in all barrier tissue sites under homeostatic conditions, where they are critical for host defense against helminths, viruses, bacteria, and xenobiotic venoms (1). MC expansion occurs across a spectrum of diseases associated with type 2 (T2) inflammation, including asthma, food allergy, eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), and atopic dermatitis. MCs participate in T2 inflammatory disease progression and severity through eicosanoid biosynthesis, cytokine production, and the release of pre-formed mediators, including histamine and proteases (1–3). Pharmacologic inhibition of the MC survival receptor CD117 using imatinib reduces airway hyperresponsiveness in subjects with refractory asthma but only modestly decreases lung MC burden (2). Thus, developing a better mechanistic understanding of MC hyperplasia in human diseases may enable more directed and effective approaches for targeting MC-dependent pathobiology.
Two major human MC subtypes distinguished by tissue microlocalization and histologically-defined protease expression patterns have been recognized within barrier tissues. Subepithelial MCs co-express the proteases tryptase and chymase (MCTC) in conjunction with cathepsin G and carboxypeptidase A3 (CPA3). Mucosal epithelial MCs express tryptase but lack chymase, cathepsin G and CPA3 (MCT) (4, 5). Rodent studies demonstrate that subepithelial compartments are seeded by fetal-derived β7 integrin (Itgβ7)-expressing MC progenitors (MCP) that maintain the MC populations in these locations through adulthood (6, 7). In contrast, mucosal epithelial MCs arise from adult bone marrow-derived Itgβ7-expressing MCP (8–10). Both the fetal- and adult bone marrow-derived murine MC compartments are strongly influenced by local microenvironments, with fetal-derived MCs expressing tissue-specific transcriptional programs (11) and both MC classes exhibiting tissue-dependent protease expression profiles (12). While a committed human MCP expressing CD34 and Itgβ7 exists in adult peripheral blood (13) and fetal cord blood (14), how mature human tissue MCs are maintained and the degree to which human MCs exhibit tissue-specific phenotypes are unknown.
T2 inflammatory airway disease markedly changes the number, distribution, phenotype, and likely the functional characteristics of MCs. Mild to moderate asthma, EoE, and chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) all involve expansion of an intraepithelial MCT population expressing CPA3, suggesting a common paradigm underlying human mucosal T2 inflammation and a broader “Inflammatory MCT” effector program (15–18). In asthma, the concentrations of these inflammatory MCT correlate with epithelial T2-induced gene signatures and therapeutic responses to inhaled glucocorticoids, while in EoE these inflammatory MCT exhibit degranulation during active disease (15, 18). The airway smooth muscle of severe asthmatics is additionally infiltrated by MCTC, where their concentration correlates with disease severity and airway hyper-responsiveness (16, 19, 20). MCTC also expand in subepithelial glandular tissue in CRSwNP (17). Although the differential effector programs of these MC phenotypes are largely unknown, MCs harvested from polyp epithelium have decreased sensitivity to IgE-mediated activation relative to those from the subepithelium (21), indicating broader functional differences accompanying protease phenotypes. Although the expanded nasal polyp MC pool likely shares key features with that observed across human mucosal T2 inflammation, the determinants of this MC expansion and phenotypic alterations remain largely unknown.
We recently used single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) to deconstruct inflammatory circuits across epithelial, stromal, and immune cells in nasal polyposis, identifying MCs as a source of both T2 inflammatory cytokines (IL5, IL13), and lipid mediator biosynthetic enzymes (ALOX5, ALOX5AP, HPGDS) (22). Here, we utilize directed scRNA-seq, CITE-seq, and flow cytometry to comprehensively characterize human MC phenotypes and hyperplasia within sinonasal tissues from CRS patients with differing degrees of disease severity. Through this approach, we identify distinct cell surface phenotypes and respiratory inflammation-linked transcript expression patterns associated with a nasal polyp intraepithelial MCT program also found in inflamed lung and subepithelial MCTCs highly distinct from those found in the sking.
Our scRNA-seq results further suggest that these divergent polyp MCT (CD38highCD117low) and MCTC (CD38lowCD117high) phenotypes represent two polarized states along a gradient of MC transcript and protein expression, linked by a CD38highCD117high intermediate MC. These CD38highCD117high MCs, present at low concentration in control tissue from CRS patients without nasal polyps (CRSsNP), are substantially expanded in CRSwNP tissue. This expansion is associated with local proliferation, a process that is significantly increased in tissue from patients with aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD), a severe CRSwNP disease variant associated with asthma, rapid nasal polyp growth and high concentrations of MC activation products in biological fluids (23). Thus, our findings identify T2I-associated MCT and MCTC phenotypes, characterize an intermediate tissue-resident CD38high CD117high MC transcriptionally linked to both archetypal MC subsets present in polyposis, and suggest MC hyperplasia found in this T2 disease arises in part from local MC proliferation.
Results
Characterization of the expanded MC population in T2 inflammation.
Consistent with prior studies (24), flow cytometric analysis demonstrated a prominent population of CD45+lin(CD3, CD19, CD11b CD11c)-FcεR1α+CD117+ MCs in human nasal polyps that was expanded relative to control tissue from patients with CRSsNP (Fig. 1A). Because patients with nasal polyposis included both aspirin-tolerant subjects and patients with AERD, we further assessed MC concentration between these clinical phenotypes. We noted a significant increase in MC concentration as both percentage of CD45+ and percentage of all live cells in AERD versus CRSwNP and in both polyp populations relative to CRSsNP (Fig. 1B). Thus, MC expansion occurred proportionately to disease severity.
Figure 1: Phenotypic characterization of sinus MC hyperplasia.
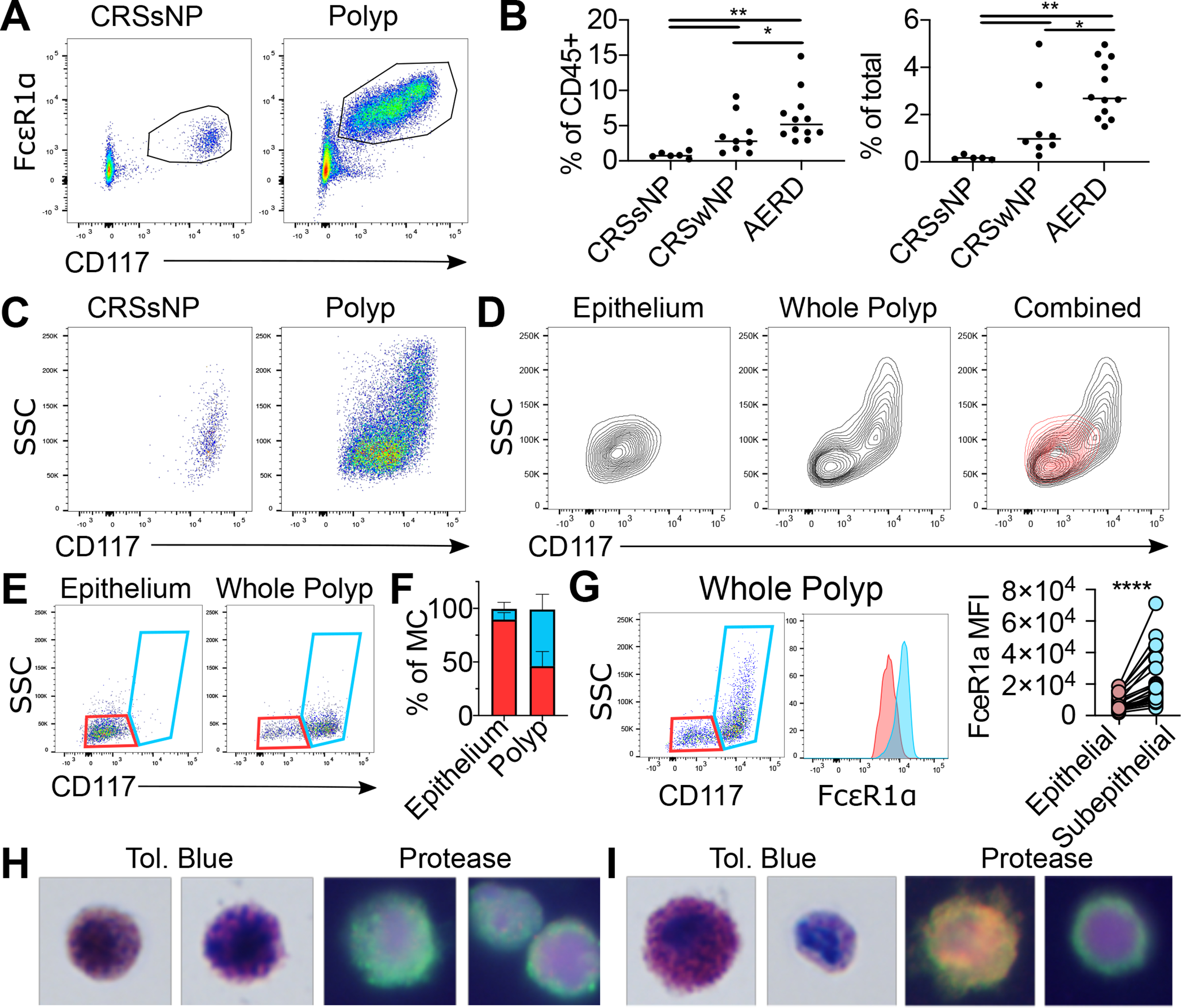
(A) Flow identification of human sinus MCs. (Additional replicates and full gating in Figure S1).
(B) MC quantification as percentage of CD45+ (left) or total cells (right) in indicated patient groups (n=6–12 donors/group). *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01 (Mann-Whitney).
(C) Representative plots showing MC heterogeneity in nasal polyp (left) or CRSsNP tissue (right).
(D) MC phenotype in polyp epithelium (left), whole polyp (center) with overlay (right). Red: epithelium; Black: whole polyp. Representative of five donors.
(E) Gating distinguishing epithelial MCs (CD117low SSClow, red) from subepithelial MCs (CD117high, blue) in epithelial fraction (left panel) vs unfractionated polyp (right panel)
(F) Quantification of epithelial and subepithelial MCs in fractionated epithelium and unfractionated polyp (n=5 donors); *, p<0.05 (paired t-test).
(G) FcεR1α expression of epithelial (red) and subepithelial MCs (blue) with quantification (right). Lines denote paired observations (n=24 donors); ****, p<5 × 10−5 (paired t-test)
(H) Toluidine blue (left) and protease immunophenotyping (right) of sorted CD117low MCs. Two examples provided to show heterogeneity. Green: tryptase; Red: chymase; Yellow: colocalization; Blue: nucleus.
(I) Toluidine blue (left) and protease immunophenotyping (right) of CD117high MCs. Two examples provided to show heterogeneity. Green: tryptase; Red: chymase; Yellow: colocalization; Blue: nucleus.
Nasal polyp MCs exhibited more heterogeneous CD117 expression and side angle light scatter (SSC) than CRSsNP MCs (Fig. 1C), suggesting the presence of one or more additional MC subsets in CRSwNP. Upon fractionating superficial epithelium to analyze intraepithelial MCs, we noted these MCs were CD117lowSSClow, in contrast to unfractionated polyp (Fig. 1D). Based on this observation, we created a flow cytometric gating scheme to distinguish CD117lowSSClow MCs from CD117high MCs (Fig. 1E) and confirmed a highly significant epithelial enrichment for CD117lowSSClow MCs, indicating that CD117high MCs were predominantly subepithelial (Fig. 1F). Epithelial MCs expressed significantly lower FcεR1α than subepithelial MCs (Fig. 1G) and lacked both CCR3 and HLA-DRA despite detection of both proteins in CD45+ CD117- cells, indicating no basophils or dendritic cell (DC) contamination (Fig. S1C–F). Additionally, no clear population expressing the stem cell lineage marker CD34 was detected within the polyp MC pool (Fig. S1G).
We next sorted CD117low SSClow epithelial and CD117high subepithelial MCs for microscopy characterization. MCs within the epithelial-enriched gate contained metachromatic granules (Fig. 1H, left) and expressed tryptase with a granular staining pattern (Fig. 1H, right, channel series shown in Fig. S2A), indicating a mature MCT phenotype. MCs within the subepithelial gate contained a mix of large cells with dense metachromatic granules and smaller less granulated cells with an immature morphology (Fig. 1I, left), suggesting that the range of SSC observed within this gate reflected granular heterogeneity (Fig. 1G). Protease immunostaining indicated that the subepithelial MC pool contained cells co-expressing tryptase and chymase, indicating a MCTC phenotype, as well as MCs exhibiting diffuse tryptase staining without chymase (Fig. 1I, right, channel series shown in Fig. S2B). Consistent with previous studies(17), immunohistologic assessment confirmed that chymase expressing cells were largely restricted to polyp subepithelium (Fig. S2C–D). Thus, MCs within the epithelial gate were MCT characterized by reduced FcεR1α and CD117 expression, while subepithelial polyp MCs, exhibiting increased FcεR1α and CD117, were a mix of MCTC and morphologically immature MCs.
Given the presence of immature-appearing MCs, we next assessed whether Itgβ7+CD34+ human MCPs might participate in polyp MC hyperplasia (13). A subset of SSClow MCs expressing Itgβ7 (Itgβ7high) was observed within both the epithelial and subepithelial gates (Fig. 2A). Polyp Itgβ7high MCs exhibited diffuse tryptase staining and, in contrast to the previously described circulating MCP, contained distinct metachromatic granules (Fig. 2B). Itgβ7high MCs were virtually absent in CRSsNP tissue (Fig. 2C) and present in similar concentrations in CRSwNP and AERD relative to total MCs (Fig. 2D). Unlike circulating MCp, Itgβ7high MCs were CD34- (Fig. 2E). Itgβ7 pairs with the integrins αE and α4, forming either αEβ7, recognizing the epithelial adhesion molecule E-cadherin, or α4β7, recognizing VCAM and MadCAM (25, 26). While circulating Itgβ7high MCP expressed only α4, a substantial subset of polyp Itgβ7high MCs co-expressed αE (Fig. 2F). These αEhigh MCs were mostly in the epithelial-enriched CD117low gate, whereas Itgβ7high cells lacking αE were not significantly enriched in either compartment (Fig. 2G). Thus, Itgβ7high polyp MCs are a heterogeneous population distinguished from circulating MCP by lack of CD34 expression, increased granulation, and expression of αE integrin, together likely reflecting maturation in response to the tissue microenvironment. As αEβ7 binds epithelial-associated E-cadherin (25), its expression could promote accumulation or retention in the epithelial compartment.
Figure 2: Identification polyp MCs with a progenitor-like cell surface phenotype.
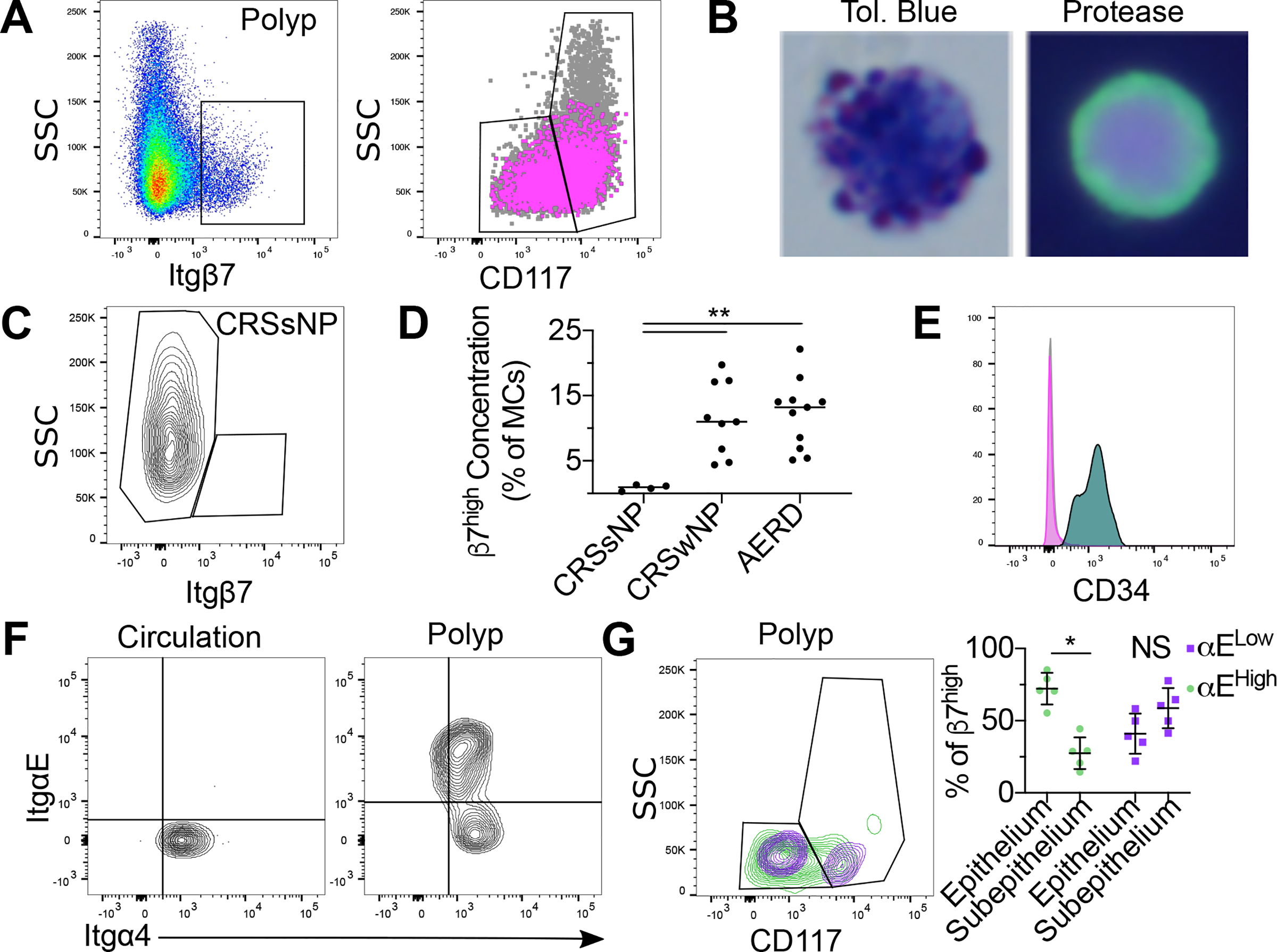
(A) Identification of nasal polyps SSClowItgβ7 high MCs (left). CD117 and SSC expression on Itgβ7high MC (magenta) relative to all polyp MCs (grey) (right).
(B) Toluidine blue (left) and protease immunophenotype (right) of sorted Itgβ7 high polyp MCs MCs. Green: tryptase; Red: chymase; Blue: nucleus
(C) Representative flow plot of Itgβ7 expression on CRSsNP MCs.
(D) Quantification of Itgβ7high MCs as a percentage of total MCs in CRSsNP, CRSwNP and AERD. **, p<0.01 (Mann-Whitney).
(E) CD34 expression on polyp Itgβ7high MCs (magenta) and circulating MCP (turquoise) vs isotype (grey), representative of three independent donors. (Magenta and grey are superimposed).
(F) Integrin expression on circulating MCP (left) and polyp Itgβ7high MCs (right), each representative of three separate donors.
(G) Distribution of polyp αEhigh (green) and αE- (purple) Itgβ7highMCs distribution within the epithelial vs subepithelial gates (left) as in Fig. 1E, with quantification (right). *, p<0.05 (paired t-test).
scRNA-seq identification of MC polarization and proliferation.
To further explore polyp MC heterogeneity, we conducted scRNA-seq using the Seq-Well platform on MCs flow sorted from 6 polyp donors (27) (Fig. 3A). We derived a unified cell-by-gene matrix for all cells passing quality control thresholds (n=7,355 cells) and identified 10 cell clusters following dimensionality reduction and unsupervised clustering (Fig. S3A, methods). Contaminating populations were identified by comparison to a series of cell identity transcriptional signatures developed in our prior scRNA-seq study of nasal polyposis (22), including small populations of fibroblasts and epithelial cells, DCs, B/plasma cells, and a population of plasmacytoid DCs (pDC) not resolved in our previous study (Fig. S3B–E, Supplementary Table 2–3). All clusters were observed in CRSwNP and AERD and in all patients aside from one lacking pDCs (Fig. S3F). The consistent presence of these contaminating cells within the sorted MC pool from 6 donors indicates the necessity of including additional markers to identify human MCs under conditions where contaminating populations cannot be computationally removed, such as bulk RNA-seq or functional assays. The four remaining clusters, designated MC1–4 (Fig. 3B), all strongly expressed the MC proteases tryptase (TPSAB1) and CPA3 (CPA3) and similar levels of transcripts encoding the histamine biosynthetic enzyme histidine decarboxylase (HDC) and the lipid mediator biosynthetic enzymes prostaglandin D2 synthase (HPGDS), 5-lipoxygenase (ALOX5), and 5-lipoxygenase activating protein (ALOX5AP) (Fig. 3C). The MC1-MC3 clusters further showed similar expression of a set of core transcripts highly enriched in nasal polyp MCs (22), including the MC granule core protein serglycin (SRGN) and the transcription factor GATA2 (GATA2) (Fig. 3D, top). Together, these observations indicated that MCs within the polyp environment share a core effector program enabling the generation of proteases, lipid mediators, and histamine.
Figure 3: scRNA-seq identification of transcriptionally distinct polyp MC subsets.
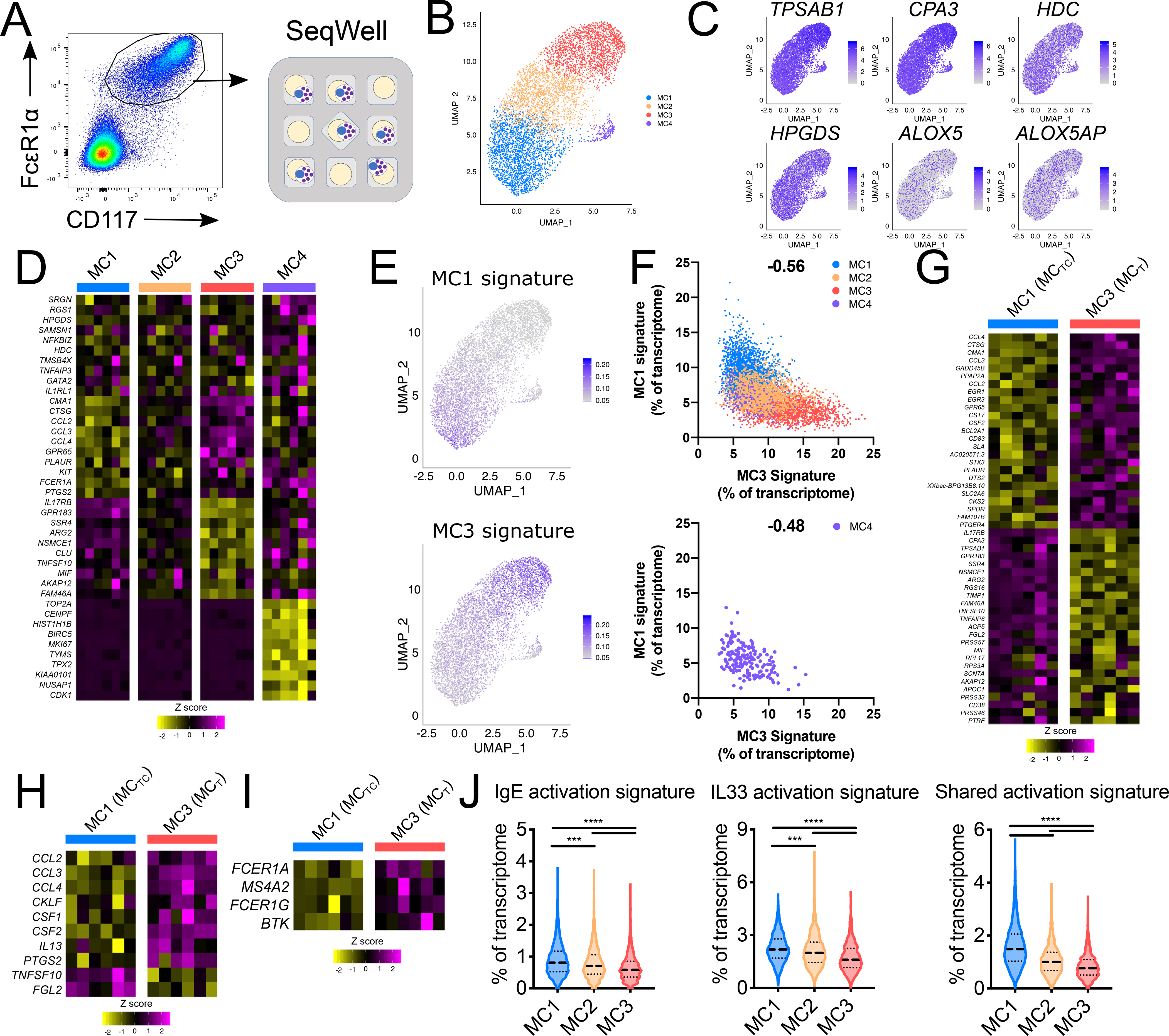
(A) Schematic representation for scRNA-seq analysis of 7,355 cells sorted polyp MCs (Fig. S1) (n=6 donors).
(B) Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) depiction of MC clusters. (Fig. S3 depicts identification of MC vs contaminating clusters).
(C) MC expression of canonical MC transcripts.
(D) Common (top rows) and cluster-enriched transcripts (columns show donor-averaged row-normalized expression). padj < 3.1 × 10−29 for cluster enriched genes (Wilcoxon).
(E) Polyp MC expression of MC1 and MC3 signatures (% of transcripts/cell).
(F) Per-cell expression of MC1 and MC3 signatures across all clusters (top) and MC4 alone (bottom). (correlation r-value).
(G) Differentially expressed transcripts between polyp MCTC (MC1) and MCT (MC3), (donor averaged, row normalized); padj < 6 × 10−9 (Wilcoxon).
(H) Immunomodulatory transcript expression in polyp MCTC and MCT, (donor averaged, row normalized); padj < 7 × 10−17 (Wilcoxon).
(I) FcεR1 signaling pathway expression in polyp MCTC and MCTC (donor averaged, row normalized); padj < 8 × 10−4 (Wilcoxon).
(J) Expression of transcript scores driven by IgE signaling, IL33 signaling, or shared by both stimuli across the MC1–3 clusters. (lines denote median and quartiles) p***, p<1×10−10, ***, p<1×10−15 (Mann-Whitney); Cohen’s effect size for MC1 vs. MC3: 0.60 (IgE), 0.79 (IL33), and 1.52 (shared).
Differential gene expression analysis between the four identified MC clusters indicated MC1-enriched expression of chymase (CMA1) and cathepsin G (CTSG) (Fig. 3D), consistent with subepithelial MCTC (Fig. 1I, Fig. S2). The MC2 cluster lacked enriched genes, while the MC3 cluster expressed minimal CMA1 and CTSG and reduced levels of transcripts encoding both CD117 (KIT) and the high-affinity IgE receptor FcεR1α (FCER1A) compared with the MC1 cluster, consistent with epithelial MCT (Fig. 3D, Fig. 1H). The MC3 cluster was additionally enriched for IL17RB, encoding the receptor for the epithelial-associated cytokine IL25, and GPR183, encoding the chemotactic receptor EBI2 (28, 29). Immunofluorescence confirmed co-localization of tryptase and EBI2 within the epithelium, although not all MCs within the epithelium expressed detectable EBI2 (Fig. S4). Unexpectedly, the MC4 cluster expressed transcripts involved in proliferation and DNA replication, including TOP2A (encoding DNA Topoisomerase IIA) and MKI67 (encoding the cell cycle phase-associated protein KI67) (Fig. 3D, Supplementary Table 4).
We further observed that the transcriptional signatures associated with MC1 and MC3 (Supplementary Table 4) were expressed along gradients (Fig. 3E). These cluster-defining signatures exhibited negative correlation on a per-cell basis, with the MC2 cluster expressing low levels of each, suggesting an intermediate state (Fig. 3F, top). Cells within the proliferative cluster showed a range of MC1 and MC3 signature expression similar to that seen in the MC2 cluster, and the MC1 and MC3 signatures were again negatively correlated on a per cell basis (Fig. 3F, bottom). This suggested that the polyp MCTC (MC1) and MCT (MC3) transcriptional programs represented polarization states layered on a common shared transcriptome and that the proliferative population (MC4) shared transcriptional overlap with unpolarized MCs (MC2).
To better understand the transcriptional differences between the two polarized MC states, we directly compared the MC1 (MCTC) cluster to the MC3(MCT) cluster. These populations exhibited differential expression of 282 transcripts (Wilcoxon, padj<0.05) (Fig. 3G, Supplementary Table 4). The MC1 (MCTC) cluster showed enhanced expression of chemokines (CCL2, CCL3, CCL4, CKLF), myeloid cell growth factors (CSF1, CSF2), the cytokine IL13 and the lipid mediator biosynthetic enzyme PTGS2 (Fig. 3H), suggesting they are poised to coordinate pro-inflammatory responses through several mechanisms. Although all MC clusters expressed transcript encoding the protease CPA3 (Fig. 3C), this was notably enriched within MC3 (MCT) cluster (Fig. 3G). MC3 additionally showed enhanced expression of TNFSF10, encoding TRAIL, which positively regulates airway inflammation and remodeling in murine models of asthma (30, 31), FGL2, which shifts DC and T cell interactions towards Th2 polarization (32) (Fig. 3H), and Il17RB (Fig. 3G), suggesting the potential for this population to modulate T2-driven responses within the epithelium and respond to epithelial-derived IL-25.
Previous studies have indicated that epithelial-derived factors inhibit IgE-dependent MC activation (33, 34). Accordingly, the MCT cluster showed reduced expression of components of the FcεR1 complex (FCER1A, MS4A2, FCER1G) and the downstream regulator BTK (Fig. 3I). In contrast, no significant difference was observed for expression of the IL-33 receptor IL1RL1 (Supplementary Table 4). To test if activation states of polyp MCTC and MCT differed more broadly, we constructed MC activation transcriptional signatures based on existing microarray datasets evaluating murine bone marrow-derived MC activation (35) (Supplementary Table 2). We found that MC1 (MCTC) expressed the highest levels of transcript signatures specific to IgE-mediated activation, specific to IL-33-mediated activation, and commonly upregulated by both signals, while the MC3 (MCT) exhibited decreased expression and MC2 expressed intermediate levels (Mann-Whitney, p<1×10−11 for all comparisons) (Fig. 3J). Thus, polyp MCTC are activated at baseline, reflected in their increased cytokine and chemokine expression, and the intermediate MC2 exhibit activation despite a lack of polarization.
Identification of a distinct MCT phenotype associated with respiratory tract inflammation.
Several genes identified as part of the MCT transcriptome, including GPR183, IL17RB and CD38, were not previously associated with human MCs. To determine whether this phenotype was restricted to nasal polyposis or associated with broader inflammatory conditions, we evaluated three lung scRNA-seq datasets from patients with fibrosis included within the idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) cell atlas (36). These datasets included analyses of IPF and interstitial lung disease (ILD) versus healthy control (37), IPF and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) versus healthy control (38), and IPF versus healthy control (39). Notably, prior studies have found increased expression of transcripts encoding the T2 cytokine signaling pathway and the MC protease CPA3 in IPF (40). Independent analysis of each of the three datasets identified a prominent TPSAB1-expressing MC cluster (Fig. S5). MCs from each dataset were separately reclustered, and substantial disease-associated MC heterogeneity was noted within each (Fig. 4A–C, left panels, supplementary table 5). We observed a cluster of MCs within each dataset exhibiting significant enrichment for CD38, GPR183, IL17RB (Fig. 4 A–C center panels, polygon gate), and further noted MCs co-expressing the proliferation-associated genes MKI67 and TOP2A in two of the three datasets (Fig. 4 A–C center panels, circle gate). Across each dataset, the CD38high populations consisted predominantly of MCs from IPF or ILD (Fig. 4 A–C, left panels). We further identified a MC cluster significantly enriched for both CD38 and CPA3 (Fig. S6A, cluster outlined in black) in a re-analysis of a prior scRNA-seq study of lung biopsy samples from asthmatic vs controls (41), in which IL17RB and GPR183 expression could also be observed, although neither reached statistical significance (Fig. S6B, Supplementary Table 5). A comparison of genes significantly enriched within the CD38high clusters across the three fibrosis datasets identified substantial transcriptional overlap, with 18 transcripts enriched in all three datasets, including CPA3, and 85 transcripts enriched within the CD38high cluster in at least two of the three datasets (Table 1; Wilcoxon, p < 0.05). Notably, these transcripts overlapped with transcripts enhanced in both polyp MCT (19 transcripts) and the CD38-enriched asthma-associated cluster (38 transcripts), indicating a common inflammation-associated transcriptional program.
Figure 4: Characterization of an IL-4-elicited MCT phenotype enriched in diseased human lung samples.
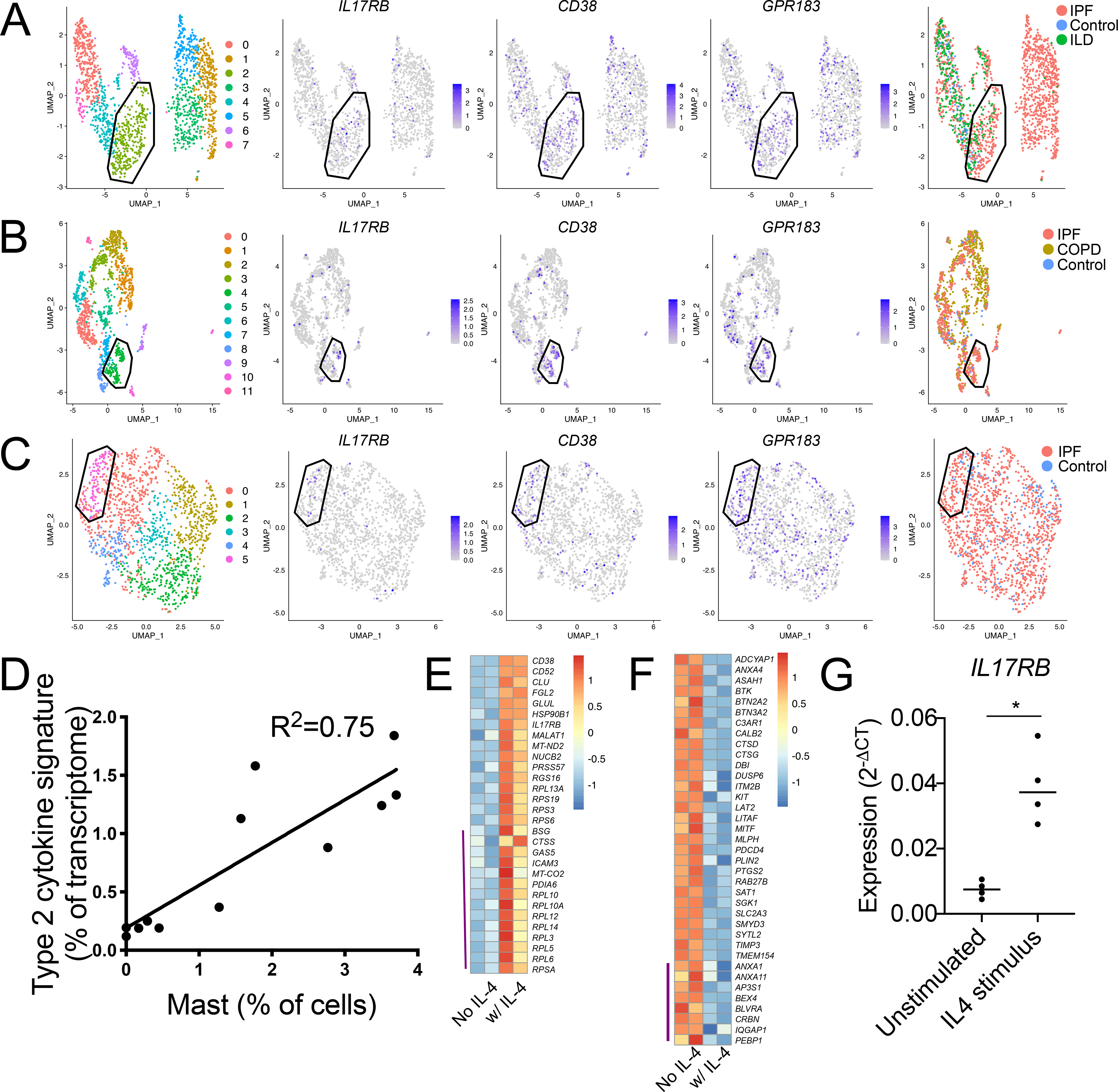
(A-C) Re-clustering of MCs from three scRNA-seq datasets accessed through the human IPF atlas: (A) control, IPF and ILD; (B) control, IPF and COPD; and (C) control and IPF. Clustering for each dataset indicated a population (polygon gate) that was statistically enriched for the polyp MC3-associated transcripts IL17RB, CD38, and GPR183 (center panels) and predominantly composed of MCs from diseased tissue relative to healthy (left panels). Circle gate indicates MCs co-expressing the proliferation-associated genes MKI67 and TOP2A.
(D) Correlation analysis of polyp scRNA-seq epithelial IL-4/13-induced signature expression, (donor averaged) versus scRNA-seq defined MC percentage for each donor. p<0.001.
(E) MC3-enriched transcripts (Supplementary table 4) upregulated in two technical replicate CBMC samples by 96-hour IL-4 stimulus (row normalized expression). Top half: FDR<0.1, bottom half (indicated by purple line): P < 0.05 (DESeq2).
(F) MC1-enriched transcripts (supplemental table 4) downregulated in two technical replicate CBMC samples by 96 hours IL-4 stimulus (row normalized expression). Top half: FDR<0.1, bottom half (indicated by purple line): P < 0.05 (DESeq2).
(G) CBMCs IL17RB expression (qPCR) following 72-hour stimulus with vehicle or IL-4, (n=4 biologic replicates across three independent experiments), * indicates p<0.05 (paired t-test).
Table 1: Identification of inflammation-associated airway MCT transcripts across datasets.
Transcripts significantly elevated in CD38, IL17RB and GPR183-enriched MCs (p<0.05) in at least two of the three lung fibrosis scRNA-seq datasets analyzed. Transcripts in bold were significantly elevated in polyp MC3 (MCT) relative to other polyp subsets. Blue transcripts were significantly elevated within the CD38-enriched asthma MC cluster analyzed in Fig S6.
| Banovich & Kropski | + | + | + | − |
| Kaminski & Rosas | + | + | − | + |
| Lafayatis | + | − | + | + |
| ACTG1 | ABRACL | B4GALT5 | AKAP12 | |
| CD38 | ACTR3 | BCL2A1 | ARHGEF6 | |
| CD52 | CAPG | CALR | CELF2 | |
| CPA3 | EEF1G | CAMK1 | EEF2 | |
| CXCR4 | EIF2A | CD83 | FBXO34 | |
| DTNBP1 | HOTAIRM1 | CDC42 | LCP2 | |
| EEF1A1 | LTC4S | CKS2 | NEDD9 | |
| GPR183 | MYL12B | CREM | PLXNC1 | |
| IL17RB | NKG7 | DUSP10 | PROM1 | |
| LDLRAD4 | RPL10A | DUSP4 | RPL28 | |
| LGALS1 | RPL13A | EHD1 | RPLP0 | |
| MAFF | RPL15 | FOSL2 | SLC9A1 | |
| NSMCE1 | RPL3 | GALNT6 | ||
| PFN1 | RPL7 | GEM | ||
| RGS16 | RPS2 | HES4 | ||
| RPL4 | RPS5 | HEY1 | ||
| RPSA | RPS6 | ICAM3 | ||
| ZC3H12A | RPS9 | ID2 | ||
| SVOPL | ISG15 | |||
| TMSB4X | KDM6B | |||
| TPI1 | KPNA2 | |||
| TPSAB1 | LMNB1 | |||
| UQCRH | MAT2A | |||
| MCL1 | ||||
| NFATC1 | ||||
| NR4A1 | ||||
| NR4A2 | ||||
| NR4A3 | ||||
| NUDT14 | ||||
| PHLDA1 | ||||
| PLAUR | ||||
| PMEPA1 | ||||
| PRKD3 | ||||
| PTGS2 | ||||
| RAB33A | ||||
| RANBP2 | ||||
| SETP9 | ||||
| RUNX3 | ||||
| SH2D2A | ||||
| SKIL | ||||
| SLC16A3 | ||||
| SRSF2 | ||||
| TGIF1 | ||||
| TNFAIP8 | ||||
| TNFRSF9 | ||||
| TPM4 | ||||
| TPT1 | ||||
| ZFAND5 | ||||
| ZNF331 |
Expression of IL17RB by MCs in the lungs of patients with fibrosis and asthma and CRSwNP polyps suggested this transcript was regulated by disease-associated signals. Mouse studies have identified a central role for IL-4 in intraepithelial MC expansion (42, 43), and a re-analysis of our prior nasal polyposis scRNA-seq dataset indicated a significant correlation between polyp MC concentration and epithelial expression of an IL-4/IL-13-driven cytokine signature (22) (Fig. 4D). Notably, IL4 expression in nasal polyposis was restricted to Th2A cells, while IL13 was expressed by both Th2A cells and MCs (22). Further, re-analysis of scRNA-seq data from a single CRSwNP donor evaluated before and after six weeks of treatment with dupilumab, a monoclonal antibody directed against the IL-4 receptor, revealed markedly reduced IL17RB expression within the MC cluster compared with pre-treatment baseline but no change in expression of the MCT-associated transcript GPR183 (Figure S7). Thus, we hypothesized that IL-4 directly influenced polyp MCTs.
To evaluate IL-4 regulation of the polyp MCT transcriptome, human cord blood-derived MCs (CBMC) were stimulated with IL-4 or vehicle for 96 hours and then analyzed via RNA-seq. IL-4 exerted a profound impact on the CBMC transcriptome (Supplementary table 6). Among the upregulated genes were 30 of 102 polyp MCT-enriched transcripts, including IL17RB and CD38 but not GPR183 (Fig. 4E, Supplementary table 6). Notably, IL-4 conditioning also downregulated 37 of 180 MCTC-enriched transcripts, including CTSG and KIT (Fig. 4F). The capacity for IL-4 to upregulate IL17RB was further confirmed through qPCR analysis (Fig. 4G). However, IL-4 stimulus also upregulated FcεR1 signaling components (Supplementary table 6) that were downregulated in polyp MCT (Fig. 3I), suggesting other signals additionally regulate the MCT transcriptome. Thus, our findings identified a distinct phenotype of MCT associated with respiratory inflammation and identified the potential for IL-4 signaling to regulate this phenotype.
Recognition of significant MCTC heterogeneity across tissues.
While chymase-expressing MCs found in mucosal tissues during inflammation are termed MCTC, the relatedness of these cells to constitutive MCTC populations present in peripheral tissues such as the skin has not been addressed. Thus, we compared nasal polyp MCs to dermal MCs derived from a scRNA-seq study of healthy and diseased human skin biopsies from patients with psoriasis, alopecia, acne, leprosy, and granuloma annulare (44). Polyp MC1 (MCTC) and dermal MCs, canonically exhibiting an MCTC phenotype (5), both showed enhanced expression of CMA1 relative to polyp MC1 (MCT), as well as a shared subset of receptors (KIT, PLAUR, ICAM1) and mediators (LIF, CSF1) (Fig. 5A). However, dermal MCTC lacked expression of other transcripts strongly expressed in polyp MCs and vice versa. Polyp MC1 (MCTC) were enriched in expression of chemokines (CCL2, CCL3, CCL4) and FcεR1α signaling pathway transcripts (FCER1A, MS4A2, BTK) relative to dermal MCs, but lacked expression of genes encoding the activating GPCRs CD88 (C5AR1) and MRGPRX2 (MRGPRX2), previously described as markers for MCTC in the skin and lung (45, 46). Supporting this observation, we found strong surface expression of MRGPRX2 on skin-derived MCs, but little to no expression on polyp MCs (Fig. 5B). To determine if the absence of these receptors reflected the polyp inflammatory environment a broader paradigm of MCTC heterogeneity, we conducted an independent analysis of an existing scRNA-seq dataset containing distal (alveolar), medial and proximal (large bronchi) fractions of healthy lung developed by Travaglini et al (47). Following normalization, we identified a prominent TPSAB1-expressing MC cluster (Fig. 5C). Despite the presence of similar numbers of MCs expressing CMA1 and CTSG in the distal and proximal lung, MRGPRX2 expression could only be detected in the large airway (Fig. 5D). Although not reaching statistical significance, this observation suggests that MCTC exhibit heterogeneity even within a single tissue. C5AR1, encoding CD88, was only weakly detected in either lung compartment. These findings indicate considerable differences in the transcriptome of chymase-expressing MCs across tissues and inflammatory milieus, and further highlight the activated state of polyp MCs and their likely pathogenic contributions. Moreover, the findings further illustrate the vast extent of MC heterogeneity that is not reflected by conventional histochemical criteria.
Figure 5: Identification of MCTC heterogeneity across tissues.
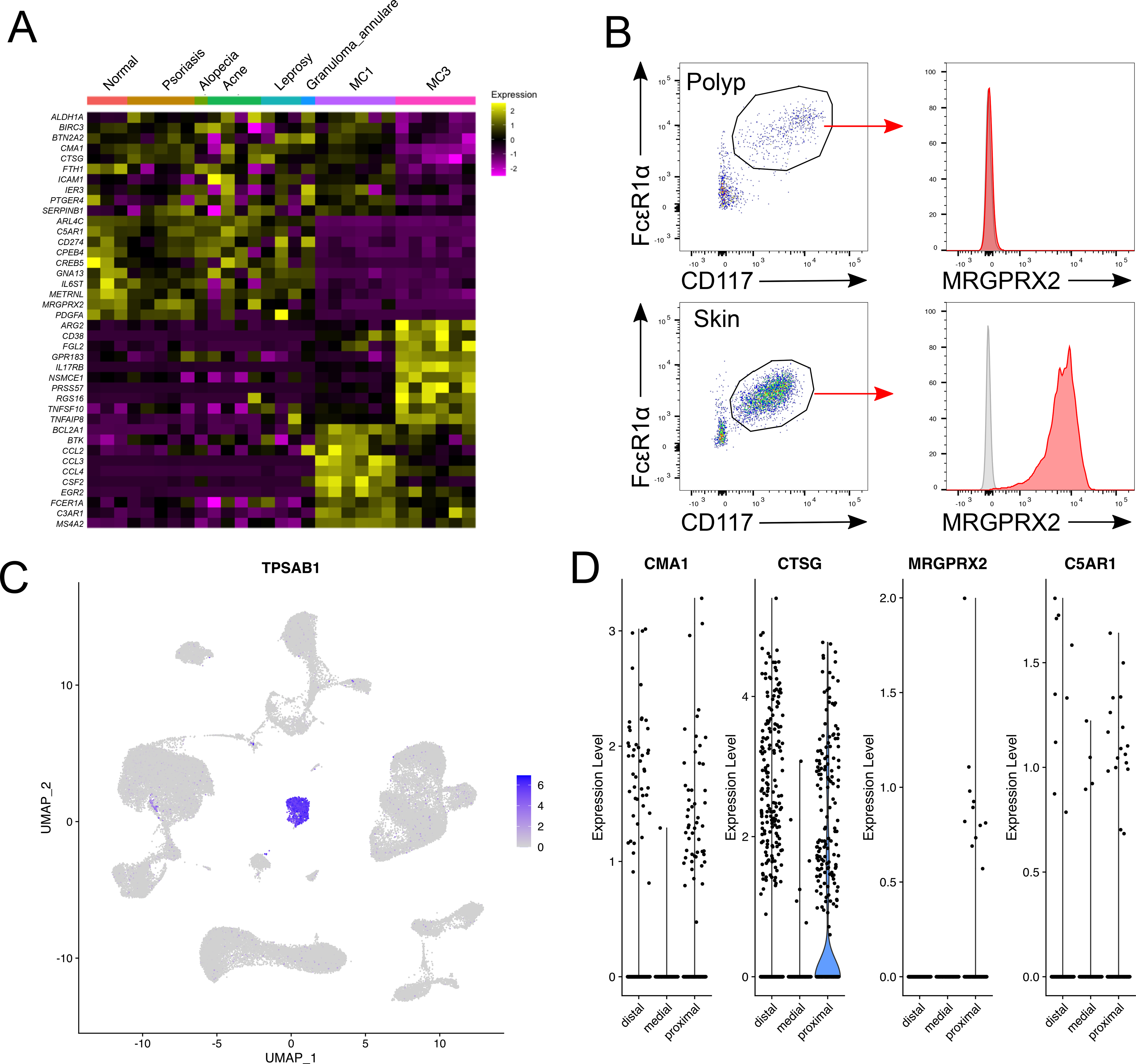
(A) Transcripts shared between diseased and control skin MCs and polyp MCTC (top) vs. enriched in skin MCs (upper middle), polyp MCT (lower middle), or polyp MCTC (bottom) (donor averaged, row normalized).
(B) Representative analysis of MRGPRX2 expression (red) on nasal poly MCs (left) and skin MCs (right) relative to isotype (grey). Staining representative of 3 donors per group.
(C) Identification of MCs based on TPSAB1 expression within a scRNAseq dataset of healthy human lung tissue containing samples from distal, medial and proximal lung generated by Travaglini et al(47).
(D) Violin plots showing expression of the MCTC-associated transcripts CMA1, CTSG, MRGPRX2, and C5AR1 in healthy human lung. No displayed transcripts were significantly differentially expressed between distal and proximal lung, MRGPRX2 expression was only observed in proximal lung.
Identification of CD117 and CD38 cell surface expression patterns defining polyp MC phenotypes.
Among the transcripts enriched in MC3 (MCT) relative to MC1 (MCTC) clusters was CD38 (Fig. 3G), suggesting a candidate cell surface marker that might further distinguish polyp MC subsets. Cell surface staining indicated virtually all CD117low epithelial MCTs exhibited high CD38 expression (Fig. 6A–B; red gate). Unexpectedly, CD38 expression also divided the heterogeneous CD117high subepithelial MC pool (Fig. 1C) into CD38highSSClow MCs (orange) and CD38neg MCs with a range of SSC (blue). Itgβ7high polyp MCs notably expressed CD38 (Fig. 6C). A subset of cells lacking both CD117 and CD38 (Fig. 6A) were likely the source of contaminants observed through scRNA-seq (Fig. S3). CD38highCD117high subepithelial MCs were also detected in CRSsNP tissue, however their relative abundance was significantly reduced when compared to CRSwNP and AERD polyps (Fig. 6D–E). No significant differences were observed in MC subset composition between CRSwNP and AERD. Thus, CD38 marks polyp epithelial MCT and Itgβ7-expressing MC, as well as a CD117high subepithelial MC subset significantly expanded in nasal polyps.
Figure 6: CD38 expression marks nasal polyp MCT and an unpolarized intermediary subset.
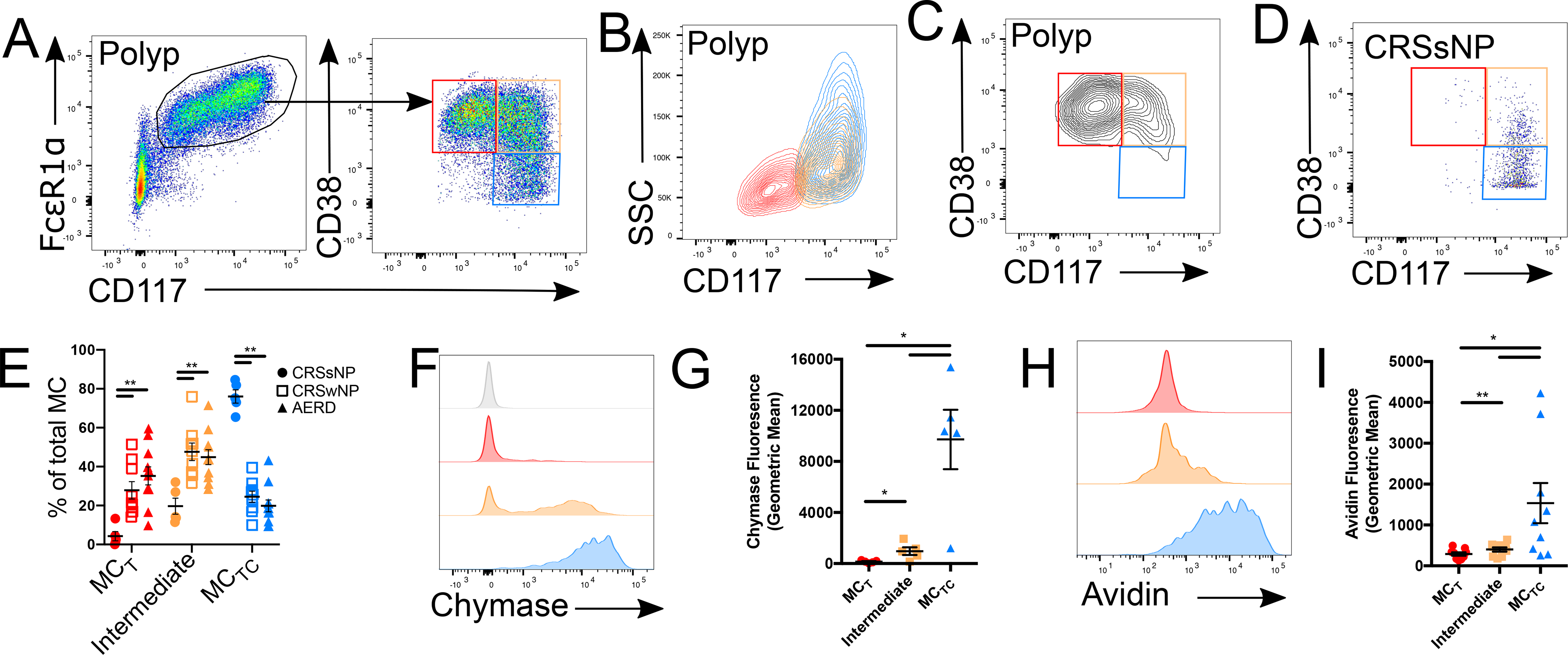
(A) Representative plot showing nasal polyp MC (gated as in Fig. S1) expression of CD38 and CD117. Arrow indicates sequential gating.
(B) SSC vs CD117 profile of CD38high epithelial MCs (red), CD38high subepithelial MCs (orange) and CD38low subepithelial MCs (blue).
(C) Representative plot showing CD38 and CD117 expression in Itgβ7high MCs.
(D) Representative plot of MC CD38 and CD117 expression in CRSsNP control tissue.
(E) Quantification of CD38highCD117low MCT (red), CD38highCD117high intermediate MCs (orange) and CD38lowCD117high MCTC (blue) in sinus tissue of patients with CRSsNP (closed circles), CRSwNP (open squares), or AERD (closed triangles). ** indicates p<0.01 (Mann-Whitney)
(F) Intracellular chymase expression in epithelial MCs (red), CD38high subepithelial MCs (orange), and CD38low subepithelial MCs (blue) versus isotype (grey).
(G) Quantification of chymase expression in indicated MC subsets (n=5 donors); *, p<0.05, ***, p<0.001 (t-test).
(H) Intracellular FITC-avidin staining in epithelial MCs (red), CD38high subepithelial MCs (orange), and CD38low subepithelial MCs (blue).
(I) Quantification of FITC-avidin fluorescence in indicated MC subsets (n=9 donors); *, p<0.05 (t-test).
Enriched CD38 expression in CD117low MCs (Fig. 6A), and reduced CD38 in MC1 relative to MC3 (Fig. 3G), suggested that CD117highCD38low subepithelial MCs were mature MCTC. Flow cytometry confirmed that CD117low intraepithelial MCs (red) lacked chymase expression (Fig. 6F), consistent with immunofluorescent staining (Fig. 1H), whereas subepithelial CD117highCD38low MCs (blue) were uniformly positive for chymase, indicating a MCTC phenotype (Fig. 6F–G). The CD38highCD117high MC gate included both chymase positive and negative cells (Fig. 6F). Similarly, staining with avidin, a reagent that binds to heparin sulfate (48) and specifically identifies human MCTC (49), was highest in subepithelial CD117highCD38low MCTC (blue), lowest in CD117lowCD38high (red) epithelial MCT, and intermediate in CD117highCD38high MCs (yellow) (Fig. 6H–I). Thus, through surface marker expression and intracellular protease and heparin staining, we could identify mature intraepithelial MCT (CD117lowCD38high; red) and subepithelial MCTC (CD117highCD38low; blue) and further identify a subepithelial population with an intermediate phenotype (CD117highCD38high; yellow), suggestive of the MC2 subset identified through scRNA-seq.
Evaluation of in situ proliferation within human polyp MCs.
To integrate our transcriptional analysis with these flow cytometrically-defined MC subsets, we used CITE-seq (50) to simultaneously assesses RNA and surface protein expression on flow-sorted polyp MCs, using oligo-tagged antibodies directed against CD117, CD38 and Itgβ7 (Fig. 7A). Clustering again identified the same four MC populations (Fig. 7B, Supplementary Table 4), indicating that MCTC (MC1) exhibited high surface CD117 and low surface CD38 while MCT (MC3) exhibited low surface CD117 and high surface CD38 (Fig. 7C). We further observed that the MC2 cluster exhibited intermediate surface CD117 and CD38 levels, confirming its identity as the flow cytometrically-defined CD38highCD117high population, and that the proliferating MC4 seen similarly exhibited elevated CD38 and CD117 levels. Surface Itgβ7 was predominantly observed in the MC3 cluster (Fig. 7D), in agreement with the previously observed epithelial enrichemnt of ItgαE+β7+ MCs (Fig. 2G), but scattered Itgβ7 expression was also observed across all clusters. A direct comparison of Itgβ7high and Itgβ7low MCs within each cluster indicated little to no impact of Itgβ7 expression on the MC transcriptome (Fig. S8).
Figure 7: Unpolarized MC proliferation underlies MC expansion in human nasal polyps.
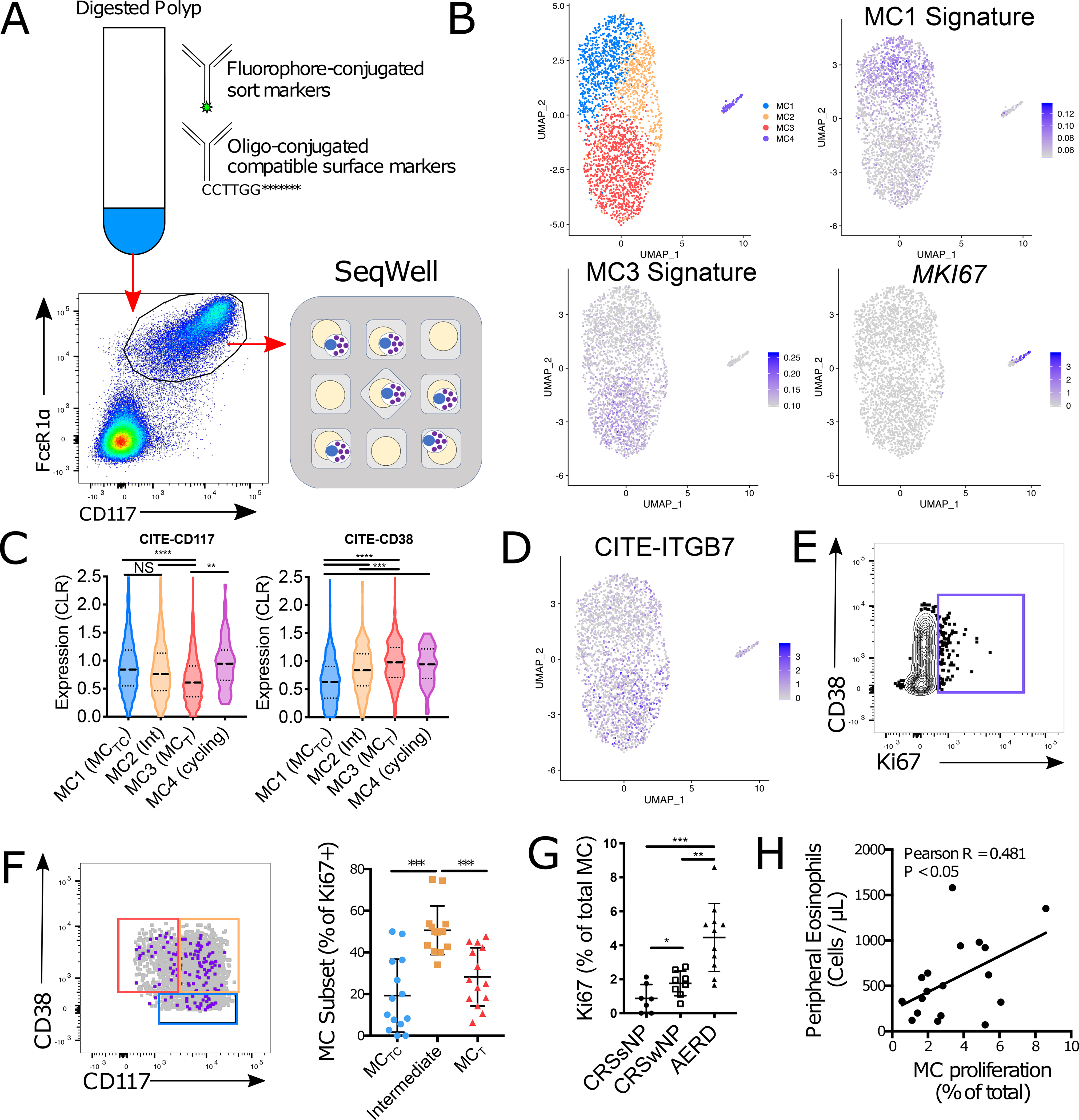
(A) Schematic approach for Cellular Indexing of Transcriptomes and Epitopes by Sequencing (CITE-seq) analysis of sorted polyp-derived MCs
(B) Identification of four clusters across 2,902 MCs from 2 donors with expression of the MC1 and MC3 gene signatures (Supplementary table 2) and MKI67.
(C) Cell surface expression of CD117 and CD38 within each MC cluster (line denotes median and quartiles); **, p<1×10−4; ***, p<1×10−12; ****, p<1×10−15; NS, not significant (Mann-Whitney).
(D) UMAP plot showing cell surface expression of Itgβ7 across nasal polyp MCs.
(E) Representative plot of nuclear Ki67 in nasal polyp MCs.
(F) Overlay showing Ki67+ MCs (purple) and all MCs (grey) with flow gates defined in Fig. 6A (left). Quantification of Ki67+ MCs by subset (right); ***, p<0.001 (t-test).
(G) Quantification of Ki67+ MCs in indicated disease endotypes. ***, p<0.00, (t-test).
(H) Correlation of MC proliferation (Ki67 staining) and peripheral blood eosinophil counts across polyp patients. Pearson R = 0.481, p < 0.05
Our CITE-seq observations suggested that the majority of proliferating MCs would be CD117highCD38high subepithelial MCs. Nuclear KI67 staining identified a distinct population of proliferating MCs (Fig. 7E), and while proliferation was observed across all three compartments, the majority of Ki67+ cells were CD117highCD38high subepithelial MCs (Fig. 7F). Combined with the detection of both MCT and MCTC-associated transcript signatures within the proliferating clusters detected through scRNA-seq (Fig. 3F), these findings suggest that the MC hyperplasia characteristic of human nasal polyposis is driven in part by in situ MC proliferation. Consistent with this hypothesis, we observed a significant increase in MC proliferation in the polyps of AERD patients relative to MC from CRSwNP donors (Fig. 7G), corresponding to the differences in polyp MC concentration between these two patient groups (Fig. 1B). We further noted a significant correlation between MC proliferation and peripheral blood eosinophilia across all polyp patients (Fig. 7H), indicating a link between MC proliferation and overall disease severity. Coupled with the previous observation that progenitor-like Itgβ7-expressing MC were present at similar concentrations in AERD and CRSwNP (Fig. 2D), our findings suggest an important role for local proliferation in MC hyperplasia during T2 airway inflammation.
Discussion
Our study provides a transcriptomic and flow cytometric characterization of MC hyperplasia during human airway inflammation, identifying proliferation as a driver of T2-associated non-neoplastic MC airway hyperplasia. We also observe that MC sensing and effector programs are closely linked to tissue microenvironments. The MCT and MCTC phenotypes in CRSwNP tissue display substantial cell surface differences and predominate in epithelial and subepithelial regions, respectively. Despite shared expression of a core transcriptome, they inhabit opposite poles of a transcriptional gradient, implying distinct functions for each. The CRSwNP MCT program, distinguished by expression of CD38, IL17RB and GPR183, is also observed within the lungs of IPF, ILD, and asthma patients. These MCT further express elevated CPA3, suggesting a link to the CPA3+ MCTs previously reported in the bronchial epithelium of asthmatics and esophagus of EoE patients (15–18). The CRSwNP MCTC program, enriched for proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, differs from classical skin and noninflamed lung MCTCs by its lack of the MCTC markers MRGPRX2 and CD88 (C5AR1) (45, 51, 52). Both MCT and MCTC populations expand markedly in CRSwNP tissue, and even more so in AERD tissue, relative to CRSsNP controls. Based on these observations, we propose that these expanded mucosal T2-inflammation-associated MC subsets be reclassified as airway inflammatory MCT and MCTC (iMCT and iMCTC), respectively, distinguishing them from their counterparts in non-mucosal tissues and tissues with less T2 inflammation (Fig. S9).
The stark transcriptional differences between iMCT and iMCTC imply both distinct functions and distinct patterns of imprinting by tissue-associated factors. Both iMCTC and transitional MC clusters display enrichment for FcεRI- and IL-33-inducible transcripts characterized by chemokines (CCL2, CCL3, CCL4), cytokines (IL13), growth factors (CSF1, CSF2), and PTGS2, (encoding cyclooxygenase-2, required for PGD2 generation). Thus, subepithelial MCs may respond to both innate (IL-33) and adaptive (IgE) immune pathways to provide mediators driving recruitment and activation of blood-born effector cells and conditioning the surrounding stroma. Although iMCT display lower levels of activation-associated transcripts, they uniquely express IL17RB, the receptor for the epithelial-derived T2 cytokine IL-25. Notably, IL17RB is also expressed by MCs in the lungs of IPF, ILD, and asthma patients, indicating it is part of a disease-associated human respiratory intraepithelial MC transcriptional program. Treatment of primary cord blood MCs with IL-4, a T2 cytokine required for murine intraepithelial MC hyperplasia during helminth infection and food allergy (42, 43), induces IL17RB expression along with other iMCT transcripts. While IL4 did not upregulate proliferation-associated transcripts in cord blood MCs, prior studies have shown that IL4 markedly amplifies SCF-dependent proliferation in human primary MCs from the intestine and peripheral blood(53, 54). The finding that treatment with the IL-4Rα blocking antibody dupilumab, highly efficacious for CRSwNP(55), sharply reduces IL17RB expression by the MC cluster further supports the concept that IL-4 contributes substantially to iMCT hyperplasia and function. Epithelial signatures of IL4/13 signaling correlated with MC concentration in our prior study of nasal polyposis (22), and this signature is also notably elevated in the lungs of asthmatics (41). Fibrosis patients similarly exhibit enhanced T2 cytokine pathway activation (40). Ultimately, an analysis of whether therapeutic interventions for polyposis and asthma, including monoclonal antibody blockade of IL-4/13 (56, 57), and CD117 inhibition (2) alter MC proliferation and transcriptional activity will allow definitive identification of tissue drivers of MC hyperplasia and differentiation.
MCs are thought to arise from rare agranular circulating CD34+Itgβ7+ precursors (13). Although Itgβ7high MCs were enriched in both aspirin tolerant CRSwNP and AERD tissue compared with controls, these cells were CD34-, contained cytoplasmic granules and expressed tryptase, suggesting maturation. Although predominantly intraepithelial, Itgβ7high MCs could be found within all populations and were transcriptionally indistinguishable from Itgβ7- MCs within the same clusters. Thus, a portion of the MC population within nasal polyps, particularly iMCT, may arise directly from recruited MCP. Two additional clusters within the polyp MC pool were not expected based on prior histologic studies: one lacking signature transcripts, and one undergoing proliferation. Both clusters expressed low levels of iMCT and iMCTC signature transcripts, suggesting they were developmentally intermediate between the two polarized populations. CITE-seq analysis linked these “intermediate” MCs to the prominent expanded CD117highCD38high MC pool, which by flow cytometry displayed variable chymase expression and avidin binding. CD117hiCD38hi MCs accounted for 40–60% of CRSwNP tissue MCs, were present (although reduced) in CRSsNP controls, and were enriched for proliferation. Moreover, Ki67+ MCs were substantially elevated in AERD and correlated with blood eosinophilia, a marker of T2 cytokine production (58). It is thus likely that MC hyperplasia results from a combination of Itgβ7high MCp recruitment and in situ MC proliferation, with the contributions from the latter being magnified in more severe disease. The combination of polarization and proliferation suggests a similar paradigm to that observed with monocytes, which have innate effector capacity, mature and take on distinct effector programs in response to local inflammatory signals, and are maintained within tissue through local IL-4 driven proliferation (59, 60).
Although our transcriptomic analysis strongly suggests the intermediate CD117hiCD38hi MCs contributes to both iMCT and iMCTC hyperplasia, future studies will be required to determine if these cells are indeed capable of polarizing towards both observed MC effector phenotypes. Furthermore, although CD117hiCD38hi MCs express similar levels of lipid mediator biosynthetic enzymes as iMCT and iMCTC, we were unable to directly assess their ability to generate inflammatory mediators. As a previous transcriptomic analysis of human circulating MCP indicated that even agranular progenitors were enriched for HGPDS expression(13), it will be important to understand whether this means that MC lineage cells are capable of producing lipid mediators at all phases of development or if, instead, the enzymes themselves are only translated following maturation. It is also unclear what role the three primary transcripts found to associate with the iMCT across disease states, CD38, GPR183 and IL17RB, may play in MC biology. EBI2, encoded by GPR183, has been shown to participate in B cell and DC localization within tissues(28, 29, 61), suggesting a similar role in MCs. While it is less clear what effects CD38 and IL17RB may have on iMCT biology, the identification of IL-4 as a signal capable of upregulating both receptors in vitro provides critical insight for future studies exploring their roles.
In summary, through transcriptional and flow cytometric characterization of MC hyperplasia in T2 airway inflammation we identify transcriptionally and phenotypically distinct MC subsets that potentially emerge from a novel, proliferative intermediate MC subtype. The polarized MC subtypes emerging from the intermediate subtype assume distinct transcriptional and morphologic characteristics based on their tissue microenvironment. The expansion of the intermediate subtype may be a critical determinant of disease severity, in turn reflecting perturbations in the surrounding stroma, mitogenic cytokines and inflammatory mediators that likely exert a substantial additional influence on the MCs within each tissue microenvironment. Uncovering the drivers of this proliferative response and the tissue signals responsible for directing MC polarization will be critical for identifying therapeutic targets for T2 inflammation-associated diseases in which MC hyperplasia is prominent and MC effector responses play an important role.
Methods
Study participants and design
Ethmoid sinus tissue was obtained from participants between the ages of 21 and 76 years, recruited from the Brigham and Women’s Hospital (Boston, Massachusetts) Allergy and Immunology clinic and Otolaryngology clinic between May 2014 and September 2020 (Supplementary Table 1). This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB), with all study participants providing written consent. Tissue was collected at the time of elective endoscopic sinus surgery from patients with physician-diagnosed CRSwNP or CRSsNP. Patients with polyps included diagnoses of both aspirin-tolerant CRSwNP and aspirin-intolerant AERD. A diagnosis of AERD was suspected for patients with asthma, nasal polyposis, and a history of respiratory reaction following usage of cyclooxygenase inhibitors, and all diagnoses were confirmed via graded oral challenge with aspirin. Subjects with cystic fibrosis and unilateral polyps were excluded. After no distinctions in MC characteristics between the two disease endotypes were noted beyond MC concentration and proliferation, the data were combined unless otherwise noted. Analysis was conducted in a non-blinded manner. Peripheral blood was obtained from patients without ethmoid sinus disease under the same protocol. De-identified human skin samples were obtained from the Brigham and Women’s Hospital surgical department under a separate IRB-approved protocol.
Flow cytometry, cell sorting and analysis
Single-cell suspensions were resuspended in FACS Buffer (HBSS, Ca/Mg-free (ThermoFisher) supplemented with 2% FCS and 1 mM EDTA) prior to flow cytometric staining. MCs were sorted on a Sony SH800 cell sorter using Sony Cell Sorter Software (SeqWell) or a BD FACSAria Fusion cell sorter using BD FACSDiva software (Histologic assessment). For all flow cytometry not involving cell sorting, cells were analyzed on a BD LSRII Fortessa or BD CANTO-II using BD FACSDiva software.
Cytologic analysis
To minimize cell loss, sorted MCs were placed on a glass slide at a concentration of 1,000 cells in 10 μl. Slides were quickly dried using a plate warmer at the lowest setting. For granule visualization, cells were stained with 100 μl toluidine blue solution (94.2% H2O, 5.8% concentrated HCl, 0.5 g toluidine blue) for 30 seconds and washed using DI H2O. For protease immunostaining, cells were fixed with Carnoy’s fixative as previously described(62).
Histologic analysis
Nasal polyp biopsies were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, embedded in paraffin, and 6 μm sections were cut for histologic analysis. Tissue sections were deparaffinized and rehydrated. Slides were quenched with 1 mg/ml sodium borohydride 3 times on ice for 10 min each. Antigen retrieval was performed with Target Retrieval Solution, pH 9 (Agilent Technologies, Inc) at 97°C for 35 min. Microscopy and photography were done using OLYMPUS BX 41 system microscope and OLYPUS DP 71 camera.
scRNA-seq and analysis
After obtaining single-cell suspensions from freshly resected sinus tissue, we utilized the Seq-Well platform for massively parallel scRNA-seq to capture transcriptomes of sorted MCs on barcoded mRNA capture beads (27), described in greater detail in supplemental methods. Read alignment was performed as in Macosko et al (63). UMI-collapsed data was utilized as input into Seurat (64) (https://github.com/satijalab/seurat) for analysis. Before incorporating a sample into our merged dataset, we individually inspected the cell-by-gene matrix of each as a Seurat object. For analysis of all sequenced samples, we merged UMI matrices across all genes detected to generate a matrix containing all cells detected (n= 8,228 cells and 25,104 genes). This table was then utilized to setup the Seurat object in which any cell with at least 200 unique genes was retained and any gene expressed in at least 3 cells was retained. Cells with greater than 10% mitochondrial genes or UMI counts less than 200 and greater than 2500 were removed from analysis. The total number of cells passing these filters captured across all patients was 7,355 cells with 18,102 genes, averaging 2,699 cells per sample with a range between 221 cells and 2,359 cells. Before performing dimensionality reduction, data was log-normalized with a scale factor of 10,000, scaled and centered, and a list of 2,000 most variable genes was generated by using the vst selection method. We then performed principal component analysis using variable genes. A shared nearest neighbor (SNN) graph and uniform manifold approximation and projection embedding (UMAP), were constructed using the first 9 principal components based on the inflection point of the elbow plot. We used FindClusters (which utilizes a SNN modularity optimization-based clustering algorithm) with a resolution of 0.4 and RunUMAP using default settings to identify 10 clusters across the 6 input samples. Additional analysis information can be found in supplemental methods.
CITE-seq computational pipelines and analysis
CITE-seq methodology can be found in the supplemental methods section. For analysis, CITE-seq tag counting and demultiplexed ADT reads were processed using the CITE-seq-Count package version 1.4.2. Reads were matched with their corresponding ADT sequences and assigned to cell barcodes within a whitelist of cells that contained between 200 and 2500 mRNA UMIs. Once binned by cell barcode, ADT reads were collapsed by their 8-bp UMI.
For data analysis, one Seurat object was created per sample. Cells with UMI counts less than 200 and greater than 2500 were removed from the analysis. For both experiments, data was log normalized with a scale factor of 10,000, scaled and centered, and the 2,000 most variable transcripts were determined using the FindVariableFeatures function. Tag counts for ADTs were scaled and centered before center log ratio normalization (CLR). Contaminating cell populations were computationally removed from each object as described in Cell Type Identification, and the two experiments were integrated within Seurat using the Harmony software package (65). For constructing a SNN graph and UMAP embedding, we utilized the first 10 principal components, reflecting the inflection point of the elbow plot. We used FindClusters with a resolution of 0.4 and RunUMAP using default settings to identify 4 clusters across the 2 input samples.
Statistical analysis
Number of samples included in analyses are listed throughout figure legends and represent distinct biological samples. Source data is provided in Supplementary table 7. No samples or cells meeting quality thresholds were excluded from analyses. Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism v7.0c and Seurat 3.0.1 implemented in RStudio. Some violin plots were generated using Graphpad Prism using data exported from Seurat to allow display of median and quartile values. Paired t tests were used when comparing protein expression across multiple subsets within individual patients and are indicated by linked points. Unpaired 2-tail t-tests were for comparisons of data found to be normally distributed using the D’Agostino & Pearson test. For all other data, the Mann Whitney U tests was used for comparisons.
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Table 3: Cell x gene matrix (raw) for sorted MCs from 6 polyp donors.
Supplementary Methods
Figure S1: In-depth characterization of nasal polyp MCs.
Figure S2: Characterization of nasal polyp MC protease phenotype and localization.
Figure S3: Characterization of sorted cells through scRNA-seq.
Figure S4: Immunohistologic localization of EBI2-expressing MCs.
Figure S5: Identification of MCs in three IPF scRNA-seq datasets.
Figure S6: Identification of an asthma-enriched CD38high MC cluster.
Figure S7: Influence of Dupilumab on nasal polyp MC transcript expression.
Figure S8: Schematic representation of strategy for evaluating the transcriptome of Itgβ7high MCs.
Figure S9: Proposed model for MC homeostasis and hyperplasia in human sinus mucosa.
Supplementary Table 5: Cluster defining marker genes for scRNA-seq datasets from the human IPF lung atlas and asthma vs healthy donors.
Supplementary Table 6: Differential gene expression analysis for human umbilical cord-derived MCs treated with IL-4 or vehicle for 96 hours.
Supplementary Table 7: Source data for figures.
Supplementary Table 1: Patient Information
Supplementary Table 4: Cluster defining marker genes, MC subset defining genes, and differential expression full gene lists presented in manuscript.
Supplementary Table 2: Gene lists derived from literature and databases used for scoring
Acknowledgements
We thank E. Lewis and N. Hallen for technical support in preparing tissue digests, the Broad Genomics Platform and Robert Chase of the BWH Channing Division of Network Medicine for RNA-seq assistance with CBMCs, members of the Shalek Laboratory for experimental and computational advice, and M. Morrison and F. Al Haddad for administrative support.
Funding
J.A.B. was supported by NIH grants R37AI052353, R01AI136041, R01AI130109, R01HL136209, and U19 AI095219; N.A.B. by NIH grants R01HL120952, R01AI134989, U19AI095219, and Steven and Judy Kaye Young Innovators Award; A.K.S. by the Searle Scholars Program, the Beckman Young Investigator Program, the Pew-Stewart Scholars Program for Cancer Research, a Sloan Fellowship in Chemistry, the NIH (5U24AI118672), the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.; T.M.L. by NIH grants R01HL128241 and U19AI095219; M.C.N acknowledges funding from the Netherlands Lung Foundation project no. 5.1.14.020 and 4.1.18.226, and the European Union’s H2020 Research and Innovation Program under grant agreement no. 874656 (discovAIR) and grant number CZF2019-002438 from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative Foundation awarded to the HCA Lung Seed Network. K.M.B. was supported by NIH AADCRC Opportunity Fund Award U19AI070535; J.O.M J.O.M is a New York Stem Cell Foundation – Robertson Investigator. J.O.M was supported by the Richard and Susan Smith Family Foundation, the HHMI Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation Fellowship (DRG-2274-16), the AGA Research Foundation’s AGA-Takeda Pharmaceuticals Research Scholar Award in IBD – AGA2020-13-01, the HDDC Pilot and Feasibility P30 DK034854, the Food Allergy Science Initiative, and The New York Stem Cell Foundation.; D.F.D. was supported by T32 AI007306 (to J.A.B.), NIH AADCRC Opportunity Fund Award U19AI070535, K22 AI146281, and by generous contributions from the Vinik family.
Footnotes
Competing interests
J.O.M. reports compensation for consulting services with Cellarity and Hovione. R.E.R. reports compensation for consulting services with Roche Genentech and Gossamer pharmaceuticals. N.A.B. reports compensation for consulting services for Regeneron. A.K.S. reports compensation for consulting and/or SAB membership from Merck, Honeycomb Biotechnologies, Cellarity, Repertoire Immune Medicines, Ocrhe Bio, Hovione, and Dahlia Biosciences.
Data and materials availability:
A cell x gene matrix generated from sorted nasal polyp-derived mast cell and analyzed during the current study is available along with the manuscript as Supplementary Table 3. Single-cell RNA sequencing raw data in FASTQ format have been deposited in dbGaP under accession no. phs002333.v1.p1. Bulk sequencing data have been deposited in the Gene Expression Omnibus under accession no. GSE165804.
References
- 1.Mukai K, Tsai M, Saito H, Galli SJ, Mast cells as sources of cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors. Immunol Rev 282, 121–150 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cahill KN et al. , KIT Inhibition by Imatinib in Patients with Severe Refractory Asthma. N Engl J Med 376, 1911–1920 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Voehringer D, Protective and pathological roles of mast cells and basophils. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 13, 362–375 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Andersson CK, Mori M, Bjermer L, Lofdahl CG, Erjefalt JS, Novel site-specific mast cell subpopulations in the human lung. Thorax 64, 297–305 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Irani AA, Schechter NM, Craig SS, DeBlois G, Schwartz LB, Two types of human mast cells that have distinct neutral protease compositions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 83, 4464–4468 (1986). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gentek R et al. , Hemogenic Endothelial Fate Mapping Reveals Dual Developmental Origin of Mast Cells. Immunity 48, 1160–1171 e1165 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Li Z et al. , Adult Connective Tissue-Resident Mast Cells Originate from Late Erythro-Myeloid Progenitors. Immunity 49, 640–653 e645 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gurish MF et al. , Intestinal mast cell progenitors require CD49dbeta7 (alpha4beta7 integrin) for tissue-specific homing. J Exp Med 194, 1243–1252 (2001). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Abonia JP et al. , Alpha-4 integrins and VCAM-1, but not MAdCAM-1, are essential for recruitment of mast cell progenitors to the inflamed lung. Blood 108, 1588–1594 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bankova LG, Dwyer DF, Liu AY, Austen KF, Gurish MF, Maturation of mast cell progenitors to mucosal mast cells during allergic pulmonary inflammation in mice. Mucosal Immunol 8, 596–606 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dwyer DF, Barrett NA, Austen KF, Immunological Genome Project C, Expression profiling of constitutive mast cells reveals a unique identity within the immune system. Nat Immunol 17, 878–887 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Xing W, Austen KF, Gurish MF, Jones TG, Protease phenotype of constitutive connective tissue and of induced mucosal mast cells in mice is regulated by the tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108, 14210–14215 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Dahlin JS et al. , Lin- CD34hi CD117int/hi FcepsilonRI+ cells in human blood constitute a rare population of mast cell progenitors. Blood 127, 383–391 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zheng S, Papalexi E, Butler A, Stephenson W, Satija R, Molecular transitions in early progenitors during human cord blood hematopoiesis. Mol Syst Biol 14, e8041 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Dougherty RH et al. , Accumulation of intraepithelial mast cells with a unique protease phenotype in T(H)2-high asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 125, 1046–1053 e1048 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Balzar S et al. , Mast cell phenotype, location, and activation in severe asthma: data from the severe asthma research program. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med 183, 299–309 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Takabayashi T et al. , Glandular mast cells with distinct phenotype are highly elevated in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 130, 410–420 e415 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Abonia JP et al. , Involvement of mast cells in eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 126, 140–149 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Brightling CE et al. , Mast-cell infiltration of airway smooth muscle in asthma. New England Journal of Medicine 346, 1699 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Siddiqui S et al. , Airway hyperresponsiveness is dissociated from airway wall structural remodeling. J Allergy Clin Immunol 122, 335–341, 341 e331–333 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Finotto S, Dolovich J, Denburg JA, Jordana M, Marshall JS, Functional heterogeneity of mast cells isolated from different microenvironments within nasal polyp tissue. Clin Exp Immunol 95, 343–350 (1994). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ordovas-Montanes J et al. , Allergic inflammatory memory in human respiratory epithelial progenitor cells. Nature 560, 649–654 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.White AA, Stevenson DD, Aspirin-Exacerbated Respiratory Disease. N Engl J Med 379, 1060–1070 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Buchheit KM et al. , Thymic stromal lymphopoietin controls prostaglandin D2 generation in patients with aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol 137, 1566–1576 e1565 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cepek KL et al. , Adhesion between epithelial cells and T lymphocytes mediated by E-cadherin and the alpha E beta 7 integrin. Nature 372, 190 (1994). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Berlin C et al. , Alpha 4 beta 7 integrin mediates lymphocyte binding to the mucosal vascular addressin MAdCAM-1. Cell 74, 185 (1993). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gierahn TM et al. , Seq-Well: portable, low-cost RNA sequencing of single cells at high throughput. Nat Methods 14, 395–398 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hannedouche S et al. , Oxysterols direct immune cell migration via EBI2. Nature 475, 524–527 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Liu C et al. , Oxysterols direct B-cell migration through EBI2. Nature 475, 519–523 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Collison A et al. , Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand regulates hallmark features of airways remodeling in allergic airways disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 51, 86–93 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Weckmann M et al. , Critical link between TRAIL and CCL20 for the activation of TH2 cells and the expression of allergic airway disease. Nat Med 13, 1308–1315 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Shalev I et al. , Targeted deletion of fgl2 leads to impaired regulatory T cell activity and development of autoimmune glomerulonephritis. J Immunol 180, 249–260 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Martin N et al. , Primary human airway epithelial cell-dependent inhibition of human lung mast cell degranulation. PLoS One 7, e43545 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hsieh FH et al. , Human airway epithelial cell determinants of survival and functional phenotype for primary human mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102, 14380–14385 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Chhiba KD, Hsu CL, Berdnikovs S, Bryce PJ, Transcriptional Heterogeneity of Mast Cells and Basophils upon Activation. J Immunol 198, 4868–4878 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Neumark N. e. a.. (www.ipfcellatlas.com, 2019).
- 37.Habermann AC et al. , Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals profibrotic roles of distinct epithelial and mesenchymal lineages in pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Adv 6, eaba1972 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Adams TS et al. , Single-cell RNA-seq reveals ectopic and aberrant lung-resident cell populations in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Adv 6, eaba1983 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Morse C et al. , Proliferating SPP1/MERTK-expressing macrophages in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J 54, (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Murray LA et al. , Targeting interleukin-13 with tralokinumab attenuates lung fibrosis and epithelial damage in a humanized SCID idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis model. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 50, 985–994 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Vieira Braga FA et al. , A cellular census of human lungs identifies novel cell states in health and in asthma. Nat Med 25, 1153–1163 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Burton OT et al. , Direct effects of IL-4 on mast cells drive their intestinal expansion and increase susceptibility to anaphylaxis in a murine model of food allergy. Mucosal Immunol 6, 740–750 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Madden KB et al. , Role of STAT6 and mast cells in IL-4- and IL-13-induced alterations in murine intestinal epithelial cell function. J Immunol 169, 4417–4422 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hughes TK et al. , Second-Strand Synthesis-Based Massively Parallel scRNA-Seq Reveals Cellular States and Molecular Features of Human Inflammatory Skin Pathologies. Immunity 53, 878–894 e877 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Oskeritzian CA et al. , Surface CD88 functionally distinguishes the MCTC from the MCT type of human lung mast cell. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol 115, 1162–1168 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Fujisawa D et al. , Expression of Mas-related gene X2 on mast cells is upregulated in the skin of patients with severe chronic urticaria. J Allergy Clin Immunol 134, 622–633 e629 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Travaglini KJ et al. , A molecular cell atlas of the human lung from single-cell RNA sequencing. Nature 587, 619–625 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kett WC et al. , Avidin is a heparin-binding protein. Affinity, specificity and structural analysis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1620, 225–234 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Weidner N, Austen KF, Heterogeneity of mast cells at multiple body sites. Fluorescent determination of avidin binding and immunofluorescent determination of chymase, tryptase, and carboxypeptidase content. Pathol Res Pract 189, 156–162 (1993). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Stoeckius M et al. , Simultaneous epitope and transcriptome measurement in single cells. Nat Methods 14, 865–868 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Motakis E et al. , Redefinition of the human mast cell transcriptome by deep-CAGE sequencing. Blood 123, e58–67 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Fureder W et al. , Differential expression of complement receptors on human basophils and mast cells. Evidence for mast cell heterogeneity and CD88/C5aR expression on skin mast cells. J. Immunol 155, 3152–3160 (1995). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Bischoff SC et al. , IL-4 enhances proliferation and mediator release in mature human mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96, 8080–8085 (1999). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kulka M, Metcalfe DD, High-resolution tracking of cell division demonstrates differential effects of TH1 and TH2 cytokines on SCF-dependent human mast cell production in vitro: correlation with apoptosis and Kit expression. Blood 105, 592–599 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bachert C et al. , Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in patients with severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (LIBERTY NP SINUS-24 and LIBERTY NP SINUS-52): results from two multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group phase 3 trials. Lancet 394, 1638–1650 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Wenzel S et al. , Dupilumab efficacy and safety in adults with uncontrolled persistent asthma despite use of medium-to-high-dose inhaled corticosteroids plus a long-acting beta2 agonist: a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled pivotal phase 2b dose-ranging trial. Lancet 388, 31–44 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ortega HG et al. , Mepolizumab treatment in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma. N. Engl. J. Med 371, 1198–1207 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Walker C et al. , Cytokine control of eosinophils in pulmonary diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol 94, 1262–1271 (1994). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Jenkins SJ et al. , Local macrophage proliferation, rather than recruitment from the blood, is a signature of TH2 inflammation. Science 332, 1284–1288 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Gordon S, Martinez FO, Alternative activation of macrophages: mechanism and functions. Immunity 32, 593–604 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Yi T, Cyster JG, EBI2-mediated bridging channel positioning supports splenic dendritic cell homeostasis and particulate antigen capture. Elife 2, e00757 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Laidlaw TM et al. , Characterization of a novel human mast cell line that responds to stem cell factor and expresses functional FcepsilonRI. J Allergy Clin Immunol 127, 815–822e811–815 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Macosko EZ et al. , Highly Parallel Genome-wide Expression Profiling of Individual Cells Using Nanoliter Droplets. Cell 161, 1202–1214 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Satija R, Farrell JA, Gennert D, Schier AF, Regev A, Spatial reconstruction of single-cell gene expression data. Nat Biotechnol 33, 495–502 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Korsunsky I et al. , Fast, sensitive and accurate integration of single-cell data with Harmony. Nat Methods 16, 1289–1296 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Table 3: Cell x gene matrix (raw) for sorted MCs from 6 polyp donors.
Supplementary Methods
Figure S1: In-depth characterization of nasal polyp MCs.
Figure S2: Characterization of nasal polyp MC protease phenotype and localization.
Figure S3: Characterization of sorted cells through scRNA-seq.
Figure S4: Immunohistologic localization of EBI2-expressing MCs.
Figure S5: Identification of MCs in three IPF scRNA-seq datasets.
Figure S6: Identification of an asthma-enriched CD38high MC cluster.
Figure S7: Influence of Dupilumab on nasal polyp MC transcript expression.
Figure S8: Schematic representation of strategy for evaluating the transcriptome of Itgβ7high MCs.
Figure S9: Proposed model for MC homeostasis and hyperplasia in human sinus mucosa.
Supplementary Table 5: Cluster defining marker genes for scRNA-seq datasets from the human IPF lung atlas and asthma vs healthy donors.
Supplementary Table 6: Differential gene expression analysis for human umbilical cord-derived MCs treated with IL-4 or vehicle for 96 hours.
Supplementary Table 7: Source data for figures.
Supplementary Table 1: Patient Information
Supplementary Table 4: Cluster defining marker genes, MC subset defining genes, and differential expression full gene lists presented in manuscript.
Supplementary Table 2: Gene lists derived from literature and databases used for scoring


