Abstract
BACKGROUND AND AIMS:
Iron is essential yet also highly chemically reactive and potentially toxic. The mechanisms that allow cells to use iron safely are not clear; defects in iron management are a causative factor in the cell-death pathway known as ferroptosis. Poly rC binding protein 1 (PCBP1) is a multifunctional protein that serves as a cytosolic iron chaperone, binding and transferring iron to recipient proteins in mammalian cells. Although PCBP1 distributes iron in cells, its role in managing iron in mammalian tissues remains open for study. The liver is highly specialized for iron uptake, utilization, storage, and secretion.
APPROACH AND RESULTS:
Mice lacking PCBP1 in hepatocytes exhibited defects in liver iron homeostasis with low levels of liver iron, reduced activity of iron enzymes, and misregulation of the cell-autonomous iron regulatory system. These mice spontaneously developed liver disease with hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and degeneration. Transcriptome analysis indicated activation of lipid biosynthetic and oxidative-stress response pathways, including the antiferroptotic mediator, glutathione peroxidase type 4. Although PCBP1-deleted livers were iron deficient, dietary iron supplementation did not prevent steatosis; instead, dietary iron restriction and antioxidant therapy with vitamin E prevented liver disease. PCBP1-deleted hepatocytes exhibited increased labile iron and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), were hypersensitive to iron and pro-oxidants, and accumulated oxidatively damaged lipids because of the reactivity of unchaperoned iron.
CONCLUSIONS:
Unchaperoned iron in PCBP1-deleted mouse hepatocytes leads to production of ROS, resulting in lipid peroxidation (LPO) and steatosis in the absence of iron overload. The iron chaperone activity of PCBP1 is therefore critical for limiting the toxicity of cytosolic iron and may be a key factor in preventing the LPO that triggers the ferroptotic cell-death pathway.
Iron is an essential nutrient for nearly every organism because cells use this metal to build the essential iron cofactors: heme, iron-sulfur (Fe-S) clusters, and mono- or dinuclear iron centers. Cells express hundreds of different iron-dependent enzymes and using these cofactors presents multiple challenges. Heme and Fe-S clusters do not assemble spontaneously, but are synthesized by complex enzymatic machines.(1,2) All of the iron cofactors require dedicated systems for their distribution within different compartments of the cell. These systems serve to (1) ensure proper delivery of the cofactor to cognate apo-enzymes, (2) protect the cofactor from chemical attack during delivery, and (3) prevent the iron cofactor from engaging in harmful oxidation-reduction chemistry.
Cells contain pools of chemically reactive, kinetically labile iron, termed the labile iron pool (LIP), which serves as the raw material for the synthesis and distribution of iron cofactors. The molecular character of the cytosolic LIP has not been fully defined, but largely exists as reduced, ferrous iron (Fe II) coordinated by a complex buffer consisting of both small and large molecules. In silico analysis suggests that >95% of the cytosolic LIP is coordinated by the free sulfhydryl of reduced glutathione (GSH).(3) Recent studies confirm that Fe-GSH is formed in cells and selectively coordinated by the iron chaperone, poly r(C) binding protein 1 (PCBP1).(4)
PCBPs are multifunctional adaptor proteins capable of binding single-stranded nucleic acids, proteins, and iron, thereby affecting the fate of each binding partner.(5) PCBP1 and Poly r(C) binding protein 2 (PCBP2) function as iron chaperones in the cytosol: They directly bind ferrous iron and mediate its transfer to or from client proteins by metal-mediated protein-protein interactions. PCBP1 and 2 are essential genes; constitutive deletion in mice results in early embryonic lethality.(6) The iron chaperone activities of PCBP1 include delivery of iron to ferritin, the major cellular iron-storage protein, to the glutaredoxin-3/bolA family member 2 [2Fe-2S] chaperone complex and nonheme iron enzymes.(7–10) These include the mono-iron prolyl hydroxylases, which regulate hypoxia-inducible transcription factor 1-α (HIF1α) and the di-iron deoxyhypusine hydroxylase, which hypusinates eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A.(11,12) In addition to cell-based studies, murine studies have confirmed the iron chaperone activity of PCBP1 in erythropoietic tissues. Mice depleted of PCBP1 in bone marrow develop a microcytic anemia similar to that observed in nutritional iron deficiency.(8)
Similar to the erythron, the liver is highly specialized in the management and utilization of iron. Dietary iron, absorbed by intestinal epithelial cells, and splenic iron, secreted by macrophages that recycle red blood cells, directly flow into the portal circulation, which is delivered to the liver. The liver efficiently extracts transferrin- and non-transferrin-bound iron from the portal circulation.(13) The liver is the primary site of iron storage and the major organ regulating body iron balance through the iron-regulatory hormone, hepcidin.(14,15) Finally, the liver itself has a high metabolic requirement for iron to carry out biosynthesis, detoxification, and enegy production. In mature adult mice, only a small fraction (<10%) of total liver iron is detected as high-spin Fe(II) coordinated by O- and N-ligands, which is the form of iron that PCBP1 delivers to mono- and di-iron centers and is predicted to form the LIP.(16) The impact of iron chaperones on liver physiology is open for study.
We investigated the function of iron chaperones in the liver by developing a murine model of hepatocyte-specific PCBP1 deletion. Using unbiased (transcriptomics, lipidomics) and targeted approaches, we found that PCBP1 iron chaperone activity was required not only for iron homeostasis and iron enzyme activity, but also for the prevention of iron-mediated oxidative damage that drives the development of liver disease in thesemice. These studies demonstrate that murine hepatocytes lack the capacity to manage the chemical reactivity of iron without the aid of iron chaperones and suggest a fundamental role in preventing ferroptosis in the liver.
Materials and Methods
ANIMAL STUDIES
PCBP1fl/fl female mice(8) were crossed with Alb-Cre PCBP1fl/fl males (Alb-Cre mice B6.Cg-Tg(Alb-cre) 21Mgn/J, #003574; The Jackson Laboratory, Bar Harbor, ME). Male offspring were weaned onto purified diets (Envigo TD.80396, Indianapolis, IN) supplemented with iron or vitamin E (vit E), with iron added as ferric citrate. Mice had ad libitum acess to diets and double-distilled water and were euthanized after 16–18 days on the iron-defined diet (age 5–6 weeks). Littermates lacking the Alb-Cre transgene served as controls. All animal study protocols were reviewed and approved by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) Animal Care and Use Committee and performed in compliance with National Institutes of Health (NIH) guidelines for the humane care of animals.
PRIMARY HEPATOCYTES
Primary hepatocytes were isolated from 8- to 12-week-old female mice maintained on standard chow (NIH-31) or defined-iron diets as described.(17) Cells were suspended in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium, 10% fetal bovine serum, and 100 U/mL of penicillin-streptomycin and plated at 1.5 × 104 live cells/cm2 in collagen-coated wells. Medium was changed after 3 hours, and hepatocytes were incubated 16–24 hours before assays.
QUANTIFICATION AND STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Fluorescent images were processed and analyzed using Fiji, ImageJ (version 2.0.0-rc-49/1.51d; NIH, Bethesda, MD). Data were analyzed with Prism software (version 8; GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA). Data are reported as means ± SD. Outliers were identified using the integrated ROUT method and excluded. Differences between two groups were analyzed by unpaired Student t tests with Welsh corrections performed in cases of unequal variance. Differences among groups were determined by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by Bonferroni’s post-hoc analysis.
ADDITIONAL METHODS
Detailed protocols and additional assays are described in the Supporting Information.
Results
INCREASED LIPOGENESIS AND STEATOSIS IN PCBP1-DEPLETED LIVERS
We developed a hepatocyte- and cholangiocyte-specific deletion model of PCBP1 deficiency by breeding mice carrying the floxed allele (PCBP1fl/fl)(8) with mice expressing Cre recombinase under the control of the albumin (Alb) promoter (Fig. 1A). We examined young mice (5–6 weeks old) fed a defined-iron diet (purified diet, normal iron at 50 parts per million [ppm]). Efficient depletion of PCBP1 mRNA and protein in livers of PCBP1fl/fl mice carrying the Alb-Cre transgene (PCBP1Δhep) was confirmed by qPCR and immunoblotting analyses (Fig. 1B). Loss of PCBP1 in hepatocytes minimally affected levels of PCBP2, confirming that phenotypic changes in PCBP1Δhep mice did not result from PCBP2 deficiency or overexpression.
FIG. 1.
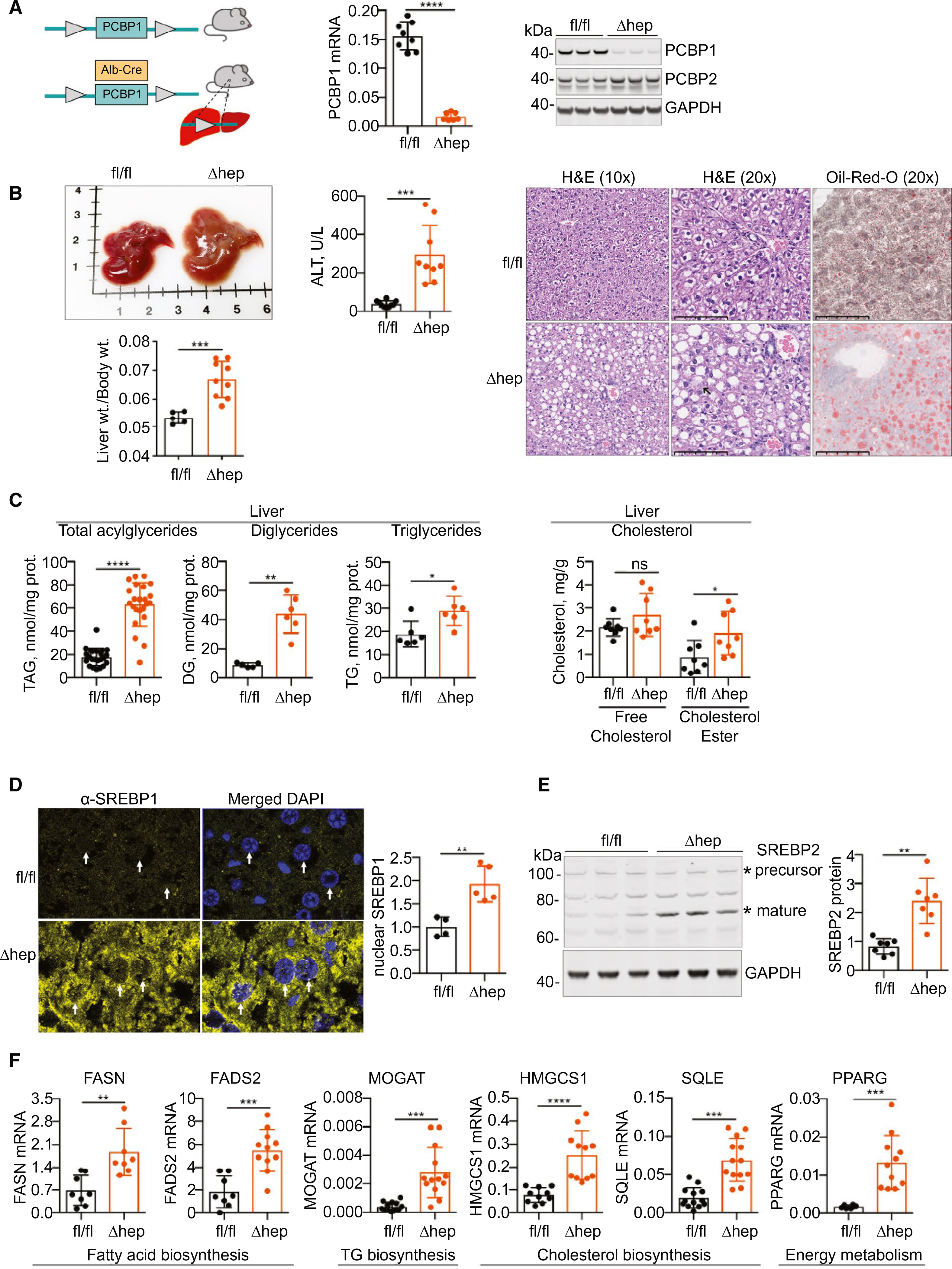
Increased lipid accumulation in PCBP1Δhep livers. (A) Construction of hepatocyte-specific knockout of PCBP1. PCBP1fl/fl females and Alb-Cre PCBP1fl/fl (PCBP1Δhep) males were crossed (left), and male littermates were weaned onto iron-defined diets (50 ppm, normal iron) for 16–18 days. Loss of PCBP1 mRNA (center), by qPCR, and protein (right), by immunoblotting, in livers of PCBP1Δhep mice. (B) Steatohepatitis in PCBP1Δhep mice. Enlarged, pale liver and increased liver/body weight ratio in PCBP1Δhep mice (left). Increased plasma ALT activity in PCBP1Δhep mice (center). Lipid accumulation in PCBP1Δhep livers by H&E and Oil Red O staining of liver sections from PCBP1fl/fl and PCBP1Δhep mice (right). Arrowhead in PCBP1Δhep, H&E (20×) indicates ballooning degeneration. (C) Increased lipids in PCBP1Δhep livers. Total acylglycerides (measured by enzymatic assay), diacylglycerides, and triacylglycerides (measured by mass spectrometry) in liver extracts from PCBP1fl/fl and PCBP1Δhep mice (left). Increased cholesteryl esters in PCBP1Δhep livers (right). Free and esterified cholesterol measured in liver extracts from PCBP1fl/fl and PCBP1Δhep mice by enzymatic assay. (D) Increased total and nuclear SREBP1 in PCBP1Δhep livers. SREBP1 was detected by fluorescent immunohistochemistry and nuclear signal (arrowheads) quantitated at right. (E) Increased mature SREBP2 in PCBP1Δhep livers. Representative immunoblotting of lysates from PCBP1fl/fl and PCBP1Δhep livers probed for SREBP2 and GAPDH. Precursor and mature forms are indicated by an asterisk (“*”), quantification of mature SREBP2 at right. (F) Increased expression of lipid biosynthesis genes in PCBP1Δhep livers. Transcripts of fatty acid, triglyceride, and cholesterol biosynthetic genes were measured by qPCR. Data represent mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001, using one-way ANOVA and an unpaired Student t test. See also Supporting Fig. S1. Abbreviations: DG, diglyceride; DAPI, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; ns, not significant; TAG, triacylglycerol; TG, triglyceride.
At necropsy, livers from PCBP1Δhep mice exhibited slightly paler coloration and a 30% increase in liver/body weight ratios (Fig. 1B), without affecting total body weight (Supporting Fig. S1A). Histological examination of the liver demonstrated chronic liver disease, with macrovesicluar steatosis, ballooning degeneration, and periportal inflammation in PCBP1Δhep livers (Fig. 1B). Accumulation of lipid was confirmed by Oil Red O staining. A 7-fold increase in plasma alanine aminotransferase (ALT) suggested ongoing liver damage. Quantitative analysis of total acyglycerides, diglycerides, and triglycerides demonstrated 4-, 5-, and 1.5-fold elevations, respectively, of these species in livers of PCBP1Δhep mice, confirming hepatic steatosis (Fig. 1C). Levels of both plasma triglyceride and apolipoprotein B, lipid and protein constituents of very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), exhibited a 40% decrease in PCBP1Δhep mice compared to PCBP1fl/fl mice, raising the possibility that impaired VLDL secretion may contribute to steatosis in PCBP1Δhep mice (Supporting Fig. S1C). Esterified cholesterol is also a component of lipid droplets, and we found a 2-fold increase in cholesteryl esters in PCBP1Δhep livers (Fig. 1C). Plasma cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein levels also were increased in PCBP1Δhep mice (Supporting Fig. S1B).
The master regulators of fatty acid and cholesterol biosynthesis are the transcription factors known as sterol-regulatory element binding proteins 1a, 1c, and 2 (SREBP1 and SREBP2),(18,19) both of which are regulated by posttranslational processing and proteolytic cleavage. Activation of SREBP-1c in the liver triggers increased expression of genes involved in fatty acid biosynthesis whereas SREBP2 predominately activates genes of cholesterol biosynthesis. Increased levels of total and nuclear SREBP1 were detected in sections of PCBP1Δhep livers (Fig. 1D), and increased levels of mature SREBP2 were detected in lysates of PCBP1Δhep livers (Fig. 1E). Transcripts involved in fatty acid and triglyceride biosynthesis—fatty acid synthase (FASN), fatty acid desaturase 2 (FADS2), and monoacylglyceride acyltransferase 1 (MOGAT)—were 2-, 3-, and 7-fold up-regulated in PCBP1Δhep livers (Fig. 1F). Similarly, transcripts involved in cholesterol biosynthesis—hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase (HMGCS1) and squalene epoxidase (SQLE)—were 3- and 4-fold up-regulated. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARG), a nuclear receptor associated with lipogenesis and the development of fatty liver disease, was also up-regulated in PCBP1Δhep livers. Thus, deletion of PCBP1 in hepatocytes resulted in rapid development of steatosis without the additional stimulation of an obesogenic diet.
LIVER IRON DEFICIENCY IN MICE WITH HEPATOCYTE-SPECIFIC PCBP1 DELETION
PCBP1 functions as an iron chaperone. Therefore, we questioned whether deletion of PCBP1 in hepatocytes would affect iron homeostasis in mouse liver tissue. We examined livers from male littermates of PCBP1fl/fl and PCBP1Δhep mice and found that nonheme iron levels were reduced by 40% in PCBP1Δhep mice compared to PCBP1fl/fl mice (Fig. 2A). ular iron levels are generally reflected in levels of ferritin protein and, consistent with reduced nonheme iron levels, PCBP1Δhep livers exhibited a 70% reduction in ferritin (Fig. 2B). Lysosomal degradation of ferritin is controlled by the autophagosomal cargo receptor, nuclear coactivator 4 (NCOA4),(20,21) which accumulates in cells under conditions of iron limitation.(22,23) NCOA4 levels exhibited a 2-fold increase in PCBP1Δhep livers and likely contributed to the lowered level of ferritin.
FIG. 2.
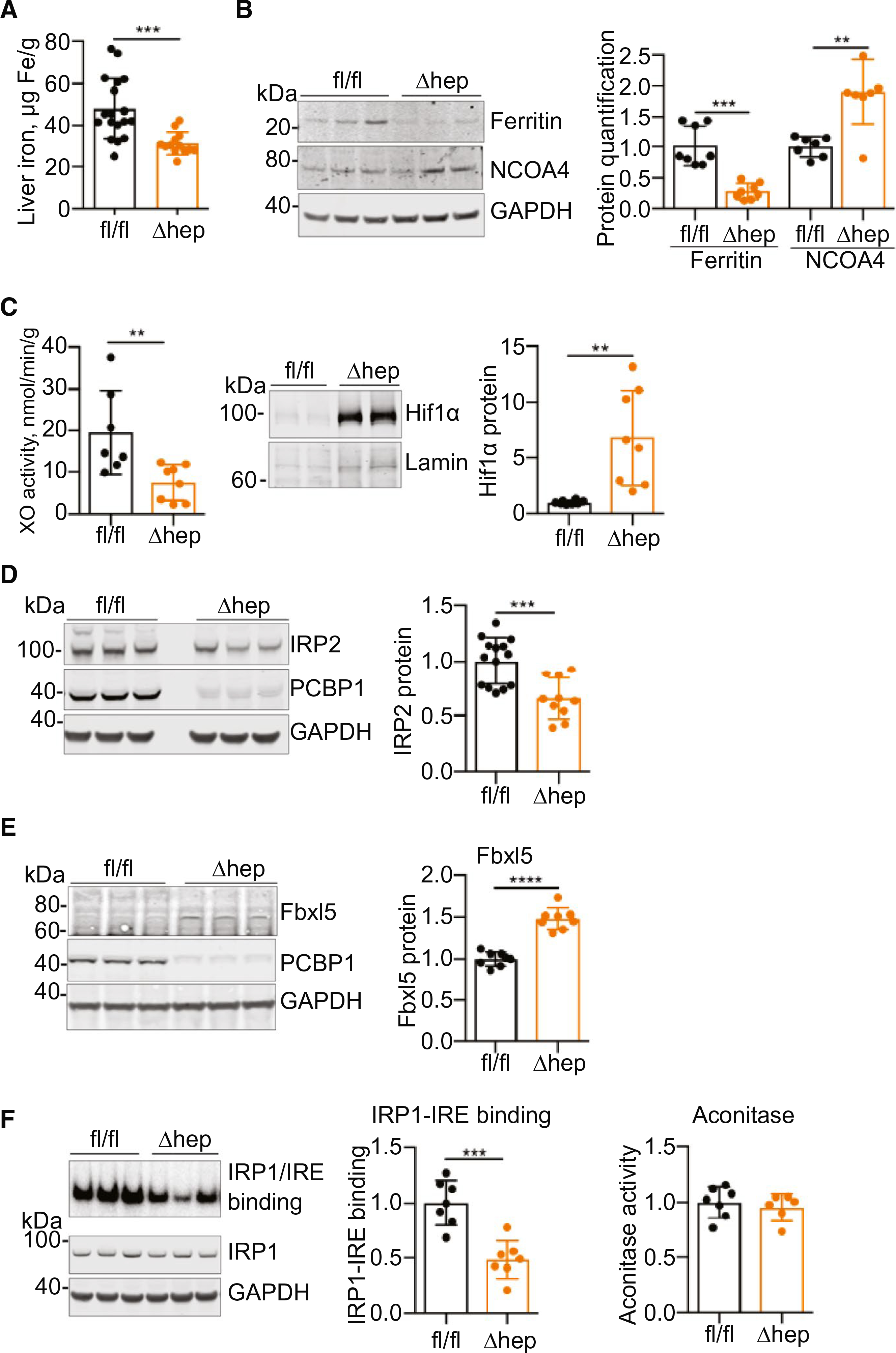
Iron depletion and dysregulation in hepatocyte-specific knockout of PCBP1. (A-C) Signs of iron deficiency in PCBP1Δhep livers. Male littermates were weaned onto iron-defined diets (50 ppm, normal iron) for 16–18 days before analysis. (A) Decreased liver nonheme iron in PCBP1Δhep mice. (B) Decreased ferritin and increased NCOA4 in PCBP1Δhep livers. Representative immunoblottings (left) and quantification of ferritin and NCOA4 proteins (right). (C) Decreased activity of iron-dependent enzymes in PCBP1-depleted livers. Xanthine oxidase activity (XO; left) in liver extracts and increased Hif1α protein in nuclear extracts (right) from PCBP1-depleted livers. (D-F) Dysregulated iron sensing in PCBP1Δhep livers. (D) Decreased IRP2 protein in livers of PCBP1Δhep mice. Representative immunoblotting of liver lysates (left) and quantification of IRP2 protein (right). (E) Increased Fbxl5 in livers of PCBP1Δhep mice. Representative immunoblotting of liver lysates probed for Fbxl5, PCBP1, and GAPDH (left) and quantification of Fbxl5 (right). (F) Decreased IRE-binding activity in livers of PCBP1Δhep mice. Extracts were analyzed for [32P]IRE-IRP1 complex formation by electrophoretic mobility shift assays. Representative assay and immunoblotting detection of IRP1 and GAPDH (left), quantification of IRE-IRP1 binding (center), and cytosolic aconitase activity (right) in PCBP1fl/fl and PCBP1Δhep liver lysates. Data represent mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001, using an unpaired Student t test. See also Supporting Fig. S2. Abbreviation: GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Because PCBP1 can deliver iron to cytosolic ferritin, the major site of cellular iron storage, loss of ferritin iron stores could account for the reduced nonheme iron levels in PCBP1Δhep livers. However, additional measurements suggested iron cofactor depletion as well. Xanthine oxidase/dehydrogenase is an abundant liver enzyme that contains a pair of [2Fe-2S] clusters.(24) Activity was reduced by 60% in PCBP1Δhep livers without a concomitant change in mRNA levels (Fig. 2C and Supporting Fig. S2A). The prolyl hydroxylases that stimulate the degradation of Hif1α require a mononuclear iron center for activity and are dependent on PCBP1 for metalation.(11) When prolyl hydroxylase activity is reduced, Hif1α accumulates; we measured a 6-fold increase in Hif1α levels in PCBP1Δhep mice (Fig. 2C and Supporting Fig. S2B), and transcriptional profiling suggested elevation of some hypoxia-inducible transcription factor 2-α–specific transcripts, as well (Supporting Fig. S2B). In hepatocytes, most hemoproteins are found in membranes containing mitochondrial respiratory complexes and the cytochrome P450 system. Membrane-associated heme levels were decreased by 20% in PCBP1Δhep mice (Supporting Fig. S2C). Thus, deletion of PCBP1 in hepatocytes resulted in depletion of both the pool of iron stored in ferritin and the pools of iron used as cofactors in enzymes. However, serum iron indices, red cell indices, and iron-regulated transcripts were not altered by PCBP1 deletion in hepatocytes (Supporting Fig. S2D,E).
PARADOXICAL REGULATION OF IRON-REGULATORY PROTEINS IN PCBP1Δhep LIVERS
Intracellular iron balance is largely controlled by the iron-regulatory, RNA binding proteins (iron-regulatory protein 1 [IRP1] and iron-regulatory protein 2 [IRP2]), which function by binding to iron-responsive elements (IREs) in the 5' and 3' untranslated regions of target mRNAs and altering their fate.(25) RNA binding activity of both IRPs is activated by cytosolic iron limitation and can be abrogated by iron repletion as well as oxidative damage. Previous studies in HEK cells indicated that PCBP depletion interferes with the activities of IRP1(12) and IRP2.(7) In mouse liver, however, IRP1 activities are not responsive to changes in iron; instead, cellular iron homeostasis is regulated by IRP2.(26) Cellular iron depletion increases the RNA binding activity of IRP2 by preventing its proteosomal degradation. We measured IRP2 levels in PCBP1Δhep livers and found that they were 35% lower than in PCBP1fl/fl livers, which was unexpected in the setting of hepatocyte iron depletion (Fig. 2D). IRP2 degradation is triggered by the iron-sensing ubiquitin ligase, F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 5 (Fbxl5).(27,28) Fbxl5 directly binds iron and is stabilized in the iron-bound form, leading to accumulation in iron-rich conditions and degradation in iron-poor conditions. Paradoxically, immunoblotting analysis demonstrated a 50% increase in Fbxl5 in PCBP1Δhep livers, suggesting stabilization of the protein (Fig. 2E). The increase in Fbxl5 likely contributes to the degradation of IRP2 protein.
We also tested the activities of IRP1 in liver lysates of PCBP1fl/fl and PCBP1Δhep mice. Although the RNA binding activity of IRP1 typically increases in iron-deficient cells, surprisingly, PCBP1Δhep livers showed only 50% of the IRP1-IRE binding activity found in PCBP1fl/fl livers (Fig. 2F). IRP1 is a bifunctional protein that can acquire aconitase activity when it coordinates a [4Fe-4S] cluster. Cytosolic aconitase activities were similar in liver lysates from PCBP1fl/fl and PCBP1Δhep mice, which is in accordance with previous findings that the majority (>95%) of IRP1 in rodent liver is in the aconitase form and resistant to regulation by iron deficiency.(26,27,29) Thus, hepatocytes lacking PCBP1 exhibited regulatory features of both lower iron levels (less storage and iron enzyme activity) and higher iron levels (suppression of IRP2 activity, stabilization of Fbxl5; Supporting Fig. S2F).
IRON RESTRICTION PREVENTS STEATOSIS IN PCBP1-DEPLEATED LIVERS
Multiple enzymes involved in cholesterol and fatty acid biosynthesis require iron cofactors for activity, and we hypothesized that changes in iron could affect the homeostatic systems controlling lipid biosynthesis. We tested whether dietary iron manipulation could affect the fatty liver phenotype in PCBP1Δhep mice by feeding weanlings a low- (5 ppm), normal- (50 ppm), or high-iron (1,000 ppm) diet(30) for 16–18 days and measuring liver parameters. Alterations of dietary iron were reflected in liver, blood, and plasma (Supporting Fig. S3A–D). PCBP1Δhep livers consistently exhibited lower levels of nonheme iron than PCBP1fl/fl livers on each diet. Even though PCBP1Δhep livers exhibited a 40% lower level of nonheme iron than PCBP1fl/fl livers on the 50-ppm diet, liver iron was further reduced, from 31 to 17 μg/g, in PCBP1Δhep mice fed the 5-ppm diet. Although PCBP1Δhep mice exhibited a 2-fold increase in liver iron when fed the 1,000-ppm diet versus the 50-ppm diet, iron supplementation was not effective in correcting liver damage. PCBP1Δhep mice fed the high- and normal-iron diets displayed similar levels of steatosis, acylglyceride accumulation, and activation of lipogenesis (Fig. 3A–C).
FIG. 3.
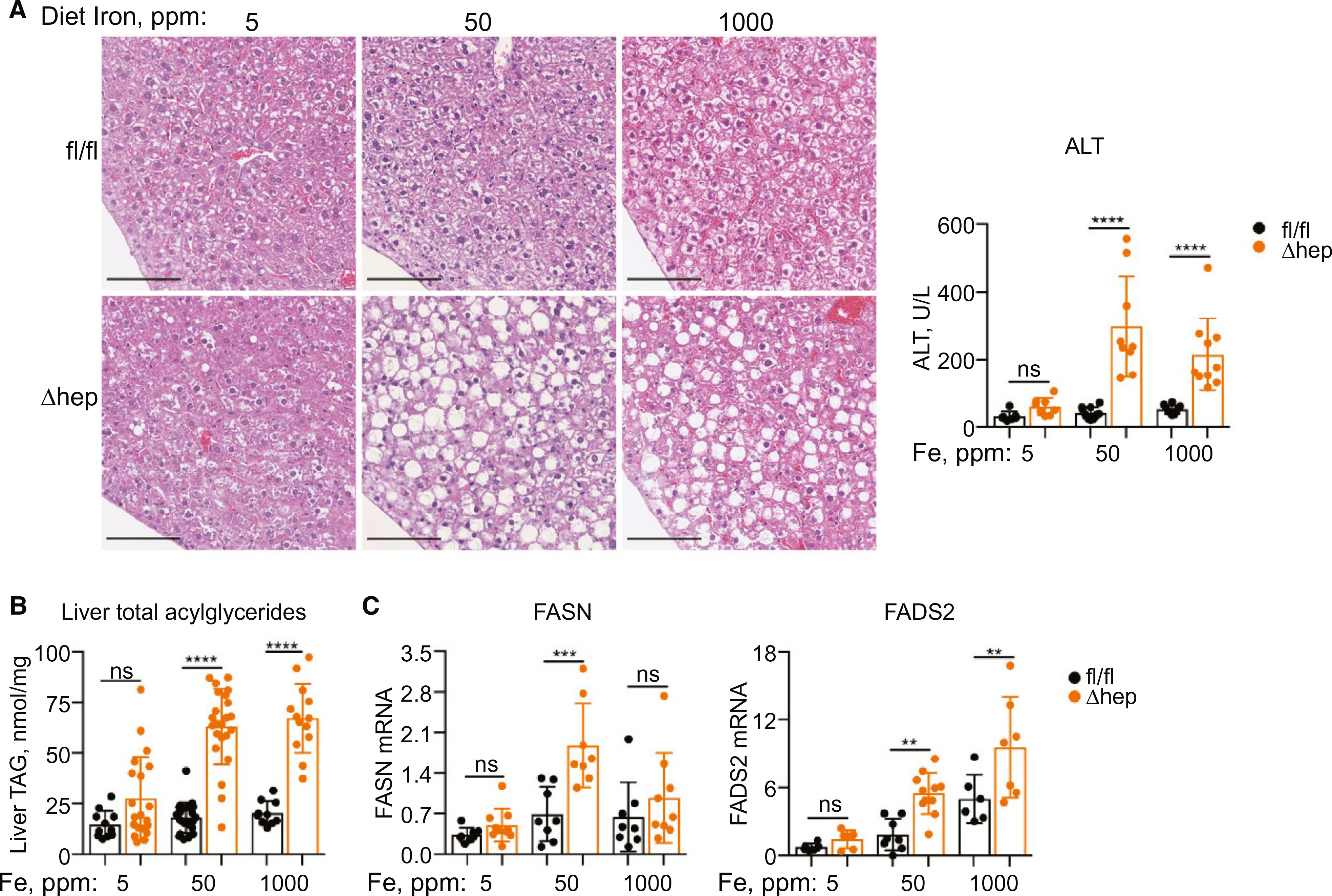
Dietary iron deficiency prevented development of steatosis. PCBP1fl/fl and PCBP1Δhep mice were fed diets containing 5, 50, or 1,000 ppm of iron for 16–18 days. (A) Decreased steatohepatitis in iron-deficient PCBP1Δhep livers by H&E staining of liver sections (left) and plasma ALT in mice fed an iron-deficient (5 ppm) diet. (B) Iron deficiency decreased accumulation of liver acylglycerides in PCBP1Δhep mice. (C) Decreased expression of fatty acid biosynthetic genes in iron-deficient livers. For clarity, data for the 50-ppm iron diet are reproduced from Fig. 1. Data represent mean ± SD. Abbreviations: H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; ns, not significant; TAG, triacylglycerol.
In contrast, the low-iron diet largely prevented development of the fatty liver phenotype in PCBP1Δhep mice. Serum ALT levels were normalized, decreased steatosis was evident in PCBP1Δhep liver, and liver acylglycerides fell to levels similar to those of PCBP1fl/fl mice (Fig. 3A,B). Expression of fatty acid biosynthesis genes FASN and FADS2 were also lowered to wild-type levels in PCBP1Δhep livers under iron deficiency (Fig. 3C). Alterations in cholesterol, however, were not normalized by the low-iron diet in PCBP1Δhep mice (Supporting Fig. S3E), suggesting that cholesterol and fatty acid biosynthesis were independently regulated in this mouse model. Furthermore, PCBP1fl/fl mice with normal levels of PCBP1 exhibitied liver acylglycerides (Fig. 3B) and transcripts of fatty acid synthesis (Fig. 3C) that were 2- to 7-fold increased on the high- versus the low-iron diet. Together, these data suggested that hepatic steatosis in PCBP1Δhep mice was more likely attributable to toxic effects of unchaperoned iron than to deficiencies of iron-dependent enzymes.
ACTIVATION OF THE NUCLEAR FACTOR ERYTHROID 2–RELATED FACTOR 2 OXIDATIVE STRESS RESPONSE IN PCBP1-DELETED LIVERS
We performed unbiased transcriptome analyses by RNA sequencing to identify genes differentially expressed in PCBP1Δhep and PCBP1fl/fl mice (Fig. 4A and Supporting Fig. S4A). Pathway analysis indicated the up-regulation of cholesterol, stearate, and triglyceride biosynthetic pathways in PCBP1Δhep mice, confirming our initial findings and suggesting increased de novo lipogenesis. Significant changes (−log2, P = 3.6) in iron homeostasis signaling in a mixed pattern was also observed. Notably, the nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2 (Nrf2)-mediated oxidative stress response and the overlapping, glutathione-mediated detoxification pathways were strongly activated in PCBPlΔhep mice.
FIG. 4.
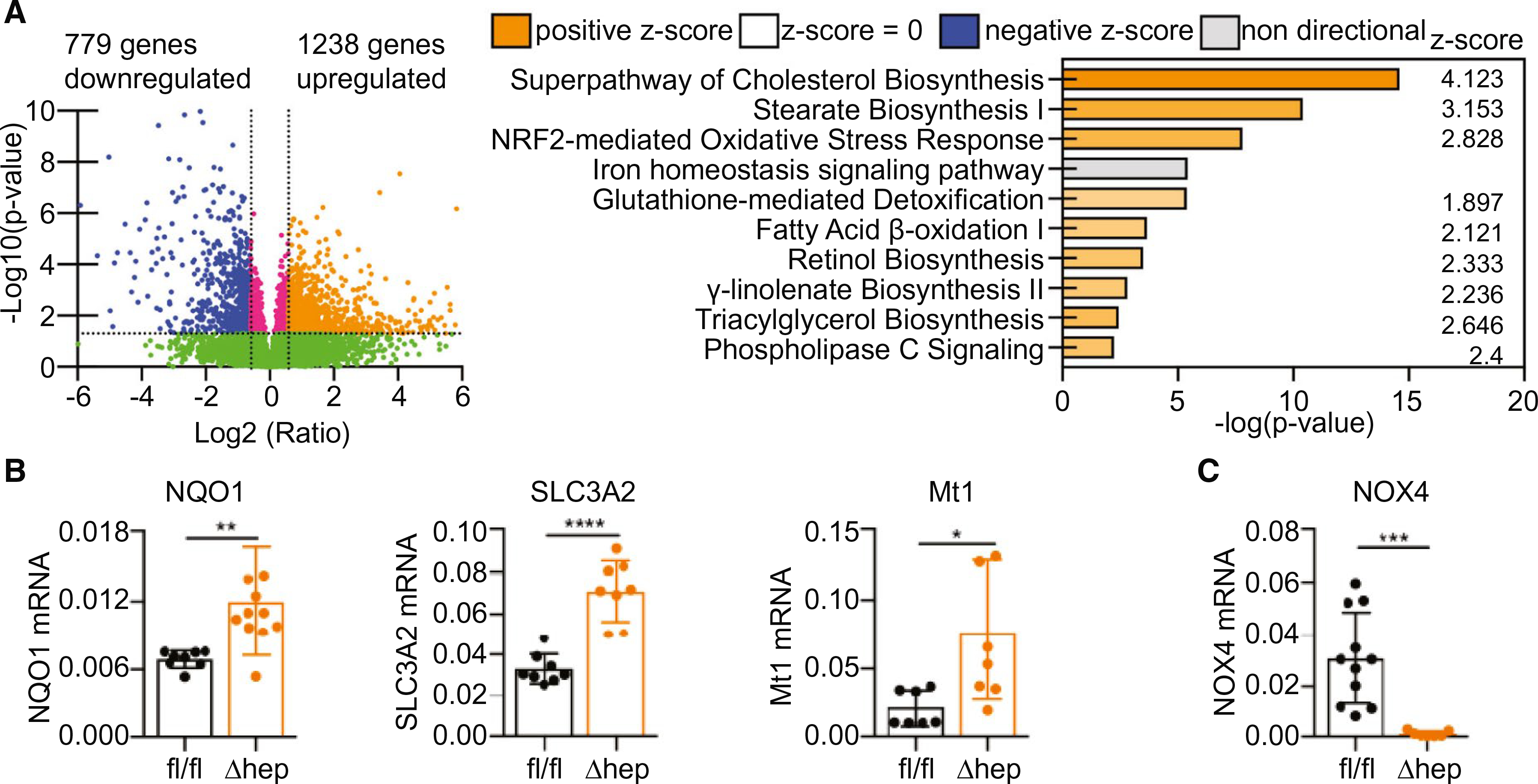
Activation of the Nrf2 oxidative stress response in PCBP1-deleted livers. Transcriptome analysis of PCBP1-deleted livers by RNA sequencing of tissue from mice on a normal-iron (50 ppm) diet. (A) Volcano plot of transcripts from PCBP1Δhep versus PCBP1fl/fl liver samples (left). Top 10 canonical pathways up-regulated in PCBP1-depleted livers identified by Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (right). (B) Increased expression of oxidative-stress resistance genes in PCBP1Δhep livers. (C) Decreased expression of NADPH oxidase 4 in PCBP1Δhep livers. RNA isolated from PCBP1fl/fl and PCBP1Δhep livers was used for qPCR analysis. Data represent mean ± SD. Abbreviation: NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate.
Nrf2 is an important regulator of the response to oxidative stress and detoxification of xenobiotics in the liver(31) and has recently been shown to influence the transcriptional response to iron in sinusoidal endothelial cells.(32) Iron is proposed to contribute to oxidative stress and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by catalyzing the Fenton reaction, in which reduced, Fe(II) promotes the single-electron reduction of endogenously produced H2O2 to form the highly reactive hydroxyl radical, OH·, and other highly reactive, high-valence iron species.(33) These pro-oxidant intermediates and oxidation products activate Nrf2 and stimulate transcription of a variety of genes involved in the antioxidant response, including NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase (Nqo1), a component of the cystine/glutamate antiporter (Slc3a2), and a metallothionein (Mt1). We measured mRNA levels of these Nrf2 target transcripts and found 2- to 4-fold increases in livers of PCBP1Δhep mice, confirming activation of Nrf2 (Fig. 4B). NADPH oxidase 4 (Nox4) is a regulatory enzyme that produces H2O2 in the liver, where it mediates signaling and may promote oxidative stress.(34) Nox4 transcripts were strongly (30-fold) repressed in PCBP1Δhep liver (Fig. 4C).
INCREASED LIPID PEROXIDATION IN PCBP1-DELETED LIVERS
Lipids with polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are abundant in the liver and major targets of iron-catalyzed ROS.(35) The methylene bridge that spans the double bonds in a PUFA is highly susceptible to radical attack. The resulting lipid radical can be propagated, resulting in the formation of lipid peroxyradicals and hydroperoxides and be terminated as oxidatively truncated, electrophilic lipids, and reactive aldehydes.(36) Glutathione peroxidase type 4 (Gpx4) repairs lipid hydroperoxides by reducing them to lipid alcohols. We measured a 40% increase in levels of Gpx4 protein in PCBP1Δhep liver (Fig. 5A), suggesting enhanced lipid hydroperoxide repair activity, whereas no changes in GSH levels were detected (Supporting Fig. S5A). 4-Hydroxynonenol (4-HNE) is an end product of lipid peroxidation (LPO), and we detected a 2-fold increase in 4-HNE modifications in sections of liver from PCBP1Δhep mice (Fig. 5B). To confirm that deletion of PCBP1 in the liver produces a state of accelerated, ongoing LPO, we isolated hepatocytes from PCBP1fl/fl and PCBP1Δhep livers and measured the production of ROS ex vivo using the oxidation-sensitive lipophilic dye, Bodipy C-11 (Fig. 5C). Hepatocytes from PCBP1Δhep mice exhibited a 2-fold higher rate of Bodipy C-11 oxidation than hepatocytes from PCBP1fl/fl mice. Sensitivity to the pro-oxidant, cumene hydroperoxide (CHP), was greater in hepatocytes from PCBP1Δhep mice than PCBP1fl/fl hepatocytes (Fig. 5D).
FIG. 5.
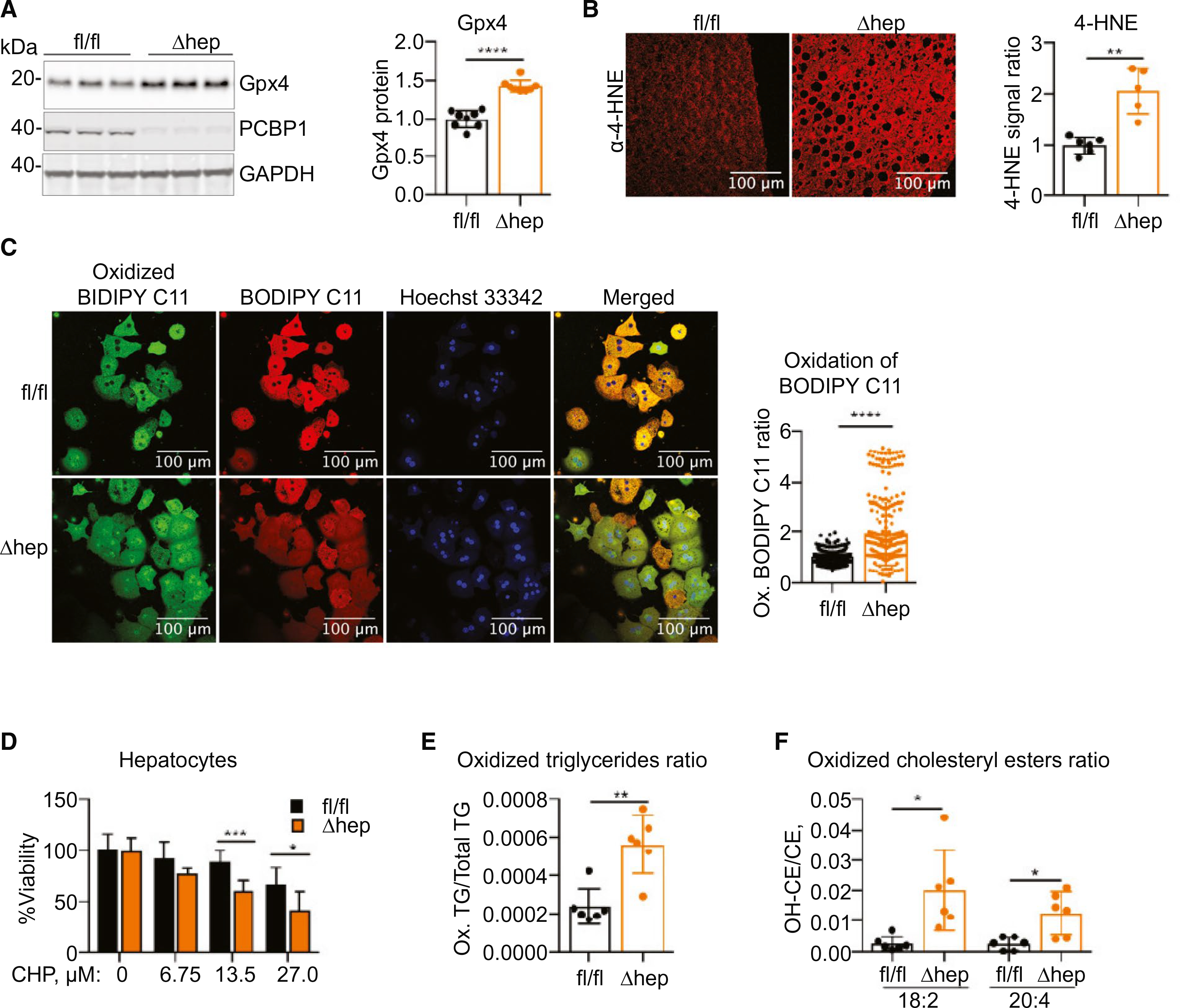
Increased LPO in PCBP1-deleted livers. (A) Increased Gpx4 in PCBP1Δhep livers. Representative immunoblotting probed for Gpx4 (left) and quantification (right). (B) Increased 4-HNE in PCBP1-depleted livers. Representative fluorescent immunohistochemistry image of liver sections stained with α-4-HNE antibody (left) and quantification (right). (C) Increased oxidation of lipophilic redox sensor in PCBP1Δhep primary hepatocytes. BODIPY C11581/591 staining (left) and quantification of oxidation in individual hepatocytes by green/red fluorescence ratio (right). (D) Increased sensitivity of PCBP1-deleted primary hepatocytes to oxidizing agent CHP. Hepatocytes were treated overnight with CHP and cell viability assayed. (E) Increased proportion of oxidized triaglycerides in PCBP1-depleted livers. Oxidatively modified and unmodified triglyceride species were measured in livers of PCBP1fl/fl and PCBP1Δhep mice by mass spectrometry and expressed as the ratio of the sum of oxidized triglycerides to the sum of total triglycerides; see also related Supporting Fig. S5D. (F) Increased proportion of oxidized cholesterol esters in PCBP1-depleted livers. Major cholesterol esters with oxidized and unmodified linoleic (18:2) and arachidonic (20:4) acids were measured in livers of PCBP1fl/fl and PCBP1Δhep mice and are expressed as a ratio; see also related Supporting Fig. S5E. Data represent mean ± SD. Abbreviations: CE, cholesterol esters; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; TG, triglyceride.
Finally, we performed an unbiased lipidomics analysis of livers from PCBP1fl/fl and PCBP1Δhep mice, measuring most of the abundant cellular phospholipid and neutral lipid species. Total triglyceride levels were elevated in PCBP1Δhep compared to PCBP1fl/fl livers (Fig. 1), as were levels of oxidized and oxidatively truncated triglycerides (Supporting Fig. S5C–E). Furthermore, the ratio of oxidized to total triglycerides was 3-fold higher in PCBP1Δhep livers compared to PCBP1fl/fl livers (Fig. 5E). Similarly, ratios of oxidized to total cholesteryl esters were increased in PCBP1Δhep livers, with the major species, linoleyl and arachidonyl CE (cholesterol esters), demonstrating 7- and 5-fold elevations, respectively (Fig. 5F). These measurements indicated that not only were levels of PUFA-containing lipids increased in PCBP1Δhep livers, but the proportion of oxidatively damaged lipids was also increased. Taken together, these data strongly indicated that a major consequence of losing iron chaperone activity in hepatocytes was the accelerated oxidative damage to cellular lipids, and that this damage occurs despite overall lower levels of iron in the liver.
Vit E SUPPLEMENTATION PARTIALLY PREVENTED STEATOSIS IN PCBP1-DELETED LIVERS
We hypothesized that unchaperoned iron in liver of PCBP1Δhep mice was catalyzing peroxidation reactions that oxidatively damaged lipids and triggered steatosis. Therefore, we tested whether antioxidants could protect PCBP1Δhep livers from LPO and prevent steatosis. Tocopherols are plant-derived, lipophilic compounds that have antioxidant properties and are collectively referred to as vit E. The major vit E species, α-to-copherol, is a potent radical scavenger and has been used in murine and human studies for its antioxidant effects.(37) We fed weanling mice for 16–18 days a normal-iron diet containing either the standard amount or a 10-fold enrichment for vit E. Vit E supplementation had no effect on any parameters in PCBP1fl/fl mice, but partially corrected fatty liver disease in PCBP1Δhep mice. PCBP1Δhep mice fed the vit E diet exhibited less steatosis in liver sections than PCBP1Δhep mice fed the normal diet (Fig. 6A). ALT elevations in PCBP1Δhep mice fell from 7- to 4-fold those of PCBP1fl/fl mice, and acylglycerides fell from 4-fold to 2-fold the level of PCBP1fl/fl livers (Fig. 6B,C). Vit E–treated PCBP1Δhep mice also suppressed expression of genes involved in fatty acid synthesis (Fig. 6D). However, vit E treatment had smaller effects on expression of genes involved in cholesterol biosynthesis in PCBP1Δhep livers (Supporting Fig. S6).
FIG. 6.
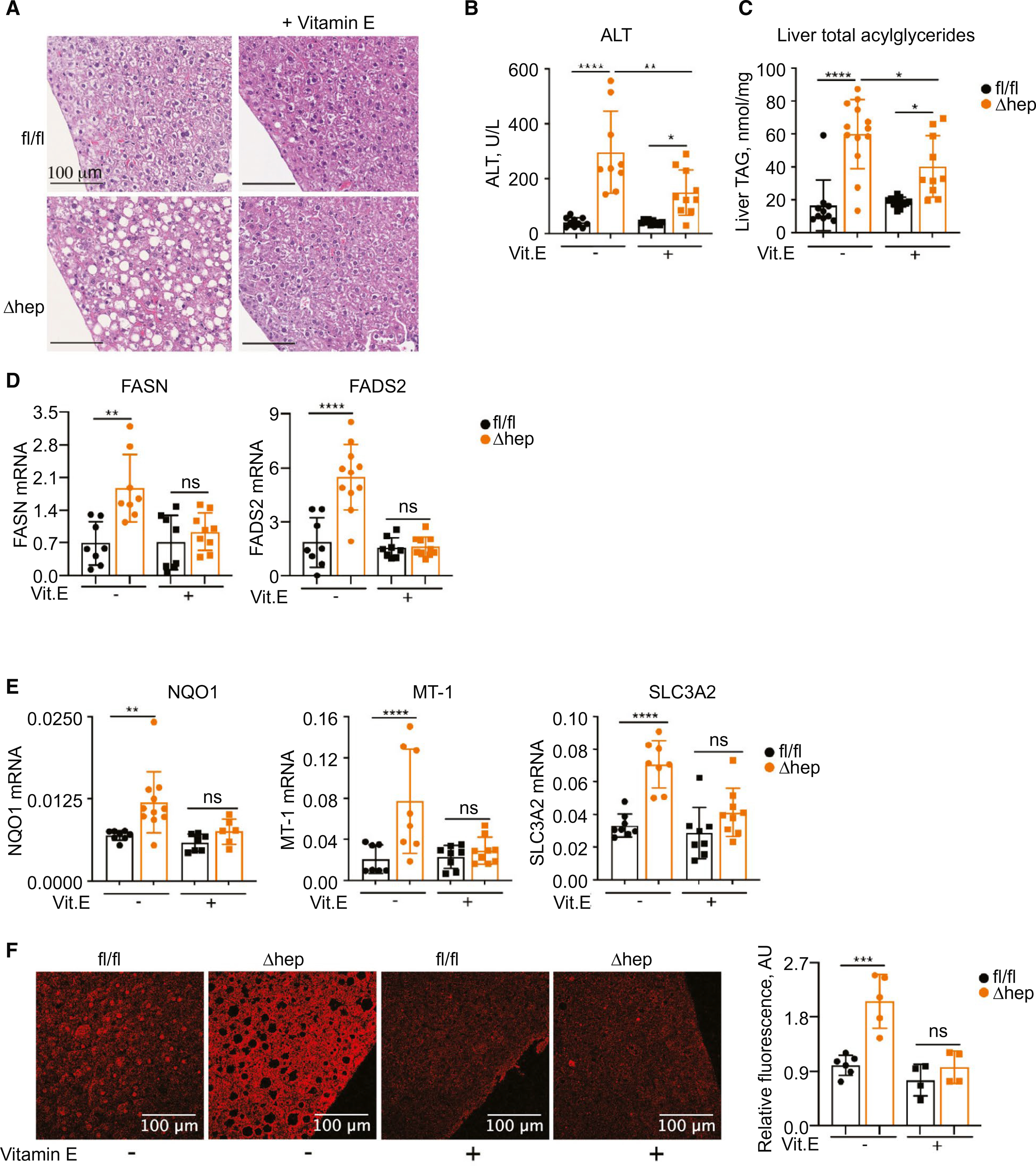
Vit E supplementation partially prevented steatosis in PCBP1Δhep mice. Mice were fed a 50-ppm iron diet or the same diet with 500 U of vit E for 16–18 days. (A) Decreased steatosis in PCBP1Δhep mice fed a vit E diet by H&E staining of liver sections. (B) Decreased plasma ALT in PCBP1Δhep mice fed a vit E diet. (C) Decreased liver acylglyceride accumulation in PCBP1Δhep mice fed a vit E diet. (D) Decreased expression of fatty acid genes and (E) oxidative-stress–related genes in livers of PCBP1Δhep mice fed a vit E diet. (F) Decreased LPO product 4-HNE in livers of PCBP1Δhep mice fed a vit E diet. Representative fluorescent immunohistochemistry images of liver sections stained with α-4-HNE antibody (left) and quantification (right). Data represent mean ± SD. For clarity, data for a 50-ppm iron diet without vit E are reproduced from Figs. 1, 4, and 5. Abbreviations: AU, arbitrary units; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; ns, not significant; TAG, triacylglycerol.
Vit E treatment appeared to mediate its effects by preventing oxidative stress and ROS-mediated damage in PCBP1Δhep mice. Nrf2 target mRNAs that were elevated in PCBP1Δhep livers were expressed at levels similar to those found in PCBP1fl/fl livers in animals fed the vit E diet (Fig. 6E), suggesting that oxidative stress had been relieved. Similarly, 4-HNE modifications in liver sections of vit E–treated PCBP1Δhep mice were suppressed to the level of PCBP1fl/fl livers (Fig. 6F). Thus, addition of a radical scavenging compound to the diet of mice lacking PCBP1 in the liver could suppress oxidative stress, lipid oxidation, hepatocellular damage, and steatosis. These data further suggested that elevated ROS in PCBP1Δhep livers initiated lipid damage and enhanced fatty acid synthesis that led to steatosis.
DELETION OF PCBP1 PRODUCES REDOX-ACTIVE, UNCHAPERONED IRON
Our data indicated that both iron restriction (Fig. 3) and antioxidant treatment (Fig. 6) could prevent the steatosis and hepatocyte damage associated with deletion of PCBP1 in the liver. To confirm that increased redox activity of unchaperoned iron in livers of PCBP1Δhep mice accounted for this disease, we compared the labile iron pools of wild-type, PCBP1-deficient, and iron-overloaded wild-type livers. Primary hepatocytes from both PCBP1fl/fl and PCBP1Δhep mice were sensitive to exogenous iron, displaying a dose-dependent decrease in viability after the addition of iron to culture medium (Fig. 7A). However hepatocytes from PCBP1Δhep mice were markedly more sensitive to iron than PCBP1fl/fl mice, indicating that PCBP1 can function to protect hepatocytes from the toxic effects of iron. Addition of vit E to the medium completely abrogated iron toxicity, suggesting that iron mediated its toxic effects, in part, through the production of ROS.
FIG. 7.

Increased labile iron pool in PCBP1-deleted livers. (A) Increased sensitivity of PCBP1Δhep primary hepatocytes to iron and protection by antioxidant vit E. Primary hepatocytes from PCBP1fl/fl and PCBP1Δhep livers were treated overnight with ferric citrate without or with 200 μM of vit E. Cell viability was measured. (B-D) Livers from iron-overloaded PCBP1fl/fl mice resemble livers from PCBP1Δhep mice on a normal iron diet. Mice were fed normal (50 ppm) or 2% carbonyl iron (20,000 ppm) diets for 16–18 days before analysis. (B) Steatosis and increased accumulation of acylglycerides in PCBP1Δhep and iron-overloaded PCBP1fl/fl livers. (C) Similar phospholipid changes in PCBP1Δhep and iron-overloaded PCBP1fl/fl livers: decreased PE, increased PC, and increased oxidatively modified phospholipids. The heatmap represents values normalized to the mean value of PCBP1fl/fl on a normal iron diet. (D) Activation of lipid biosynthesis and Nrf-2 oxidative-stress response genes in PCBP1Δhep and iron-overloaded PCBP1fl/fl livers. RNA-Seq analysis of PCBP1fl/fl and PCBP1Δhep livers from mice fed indicated iron-defined diets. The heatmap represents expression values (log2 ratio) normalized to the mean value of PCBP1fl/fl on a normal iron diet. (E) Increased labile iron pool in PCBP1Δhep and iron-overloaded primary hepatocytes visualized by FIP-1 staining. Schematic of labile iron detection by FIP-1 (left). Labile Fe(II) is indicated by the ratio of green/FRET fluorescence. Quantification of fluorescence ratio (left) and FIP-1 fluorescence in primary hepatocytes (right). See also related Supporting Fig. S7F. Graphs represent mean ± SD. (F) Unchaperoned iron in hepatocytes lacking PCBP1 catalyzes oxidative damage to cellular PUFA-containing lipids. Abbreviations: Acat2, acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase 2; Acsl4, Acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4; Agpat4, 1-acyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase delta; Cdkn1a, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A; Cyp51, sterol 14α-demethylase; Dnaja4, DnaJ heat shock protein family (Hsp40) member A4; Enc1, ectoderm-neural cortex protein 1; Ephx1, epoxide hydrolase 1; Fdft1, farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyltransferase 1; Fdps, farnesyl diphosphate synthase; Gclc, glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit; Gstm3, glutathione S-transferase mu 3; Gstm4, glutathione S-transferase mu 4; Gstp1, glutathione S-transferase Pi 1; Hmgcr, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase; Hmgcs1, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 1; Hmox1, heme oxygenase 1; Idi1, isopentenyl-diphosphate delta isomerase 1; Lpin2, lipin 2; Map2k7, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 7; Msmo1, methylsterol monooxygenase 1; Myd, myeloid differentiation; ns, not significant; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; Plpp5, phospholipid phosphatase 5; RNA-Seq, RNA sequencing; Prkd3, protein kinase D3; TAG, triacylglycerol.
We hypothesized that if unchaperoned iron were driving the production of ROS that caused lipid peroxidation and steatosis, then liver iron overload in a wild-type animal could exhibit a similar phenotype by saturating the iron-handling systems of the hepatocyte. Although our high-iron diet (1,000 ppm) enhanced iron loading of the liver, it did not produce iron toxicity in the PCBP1fl/fl mouse. In contrast, a diet containing 2% carbonyl iron (20,000 ppm) was associated with impaired weight gain and a 30-fold increase in liver nonheme iron compared to the normal-iron diet (Supporting Fig. S7A,B). Liver tissue from mice fed the 20,000-ppm diet exhibited very high levels of ferritin protein (by western blotting) and ferritin iron accumulation (by Perls’ stain). Most of this ferritin iron was present in hepatocytes and preferentially accumulated in the periportal areas while sparing the pericentral regions (Supporting Fig. S7C).
PCBP1fl/fl mice fed the 2% iron diet developed hepatic steatosis similar to PCBP1Δhep mice fed the normal-iron diet (Fig. 7B). Similar to the accumulation of iron, steatosis was mainly present in periportal areas and spared the pericentral hepatocytes. This histological pattern of lipid accumulation was present in both livers from PCBP1fl/fl mice fed the 2% iron diet and PCBP1Δhep mice fed the normal-iron diet, suggesting that unchaperoned, labile iron in both settings triggered steatosis (Supporting Fig. S7C). Total acylglyceride levels in livers of PCBP1fl/fl mice on 2% iron were 4-fold higher than PCBP1fl/fl mice fed the normal-iron diet and equal to those of PCBP1Δhep mice. Phospholipid analysis of PCBP1fl/fl livers on the 2% iron diet was compared to PCBP1fl/fl and PCBP1Δhep livers on the normal-iron diet, and the pattern of lipid accumulation was similar to that of PCBP1Δhep mice, including the accumulation of oxidized phospholipids (Fig. 7C). We analyzed gene expression patterns in livers from these mice and again found that both PCBP1Δhep mice on normal iron and PCBP1fl/fl on 2% iron were similar to each other and different from PCBP1fl/fl mice on a normal-iron diet (Fig. 7D). Furthermore, levels of mature SREBP2 were elevated in livers of both PCBP1Δep mice and PCBP1fl/fl mice on 2% iron (Supporting Fig. S7C). These data all support the hypothesis that unchaperoned iron in the PCBP1Δhep liver causes LPO and steatosis.
Direct measurement of the LIP in cells is challenging. FRET iron probe 1 (FIP-1) is a ratiometric, fluorescent iron sensor that detects labile ferrous iron in cells(38) (Fig. 7E). Fluorescence analysis of primary hepatocytes stained with FIP-1 showed a 30% increase in the mean ratio of green/fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) fluorescence in PCBP1Δhep hepatocytes compared to PCBP1fl/fl hepatocytes. Furthermore, hepatocytes from PCBP1fl/fl mice fed 2% iron also exhibited a 26% increase in FIP-1 cleavage versus mice fed 50 ppm of iron. Thus both PCBP1Δhep and iron-overloaded PCBP1fl/fl hepatocytes exhibited an increase in the reactive LIP. We confirmed the sensitivity and specificity of FIP-1 to the LIP in PCBP1fl/fl hepatocytes treated with exogenous iron, or cumine hydroperoxide (Supporting Fig. S7F).
Discussion
Here, we have shown that mice lacking the PCBP1 iron chaperone system in the liver develop steatosis, LPO, and hepatocellular death because of the chemical reactivity of unchaperoned iron. Previous studies of cytosolic iron chaperones have focused on their roles in facilitating the transfer of iron from the chaperone to a client protein or to the chaperone from a transporter or enzyme. Our studies indicate that PCBP1 is further required to coordinate iron from the LIP and prevent it from catalyzing the production of ROS that oxidatively damage cellular components. Surprisingly, redox activity of the LIP is increased in hepatocytes lacking PCBP1 even though cells are, overall, iron depleted.
PCBP1 IS REQUIRED TO MAINTAIN IRON BALANCE IN THE LIVER
Deletion of PCBP1 in hepatocytes severely perturbed cell-autonomous iron homeostatic systems in the liver. Lower iron levels in PCBP1Δhep livers could be attributable to reduced iron uptake or enhanced efflux. Although no defects in uptake have been observed in PCBP1-depleted cells, PCBP2 functions in iron efflux through ferroportin.(39) Iron taken up by PCBP1-deleted hepatocytes may be coordinated by PCBP2 and preferentially delivered to ferroportin for efflux.
More surprising is the apparent dysregulation of IRP1, IRP2, and Fbxl5. RNA binding activities of both IRP1 and IRP2 were reduced in hepatocytes lacking PCBP1, despite the cellular iron deficiency. Elevated production of ROS in PCBP1-deficient cells may impair IRP1 activity,(40) and IRP2 is also sensitive to iron, oxygen, and ROS, undergoing degradation at elevated levels of all three(41,42) and may occur through stabilization of Fbxl5. Although Fbxl5 senses and is stabilized in the presence of oxygen, how it might be regulated by ROS is not clear. Fbxl5 and NCOA4 are stabilized and destabilized, respectively, by binding iron. The differential effect of PCBP1 deletion on these iron sensors suggests that there is more to learn about interactions between the sensors, the LIP, ROS, and iron chaperones.
IRON-CATALYZED OXIDATIVE STRESS CAUSES STEATOSIS IN MICE
This mouse model of liver-specific PCBP1 deletion demonstrates that ongoing oxidative stress alone is sufficient to cause steatosis in mice. Under normal conditions, hepatocytes do not accumulate and store significant quantities of neutral lipids. Mice lacking PCBP1 in hepatocytes simultaneously accumulated intracellular lipids and elevated levels of oxidatively damaged lipids. Improvement of steatosis and markers of oxidative stress in mice on the low-iron and vit E–supplemented diets, as well as the manifestation of all these abnormalities in wild-type mice on a 2% iron diet, support the hypothesis that unchaperoned iron is initiating this cascade of cellular damage. Wild-type mice fed a 2% iron diet exhibited a 50-fold greater amount of liver iron than PCBP1Δhep mice fed a normal-iron diet; however, most of the excess iron was safely sequestered in ferritin. Nevertheless, our data indicate that iron absorbed from the 2% iron diet exceeded the liver’s capacity to detoxify and sequester iron. The resulting iron overload was accompanied by increases in the labile iron pool that produced a phenotype of oxidative stress, LPO, and steatosis that was similar to the effects of unchaperoned iron in PCBP1Δhep mice.
Rodent models of fatty liver disease show interactions between liver iron and the development of steatosis and hepatocyte injury. Rats fed a high-iron diet developed steatosis with evidence of oxidative stress and activation of SREBP-1c.(43) Conversely, mice with genetic iron deficiency were resistant to obesity and liver disease on a high-fat diet.(44) In humans, oxidative stress is implicated as the “second hit” that leads some patients with fatty liver disease to progress to steatohepatitis, which is associated with inflammation, hepatocyte death, and fibrosis. Many patients with fatty liver or steatohepatitis exhibit varying degrees of iron loading in the liver, which correlates with more-advanced disease.(45)
PCBP1 CONTROLS THE REACTIVITY OF THE LABILE IRON POOL IN LIVER OF MICE
Our studies indicate that PCBP1 controls the redox activity of the LIP, thereby inhibiting iron-mediated LPO and cell death. Whereas multiple mechanisms likely account for the cell death detected in PCBP1-deleted livers, ferroptosis is a term used to describe the nonapoptotic cell-death pathway that is characterized by elevated levels of iron-catalyzed phospholipid peroxidation. This damage can compromise the integrity of cellular membranes, leading to cell death.(36,46) Both bulk phospholipid peroxidation and enzymatically driven lipoxygenation of phosphatidylethanolamine have been described as mechanisms of ferroptosis.(47,48) This cell-death pathway is inhibited by lipid repair and protection processes that are primarily mediated by GSH-dependent, Gpx4, and the recently described coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) reductase, FSP1.(49) Thus, both GSH and CoQ10 serve as small-molecule inhibitors of LPO in cells.
Although GSH is regarded as a general cellular antioxidant and cosubstrate for glutathione peroxidases, it has a more direct role in controlling the cytosolic LIP. At the high concentrations found in the cytosol, GSH can directly coordinate Fe(II) through its free sulfhydryl, and Fe-GSH complexes likely constitute the majority (>95%) of the low-molecular-weight LIP.(3) A recent study confirms that Fe-GSH complexes can be captured in the cytosol of cells; these complexes are the endogenous ligands for PCBP1.(4) Equilibrium binding analyses indicate that a major portion of the cytosolic LIP consists of Fe-GSH complexes bound to PCBP1. The studies presented here demonstrate that hepatocytes lacking PCBP1 complexes within the LIP undergo continuous, iron-mediated, oxidative damage to cellular lipids, which results in hepatocellular damage and, potentially, ferroptosis (Fig. 7F). Thus, the iron chaperone complex consisting of PCBP1-Fe-GSH is the critical cellular species that controls the redox activity of the LIP and holds ferroptosis in check.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgment:
We thank David E. Kleiner of the National Cancer Institute for hepatic histopathology interpretation, Harold Smith of the NIDDK Genomics Core, Yinyan Ma of the NIDDK Mouse Metabolism Core, and members of the Rouault Lab of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) and the Liver Diseases Branch of the NIDDK for technical assistance and helpful discussions.
These studies were supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and the Office of Dietary Supplements Research Scholars Program, National Institutes of Health. M.G. is supported by the intramural program of the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, NIH. J.E.C. and J.A.M. are supported by NIDDK U54DK11085804, Office of Director, NIH 1S10OD018210-01A1, and 1S10OD021505-01. V.A.T., Y.Y.T., H.B., and V.E.K. are supported by NIH U19AI068021 and HL114453-06. We thank the NIH (GM79645 to C.J.C.) for research support. A.T.A thanks the NSF for a graduate fellowship and was partially supported by an NIH Chemical Biology Interface Training Grant (T32 GM066698).
Abbreviations:
- ALT
alanine aminotransferase
- CE
cholesterol esters
- CHP
cumene hydroperoxide
- FADS2
fatty acid desaturase 2
- FASN
fatty acid synthase
- Fbxl5
F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 5
- Fe II
ferrous iron
- Fe-S
iron-sulfur
- FIP-1
FRET iron probe 1
- FRET
fluorescence resonance energy transfer
- Gpx4
glutathione peroxidase type 4
- GSH
reduced glutathione
- HIF1a
hypoxia-inducible transcription factor 1-α
- HNE
4-hydroxynonenol
- IREs
iron-responsive elements
- IRPs
iron-regulatory proteins
- IRP1
iron-regulatory protein 1
- IRP2
iron-regulatory protein 2
- LIP
labile iron pool
- LPO
lipid peroxidation
- MOGAT
monoacylglyceride acyltransferase 1
- Mt1
metallothionein
- NCOA4
nuclear coactivator 4
- NIDDK
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
- NIH
National Institutes of Health
- Nox4
NADPH oxidase 4
- Nqo1
NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase
- Nrf2
nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2
- PCBP1
poly r(C) binding protein 1
- PCBP2
poly r(C) binding protein 2
- PCBP1fl/fl
PCBP1 floxed allele
- PCBP1Δhep
PCBP1fl/fl with Alb-Cre transgene
- PPARG
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ
- ppm
parts per million
- PUFAs
polyunsaturated fatty acids
- ROS
reactive oxygen species
- Slc3a2
cystine/glutamate antiporter
- SQLE
squalene epoxidase
- SREBPs
sterol-regulatory element binding proteins
- vit E
vitamin E
- VLDL
very-low-density lipoprotein
Footnotes
Potential conflict of interest: Nothing to report.
Additional Supporting Information may be found at onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/hep.31328/suppinfo.
REFERENCES
- 1).Lill R, Dutkiewicz R, Freibert SA, Heidenreich T, Mascarenhas J, Netz DJ, et al. The role of mitochondria and the CIA machinery in the maturation of cytosolic and nuclear iron-sulfur proteins. Eur J Cell Biol 2015;94:280–291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2).Hamza I, Dailey HA. One ring to rule them all: trafficking of heme and heme synthesis intermediates in the metazoans. Biochim Biophys Acta 2012;1823:1617–1632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3).Hider RC, Kong XL. Glutathione: a key component of the cytoplasmic labile iron pool. Biometals 2011;24:1179–1187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4).Patel SJ, Frey AG, Palenchar DJ, Achar S, Bullough KZ, Vashisht A, et al. A PCBP1-BolA2 chaperone complex delivers iron for cytosolic [2Fe-2S] cluster assembly. Nat Chem Biol 2019;15:872–881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5).Philpott CC, Jadhav S. The ins and outs of iron: escorting iron through the mammalian cytosol. Free Radic Biol Med 2019;133:112–117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6).Ghanem LR, Kromer A, Silverman IM, Chatterji P, Traxler E, Penzo-Mendez A, et al. The poly(C) binding protein Pcbp2 and its retrotransposed derivative Pcbp1 are independently essential to mouse development. Mol Cell Biol 2016;36: 304–319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7).Shi H, Bencze KZ, Stemmler TL, Philpott CC. A cytosolic iron chaperone that delivers iron to ferritin. Science 2008;320:1207–1210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8).Ryu MS, Zhang D, Protchenko O, Shakoury-Elizeh M, Philpott CC. PCBP1 and NCOA4 regulate erythroid iron storage and heme biosynthesis. J Clin Invest 2017;127:1786–1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9).Patel S. A PCBP1-BolA2 chaperone complex delivers iron for cytosolic 1 [2Fe-2S] cluster assembly. Nat Chem Biol 2019;15:872–881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10).Frey AG, Palenchar DJ, Wildemann JD, Philpott CC. A glu-taredoxin·BolA complex serves as an iron-sulfur cluster chaperone for the cytosolic cluster assembly machinery. J Biol Chem 2016;291:22344–22356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11).Nandal A, Ruiz JC, Subramanian P, Ghimire-Rijal S, Sinnamon RA, Stemmler TL, et al. Activation of the HIF prolyl hydroxylase by the iron chaperones PCBP1 and PCBP2. Cell Metab 2011;14:647–657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12).Frey AG, Nandal A, Park JH, Smith PM, Yabe T, Ryu MS, et al. Iron chaperones PCBP1 and PCBP2 mediate the metallation of the dinuclear iron enzyme deoxyhypusine hydroxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014;111:8031–8036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13).Knutson MD. Non-transferrin-bound iron transporters. Free Radic Biol Med 2019;133:101–111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14).Wang CY, Babitt JL. Liver iron sensing and body iron homeostasis. Blood 2019;133:18–29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15).Ganz T. Erythropoietic regulators of iron metabolism. Free Radic Biol Med 2019;133:69–74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16).Chakrabarti M, Cockrell AL, Park J, McCormick SP, Lindahl LS, Lindahl PA. Speciation of iron in mouse liver during development, iron deficiency, IRP2 deletion and inflammatory hepatitis. Metallomics 2015;7:93–101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17).Neufeld DS. Isolation of rat liver hepatocytes. Methods Mol Biol 1997;75:145–151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18).Madison BB. Srebp2: a master regulator of sterol and fatty acid synthesis. J Lipid Res 2016;57:333–335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19).Horton JD, Goldstein JL, Brown MS. SREBPs: activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver. J Clin Invest 2002;109:1125–1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20).Mancias JD, Wang XX, Gygi SP, Harper JW, Kimmelman AC. Quantitative proteomics identifies NCOA4 as the cargo receptor mediating ferritinophagy. Nature 2014;509:105–109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21).Dowdle WE, Nyfeler B, Nagel J, Elling RA, Liu S, Triantafellow E, et al. Selective VPS34 inhibitor blocks autophagy and uncovers a role for NCOA4 in ferritin degradation and iron homeostasis in vivo. Nat Cell Biol 2014;16:1069–1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22).Ryu MS, Duck KA, Philpott CC. Ferritin iron regulators, PCBP1 and NCOA4, respond to cellular iron status in developing red cells. Blood Cells Mol Dis 2018;69:75–81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23).Mancias JD, Vaites LP, Nissim S, Biancur DE, Kim AJ, Wang XX, et al. Ferritinophagy via NCOA4 is required for erythropoiesis and is regulated by iron dependent HERC2-mediated proteolysis. eLife 2015;4:e10308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24).Nishino T, Okamoto K, Eger BT, Pai EF, Nishino T. Mammalian xanthine oxidoreductase—mechanism of transition from xanthine dehydrogenase to xanthine oxidase. FEBS J 2008;275:3278–3289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25).Rouault TA, Maio N. Biogenesis and functions of mammalian iron-sulfur proteins in the regulation of iron homeostasis and pivotal metabolic pathways. J Biol Chem 2017;292:12744–12753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26).Meyron-Holtz EG, Ghosh MC, Iwai K, LaVaute T, Brazzolotto X, Berger UV, et al. Genetic ablations of iron regulatory proteins 1 and 2 reveal why iron regulatory protein 2 dominates iron homeostasis. EMBO J 2004;23:386–395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27).Vashisht AA, Zumbrennen KB, Huang X, Powers DN, Durazo A, Sun D, et al. Control of iron homeostasis by an iron-regulated ubiquitin ligase. Science 2009;326:718–721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28).Ruiz JC, Bruick RK. F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 5 (FBXL5): sensing intracellular iron and oxygen. J Inorg Biochem 2014;133:73–77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29).Salahudeen AA, Thompson JW, Ruiz JC, Ma HW, Kinch LN, Li Q, et al. An E3 ligase possessing an iron-responsive hemerythrin domain is a regulator of iron homeostasis. Science 2009;326:722–726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30).Benevenga NJ (ed). Nutrient requirements of the mouse. In: Nutrient Requirements of Laboratory Animals: 4th Revised Edition. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 1995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31).Klaassen CD, Reisman SA. Nrf2 the rescue: effects of the antioxidative/electrophilic response on the liver. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2010;244:57–65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32).Lim PJ, Duarte TL, Arezes J, Garcia-Santos D, Hamdi A, Pasricha SR, et al. Nrf2 controls iron homeostasis in haemochromatosis and thalassaemia via Bmp6 and hepcidin. Nat Metab 2019;1:519–531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33).Galaris D, Barbouti A, Pantopoulos K. Iron homeostasis and oxidative stress: an intimate relationship. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 2019;1866:118535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34).Liang S, Kisseleva T, Brenner DA. The role of NADPH oxidases (NOXs) in liver fibrosis and the activation of myofibroblasts. Front Physiol 2016;7:17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35).Gaschler MM, Stockwell BR. Lipid peroxidation in cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2017;482:419–425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36).Stoyanovsky DA, Tyurina YY, Shrivastava I, Bahar I, Tyurin VA, Protchenko O, et al. Iron catalysis of lipid peroxidation in ferroptosis: Regulated enzymatic or random free radical reaction? Free Radic Biol Med 2019;133:153–161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37).El Hadi H, Vettor R, Rossato M. Vitamin E as a treatment for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: reality or myth? Antioxidants (Basel) 2018;7:12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38).Aron AT, Loehr MO, Bogena J, Chang CJ. An endoperoxide reactivity-based FRET probe for ratiometric fluorescence imaging of labile iron pools in living cells. J Am Chem Soc 2016;138:14338–14346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39).Yanatori I, Richardson DR, Imada K, Kishi F. Iron export through the transporter ferroportin 1 is modulated by the iron chaperone PCBP2. J Biol Chem 2016;291:17303–17318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40).Hanson ES, Leibold EA. Regulation of the iron regulatory proteins by reactive nitrogen and oxygen species. Gene Expr 1999;7:367–376. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41).Meyron-Holtz EG, Ghosh MC, Rouault TA. Mammalian tissue oxygen levels modulate iron-regulatory protein activities in vivo. Science 2004;306:2087–2090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42).Hanson ES, Rawlins ML, Leibold EA. Oxygen and iron regulation of iron regulatory protein 2. J Biol Chem 2003;278:40337–40342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43).Valenzuela R, Rincon-Cervera MA, Echeverria F, Barrera C, Espinosa A, Hernandez-Rodas MC, et al. Iron-induced pro-oxidant and pro-lipogenic responses in relation to impaired synthesis and accretion of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in rat hepatic and extrahepatic tissues. Nutrition 2018;45:49–58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44).Folgueras AR, Freitas-Rodriguez S, Ramsay AJ, Garabaya C, Rodriguez F, Velasco G, et al. Matriptase-2 deficiency protects from obesity by modulating iron homeostasis. Nat Commun 2018;9:1350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45).Nelson JE, Klintworth H, Kowdley KV. Iron metabolism in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 2012;14:8–16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46).Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012;149:1060–1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47).Wenzel SE, Tyurina YY, Zhao J, St Croix CM, Dar HH, Mao G, et al. PEBP1 wardens ferroptosis by enabling lipoxygenase generation of lipid death signals. Cell 2017;171:628–641.e26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48).Kagan VE, Mao G, Qu F, Angeli JP, Doll S, Croix CS, et al. Oxidized arachidonic and adrenic PEs navigate cells to ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol 2017;13:81–90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49).Bersuker K, Hendricks JM, Li Z, Magtanong L, Ford B, Tang PH, et al. The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature 2019;575: 688–692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


