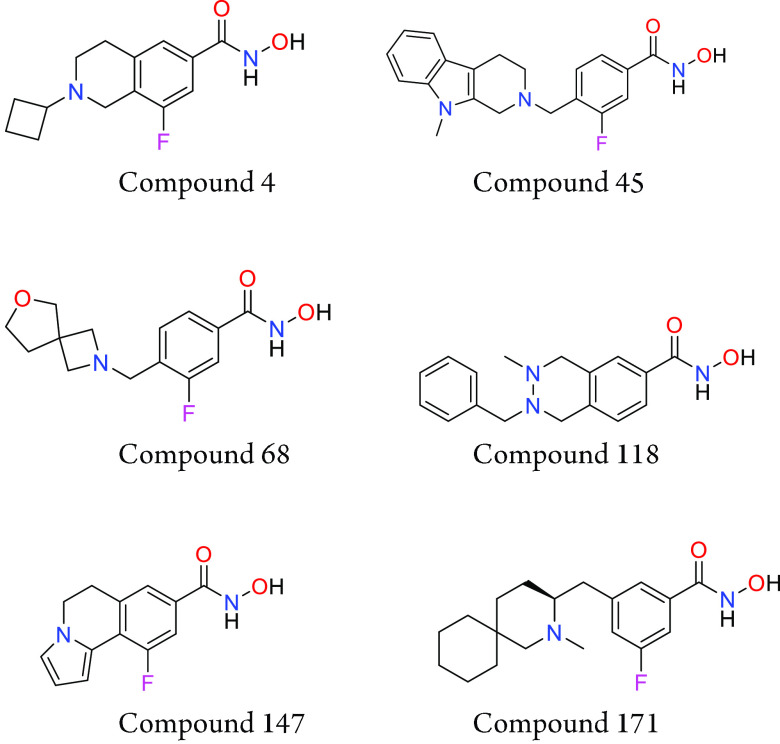
Important Compound Classes
Title
HDAC6 Inhibitors and Uses Thereof
Patent Publication Number
WO 2021/021979 A2
Publication Date
February 4, 2021
Priority Application
US 62/880,284
Priority Date
July 30, 2019
Inventors
Wagner, F. F.; Hooker, J. M.; Ouellet, S.
Assignee Company
Eikonizo Therapeutics Inc., USA
Disease Area
Alzheimer’s disease, cancer
Biological Target
Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC) 6
Summary
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) are divided into four classes based on sequence homology. HDAC6, a class II HDAC, is a cytoplasmic, microtubule-associated enzyme. HDAC6 has unique features among the HDAC paralogues. Unlike other HDACs, HDAC6 contains two deacetylase domains and an ubiquitin binding domain allowing HDAC6 to function in distinct cell signaling systems involving protein acetylation and ubiquitination, respectively. Importantly, it does not deacetylate histones. HDAC6 deacetylates tubulin, tau, Hsp90, cortactin, and other emerging targets. HDAC6 deacetylase function is involved in microtubule-based cargo transport, protein degradation/recycling and stress-induced glucocorticoid receptor signaling. HDAC6 deacetylase function is also involved in cell morphology, motility, migration, and cell growth and survival. HDAC6 expression was shown to be elevated in postmortem brain samples from Alzheimer’s disease patients. Aberrant expression of HDAC6 also correlates with tumorigenesis and is linked to the metastasis of cancer cells.
The present application describes a series of novel HDAC6 inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease and cancer. Further, the application discloses compounds, their preparation, use, pharmaceutical composition, and treatment.
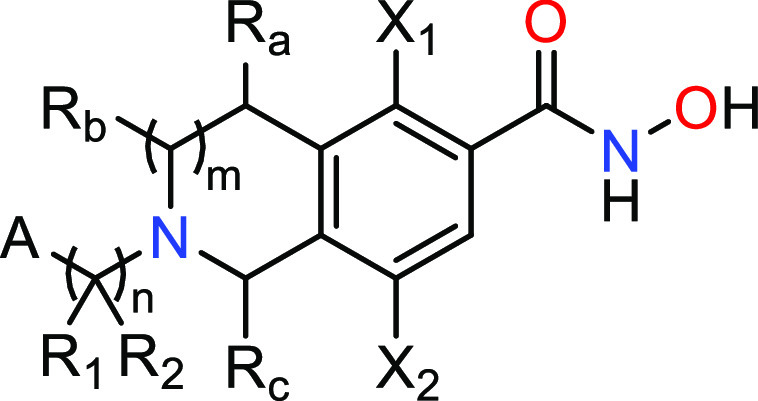
Definitions
X1 = hydrogen or fluoro;
X2 = hydrogen or fluoro, provided that at least one of X1 and X2 is fluoro;
A = substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, substituted or unsubstituted carbocyclyl, substituted or unsubstituted heterocyclyl, substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl or substituted or unsubstituted aryl;
R1 = hydrogen or substituted or unsubstituted alkyl;
R2 = hydrogen or substituted or unsubstituted alkyl; or
R1 and R2 together form a substituted or unsubstituted heterocyclyl or a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl;
Ra = hydrogen or is joined with Rc to form a substituted or unsubstituted bridged ring;
Rb = hydrogen or is joined with Rc to form a substituted or unsubstituted bridged ring;
Rc = hydrogen or substituted or unsubstituted alkyl or is joined with at least one of Ra and Rb to form a substituted or unsubstituted bridged ring;
m = 0 or 1; and n = 0 or 1.
Key Structures
Biological Assay
The in vitro HDAC enzymatic assay was performed. The compounds described in this application were tested for their ability to inhibit HDAC6. The HDAC6 IC50 (μM) are shown in the following table.
Biological Data
The table below shows representative compounds were tested for HDAC6 inhibition. The biological data obtained from testing representative examples are listed in the following table.
For IC50 ranges: A: 0.001–0.1 μM; B: >0.1–1.0
μM; C: >1–10 μM; D: >10–100 μM;
E:
>100 μM.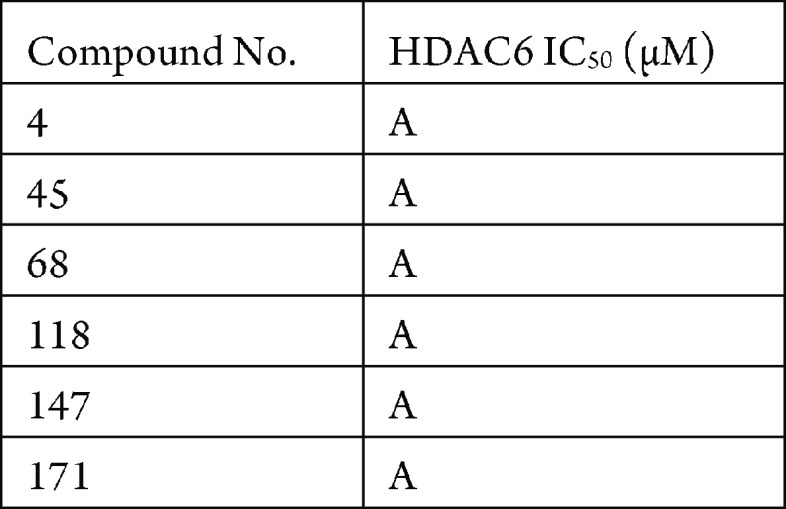
Claims
Total claims: 136
Compound claims: 124
Pharmaceutical composition claims: 1
Method of treatment claims: 10
Kit claims: 1
Recent Review Articles
-
1.
Ramaiah M. J.; Tangutur A. D.; Manyam R. R.. Life Sci. 2021, 277, 119504.
-
2.
Zhang X.; Ma Q.; Wu H.; Khamis M. Y.; Li Y.; Ma L.; Liu H.. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 1362.
-
3.
Vaidya G. N.; Rana P.; Venkatesh A.; Chatterjee D. R.; Contractor D.; Satpute D. P.; Nagpure M.; Jain A.; Kumar D.. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 209, 112844.
-
4.
Rroji O.; Kumar A.; Karuppagounder S. S.; Ratan R. R.. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 147, 105145.
-
5.
Pulya S.; Amin S. A.; Adhikari N.; Biswas S.; Jha T.; Ghosh B.. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 163, 105274.
-
6.
Diteepeng T.; del Monte F.; Luciani M.. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2021, 51, e13504.
The author declares no competing financial interest.
Special Issue
Published as part of the ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters special issue “Epigenetics 2022”.