A 77-year-old woman underwent orthopedic surgery in our hospital because of a proximal humerus fracture. She presented herself with a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) as precondition which was not responsive to standard therapy (e.g. inhalative corticosteroids or beta-agonists) [1] and needed 4 L/min of oxygen over a nasal canula to sustain an adequate peripheral oxygen-level (SpO2 > 90%). During her last hospital stay, the patient’s COPD was classified as GOLD II type C (GOLD = Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease) with an FEV1/FVC of 56% (FEV1 = forced expiration volume in 1 second, FVC = forced vital capacity).
For surgery, general anesthesia was performed requiring endotracheal intubation. During video-laryngoscopy, the patient showed what seemed to be an internal laryngocele which led to an almost complete airway obstruction (Figure 1). After securing the airway with a smaller endotracheal tube than anticipated, the surgery underwent uneventful and our patient was admitted to the intensive care unit for further surveillance.
Figure 1 .
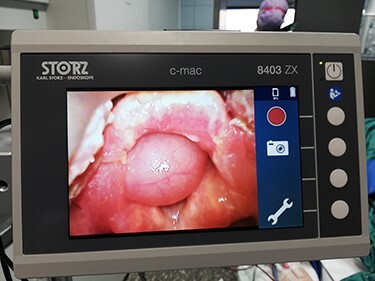
Presentation of an internal laryngocele during video-laryngoscopy in the operating room.
Subsequently we informed the patient about our finding and the obstruction was surgically removed the next day. Histopathology ruled out malignancy and confirmed the diagnosis of an internal laryngocele.
Laryngoceles are extremely rare with an incidence of 1: 2.500.000 and five times more common in men than in women [2]. Although external laryngoceles become visible quickly, internal laryngoceles might be undetected for long periods and can rapidly cause obstructive symptoms with hoarseness and dyspnea. Risk factors for developing laryngoceles are high airway pressures e.g. due to excessive coughing or playing wind instruments, with coughing owing to our patient’s COPD being the most feasible explanation in this case [3]. Interestingly, we were able to discharge the patient without any additional oxygen-supply, leading to the assumption that the laryngocele was responsible for a great margin of the patient’s COPD-symptoms.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Not applicable. No funding was received for this article.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
None declared.
ETHICAL APPROVAL
Not applicable.
CONSENT
Written informed consent about the publication of this article was obtained from the patient.
GUARANTOR
H.B.
REFERENCES
- 1.Vogelmeier CF, Criner GJ, Martinez FJ, Anzueto A, Barnes PJ, Bourbeau J, et al. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease 2017 Report. GOLD Executive Summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195(5):557–582. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201701-0218PP. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Al-Yahya SN, Baki MM, Saad SM, Azman M, Mohamad AS. Laryngopyocele: report of a rare case and systematic review. Ann Saudi Med 2016; 36:292–297. DOI: 10.5144/0256-4947.2016.292 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mobashir MK, Basha WM, Mohamed AE, Hassaan M, Anany AM. Laryngoceles: concepts of diagnosis and management. Ear Nose Throat J 2017;96:133–8. 10.1177/014556131709600313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


