Correction to: Chin Med (2021) 16:57 10.1186/s13020-021-00467-6
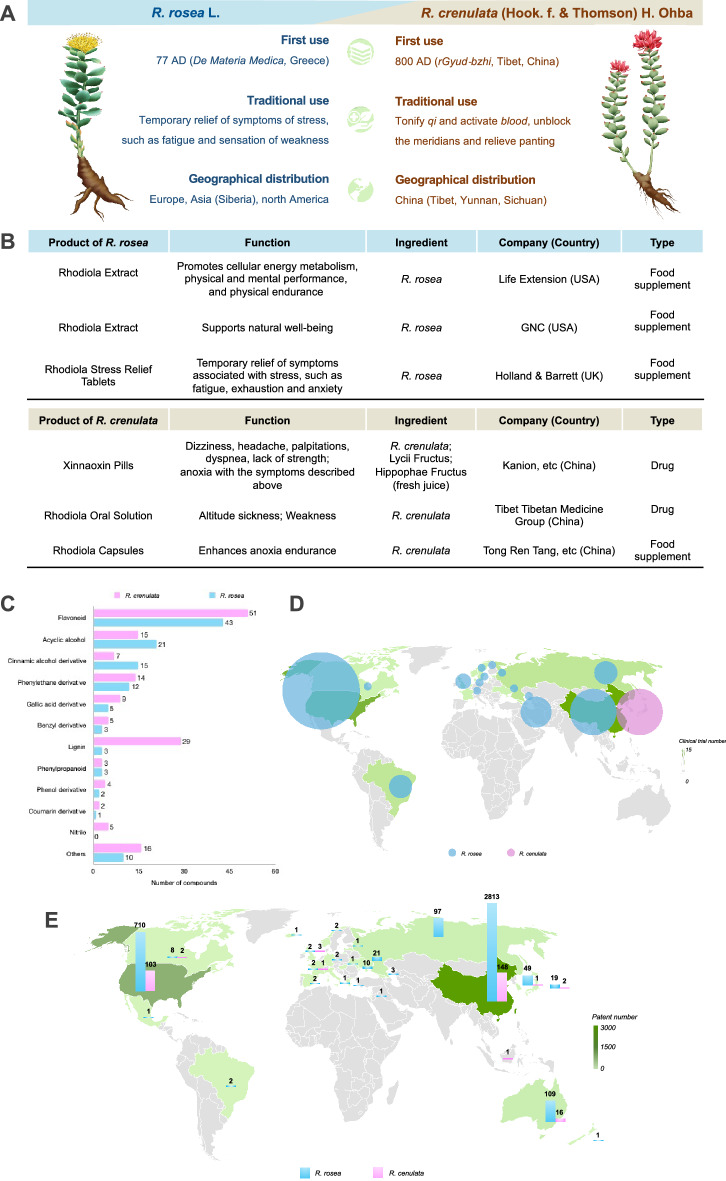
Following the publication of the original article [1], the authors identified an error in Fig. 1. The bubbles in Fig. 1D are missing
The correct figure (Fig. 1) has been included in this correction, and the original article has been corrected.
Fig. 1.
Comparison of history, products, active constituents, clinical trials and patens of two Rhodiola species. A Basic information of R. crenulata and R. rosea. B Representative products developed based on R. crenulata and R. rosea. C Number of main active constituents contained in R. crenulata and R. rosea. D Advanced in clinical trials of R. crenulata and R. rosea. Data collected from PubMed (searching term of “Rhodiola” plus flter of “Clinical trial”, language limited to English) and ClinicalTrials.gov (searching term of “Rhodiola”) as of 15 June 2021. E Patent application of R. crenulata and R. rosea. Data collected from the Lens (https://www.lens.org, Searching term: Rhodiola) as of 15 June 2021
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Xiuzhu Li and Weijie Chen contributed equally to this work
Reference
- 1.Li X, Chen W, Simal-Gandara J, Georgiev MI, Li H, Hu H, Wu X, Efferth T, Wang S. West meets east: open up a dialogue on phytomedicine. Chin Med. 2021;16:57. doi: 10.1186/s13020-021-00467-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]