Abstract
Unilateral axillary lymphadenopathy is a frequent mild side effect of COVID-19 vaccination. European Society of Breast Imaging (EUSOBI) proposes ten recommendations to standardise its management and reduce unnecessary additional imaging and invasive procedures: (1) in patients with previous history of breast cancer, vaccination should be performed in the contralateral arm or in the thigh; (2) collect vaccination data for all patients referred to breast imaging services, including patients undergoing breast cancer staging and follow-up imaging examinations; (3) perform breast imaging examinations preferentially before vaccination or at least 12 weeks after the last vaccine dose; (4) in patients with newly diagnosed breast cancer, apply standard imaging protocols regardless of vaccination status; (5) in any case of symptomatic or imaging-detected axillary lymphadenopathy before vaccination or at least 12 weeks after, examine with appropriate imaging the contralateral axilla and both breasts to exclude malignancy; (6) in case of axillary lymphadenopathy contralateral to the vaccination side, perform standard work-up; (7) in patients without breast cancer history and no suspicious breast imaging findings, lymphadenopathy only ipsilateral to the vaccination side within 12 weeks after vaccination can be considered benign or probably-benign, depending on clinical context; (8) in patients without breast cancer history, post-vaccination lymphadenopathy coupled with suspicious breast finding requires standard work-up, including biopsy when appropriate; (9) in patients with breast cancer history, interpret and manage post-vaccination lymphadenopathy considering the timeframe from vaccination and overall nodal metastatic risk; (10) complex or unclear cases should be managed by the multidisciplinary team.
Keywords: COVID-19 vaccines, Lymphadenopathy, Mammography, Ultrasonography (breast), Magnetic resonance imaging
Key points
Worldwide COVID-19 vaccination campaigns are currently underway and could become commonplace.
Post-vaccination COVID-19 lymphadenopathy has been reported in up to 16% of cases.
Breast imaging should be performed before or 12 weeks after the last dose of vaccine.
European Society of Breast Imaging (EUSOBI) provides ten recommendations to manage COVID-19 post-vaccination unilateral axillary lymphadenopathy.
Background
Alongside staple preventive measures such as physical distancing, consistent use of face masks, prompt deployment of testing, tracing and isolation protocols [1], a quick and effective rollout of vaccination campaigns throughout the world represents the key element to contain the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic and begin a transition towards normal social and economic activity [2–4]. As of July 27, 2021, the World Health Organization lists 292 candidate vaccines in clinical development, 184 in the pre-clinical phase and 108 in the clinical phase [5]. The European Commission, through the European Medicines Agency, has up to now issued four conditional marketing authorisations for vaccines developed by Pfizer–BioNTech, Moderna, AstraZeneca, and Janssen Pharmaceuticals [6, 7]. These companies used different development strategies, including messenger RNA (mRNA)-based and adenovirus vector-based vaccines, and proposed different vaccination programs (Table 1). Despite the unquestionable positive protective effect, a number of widespread local and systemic reactions, mostly mild and following the second dose, have been observed both in clinical trials and in the population-wide rollout of vaccines, the main being pain at the site of injection, ipsilateral axillary lymph node enlargement, tiredness, headache, and fever [7–9]. In this paper, we focus on the reaction which could have a sizable impact on breast imaging, namely axillary lymph node enlargement, and provide recommendations on the management of this side effect.
Table 1.
Main characteristics of the four COVID-19 vaccines approved in Europe as of July 28, 2021
| Developer | Commercial name | Type | Number of doses | Dosage interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pfizer–BioNTech | Comirnaty | mRNA-based | 2 | 3–12 weeks |
| Moderna | COVID-19 Vaccine Moderna | mRNA-based | 2 | 4 weeks |
| AstraZeneca | Vaxzevria | Adenovirus vector-based | 2 | 4–12 weeks |
| Johnson and Johnson - Janssen Pharmaceuticals | COVID-19 Vaccine Janssen | Adenovirus vector-based | 1 | – |
The pre-COVID-19 scenario
In breast imaging, axillary lymphadenopathy can be detected at mammography, digital breast tomosynthesis, ultrasonography, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and chest computed tomography or positron emission tomography/computed tomography staging exams, being potentially related to a wide spectrum of benign (e.g., mastitis, breast abscess, infected skin lesions, cat-scratch fever) and malignant (e.g., breast cancer, lymphoma, melanoma, ovarian cancer) conditions [10, 11]. According to the 2013 edition of the American College of Radiology Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (ACR BI-RADS) Atlas [11], isolated unilateral axillary lymphadenopathy without underlying abnormal breast findings or known infection or inflammation should be considered suspicious (BI-RADS 4 category). In this scenario, an additional imaging work-up to rule out breast cancer is recommended and, if negative, fine-needle aspiration or core biopsy of the enlarged lymph node should be performed. Of note, occult primary breast cancer presenting with lymph node metastases but negative conventional imaging accounts for up to 1% of all breast cancers [12, 13], although in 75–85% of cases the cancer is detectable on breast MRI [14, 15].
The post-COVID-19 scenario and the relationship with vaccination
Just as lymphadenopathy is a common feature of severe COVID-19 presentation [16], lymph node swelling is a common side effect of vaccinations that evoke a robust immune response [17, 18] and has been described after COVID-19 vaccination in the axilla ipsilateral to the injected deltoid muscle [19]. In the phase III trial of the Moderna vaccine [20], palpable axillary lymphadenopathy ipsilateral to the vaccination arm was reported in 11.6% of recipients after the first dose and in 16.0% of recipients after the second dose, occurring within 2–4 days and with a median duration of 1–2 days. Conversely, in the phase III trial of the Pfizer–BioNTech vaccine [21], lymphadenopathy was reported in 0.3% of recipients, occurred within 2–4 days, and lasted approximately 10 days. Notably, both these trials reported only clinically assessed lymphadenopathy and probably underestimated the rate of subclinical lymphadenopathy, which could be detected by imaging [22]. Of note, a recent study on 169 positron emission tomography–computed tomography examinations has revealed that as many as 29% of examined patients still showed avid uptake of fluorodeoxyglucose in ipsilateral lymph nodes 7–10 weeks after the second dose of the Pfizer–BioNTech vaccine [23]. Since the beginning of the vaccination campaigns in the USA and Europe, several case series have described lymphadenopathy presenting both as a palpable mass or as an incidental finding during routine breast imaging after COVID-19 vaccination [24–27].
Thus, when facing an incidental or symptomatic unilateral axillary lymphadenopathy, while malignancy remains the most critical aetiology, COVID-19 vaccination needs to be recognised as a potential differential diagnosis. Examples of axillary lymphadenopathy after COVID-19 vaccination are presented in Figs. 1 and 2.
Fig. 1.
Ultrasonography of the left axilla showing an enlarged 17 mm reactive lymph node in a 45-year-old woman about a week after receiving the first dose of the Vaxzevria COVID-19 vaccine. Note the asymmetrical cortical thickening (white arrow) associated with a well-represented central fatty hilum
Fig. 2.
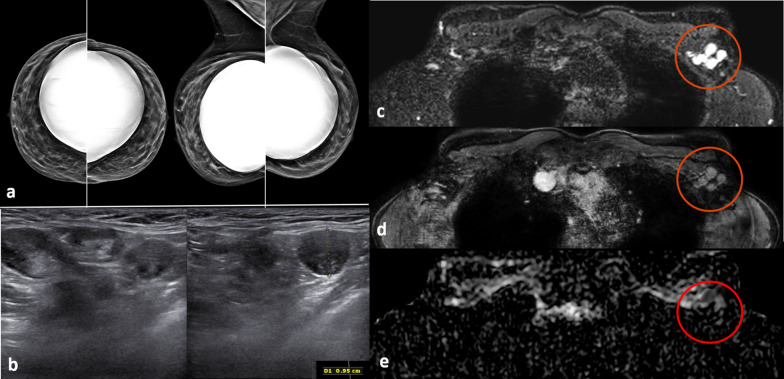
Screening mammography performed in a 44-year-old woman with a positive family history for breast cancer (mother and aunt), bearing implants for aesthetic purposes. Mammography (a) was considered negative. Breast ultrasonography was also performed because of her family history and high breast density (ACR category d). While ultrasonography was negative for both breasts, multiple round, enlarged, hypoechoic lymph nodes (measuring up to 1 cm in axial diameter), with a thickened (< 3 mm) cortex, were seen in the left axilla (b). There were no skin changes and there was no history of any infection or trauma. On the right side, axillary lymph nodes were normal. Because of her family history and the presence of breast implants, magnetic resonance imaging was performed (c T2-weighted short-time inversion recovery; d fat-sat contrast-enhanced T1-weighted gradient-echo; e apparent diffusion coefficient map). No suspicious mass or non-mass lesions were seen in both breasts. Implants showed no signs of rupture (not shown). In the left axilla, multiple enlarged lymph nodes were well visible in c and d (red circles); on the apparent diffusion coefficient map (e, red circle), they mainly exhibited low signal (restricted diffusivity). When an ultrasound-guided biopsy of the most suspicious lymph node was proposed, the patient mentioned that she had a Comirnaty COVID-19 vaccination one week before in the left arm. The attending radiologist was more than surprised to hear this, as at that time, a COVID-19 vaccination was only administered to people older than 70 years. Follow-up performed four weeks after the second vaccination was negative and showed no residual enlarged lymph nodes
Recommendations
Since worldwide mass vaccination campaigns against COVID-19 are currently underway, breast radiologists should be aware of reactive axillary lymphadenopathy as a possible side effect of vaccination, to limit patients’ anxiety and avoid unnecessary diagnostic imaging and invasive procedures. We carefully considered the Recommendations for the Management of Axillary Adenopathy in Patients with Recent COVID-19 Vaccination [28] issued by the Society of Breast Imaging, the statements by Becker et al. [22], Edmonds et al. [29], and Lehman et al. [30, 31].
EUSOBI provides the following recommendations regarding general issues (number 1, 2), asymptomatic subjects, including women attending screening programs (number 3), cases with symptoms or imaging-detected findings (number 4–9), and complex cases (number 10).
In patients with previous history of breast cancer, vaccine injection (both doses for two-doses vaccines) should be performed in the contralateral arm or in the anterolateral thigh.
COVID-19 vaccination data (vaccination status, date, dose, injection site) of all patients presenting for breast imaging with any modality should be collected and made available to radiologists, including the cases of breast imaging performed for cancer staging and of follow-up imaging examinations.
Breast examinations should be preferentially performed before the first dose of a COVID-19 vaccine or at least 12 weeks after the injection. For vaccines with a two-dose schedule, the 12-weeks rule applies from the day of the second injection.
In patients newly diagnosed with breast cancer, all necessary breast imaging examinations with any modality must be performed without any delay due to vaccination, taking into consideration the risk of false positive lymph node findings.
The contralateral axilla and both breasts should be clinically examined using appropriate imaging to exclude malignancy in all patients with axillary symptoms and in all cases of imaging-detected unilateral axillary lymphadenopathy before vaccination or at least 12 weeks after.
In patients with or without previous breast cancer history, imaging-detected suspicious axillary lymphadenopathy contralateral to the vaccination side should be managed according to standard work-up protocols, including, when necessary, tissue sampling.
In patients without breast cancer history and no suspicious breast imaging findings, imaging-detected unilateral axillary lymphadenopathy on the same side of recent COVID-19 vaccination (i.e., within 12 weeks) should be managed according to the clinical setting (Table 2). In asymptomatic patients it should be classified as a benign finding (BI-RADS 2) and no further work-up should be pursued. In case of patients reporting symptoms of axillary lymphadenopathy more than 12 weeks after vaccination, ultrasound examination of the axilla is recommended. In patients with axillary symptoms, incidental unilateral axillary lymphadenopathy ipsilateral to the vaccination side without any suspicious finding in the breast should be classified as a probably benign finding (BI-RADS 3), requiring a 12-week follow-up. In case of persistent suspicion at this 12-week follow-up, ACR BI-RADS recommendations for the management of axillary lymphadenopathy should be followed, with further work-up including, when necessary, tissue sampling [11].
In patients without breast cancer history, incidental unilateral axillary lymphadenopathy after COVID-19 vaccination coupled with ipsilateral suspicious findings in the breast at any imaging modality should be managed according to clinical practice, including biopsy when appropriate [11].
In patients with personal breast cancer history, lymphadenopathy after vaccination should be interpreted considering the time since vaccination and overall nodal metastatic risk (cancer type, location, stage, etc.) [32]. For patients at low risk of axillary or supraclavicular nodal metastases in whom the lymphadenopathy is overwhelmingly more likely due to the vaccination than to the underlying neoplasm (considering time frame, pain, type, and location of cancer), a cautious management strategy without default follow-up imaging is appropriate. Short-interval follow-up imaging with ultrasonography (with at least a 12-week delay) may be performed in patients with higher risk of metastatic lymphadenopathy (e.g., breast cancer, head and neck cancer, upper extremity/trunk melanoma or lymphoma). Node biopsy should be considered in the setting of high nodal metastatic risk when immediate histopathologic confirmation is necessary for timely patient management.
All complex or unclear cases (e.g., axillary lymphadenopathy ipsilateral to the cancer and the side of vaccination within 12 weeks after vaccination in patients with previous bilateral breast cancer; vaccinations performed on different sides) should follow a personalised management, considering the risk of malignant lymphadenopathy, opting for tissue sampling when appropriate after multidisciplinary team discussion.
Table 2.
Management of incidental unilateral axillary lymphadenopathy after recent (within 12 weeks) COVID-19 vaccination
| Patients | Clinical context | Management |
|---|---|---|
| Without any history of breast cancer |
No symptoms No suspicious breast findings at imaging |
Unilateral axillary lymphadenopathy ipsilateral to the vaccination side should be classified as a benign (BI-RADS 2) finding and no further work-up should be pursued. Ultrasonography should be performed in case of symptoms of axillary lymphadenopathy more than 12 weeks after vaccination |
|
Breast imaging for breast symptoms No suspicious breast findings at imaging |
Unilateral axillary lymphadenopathy ipsilateral to the vaccination side should be classified as a probably benign (BI-RADS 3) finding, and clinical follow-up of the axilla is indicated. In case of symptoms of axillary lymphadenopathy more than 12 weeks after vaccination, ACR BI-RADS recommendations should be followed for the management of axillary lymphadenopathy | |
| With personal breast cancer history | Any context | Avoid vaccination at the breast cancer side. Manage unilateral axillary lymphadenopathy ipsilateral to the vaccination side according to overall nodal metastatic risk. For patients at low risk, define a case-by-case cautious management strategy. For patients at high risk, perform short-interval follow-up imaging with ultrasonography with at least a 12-week delay post vaccination, with node biopsy when necessary |
BI-RADS Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System, ACR American College of Radiology
Recommendation number 3 could be difficult to be applied in organised population-based screening programs. In this case, we suggest to carefully apply recommendation number 2.
These recommendations should be applied to both female and male patients. The latter, of course, do not undergo breast cancer screening with the exception of BRCA2 mutation carriers, who could be included in high-risk screening programs [33].
Of note, sites for vaccination alternative to the proximal arm (such as the thigh) [31] could be considered to avoid most breast care-related problems ensuing from the current vaccine administration practice.
Conclusions
Since the rollout of COVID-19 vaccines is rapidly proceeding, radiologists will increasingly encounter in their practice COVID-19 vaccination-induced lymphadenopathy detected by breast imaging [19]. Moreover, the emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 variants and the unclear durability of vaccine-induced immunity [34] will likely lead to re-vaccination or to the administration of new vaccines, further extending this issue. Thus, further research and adherence to evidence-based recommendations are paramount to standardise the management of these findings, avoiding unnecessary additional imaging and invasive procedures.
Abbreviations
- ACR
American College of Radiology
- BI-RADS
Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
- COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019
- EUSOBI
European Society of Breast Imaging
- MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging
- SARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
Authors' contributions
S.S., K.P., V.M., A.C., and F.S. were involved in the first drafting of the manuscript, which was then internally reviewed by all other authors. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
None.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
R. Mann is member of the Insights into Imaging Advisory Editorial Board. He has not taken part in the review or selection process of this article. All remaining authors declare to have no competing interest.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Honein MA, Christie A, Rose DA, et al. Summary of guidance for public health strategies to address high levels of community transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and related deaths, December 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:1860–1867. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6949e2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jeyanathan M, Afkhami S, Smaill F, Miller MS, Lichty BD, Xing Z. Immunological considerations for COVID-19 vaccine strategies. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020;20:615–632. doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-00434-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wouters OJ, Shadlen KC, Salcher-Konrad M, et al. Challenges in ensuring global access to COVID-19 vaccines: production, affordability, allocation, and deployment. Lancet. 2021;397:1023–1034. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00306-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Skegg D, Gluckman P, Boulton G, et al. Future scenarios for the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet. 2021;397:777–778. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00424-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.World Health Organization (2021) Draft landscape and tracker of COVID-19 candidate vaccines. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/draft-landscape-of-covid-19-candidate-vaccines. Accessed 28 Jul 2021
- 6.Cavaleri M, Enzmann H, Straus S, Cooke E. The European Medicines Agency’s EU conditional marketing authorisations for COVID-19 vaccines. Lancet. 2021;397:355–357. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00085-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) (2021) COVID-19 vaccines. https://vaccination-info.eu/en/covid-19/covid-19-vaccines. Accessed 28 Jul 2021
- 8.Chapin-Bardales J, Gee J, Myers T. Reactogenicity following receipt of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines. JAMA. 2021;325:2201–2202. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.5374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Brown A, Shah S, Dluzewski S, et al. Unilateral axillary adenopathy following COVID-19 vaccination: a multimodality pictorial illustration and review of current guidelines. Clin Radiol. 2021;76:553–558. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2021.04.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cao MM, Hoyt AC, Bassett LW. Mammographic signs of systemic disease. Radiographics. 2011;31:1085–1100. doi: 10.1148/rg.314105205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.D’Orsi CJ, Sickles EA, Mendelson EB, Morris EA (2013) ACR BI-RADS® Atlas, breast imaging reporting and data system, 5th edn. American College of Radiology, Reston, VA, USA
- 12.Gorkem SB, Oconnell A. Abnormal axillary lymph-nodes on negative mammograms: causes except breast cancer. Diagnostic Interv Radiol. 2012;18:473–479. doi: 10.4261/1305-3825.DIR.5491-11.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ikeda DM, Miyake KK (2017) Clinical breast problems and unusual breast conditions. In: Ikeda DM, Miyake KK (eds) Breast imaging: the requisites, 3rd edn. Elsevier, St. Louis, MO, USA, pp 397–437
- 14.Mann RM, Kuhl CK, Kinkel K, Boetes C. Breast MRI: guidelines from the European Society of Breast Imaging. Eur Radiol. 2008;18:1307–1318. doi: 10.1007/s00330-008-0863-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sardanelli F, Boetes C, Borisch B, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the breast: recommendations from the EUSOMA working group. Eur J Cancer. 2010;46:1296–1316. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2010.02.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sardanelli F, Cozzi A, Monfardini L, et al. Association of mediastinal lymphadenopathy with COVID-19 prognosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020;20:1230–1231. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30521-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Studdiford J, Lamb K, Horvath K, Altshuler M, Stonehouse A. Development of unilateral cervical and supraclavicular lymphadenopathy after human papilloma virus vaccination. Pharmacotherapy. 2008;28:1194–1197. doi: 10.1592/phco.28.9.1194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shirone N, Shinkai T, Yamane T, et al. Axillary lymph node accumulation on FDG-PET/CT after influenza vaccination. Ann Nucl Med. 2012;26:248–252. doi: 10.1007/s12149-011-0568-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tu W, Gierada DS, Joe BN. COVID-19 vaccination-related lymphadenopathy: what to be aware of. Radiol Imaging Cancer. 2021;3:e210038. doi: 10.1148/rycan.2021210038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Baden LR, El Sahly HM, Essink B, et al. Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:403–416. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2035389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Polack FP, Thomas SJ, Kitchin N, et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:2603–2615. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2034577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Becker AS, Perez-Johnston R, Chikarmane SA et al (2021) Multidisciplinary recommendations regarding post-vaccine adenopathy and radiologic imaging: radiology scientific expert panel. Radiology 300:E323–E327. 10.1148/radiol.2021210436 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 23.Eshet Y, Tau N, Alhoubani Y, Kanana N, Domachevsky L, Eifer M. Prevalence of increased FDG PET/CT axillary lymph node uptake beyond 6 weeks after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination. Radiology. 2021 doi: 10.1148/radiol.2021210886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ahn RW, Mootz AR, Brewington CC, Abbara S. Axillary lymphadenopathy after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination. Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging. 2021;3:e210008. doi: 10.1148/ryct.2021210008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mortazavi S. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) vaccination associated axillary adenopathy: imaging findings and follow-up recommendations in 23 women. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021 doi: 10.2214/AJR.21.25651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cellina M, Irmici G, Carrafiello G. Unilateral axillary lymphadenopathy after coronavirus disease (COVID-19) vaccination. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021;216:W27–W27. doi: 10.2214/AJR.21.25683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Dominguez JL, Eberhardt SC, Revels JW. Unilateral axillary lymphadenopathy following COVID-19 vaccination: a case report and imaging findings. Radiol Case Reports. 2021;16:1660–1664. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2021.04.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Grimm L, Destounis S, Dogan B et al (2021) SBI recommendations for the management of axillary adenopathy in patients with recent COVID-19 vaccination. Reston, VA, USA
- 29.Edmonds CE, Zuckerman SP, Conant EF. Management of unilateral axillary lymphadenopathy detected on breast MRI in the era of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) vaccination. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021 doi: 10.2214/AJR.21.25604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lehman CD, Lamb LR, D’Alessandro HA. Mitigating the impact of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) vaccinations on patients undergoing breast imaging examinations: a pragmatic approach. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021 doi: 10.2214/AJR.21.25688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lehman CD, D’Alessandro HA, Mendoza DP, Succi MD, Kambadakone A, Lamb LR. Unilateral lymphadenopathy after COVID-19 vaccination: a practical management plan for radiologists across specialties. J Am Coll Radiol. 2021;18:843–852. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2021.03.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Özütemiz C, Krystosek LA, Church AL, et al. Lymphadenopathy in COVID-19 vaccine recipients: diagnostic dilemma in oncologic patients. Radiology. 2021;300:E296–E300. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2021210275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Giordano SH. Breast Cancer in Men. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:2311–2320. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1707939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Teijaro JR, Farber DL. COVID-19 vaccines: modes of immune activation and future challenges. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021;21:195–197. doi: 10.1038/s41577-021-00526-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.