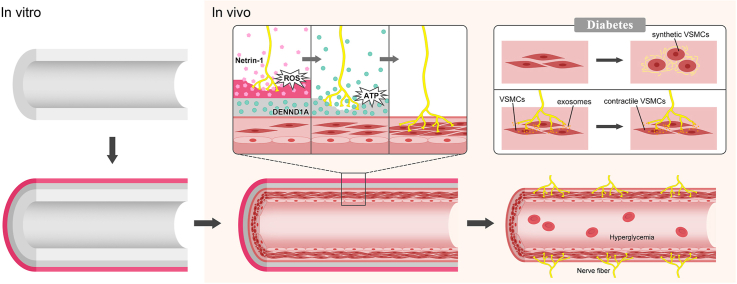
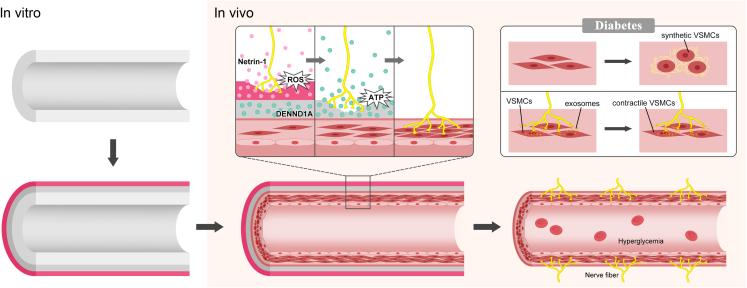
Abstract
Small-diameter tissue-engineered vascular grafts (sdTEVGs) with hyperglycemia resistance have not been constructed. The intimal hyperplasia caused by hyperglycemia remains problem to hinder the patency of sdTEVGs. Here, inspired by bionic regulation of nerve on vascular, we found the released neural exosomes could inhibit the abnormal phenotype transformation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). The transformation was a prime culprit causing the intimal hyperplasia of sdTEVGs. To address this concern, sdTEVGs were modified with an on-demand programmable dual-responsive system of ultrathin hydrogels. An external primary Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-responsive Netrin-1 system was initially triggered by local inflammation to induce nerve remolding of the sdTEVGs overcoming the difficulty of nerve regeneration under hyperglycemia. Then, the internal secondary ATP-responsive DENND1A (guanine nucleotide exchange factor) system was turned on by the neurotransmitter ATP from the immigrated nerve fibers to stimulate effective release of neural exosomes. The results showed nerve fibers grow into the sdTEVGs in diabetic rats 30 days after transplantation. At day 90, the abnormal VSMCs phenotype was not detected in the sdTEVGs, which maintained long-time patency without intima hyperplasia. Our study provides new insights to construct vascular grafts resisting hyperglycemia damage.
Keywords: sdTEVGs, On-demand programmed responsive systems, Neural exosomes, Nerve reconstruction, Intimal hyperplasia
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
•
VSMCs undergo a phenotypic transformation under high glucose, which lead to intimal hyperplasia in sdTEVGs.
-
•
Neural exosomes could inhibit the abnormal phenotype transformation of VSMCs from contractile to synthetic.
-
•
SdTEVGs with on-demand programmable dual responsive system inhibited intimal hyperplasia in diabetes.
1. Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases are a serious threat to human health, and approximately 170,000 people die of cardiovascular diseases every year worldwide. SdTEVGs (<6 mm) have been increasingly in demand for peripheral vascular occlusion, coronary artery bypass grafting, hemodialysis arteriovenous fistula, etc. [1]. However, thrombosis and intimal hyperplasia are serious problems associated with sdTEVGs after transplantation. Thrombosis is mainly controlled by drugs, but intimal hyperplasia causes restenosis of vascular grafts, seriously shortening their patency time and restricting further clinical application of sdTEVGs [[2], [3], [4]]. Small-diameter TEVG transplantation is an important method to treat diseases of small- or medium-sized vessels in the context of diabetes [5]. However, disordered lipid metabolism and the accumulation of advanced glycation end products cause severe intimal hyperplasia in sdTEVGs and then lead to the rapid decay of graft patency [6,7]. Therefore, preventing intimal hyperplasia in sdTEVGs to support their long-term patency in diabetes has become a critical problem to be solved.
Intimal hyperplasia is characterized by abnormal migration and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). Although many studies have focused on inhibiting VSMCs proliferation by blocking related signaling pathways, such as TGF-β, the control of intimal hyperplasia is still limited [8,9]. VSMCs can be divided into two subtypes: contractile and synthetic. The transformation from a contractile to a synthetic phenotype is a common pathological feature of restenosis after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA), atherosclerosis, and vascular graft blockage [8,10], which suggests that the abnormal phenotypic transformation of VSMCs is a key initial step of intimal hyperplasia.
From the perspective of either structure or function, nerves and blood vessels are interweaved. Almost all blood vessel networks except capillaries are innervated by sympathetic fibers. Nerves regulate the activity and nutrition exchange of blood vessels [[11], [12], [13]]. Nerve fibers have been reported to branch multiple times to innervate VSMCs in the form of varicose bodies. In addition, finger-like axon terminals can grab VSMCs by forming synaptic microspurs [14], through which neural exosomes containing active substances are then released and taken up by VSMCs [15]. However, hyperglycemia inhibits nerve fiber growth into sdTEVGs because of distal degenerative neuropathy and axonal growth suppression induced by related gene expression changes and nerve fiber structural disorders [16,17]. In addition, hyperglycemia decreases the activity of the protein that controls neural exosome-containing multivesicular body (MVB) transport.
Among the family of axon growth-inducing molecules, only Netrins can promote axon outgrowth and attraction [18,19]. In particular, Netrin-1 effectively induces the growth of nerve axons. The effect of growth cones on the regeneration of axons is 9 times stronger than that of nerve growth factor (NGF) [20,21]. In addition, as a molecular switch for MVB transport, Rab proteins regulate the formation, transport, adhesion, fusion and release of exosomes [22]. Rab35 activation can specifically promote neural exosome release from synapses carrying their wrapped active substances [23]. Under physiological conditions, the guanine nucleotide exchange factor DENND1A can specifically bind to the most sensitive glutamine Q67 position in the amino acid sequence and activate Rab35 [24].
Inspired by the interaction between nerves and blood vessels, we propose here that functional nerve reconstruction can regulate intimal hyperplasia in sdTEVGs. A programmable dual-responsive release system was mounted on the adventitia of the sdTEVGs. After transplantation into Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats, the primary ROS-responsive Netrin-1 system was initially triggered by local inflammation, inducing the integration of nerve fibers into the sdTEVGs. With increased levels of the neurotransmitter ATP from the immigrated nerve fibers, the secondary ATP-responsive system was turned on. DENND1A was then delivered to nerve fibers, which promote the release of neuronal exosomes to maintain the normal phenotype of VSMCs. For up to 90 days, the transplanted sdTEVGs (1 mm) remained patent without intimal hyperplasia in diabetic rats.
2. Results
DENND1A activated Rab35 to restore the release of neural exosomes inhibited by high glucose simulation. The secretion process of neural exosomes and their characteristics including typical saucer-like morphology, average particle size and surface markers were identified. Their numbers were significantly reduced under high glucose simulation. Rab35 was inactivated and exosomes numbers were obviously reduced under high glucose simulation (Supplementary Fig. 1). DENND1A, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF), specifically bound to Rab35 and dissociated from GDP to combine with GTP, thereby the Rab35 became active (Fig. 1A and B). Our results confirmed the DENDD1A effect on secretion of neural exosomes (Fig. 1C and D). When the concentration of DENND1A was slowly increased to 500 ng/ml, most of the intracellular inactive Rab35 was reactivated to the activated state (Supplementary Fig. 2). Therefore, 500 ng/ml could be used as the minimum effective concentration of DENND1A. When the neurons were stimulated by DENND1A for only 1 day, neural Rab35 maintained its activation state 7 days later (Supplementary Fig. 3), indicating that the effect of DENND1A was persistent.
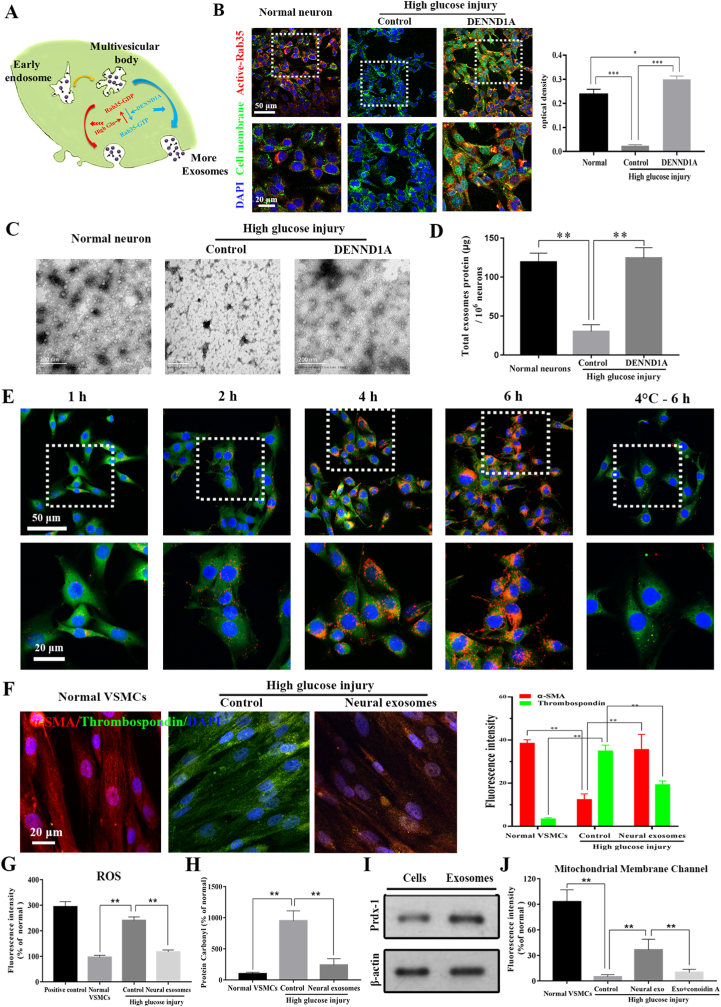
Fig. 1.
Neural exosomes' secretion and protection on VSMCs was inhibited under high-glucose stimulation. (A) Schematic of Rab35 activation by DENND1A. (B) DENND1A stimulation reactivated Rab35 in neurons, which was inhibited under high-glucose conditions. optical density (OD) values were statistically estimated. (C) The morphology and numbers of neural exosomes in the three groups were observed by TEM. (D) The total protein contents of exosomes in three groups were measured by a BCA assay. (E) Neural exosomes were labeled with PKH26 (red). VSMCs were labeled with CMFDA (green) and DAPI. (F) Immunofluorescence staining of VSMCs in the blank, high glucose simulation and exosome groups. Thrombospondin (labeled synthetic VSMCs, green), α-SMA (labeled contractile VSMCs, red), and DAPI (blue). (G) Intracellular ROS levels were detected by chemiluminescence. (H) Intracellular protein carbonyl levels were detected by a fluorescence probe binding assay. The effects of oxidative stress on mitochondrial membrane potential and membrane channels were investigated in VSMCs. (I) The expression of Prdx-1 in neurons and neural exosomes under high glucose simulation. (J) MPTP permeability changes in VSMCs were detected using the BBcellProbeTMCA1 probe. All data are expressed as the mean ± s.e.m. (n = 5 independent experiments). A two-tailed Student's t-test was used. Asterisks indicate P values (***P < 0.001).
Neural exosomes inhibited abnormal phenotypic transformation of VSMCs under high-glucose stimulation. PKH-26 labeled neural exosomes were gradually aggregated inside the cytoplasm of VSMCs at 37 °C, which was inhibited at 4 °C. The results confirmed that endocytosis of neural exosomes by VSMCs is an active physiological process (Fig. 1E). The VSMC phenotype was abnormally transformed from contractile (α-SMA+) to synthetic (THBS1+) 2 days after high-glucose stimulation. After neural exosomes were added to the supernatant, the proportion of cells with a contractile phenotype was significantly restored (Fig. 1F). According to cell damage tests, the intracellular ROS level and carbonyl content of VSMCs obviously increased after high-glucose stimulation and significantly decreased after addition of neural exosomes (Fig. 1G and H). To identify the key proteins that have protective effects on VSMCs in neural exosomes, we performed secondary protein mass spectrometry analysis of exosomes and compared the results with the protein types in the UniProt database (Supplementary Table 1). Based on the confidence scores and functions of the proteins, peroxidase-1 (Prdx-1), a protein related to the removal of oxidative stress factors in cells [25], was selected. It was further verified by Western blot that the Prdx-1 protein existed in neural exosomes with high-glucose stimulation (Fig. 1I). In mitochondrial membrane channel pore (MPTP) fluorescence and mitochondrial membrane potential assays in VSMCs, we found that the protective effect of neural exosomes no longer existed after adding Conoidin A, a Prdx-1 inhibitor (Fig. 1J). In addition, calcification nodules was observed in all the VSMCs 2 days after high-glucose stimulation, and a protein content of 80 μg/ml was the lowest effective stimulation concentration. After adding 80 μg/ml neural exosomes to the culture supernatant, abnormal migration, proliferation and calcification of VSMCs was alleviated. However, neural exosomes’ reversal effect was inhibited by Conoidin A (Supplementary Figs. 4 and 5). Therefore, the above results indicated that Prdx-1 might be the key factor in neural exosomes that protects VSMCs.
Design and properties of sdTEVGs with an on-demand programmable dual-responsive system. Decellularized vascular matrix coupled with Netrin-1 was transplanted into the carotid artery of normal rats. Two months later, the sdTEVGs were unobstructed, and the neural marker PGP9.5 was expressed in large amounts in the adventitia, but intimal hyperplasia appeared with blockade of DCC, an axon-induced receptor of Netrin-1 (Supplementary Fig. 6). Then, the time regularity of nerve fiber growth into Netrin-1-modified sdTEVGs and fiber connections with nearby ganglia were detected (Supplementary Fig. 7). Netrin-1-modified sdTEVGs (1 mm) maintained 100% patency 24 months after transplantation (n = 5). PGP9.5 was also expressed in the adventitia (Supplementary Fig. 8). The anterograde neuronal tracing technique proved that the nerve fibers grown on the sdTEVGs came from the superior cervical ganglion at 24 months after transplantation (Supplementary Fig. 9). In view of the difficulty of nerve regeneration and maintenance of normal nerve function in diabetes, on-demand programmable dual-responsive release systems were designed to modify the adventitia of the sdTEVGs. The external hydrogel was a primary ROS-responsive system with Netrin-1, and the internal hydrogel was a secondary ATP-responsive system with DENND1A. After sdTEVGs implantation in vivo, nerve reconstruction required at least 2–4 weeks. The primary ROS-responsive Netrin-1 system was initially triggered by ROS produced from local inflammation that reacted with the long-chain hydrophobic thioketone group of the external PEG hydrogel. The hydrogel was gradually hydrolyzed, and then Netrin-1 underwent controlled release, inducing the integration of nerve fibers into sdTEVGs. Later, with the increase in neurotransmitter ATP from the immigrated nerve fibers, the secondary ATP-responsive DENND1A system was activated, which promoted the hydrolysis of the internal hydrogel and the release of DENND1A. Nerve fibers enhanced the release of neural exosomes after internalization of DENND1A, thereby restoring nerve regulation of VSMCs in diabetes (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
Design of an on-demand programmable dual-responsive release system in sdTEVGs. Dual-responsive hydrogels were successively modified on the adventitia of the sdTEVGs in vitro, which were than implanted into SD rats. Increasing ROS reacted with the external responsive hydrogel, which gradually released Netrin-1 to attract and guide nerve fibers to grow into the sdTEVGs. With the increased levels of the neurotransmitter ATP from the immigrated nerve fibers, single-stranded (ssDNA) of the ATP ligand in the internal responsive hydrogel was turned on. Then, the hydrogel released DENND1A, which was internalized by nerve fibers to promote the release of neural exosomes, which could inhibit the abnormal transformation of VSMCs into synthetic VSMCs in diabetic rats.
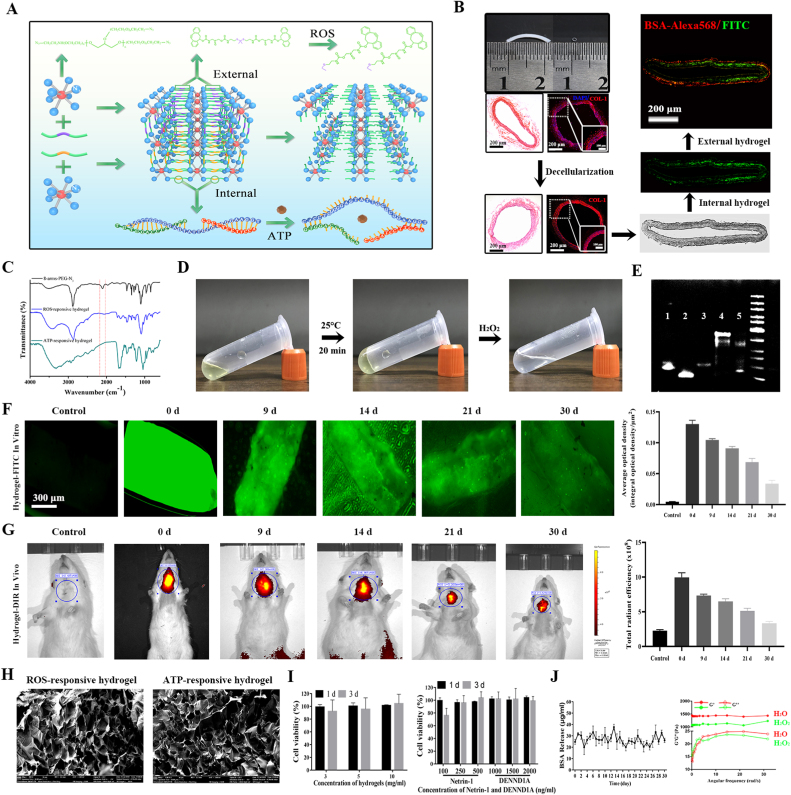
The hydrogel could be easily and rapidly formed through a copper-free click reaction between the eight-arm PEG and a crosslinker. The external and internal hydrogels could respond to ROS and ATP, respectively, and later, the hydrogel was disintegrated (Fig. 3A). The internal ATP-responsive hydrogel containing BSA-FITC and the external ROS-responsive hydrogel containing BSA-Alexa568 successively adhered to the adventitia of the decellularized vascular matrix (Fig. 3B). Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy showed that the characteristic absorptions at 2105 for azide groups in eight-arm PEG nearly disappeared after adding the crosslinker, indicating that the alkyne–azide reaction was successful in both hydrogels (Fig. 3C). It was clear that the monomer formed a hydrogel at 25 °C, and the hydrogel turned into a liquid again after adding H2O2 (Fig. 3D). The ATP aptamer and the two single-stranded ssDNAs could successfully polymerize into a chain, which was again decomposed into a single chain after adding ATP to combine with its aptamer (Fig. 3E). The sdTEVGs modified with double-layered BSA-FITC or DiR dye molecules were placed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) or implanted in rats. After observation for a period of time, the hydrogel-modified sdTEVGs had strong green fluorescence at Days 9 and 14, and this fluorescence remained at Day 30 both in vitro and in vivo (Fig. 3F and G), suggesting that the hydrogel could maintain sustained release for more than 1 month in vivo, thus providing sufficient time for nerve fibers to grow into the sdTEVGs. The hydrogel we synthesized had a uniform loose structure, which was necessary for increasing its contact area with the responsive substrate and promoting the ingrowth of nerve fibers (Fig. 3H). The responsive PEG hydrogel was almost noncytotoxic to neurons, and Netrin-1 and DENND1A also did not show significant cytotoxicity, even when their concentrations reached 500 and 2000 ng/ml, respectively (Fig. 3I). To achieve our purpose in vivo, the inner hydrogel was designed to respond only to the neurotransmitter ATP and release DENND1A immediately, but the external hydrogel needed to sustain the controlled release of netrin-1 for a period of time to induce nerve growth after the response to ROS. The average ROS concentration of the sdTEVGs in vivo from 0 to 30 days was approximately 3 mM (data not shown). Thus, H2O and 3 mM H2O2 were used to treat ROS-responsive hydrogels containing BSA. The frequency sweep demonstrated that the storage modulus (G′) was greater than the loss modulus (G″) in the gel phase. Compared with those in the H2O group, both G′ and G″ decreased in the H2O2 group, reflecting a reduction in hydrogel viscoelasticity. The daily BSA release rate within 30 days in the H2O2 group was approximately 3.6% ± 0.7%, indicating that the hydrogel had a specific response to H2O2 and sustained stable release (Fig. 3J).
Fig. 3.
Characteristics of the dual-responsive hydrogel. (A) Through a Michael addition conjugation reaction, diaminoacetic acid reacted with an acrylamide thioketone crosslinker and then polymerized oligoamine to synthesize ROS-responsive compounds with modified amino groups at both ends. Then, it reacted with eight-arm PEG-azide to form a hydrogel. The ATP-responsive compound was a trimeric molecule consisting of the ATP aptamer and corresponding ssDNA. The added ATP bound to its aptamer and disengaged from the ssDNA, and the trimer was depolymerized. (B) The rat common carotid artery (length: 1 cm, diameter: 1 mm) was decellularized, the cells (blue) were removed, and collagen (red) was left completely. The internal and external hydrogels encapsulating fluorescent molecules were bound to the outer surface of the adventitia, and the double-layered gel structure of the cross-section of the blood vessel was observed under a fluorescence microscope. (C) FT-IR spectra of the 8-arm PEG-azide, ROS-responsive hydrogel and ATP-responsive hydrogel. (D) The solution changed to a gel state with increasing temperature, and the gel degraded back to a solution state after incubation with H2O2. (E) PAGE verified that the DNA polymer was responsive to ATP. Lane 1: ATP aptamer; Lanes 2 and 3: ssDNA1 and 2 monomers; Lane 4: DNA polymer; Lane 5: ATP hydrolysis of DNA polymer. (F, G) sdTEVGs modified by control hydrogels were soaked in PBS or implanted into rats. Fluorescence intensity was observed under a fluorescence microscope, and bioluminescence images were obtained at different times. (H) SEM photographs of the internal structure of ROS- and ATP-responsive hydrogels frozen in liquid nitrogen. (I) The MTT method was used to detect the effects of different concentrations of hydrogel and the functional molecules Netrin-1 and DENND1A on cell viability. The cell type for the MTT test is HUVEC. (J) ROS-responsive hydrogels were stimulated with H2O or 3 mM H2O2, protein release was detected by ELISA, and changes in the hydrogel elastic modulus G′ and viscous modulus G″ were measured by rheometry. All data are expressed as the mean ± s.e.m. (n = 5 independent experiments).
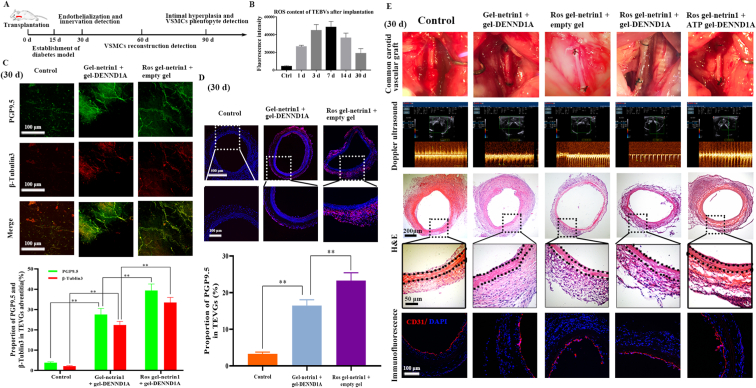
The primary ROS-responsive system released Netrin-1 to induce nerve fiber growth into sdTEVGs. Because the 60-day survival rate of the diabetic rats was reduced to 20% [26], we injected streptozocin into Sprague Dawley (SD) rats on day 15 after sdTEVGs transplantation, and various indicators were detected in the rats within 90 days (Fig. 4A). ROS produced by inevitable local inflammation associated with the implanted sdTEVGs in diabetic rats were able to trigger the degradation of the external hydrogels gradually, thereby releasing Netrin-1 (Fig. 4B). According to the responsive system and the functional factors contained in the hydrogels of the sdTEVGs, the rats were divided into the following 5 groups: Group 1: Control (empty gel + empty gel); Group 2: Gel-Netrin1+gel-DENND1A; Group 3: ROS gel-Netrin1+empty gel; Group 4: ROS gel-Netrin1+gel-DENND1A; and Group 5: ROS gel-Netrin1+ATP gel-DENND1A. Large amounts of the nerve-specific markers β3-tubulin and PGP9.5 were observed in the adventitia of the sdTEVGs in Group 3 at Day 30 after implantation, confirming that nerve fibers had been reconstructed. The number of nerve fibers was much higher in Group 3 than in Group 2, and the sdTEVGs with no Netrin-1 modification in Group 1 had no nerve fibers (Fig. 4C). The highest nerve fiber density was also demonstrated in Group 3 (Fig. 4D). Excluding the control group, the intima-media thickness ratio (IMTR) of the sdTEVGs in the other 4 groups was below 0.41 ± 0.024, and the blood flow velocity was above 80.31 ± 6.24 cm/s at Day 30. The sdTEVGs completed endothelialization in all groups, and nourishing blood vessels also formed on the adventitia of some sdTEVGs at Day 30 (Fig. 4E). The primary ROS-responsive Netrin-1 system played a role in inducing the integration of nerve fibers into the sdTEVGs. Early patency of sdTEVGs ensured by endothelialization was the basis of further studies on the relationship between nerve reconstruction and VSMC function.
Fig. 4.
Netrin-1 was released from the primary ROS-responsive system to induce nerve fiber growth into sdTEVGs. (A) Streptozocin was injected on day 15 after TEVG implantation to establish a diabetic rat model. Patency, nerve ingrowth, and endothelialization were examined on Day 30. Smooth muscle reconstruction was detected on Day 60, and intimal hyperplasia and VSMC phenotypes were detected on Day 90. (B) The ROS content in the sdTEVGs was measured by chemiluminescence within 30 days. (C) SdTEVGs were labeled with both anti-PGP9.5 (green) and anti-β-tubulin3 (red) antibodies to detect nerve fibers growing in the adventitia at 30 days after implantation. The fluorescent signals in each group were statistically analyzed. (D) Immunofluorescence staining and statistical analysis showed nerve fibers growing in cross-sections of sdTEVGs by labeling PGP9.5 at Day 30. (E) On Day 30, the patency and blood flow velocity of the sdTEVGs were determined with a portable ultrasound scanner. The sdTEVGs in all groups were removed, and endothelialization was observed by H&E staining and staining with anti-CD31 (red) and DAPI (blue). The dot lines mean dividing lines between the vascular adventitia, media and intima. All data are expressed as the mean ± s.e.m. (n = 4 SD rats per group). Asterisks indicate P values (**P < 0.01).
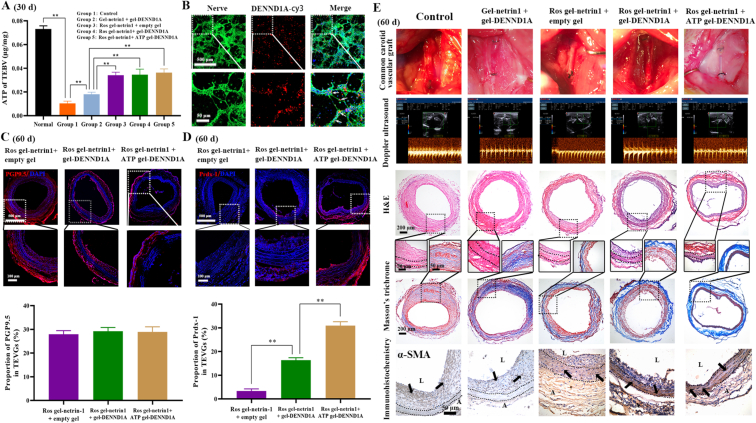
The secondary ATP-responsive system released DENND1A to promote normal VSMC rebuilding in the sdTEVGs. At day 30 after implantation, the level of the neurotransmitter ATP in decellularized sdTEVGs was detected by the chemiluminescence method. The ATP content in the sdTEVGs was high in Groups 3, 4 and 5 and positively correlated with nerve fiber density. This result suggested that innervated sdTEVGs contained sufficient ATP to initiate the degradation of the internal hydrogel and the release of DENND1A (Fig. 5A). DENND1A was internalized by neurons and axons after being cocultured at 37 °C (Fig. 5B), thus activating Rab35 and promoting exosome secretion under high-glucose stimulation. Compared with those in the other groups, the nerve fibers on the sdTEVGs with the ROS-responsive Netrin-1 system were more abundant at Day 60 (Fig. 5C). There was more Prdx-1 on the sdTEVGs in Group 5 than on those in Group 4 and Group 3, which proved that internal hydrogel degradation caused the release of DENND1A and promoted neural exosome secretion under hyperglycemia stimulation in vivo (Fig. 5D). Sixty days after implantation, the sdTEVGs in Groups 1 and 2 had more severe intimal hyperplasia and lower blood flow velocity, and the IMTR increased to 2.33 ± 0.21 and 0.92 ± 0.085, respectively. In contrast, the sdTEVGs had blood flow velocities above 76.25 ± 6.47 cm/s and slight intimal hyperplasia with an IMTR below 0.51 ± 0.047 in Groups 3, 4 and 5, in which a large number of VSMCs migrated into the media of the sdTEVGs, with patency maintained. The Masson's trichrome staining assay showed that the proportion of collagen fibers in the intima of Groups 1 and 2 could reach more than 25.7 ± 2.1%, while the proportion of collagen fibers in the intima of Groups 3, 4 and 5 dropped to a maximum of 18.6 ± 1.9%, indicating that enhanced nerve reconstruction could reduce intimal hyperplasia by inhibiting collagen fiber secretion from VSMCs. Notably, the proportion of collagen in the intima in Group 5 was only 15.8 ± 1.3%, suggesting that the ability of DENND1A to promote the release of neural exosomes could facilitate the inhibition of collagen secretion from VSMCs in the neointima. In addition, VSMC rebuilding was almost complete in the media of the sdTEVGs in Groups 3, 4 and 5 at Day 60, which was positively related to the density of nerve fibers on the sdTEVGs. However, there was a certain degree of intimal hyperplasia in Groups 3 and 4. In addition, a large number of VSMCs were observed in the thick neointima of the sdTEVGs in Groups 1 and 2, and which were disorder in the media of the sdTEVGs (Fig. 5E). The results demonstrated that the on-demand ATP-responsive DENND1A system increased the expression of Prdx-1, which was speculated to come from neural exosomes and to be beneficial for inhibiting intimal hyperplasia of the sdTEVGs. In addition, the rebuilding of VSMCs was more orderly in Group 5.
Fig. 5.
DENND1A was released from the internal ATP-responsive hydrogel to promote VSMC rebuilding in sdTEVGs. (A) The content of ATP inside the sdTEVGs in each group was measured by chemiluminescence at Day 30. (B) DENND1A labeled with Cy3 was used to treat neural cells in vitro. Immunofluorescence staining showed that DENND1A (red) entered the neurons and axons (green). (C) Immunofluorescence staining and statistical analysis showed nerve fibers growing in the adventitia of the sdTEVGs after labeling PGP9.5 at Day 60. (D) Immunofluorescence staining and statistical analysis showed Prdx-1 in the media and adventitia of the sdTEVGs at Day 60. (E) On day 60 after implantation, H&E and Masson's trichrome staining were used to show intimal hyperplasia and collagen secretion. Blood flow and velocity were measured by laser Doppler ultrasonography, and smooth muscle reconstruction in the sdTEVGs was investigated by α-SMA staining. The dot lines mean dividing lines between the vascular adventitia, media and intima. The meaning of arrows is VSMCs. Data are presented as the mean ± s.e.m. (n = 4 SD rats per group). Comparisons between groups were performed using a two-tailed Student's t-test (**P < 0.01). The absence of asterisks indicates no significant difference.
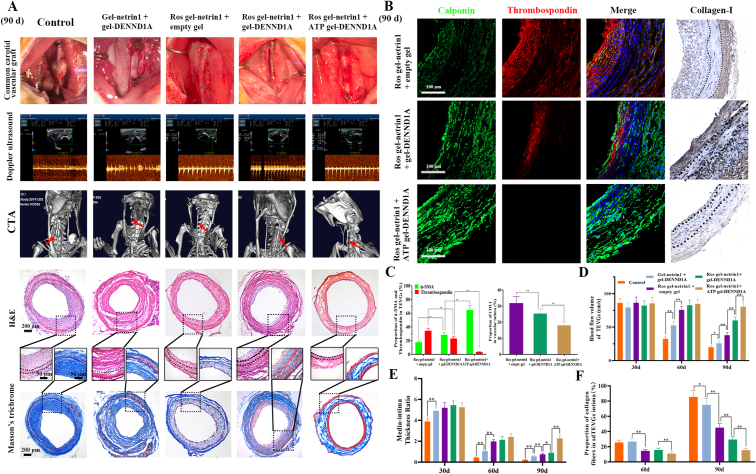
SdTEVGs with an on-demand programmable dual-responsive release system prevented intima hyperplasia in diabetic rats. Aneurysm was observed in the sdTEVGs in Group 1 at 90 days after implantation, possibly caused by sdTEVGs that lacked VSMC rebuilding and failed to resist blood flow stress. H&E staining and carotid ultrasound scanning showed that the sdTEVGs were severely blocked in Groups 1 and 2. Computed tomography angiography (CTA) results demonstrated the blood flow status of the carotid artery and showed worse stenosis for the sdTEVGs in Groups 1 and 2 than for those in the other groups. Intimal hyperplasia and lumen blockage gradually became aggravated from Day 30 in the sdTEVGs in Group 3, and the blood flow velocity decreased to 41.90 ± 5.22 cm/s with an IMTR of 0.74 ± 0.087 at Day 90. The changes in blood flow velocity and IMTR were smaller in Group 4, and almost no obvious neointima was observed in Group 5 (Fig. 6A, D and E). The proportion of collagen fibers in the intima remained 15.8 ± 1.3% in Group 5 at Day 90, which was obviously lower than that in the other four groups, and showed no significant difference compared with that at Day 60 (Fig. 6A and F). The above results indicated that the secretion of neural exosomes could be improved by DENND1A, which provided new insights into the development of the ability of sdTEVGs ability to resist intima hyperplasia and maintain long-term patency. Furthermore, the rebuilt VSMCs in the sdTEVGs in Group 3 exhibited an obvious synthetic phenotype and had abundant collagen I in the intima. In comparison, the expression of the contractile phenotype marker significantly increased and that of collagen I decreased in Group 4. In Group 5, the VSMCs showed an obviously contractile phenotype and had a normal distribution of collagen I (Fig. 6B and C). All these results indicated that sdTEVGs with an on-demand programmable dual-responsive release system can improve the neural modulation of VSMCs under hyperglycemic conditions, preventing the abnormal phenotypic transformation of VSMCs and inhibiting intima hyperplasia of the sdTEVGs.
Fig. 6.
SdTEVGs with programmed responsive release systems showed a normal VSMC phenotype without intimal hyperplasia. (A) On day 90 after sdTEVGs implantation, H&E and Masson's trichrome staining showed intimal hyperplasia and collagen secretion. Blood flow and velocity were measured by laser Doppler ultrasonography. Micro-CT was used to observe the overall patency of the sdTEVGs. (B) The phenotype of VSMCs was investigated by α-SMA (green) and thrombospondin (red) immunofluorescence. In addition, collagen I was used to detect the content of type I collagen in the hyperplastic intima of the sdTEVGs. The dot lines mean dividing lines between the vascular adventitia, media and intima. (C) Statistical analysis of α-SMA, thrombospondin and COL1 expression in the neointima of the sdTEVGs. (D–F) Statistical analysis of blood flow volume (D), the IMTR (E), and the proportion of collagen fibers in the intima (F) of the sdTEVGs in each group at days 30, 60 and 90. For C–F, data are presented as the mean ± s.e.m. (n = 4 SD rats per group). Comparisons between groups were performed using a two-tailed Student's t-test with Welch's correction. Asterisks indicate P values (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01).
3. Discussion
Intimal hyperplasia has long been known to be a cause of restenosis in vascular grafts and intravascular stents [27]. Likewise, anastomotic intimal hyperplasia of sdTEVGs is a critical issue, especially in diabetic patients [[28], [29], [30]]. Our study found that even after endothelialization of sdTEVGs, the intimal hyperplasia in diabetic rats was still serious. To date, there is no satisfactory solution to the problem of intimal hyperplasia. Consistently, we found that sdTEVGs (1 mm) with nerve fibers remained patent for more than 24 months in normal rats. In contrast, when nerve growth was blocked, the sdTEVGs showed severe intimal hyperplasia and obstruction. Thus, nerves may have a regulatory effect on intimal hyperplasia. Synaptic microspurs of nerve fibers through varicose bodies contacting VSMCs became the foundation of the spatial structure. Exosomes, which are known to contain lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins that regulate the biological activity of recipient cells and activate signaling pathways in target cells, may be the liaison between nerve fibers and VSMCs [31,32]. We demonstrated that under high-glucose stimulation, the release of neural exosomes was reduced sharply, but this reduction could be reversed by DENND1A. The transformation of Rab35 from the inactive GDP-bound state to the active GTP-bound form can be promoted by DENND1A, which triggers the continuous release of exosomes [24].
Abnormal phenotypic transformation and proliferation of VSMCs are mechanisms of vascular intimal hyperplasia and stenosis [33]. Synthetic VSMCs mainly exist in pathological blood vessels and synthesize and secrete abnormal ECM proteins, causing the intima to thicken and the lumen to narrow. We found that VSMCs undergo a phenotypic transformation from contractile to synthetic under high-glucose stimulation, which was the initial key factor causing intimal hyperplasia of sdTEVGs. Neural exosomes were found to prevent the phenotypic transformation of VSMCs under high-glucose stimulation. Oxidative stress, chronic inflammation, and apoptosis are factors that induce VSMC phenotypic transformation, which generally produces high levels of ROS, leading to mitochondrial function and structural disorders [34,35]. We further found that the Prdx-1 protein was present in neural exosomes, which maybe a key factor in the protective effects on VSMCs.
In response to the functional and metabolic disorders of nerves and VSMCs in sdTEVGs under hyperglycemia stimulation, we designed sdTEVGs with on-demand programmable responsive release systems to induce nerve ingrowth and enhance the neural regulation of VSMCs. The primary ROS-responsive hydrogel containing Netrin-1 maintained stability in the adventitia of the sdTEVGs in vivo and in vitro, with a loose pore structure, excellent mechanical properties and biocompatibility. In this study, a long-chain PEG with a thiol group at the terminal modified cyclooctyne was selected as the crosslinking agent for the external ROS-responsive hydrogel of the sdTEVGs, which protected Netrin-1 from diffusing and degrading before the inflammatory reaction occurred. After local ROS reacted with the thione group in the hydrogel, which was then gradually hydrolyzed. Since nerve fiber regeneration takes approximately 2–4 weeks, the primary ROS-responsive Netrin-1 system extended the time of sustained Netrin-1 release in vivo for 30 days, thus enhancing the efficacy of Netrin-1 in promoting nerve fiber rebuilding of sdTEVGs in the context of diabetes. Axon guidance factor Netrin-1 is present in the ECs of natural blood vessels, which has both anti-inflammatory and promoting nerve growth effects. In our previous research, we have found netrin-1 could promote the inflammation resolution and endothelialization of sdTEVGs [36]. In this study, we utilized Netrin-1 to promote the nerve regeneration of sdTEVGs. Our researches suggested that there might exist relevance between endothelialization and neurotization of vascular grafts, which is consist with recent finding on recellularization of human acellular vessels [2].
ATP is released as a common neurotransmitter together with other types of neurotransmitters and directly activates the P2X1 receptor on the cell surface at neuromuscular junctions, causing rapid depolarization and contraction of smooth muscle [37]. We designed the secondary ATP-responsive DENND1A system with aptamer sequence ssDNA as a crosslinking agent to modify the internal hydrogel of the sdTEVGs. Thirty days after implantation, the neurotransmitter ATP secreted by immigrated nerve fibers triggered hydrolysis of the inner hydrogel to release DENND1A. VMSCs were rebuilt, and the intimal hyperplasia of sdTEVGs in Group 5 was significantly reduced compared with that in the other groups. We speculated that the possible reason why nerve reconstruction promoted VSMC rebuilding of the sdTEVGs was that peripheral nerves and Schwann cells continued to secrete growth factors, such as PDGF, which activated signaling pathways, including Ras ERK, c-Src and rap-1-rac, and might promote the proliferation and migration of VSMCs or smooth muscle progenitor cells in vivo [38,39]. The formation of a neuroimmune homeostasis interface in the sdTEVGs in vivo is another possible reason [40]. This topic warrants further study. Ninety days after TEVG implantation, in contrast to sdTEVGs with normal blood flow velocity in Group 5, the intimal hyperplasia of the other groups was further aggravated, collagen secretion was further increased, and abnormal phenotypic transformation of VSMCs was detected. This result indicated that the on-demand programmable responsive release systems were beneficial for inducing nerve fiber reconstruction and enhancing the release of neural exosomes, leading to inhibition of the abnormal phenotypic transformation of VSMCs in the sdTEVGs.
In conclusion, this study indicates that, in diabetes, functional nerve reconstruction is beneficial to prevent intimal hyperplasia of small-diameter TEVGs, which lays a foundation for the development of TEVGs from structural bionics to functional bionics. Design of on-demand programmed responsive systems match such processes of nerve reconstruction and the release of neural exosomes effectively. It provides a new approach to overcome the intimal hyperplasia for other vascular implants. Meanwhile, there still need more work before the clinical application, cause we hadn't perform the large animal experiment, in which sdTEVGs occur thrombotic occlusion more easily compared to SD rats. In addition to normal VSMCs, we also found circulating monocytes also participated in intimal hyperplasia of sdTEVGs during the research, which could also transform to VSMCs phenotype by the mechanical stimulation in special inflammatory microenvironment. We will continue our efforts for the early complete solution on intima hyperplasia of vascular grafts.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Yanzhao Li: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing – original draft. Yeqin Wang: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing – original draft. Fangchao Xue: Methodology, Investigation, Software. Xuli Feng: Methodology. Zhaojing Ba: Investigation. Junjie Chen: Investigation. Zhenhua Zhou: Methodology. Yanhong Wang: Investigation. Ge Guan: Investigation. Guanyuan Yang: Investigation. Ziwei Xi: Writing – original draft. Hao Tian: Writing – original draft. Yong Liu: Investigation. Ju Tan: Validation. Gang Li: Validation. Xiewan Chen: Writing – original draft. Mingcan Yang: Investigation. Wen Chen: Methodology, Investigation. Chuhong Zhu: Supervision, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft. Wen Zeng: Supervision, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Xing Shen and Yaqing Tang in the Innovative Drug Research Center of Chongqing University and Jing Zhou in the Department of Physiology, Basic Medical College, Peking University, for their support with the work. Thank Zhang San from Shiyanjia Lab (www.shiyanjia.com) for the modulus analysis. This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Plan Young Scientists Program (No: 2017YFA0106000); The National Science Fund for Outstanding Young Scholars (No. 31822021); the National Science Foundation of China (No: 31771057); and The National Key Research and Development Plan (No: 2016YFC1101100).
Footnotes
Peer review under responsibility of KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.05.034.
Contributor Information
Wen Chen, Email: 1607283686@qq.com.
Chuhong Zhu, Email: zhuch99@tmmu.edu.cn.
Wen Zeng, Email: zengw0105@163.com.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
The following is the Supplementary data to this article:
References
- 1.L'Heureux N., Dusserre N., Marini A., Garrido S., de la Fuente L., McAllister T. Technology insight: the evolution of tissue-engineered vascular grafts--from research to clinical practice. Nat. Clin. Pract. Cardiovasc. Med. 2007;4(7):389–395. doi: 10.1038/ncpcardio0930. 2007-07-01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kirkton R.D., Santiago-Maysonet M., Lawson J.H., Tente W.E., Dahl S., Niklason L.E. Bioengineered human acellular vessels recellularize and evolve into living blood vessels after human implantation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019;(485):11. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aau6934. 2019-03-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Issa Bhaloo S., Wu Y., Le Bras A., Yu B., Gu W., Xie Y. Binding of dickkopf-3 to CXCR7 enhances vascular progenitor cell migration and degradable graft regeneration. Circ. Res. 2018;123(4):451–466. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.312945. 2018-08-03. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Isenberg B.C., Williams C., Tranquillo R.T. Small-diameter artificial arteries engineered in vitro. Circ. Res. 2006;98(1):25–35. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000196867.12470.84. 2006-01-06. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dhulekar J., Simionescu A. Challenges in vascular tissue engineering for diabetic patients. Acta Biomater. 2018;70:25–34. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.01.008. 2018-04-01. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Abi K.C., Travert F., Fetita S., Rouzet F., Porcher R., Riveline J.P. Fetal exposure to maternal type 1 diabetes is associated with renal dysfunction at adult age. DIABETES. 2010;59(10):2631–2636. doi: 10.2337/db10-0419. 2010-10-01. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kohen A.R., Laplante M.A., Le Quang K., Deshaies Y., Despres J.P., Larose E. The genetic and metabolic determinants of cardiovascular complications in type 2 diabetes: recent insights from animal models and clinical investigations. Can. J. Diabetes. 2013;37(5):351–358. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjd.2013.08.262. 2013-10-01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ardila D.C., Tamimi E., Danford F.L., Haskett D.G., Kellar R.S., Doetschman T. TGFbeta2 differentially modulates smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration in electrospun gelatin-fibrinogen constructs. Biomaterials. 2015;37:164–173. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.10.021. 2015-01-01. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ardila D.C., Tamimi E., Doetschman T., Wagner W.R., Vande G.J. Modulating smooth muscle cell response by the release of TGFbeta2 from tubular scaffolds for vascular tissue engineering. J CONTROL RELEASE. 2019;299:44–52. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.02.024. 2019-04-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Liu M., Gomez D. Smooth muscle cell phenotypic diversity. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019;39(9):1715–1723. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.312131. 2019-09-01. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Matsuyama A., Takatori S., Sone Y., Ochi E., Goda M., Zamami Y. Effect of nerve growth factor on innervation of perivascular nerves in neovasculatures of mouse cornea. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017;40(4):396–401. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b16-00583. 2017-01-20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Coote J.H. Landmarks in understanding the central nervous control of the cardiovascular system. Exp. Physiol. 2007;92(1):3–18. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2006.035378. 2007-01-01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sun Y., Yang Z., Zheng B., Zhang X.H., Zhang M.L., Zhao X.S. A novel regulatory mechanism of smooth muscle alpha-actin expression by NRG-1/circACTA2/miR-548f-5p Axis. Circ. Res. 2017;121(6):628–635. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.311441. 2017-09-01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kourembanas S. Exosomes: vehicles of intercellular signaling, biomarkers, and vectors of cell therapy. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2015;77:13–27. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021014-071641. 2015-01-20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Oh H.J., Shin Y., Chung S., Hwang D.W., Lee D.S. Convective exosome-tracing microfluidics for analysis of cell-non-autonomous neurogenesis. Biomaterials. 2017;112:82–94. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.10.006. 2017-01-01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jia L., Chopp M., Wang L., Lu X., Zhang Y., Szalad A. MiR-34a regulates axonal growth of dorsal root ganglia neurons by targeting FOXP2 and VAT1 in postnatal and adult mouse. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018;55(12):9089–9099. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1047-3. 2018-12-01. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Roy Chowdhury S.K., Smith D.R., Saleh A., Schapansky J., Marquez A., Gomes S. Impaired adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase signalling in dorsal root ganglia neurons is linked to mitochondrial dysfunction and peripheral neuropathy in diabetes. Brain. 2012;135(6):1751–1766. doi: 10.1093/brain/aws097. 2012-06-01. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Seiradake E., Jones E.Y., Klein R. Structural perspectives on axon guidance. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016;32:577–608. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-111315-125008. 2016-10-06. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Finney A.C., Orr A.W. Guidance molecules in vascular smooth muscle. Front. Physiol. 2018;9:1311. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01311. 2018-01-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Moore S.W., Biais N., Sheetz M.P. Traction on immobilized netrin-1 is sufficient to reorient axons. Science. 2009;325(5937):166. doi: 10.1126/science.1173851. 2009-07-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wilson B.D., Ii M., Park K.W., Suli A., Sorensen L.K., Larrieu-Lahargue F. Netrins promote developmental and therapeutic angiogenesis. Science. 2006;313(5787):640–644. doi: 10.1126/science.1124704. 2006-08-04. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chadt A., Immisch A., de Wendt C., Springer C., Zhou Z., Stermann T. Deletion of both Rab-GTPase-activating proteins TBC14KO and TBC1D4 in mice eliminates insulin- and AICAR-stimulated glucose transport. Diabetes. 2015;64:746–759. doi: 10.2337/db14-0368. DIABETES 2015 2015-04-01;64(4):1492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hsu C., Morohashi Y., Yoshimura S., Manrique-Hoyos N., Jung S., Lauterbach M.A. Regulation of exosome secretion by Rab35 and its GTPase-activating proteins TBC1D10A-C. J. Cell Biol. 2010;189(2):223–232. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200911018. 2010-04-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Allaire P.D., Marat A.L., Dall'Armi C., Di Paolo G., McPherson P.S., Ritter B. The Connecdenn DENN domain: a GEF for Rab35 mediating cargo-specific exit from early endosomes. Mol. Cell. 2010;37(3):370–382. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.12.037. 2010-02-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Rhee S.G. Overview on peroxiredoxin. MOL CELLS. 2016;39(1):1–5. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2016.2368. 2016-01-01. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wang G., Li Y., Wang Y., Dong Y., Wang F.S., Ding Y. Roles of the co-culture of human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells with rat pancreatic cells in the treatment of rats with diabetes mellitus. EXP THER MED. 2014;8(5):1389–1396. doi: 10.3892/etm.2014.1985. 2014-11-01. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sugiura T., Agarwal R., Tara S., Yi T., Lee Y.U., Breuer C.K. Tropoelastin inhibits intimal hyperplasia of mouse bioresorbable arterial vascular grafts. Acta Biomater. 2017;52:74–80. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.12.044. 2017-04-01. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Huang Q., Zhang J., Liang L., Lan Z., Huo T., Li S. The significance of neuregulin-1/ErbB expression in autogenous vein grafts in a diabetic rat model. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2015;66(3):300–306. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000279. 2015-09-01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Davies M.G., Dalen H., Kim J.H., Barber L., Svendsen E., Hagen P.O. The influence of the combined presence of diabetes mellitus and hypercholesterolaemia on the function and morphology of experimental vein grafts. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 1995;10(2):142–155. doi: 10.1016/s1078-5884(05)80105-4. 1995-08-01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lawson J.H., Glickman M.H., Ilzecki M., Jakimowicz T., Jaroszynski A., Peden E.K. Bioengineered human acellular vessels for dialysis access in patients with end-stage renal disease: two phase 2 single-arm trials. Lancet (N. Am. Ed.) 2016;387:2026–2034. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00557-2. 2016-05-14. 10032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.EL A.S., Mager I., Breakefield X.O., Wood M.J. Extracellular vesicles: biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013;12(5):347–357. doi: 10.1038/nrd3978. 2013-05-01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Colombo M., Raposo G., Thery C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014;30:255–289. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-101512-122326. 2014-01-20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Cao H., Hu X., Zhang Q., Wang J., Li J., Liu B. Upregulation of let-7a inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in vitro and in vein graft intimal hyperplasia in rats. J. Surg. Res. 2014;192(1):223–233. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2014.05.045. 2014-11-01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Dyson A., Dal-Pizzol F., Sabbatini G., Lach A.B., Galfo F., Dos S.C.J. Ammonium tetrathiomolybdate following ischemia/reperfusion injury: chemistry, pharmacology, and impact of a new class of sulfide donor in preclinical injury models. PLoS Med. 2017;14(7) doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002310. 2017-07-01, e1002310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Duan W.J., Li Y.F., Liu F.L., Deng J., Wu Y.P., Yuan W.L. A SIRT3/AMPK/autophagy network orchestrates the protective effects of trans-resveratrol in stressed peritoneal macrophages and RAW 264.7 macrophages. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016;95:230–242. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.03.022. 2016-06-01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Li Y., Wan S., Liu G., Cai W., Huo D., Li G. Netrin-1 promotes inflammation resolution to achieve endothelialization of small-diameter tissue engineering blood vessels by improving endothelial progenitor cells function in situ. Adv. Sci. 2017;4(12) doi: 10.1002/advs.201700278. 2017-12-01, 1700278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Burnstock G. Purinergic signaling in the cardiovascular system. Circ. Res. 2017;120(1):207–228. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.309726. 2017-01-06. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Yan J., Huang W., Zhao J., Fu H., Zhang G., Huang X. The platelet-derived growth factor receptor/STAT3 signaling pathway regulates the phenotypic transition of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle in rats. PloS One. 2017;12(2) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172191. 2017-02-28, e172191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mamer S.B., Chen S., Weddell J.C., Palasz A., Wittenkeller A., Kumar M. Discovery of high-affinity PDGF-VEGFR interactions: redefining RTK dynamics. SCI REP-UK. 2017;7(1) doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16610-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chavan S.S., Pavlov V.A., Tracey K.J. Mechanisms and therapeutic relevance of neuro-immune communication. Immunity. 2017;46(6):927–942. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.06.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.