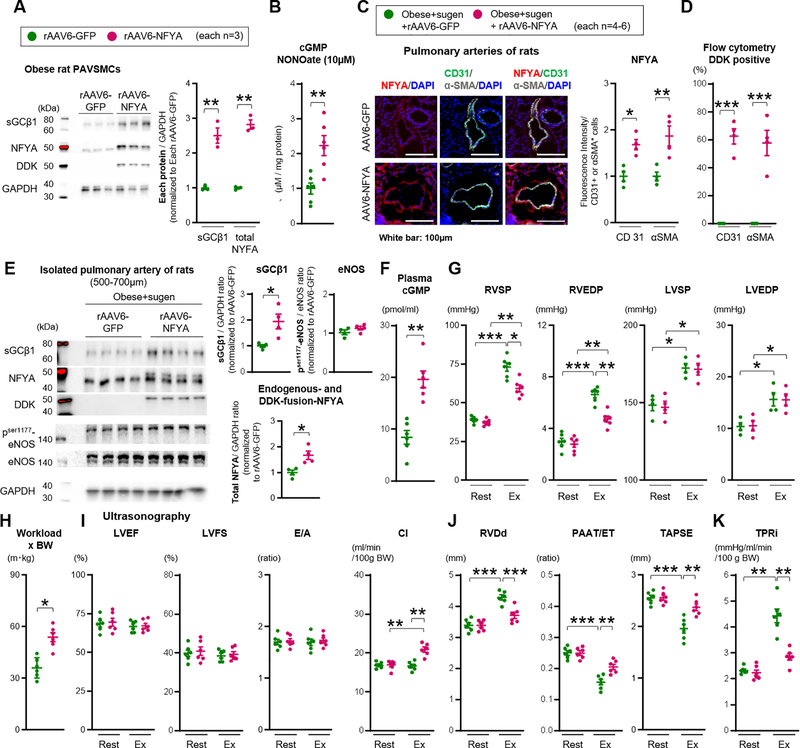
Figure 7. Forced sGC activity and NFYA expression rescue exercise induced pulmonary hypertension in CpcPH rats.
(A) Representative Western blot and quantification of sGCβ1, total NFYA (endogenous 44kDa and DDK-fusion 50kDa), DDK, and GAPDH in PAVSMCs infected with rAAV6-GFP or rAAV6-NFYA-DDK (each n=3). Each plot represents the PAVSMCs sample cultured from one individual rat. (B) cGMP level in PAVSMCs of obese treated with rAAV6-NFYA-DDK or rAAV6-GFP and NO donor DETA NONOate (10μM, 24 hours) (each n=6). (C) Administration of rAAV6-GFP or rAAV6-NFYA-DDK to obese+sugen rats. Representative immunofluorescence images and quantification of NFYA, CD31, αSMA, and DAPI of pulmonary arteries (each n=4). (D) Flow cytometry showing the percent of DDK in CD31 or αSMA positive cells (each n=4). (E) Representative Western blot and quantification of sGCβ1, total NFYA (endogenous 44kDa and DDK-fusion 50kDa), phosphorylation ser 177 eNOS, total eNOS and GAPDH in isolated pulmonary arteries of rats (diameter of PAs: 500–700μm) (each n=4). (F) Quantification of plasma levels of cGMP of the rats (each n=6). (G-H) Right ventricular systolic and end-diastolic pressure (RVSP and RVEDP, each n=6), left ventricular systolic and end-diastolic blood pressure (LVSP and LVEDP, each n=4), and Workload (each n=6) were measured at rest and during exercise (obese+sugen rats infected with rAAV6-GFP or rAAV6-NFYA-DDK). (I-K) Left ventricular Ejection fraction (LVEF), Fraction shortening (LVFS), E wave/A wave ratio (E/A), cardiac index (CI), RVDd, PAAT/ET, TAPSE, and TPRi were measured at rest and during exercise. Rats per group; obese+sugen rats infected with rAAV6-GFP or rAAV6-NFYA-DDK (each n=6). Results are expressed as mean±SEM. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. Statistical analyses were performed as described in Figure 1 legend.