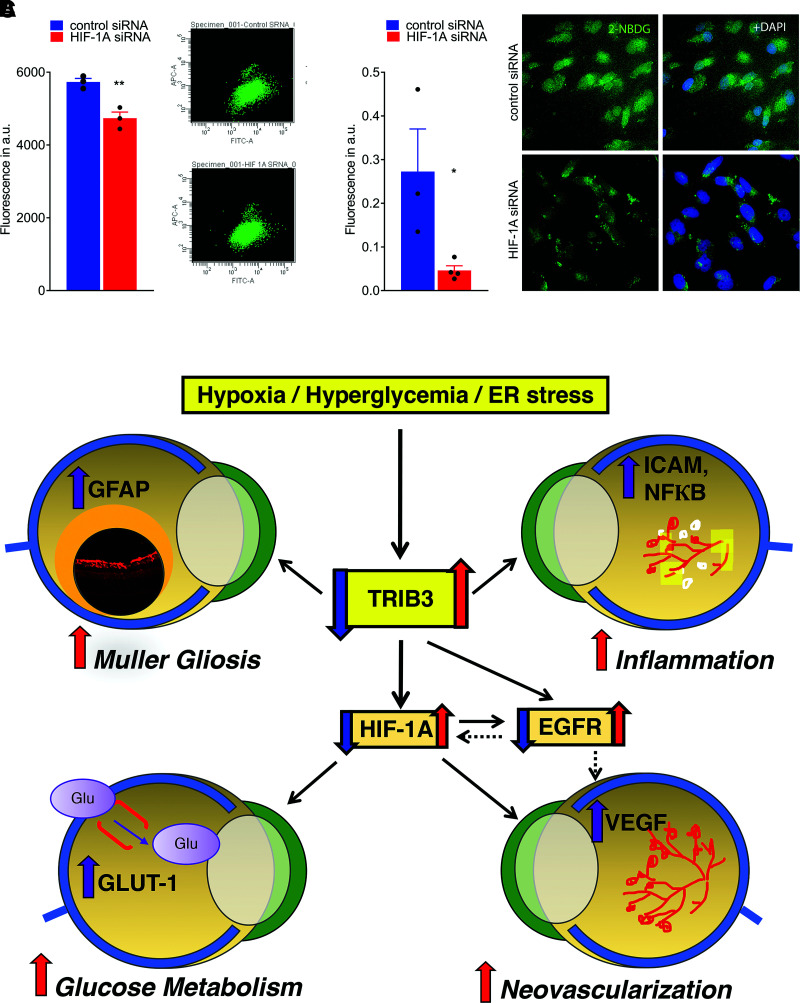
Figure 8.
Treatment of hypoxic Müller cells with siRNA targeting HIF1α results in reduction of GLUT1 and fluorescent signal from 2-NBDG cellular uptake. A: Reduction of fluorescent signal from 2-NBDG uptake measured by flow cytometry (n = 3). B: Reduction of fluorescent signal from 2-NBDG cellular uptake registered in fixed cultured MIO-M1 cells using microscopy (n = 3–4). The calculation of fluorescent signal was performed using ImageJ. C: Schematic presentation of the proposed molecular mechanism of DR controlled by TRIB3. Under hyperglycemic and hypoxic conditions, TRIB3 overexpression leads to upregulation of HIF1α, EGFR, and GFAP. HIF1α overexpression results in GLUT1 activation followed by an increase in retinal glucose flux, overall affecting retinal metabolism. Additionally, HIF1α mediates VEGF expression, which compromises vascular cell integrity and triggers angiogenesis. EGFR is upregulated as a result of TRIB3 upregulation as well. This protein reportedly induces VEGF and cytokines, leading to vascular dysfunction. TRIB3 promotes expression of GFAP and reactivation of gliosis in hypoxic retinas. Red and purple arrows indicate upregulation, and blue arrows indicate downregulation signaling validated in our study. Solid lines represent data of the current study. Dashed lines denote the regulation proposed in the literature. Data are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. a.u., arbitrary units; ER, endoplasmic reticulum.