Abstract
Somatostatin-expressing interneurons (SOM-INs) are a major subpopulation of GABAergic cells in CA1 hippocampus that receive excitation from pyramidal cells (PCs), and, in turn, provide feedback inhibition onto PC dendrites. Excitatory synapses onto SOM-INs show a Hebbian long-term potentiation (LTP) mediated by type 1a metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR1a) that is implicated in hippocampus-dependent learning. The neuropeptide somatostatin (SST) is also critical for hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity, as well as learning and memory. SST effects on hippocampal PCs are well documented, but its actions on inhibitory interneurons remain largely undetermined. In the present work, we investigate the involvement of SST in long-term potentiation of CA1 SOM-IN excitatory synapses using pharmacological approaches targeting the somatostatinergic system and whole cell recordings in slices from transgenic mice expressing eYFP in SOM-INs. We report that application of exogenous SST14 induces long-term potentiation of excitatory postsynaptic potentials in SOM-INs via somatostatin type 1–5 receptors (SST1-5Rs) but does not affect synapses of PC or parvalbumin-expressing interneurons. Hebbian LTP in SOM-INs was prevented by inhibition of SSTRs and by depletion of SST by cysteamine treatment, suggesting a critical role of endogenous SST in LTP. LTP of SOM-IN excitatory synapses induced by SST14 was independent of NMDAR and mGluR1a, activity-dependent, and prevented by blocking GABAA receptor function. Our results indicate that endogenous SST may contribute to Hebbian LTP at excitatory synapses of SOM-INs by controlling GABAA inhibition, uncovering a novel role for SST in regulating long-term synaptic plasticity in somatostatinergic cells that may be important for hippocampus-dependent memory processes.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s13041-021-00830-6.
Keywords: GABA interneurons, Somatotropin-release inhibitory factor—SRIF, Whole cell recordings, Cysteamine, SST1-5 receptors, Disinhibition, GABAA inhibition, Hebbian LTP
Introduction
Hippocampal GABAergic interneurons are highly heterogenous with different types distinguished according to their morphology, connectivity, physiologic characteristics, and molecular makers [1]. Somatostatin-expressing interneurons (SOM-INs) are a major subpopulation of GABAergic cells [2]. Characteristically, CA1 SOM-INs receive a major excitation from local pyramidal cells (PCs), and, in turn, provide feedback inhibition onto dendrites of PCs [3]. SOM-INs are comprised of distinct subtypes, including the Oriens-Lacunosum/Moleculare (O-LM) cells, bistratified cells, and also projection cells with additional subicular, retro-hippocampal or septal projections [3, 4]. SOM-INs regulate PC synaptic integration [5], action potential rate and burst firing [6] as well as synaptic plasticity [7–9], and play a critical role in contextual fear learning [10, 11].
A notable feature of CA1 SOM-INs is the long-term plasticity occurring at their excitatory synapses. These synapses show a Hebbian long-term potentiation (LTP) mediated by type 1a metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR1a) [8, 12, 13]. Excitatory synapses onto parvalbumin-expressing interneurons (PV-INs) do not display this form of long-term plasticity [8]. In addition, SOM-INs excitatory synapses show a late form of mGluR1a-dependent LTP, that can last from a few to 24 h and involves mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) mediated translation [9, 14, 15]. Interestingly, cell-specific conditional down-regulation of mTORC1 in SOM-INs impairs late mGluR1a-dependent LTP, as well as contextual fear and spatial memory consolidation [9]. Conversely, conditional up-regulation of mTORC1 activity in SOM-INs facilitates late mGluR1a-dependent LTP, as well as hippocampal-dependent memory [9]. Contextual fear learning induces mGluR1a- and mTORC1-dependent LTP at SOM-IN excitatory synapses, suggesting a critical implication of SOM-IN long-term synaptic plasticity in hippocampal learning and memory [9]. More recently, cell-specific conditional knock-in of the non-phosphorylatable translation initiation factor eIF2α (eIF2αS51A) in SOM interneurons was found to upregulate general mRNA translation in these cells and be sufficient to gate CA1 network plasticity and increase long-term contextual fear memory, further supporting a critical role of SOM-INs in hippocampal long-term memory consolidation [11].
Somatostatin (SST; also known as somatotropin-release inhibitory factor, SRIF) is a peptide expressed in central nervous system. It was first discovered in the hypothalamus where it exerts an inhibitory action on growth hormone [16]. SST is implicated in multiple brain functions like olfaction, vision, cognition and locomotion, as well as in pathologies such as Alzheimer’s disease, schizophrenia and major chronic depression [17]. SST acts via five metabotropic receptors (SST1R to SST5R) that are coupled to G proteins and target many effectors [18]. SSTRs have a wide distribution in brain with overlapping regional localization of receptor types [19]. In the hippocampus, mRNA for all five SSTRs is present, although expression is weaker for SST5R [20, 21]. Subcellular localization of SSTRs is highly specific to the receptor type. SST1R is targeted pre-synaptically to axons, while SST2,4,5R are mostly distributed post-synaptically to neuronal somata and dendrites, and SST3R appears excluded from classic pre- and post-synaptic sites [19]. Consistent with the subcellular localization of its receptors, SST modulates neuronal activity via both pre- and post-synaptic mechanisms [17, 18]. In the hippocampus, exogenous SST14 hyperpolarizes PCs by activation of two distinct K+ currents (M-current and voltage-insensitive leak current) [22–24]. SST14 also induces a presynaptic inhibition of excitatory synaptic transmission in hippocampal PCs [25]. The presynaptic inhibition may involve a G-protein mediated inhibition of N-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channels [26, 27] and activation of presynaptic K+ channels [25]. Although SST14 presynaptic inhibition of hippocampal excitatory synaptic transmission is well documented, presynaptic inhibition of GABAergic inhibitory synaptic transmission has also been reported [28] as in other brain regions [29].
SST is critical for hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity, as well as learning and memory. Depletion of SST by cysteamine treatment, or knock-out of the SST gene in transgenic mice, impairs contextual fear memory but not auditory fear learning [30]. The memory impairment is associated with a decrease in LTP in CA1 PCs [30]. Interestingly, blocking LTP at excitatory synapses of SOM-INs was found to impair contextual fear memory and facilitation of LTP in PCs by SOM-INs [9]. The analogous effects of manipulating SST or SOM-IN synaptic plasticity on contextual fear memory and PC synaptic plasticity, suggest a possible link between SST and long-term plasticity at SOM-IN excitatory synapses.
Here, we investigate the involvement of SST in long-term potentiation of CA1 SOM-IN excitatory synapses using pharmacological approaches targeting the somatostatinergic system and whole cell recordings in slices from transgenic mice expressing eYFP in SOM-INs. We report that application of exogenous SST14 induces long-term potentiation of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) of SOM-INs via SST1-5Rs, but not of PC and PV-IN synapses. Also, Hebbian LTP in SOM-INs was prevented by inhibition of SSTRs and depletion of SST by cysteamine treatment, suggesting a critical role of endogenous SST in LTP. LTP of SOM-IN synapses induced by SST14 was independent of NMDAR and mGluR1a, activity-dependent, and prevented by blocking GABAA receptor function. Our results indicate that endogenous SST may contribute to Hebbian LTP at excitatory synapses of SOM-INs by controlling GABAA inhibition, uncovering a novel role for SST in regulating long-term synaptic plasticity in somatostatinergic cells that may be important for hippocampus-dependent memory processes.
Results
The excitatory synapses onto CA1 SOM-INs show long-term plasticity [8, 9]. Here we investigate if the peptide SST14, that is expressed specifically in SOM-INs, is involved in long-term plasticity of their excitatory synapses, using whole cell recordings in acute slices from SOM-eYFP mice (Sstires−Cre;Rosa26lsl−EYFP) that express eYFP in SOM-INs (Fig. 1a). Statistical results are summarized in the supplemental statistical table (Additional file 1).
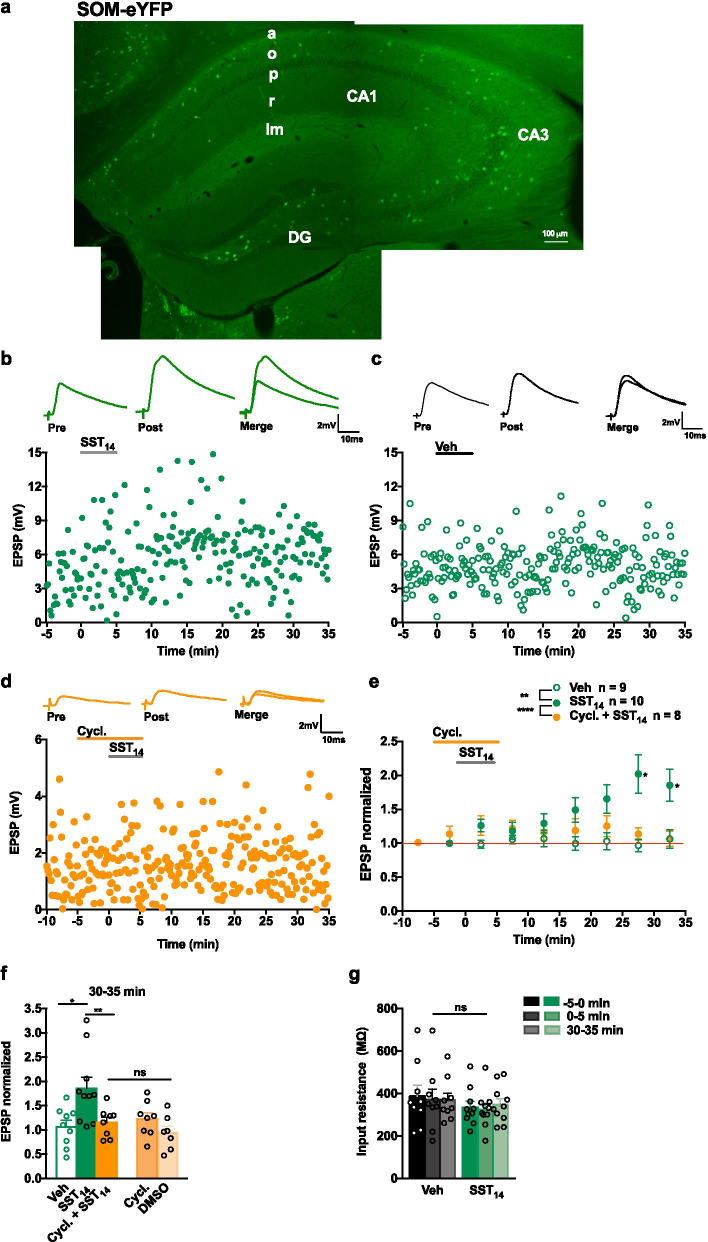
Fig. 1.
SST14 induces a long-term potentiation of EPSPs in SOM-INs via SSTRs. a Fluorescence images showing eYFP expression in SOM-INs in hippocampus of SOM-eYFP mouse. b–d Current clamp recording of EPSPs (top) and time plots of EPSP amplitude from representative cells receiving 5 µM SST14 (b), vehicle (c) or SST14 in the presence of 1 µM of the SST1-5R antagonist cyclosomatostatin (cycl. + SST14) (d). EPSPs are average for − 5 to 0 min baseline (pre) and 30 to 35 min after application (post). e Summary time plots of EPSPs (normalized to baseline), showing potentiation of EPSPs after SST14 application (filled green circle), prevented by co-application of the SST1-5R antagonist cyclosomatostatin (filled orange square), and lack of effect of vehicle application (open green circle). For SST14 group, n = 10 cells and 9 mice, rmANOVA, Dunnett’s multiple comparisons (25–30 min p = 0.025, 30–35 min p = 0.023). For vehicle group, n = 9 cells and 6 mice, rmANOVA p = 0.864. For cyclostomatostatin + SST14 group, n = 8 cells and 5 mice, rmANOVA p = 0.382. f Summary bar graph of EPSP amplitude at 30–35 min after application, showing long-term potentiation after SST14, and no effect after either SST14 with SST1-5R antagonist, vehicle, cyclosomatostatin alone, or DMSO (vehicle for cyclosomatostatin) (Veh vs SST14 group, two-way mixed ANOVA, univariate analysis at 30–35 min p = 0.010; SST14 vs Cycl. + SST14 group, two-way mixed ANOVA, univariate analysis at 30–35 min p = 0.002; Cycl. + SST14 vs Cycl. and vs DMSO group, two-way mixed ANOVA p = 0.602). g Summary bar graph showing no change in cell input resistance before (− 5–0 min), during (0–5 min) and after (30–35 min) vehicle or SST14 application. Two-way mixed ANOVA, p = 0.554. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ns not significant
SST14 induces LTP via SSTRs
We examined with current clamp recordings the effects of application of exogenous SST14 on EPSPs evoked in eYFP-expressing SOM-INs in CA1 stratum oriens. Bath application of 5 µM SST14 for 5 min induced a gradual slow onset potentiation of EPSP amplitude that developed over 10–35 min after SST14 application (201.9 ± 28.1% of control at 25–30 min; 185.4 ± 23.4% of control at 30–35 min; Fig. 1b, e, f). Similar vehicle application did not induce change in EPSPs over the same time period, ruling out non-specific effects due to recording conditions (96.8 ± 9.4% of control at 25–30 min; 106.1 ± 13.4% of control at 30–35 min; Fig. 1c, e, f). These results indicate that exogenous SST14 induces long-term potentiation of EPSPs in SOM-INs.
We verified that the effects of SST14 were mediated by SSTRs using the non-selective SST1-5R antagonist cyclosomatostatin [31]. Co-application of 1 µM cyclosomatostatin with SST14 blocked the long-lasting increase in EPSP amplitude induced by SST14 (113.4 ± 9.4% of control at 25–30 min; 106.8 ± 11.4% of control at 30–35 min; Fig. 1d–f). These results indicate that the potentiation induced by exogenous SST14 is mediated by SST1-5Rs, thus ruling out non-specific drug effects of SST14. Interestingly, bath application of cyclosomatostatin alone, or its vehicle DMSO, did not affect EPSPs (122.7 ± 12.8% and 94.0 ± 13.4% of control at 30–35 min, respectively; Fig. 1f), suggesting the absence of endogenous activation of SST1-5Rs and modulation of EPSPs during low frequency stimulation alone.
Bath application of SST14 affected EPSPs but had no effect on cell input resistance in the same cells. Cell input resistance was unchanged during and after SST14 or vehicle application (96.1 ± 13.3% of control during and 95.3 ± 9.1% of control at 30–35 min after SST14; 97.1 ± 8.5% of control during and 103.8 ± 8.0% of control at 30–35 min after vehicle; Fig. 1g). Thus, SST14 effects on EPSPs may not involve postsynaptic changes in cell input resistance.
SST1-5R antagonist or cysteamine treatment prevent Hebbian LTP
Excitatory synapses onto CA1 SOM-INs show a mGluR1a-dependent Hebbian LTP [8, 12]. Since SST14 induces LTP of EPSPs in SOM-INs via SSTRs, next we examined if endogenous SST could be involved in Hebbian LTP.
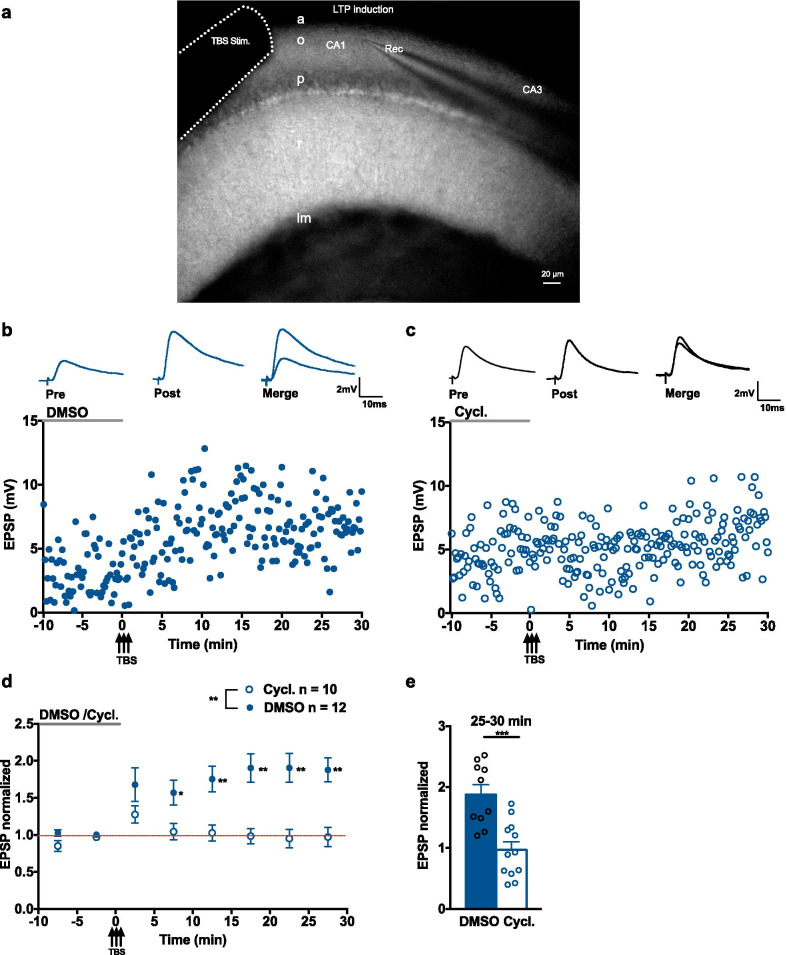
We used whole cell current clamp recordings to monitor Hebbian LTP elicited in SOM-INs by theta burst stimulation (TBS), and bath application of the SST1-5R antagonist cyclosomatostatin to test for a possible role of SST (Fig. 2). Cyclosomatostatin or its vehicle (DMSO) were applied 10 min prior to and during TBS, and then washed out (Fig. 2b–d). In the presence of DMSO, TBS induced a slow onset LTP of EPSP amplitude (157.0 ± 16.7% of control at 5–10 min; 175.3 ± 17.2% of control at 10–15 min; 190.3 ± 19.2% of control at 15–20 min; 190.4 ± 19.4% of control at 20–25 min; 187.7 ± 16.2% of control at 25–30 min; Fig. 2d, e). However, in the presence of 1 µM cyclosomatostatin, a concentration that prevents SST14 potentiation of EPSPs, TBS failed to induce LTP of EPSP amplitude (97.1 ± 13.1% of control at 25–30 min; Fig. 2d, e). These results suggest that endogenous SST may be released and activate SSTRs in Hebbian LTP induced by TBS in SOM-INs.
Fig. 2.
SST1-5R antagonist cyclosomatostatin prevents Hebbian LTP. a Image showing microelectrodes configuration for stimulation and recording during TBS-induced LTP experiments. b, c Current clamp recording of EPSPs (top) and time plots of EPSP amplitude from representative cells receiving TBS in the presence of DMSO (0.01%) (b) or the SST1-5R antagonist cyclosomatostatin (1 µM) (c). d Summary time plots of EPSPs (normalized to baseline), showing that TBS in the presence of DMSO induces LTP of EPSPs (filled blue circle), but TBS in the presence of cyclosomatostatin does not (open blue circle). For DMSO group, n = 10 cells and 6 mice, rmANOVA, Dunnett’s multiple comparisons (5–10 min p = 0.040, 10–15 min p = 0.009, 15–20 min p = 0.006, 20–25 min p = 0.006, 25–30 min p = 0.002). For cyclosomatostatin group, n = 12 cells and 6 mice, rmANOVA, p = 0.124. e Summary bar graph of EPSP amplitude at 25–30 min after TBS showing LTP in DMSO but not in cyclosomatostatin. Two-way mixed ANOVA with univariate analysis of variance, 25–30 min p = 0.0003. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ns not significant
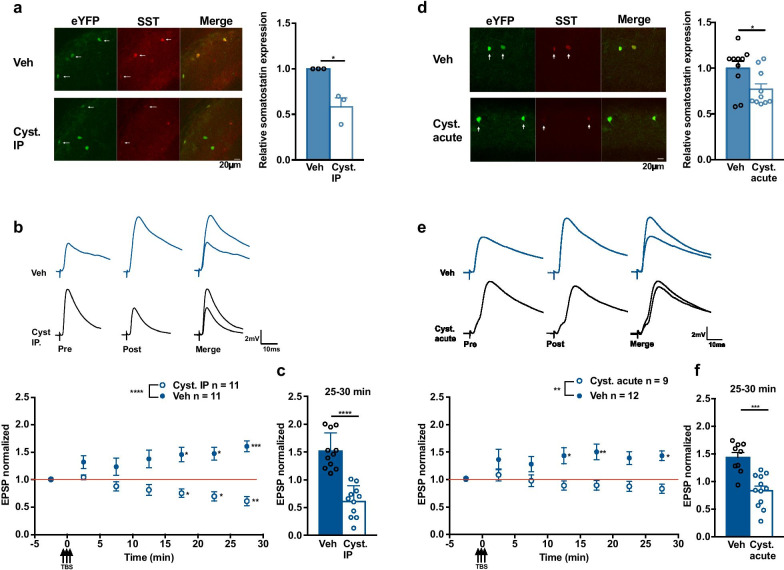
To investigate the implication of endogenous SST in Hebbian LTP by a different approach, we used cysteamine, a compound that depletes SST levels in brain and other tissues [32, 33]. Mice received an intraperitoneal (IP) injection of cysteamine (150 mg/kg) and hippocampal slices were harvested 4 h later. The effect of cysteamine injection on SST levels in hippocampus was verified with immunofluorescence. SST immunofluorescence in CA1 SOM-INs expressing eYFP was decreased in cysteamine injected mice relative to vehicle injected mice (58.3 ± 9.7% of control; Fig. 3a), suggesting an effective lowering of SST levels in SOM-INs. Next, we examined Hebbian LTP in SOM-INs in slices of mice after vehicle or cysteamine IP injection. In vehicle injected mice, TBS elicited long-term potentiation of EPSP amplitude (145.8 ± 12.9% of control at 15–20 min, 147.5 ± 11.8% of control at 20–25 min and 160.7 ± 9.6% of control at 25–30 min) (Fig. 3b, c). In cysteamine injected mice, TBS failed to induce LTP of EPSP amplitude, but instead a slow onset depression of EPSPs was elicited (75.3 ± 7.7% of control at 15–20 min, 69.6 ± 8.7% at 20–25 min and 60.1 ± 8.5% of control at 25–30 min; Fig. 3b, c). Thus, lowering SST levels in SOM-INs by cysteamine IP injection, prevents Hebbian LTP induced by TBS.
Fig. 3.
Cysteamine treatment lowers SST levels and prevents Hebbian LTP. a Representative images (left) and summary bar graph (right) showing reduction of SST immunofluorescence in eYFP-expressing SOM-INs after cysteamine injection (vehicle n = 3 mice, cysteamine n = 3 mice, unpaired t-test p = 0.047). b EPSPs from representative cells (top) and summary time plots of EPSPs (bottom), showing LTP induced by TBS in vehicle injected mice (filled blue square), and absence of LTP (but EPSP depression) in cysteamine injected mice (open blue circle). For vehicle group, n = 11 cells and 8 mice, rmANOVA, Dunnett’s multiple comparisons (15–20 min p = 0.028, 20–25 min p = 0.016, 25–30 min p = 0.0007). For cysteamine group, n = 11 cells and 6 mice, rmANOVA, Dunnett’s multiple comparisons (15–20 min p = 0.040, 20–25 min p = 0.026, 25–30 min p = 0.005). c Summary bar graph, showing absence of LTP at 25–30 min after TBS in cysteamine injected mice (two-way mixed ANOVA with univariate analysis of variance, p < 0.0001). d–f Similar data presentation showing effects of incubation for one hour of slices with cysteamine. (d) Cysteamine treatment reduces SST immunofluorescence in SOM-INs (vehicle n = 4 mice, cysteamine n = 4 mice, unpaired t-test p = 0.029). (e) Cysteamine treatment prevents TBS induction of LTP. For vehicle group, n = 9 cells and 7 mice, rmANOVA, Dunnett’s multiple comparisons (10–15 min p = 0.027, 15–20 min p = 0.008, 25–30 min p = 0.027). For cysteamine group, n = 12 cells and 7 mice, rmANOVA p = 0.097. (f) Summary bar graph showing absence of LTP after cysteamine treatment (two-way mixed ANOVA with univariate analysis of variance, 25–30 min p = 0.0001). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001; ns not significant
To rule out extra-hippocampal effects of cysteamine IP injection, hippocampal slices from untreated mice were incubated in ACSF containing 200 µM cysteamine for 1 h. In cysteamine-treated slices, SST immunofluorescence was decreased in CA1 SOM-INs compared to vehicle-treated slices (76.9 ± 6.1% of control; Fig. 3d). Whole cell recordings showed that TBS failed to induce LTP of EPSP amplitude in SOM-INs of cysteamine-treated slices (89.2 ± 8.4% of control at 10–15 min, 89.4 ± 9.0% at 15–20 min and 83.3 ± 8.5% of control at 25–30 min). In contrast, TBS elicited LTP in SOM-INs of vehicle-treated slices (143.3 ± 14.8% of control at 10–15 min, 150.3 ± 14.0% of control at 15–20 min and 143.3 ± 9.1% of control at 25–30 min; Fig. 3e, f). Thus, lowering hippocampal SST levels interferes with Hebbian LTP induced by TBS in SOM-INs.
Taken together, the results of these experiments with cyclostomatostatine and cysteamine suggest that TBS may lead to the release of endogenous SST and the activation SSTRs in Hebbian LTP in SOM-INs.
SST14 induced potentiation is independent of NMDAR and mGluR1a
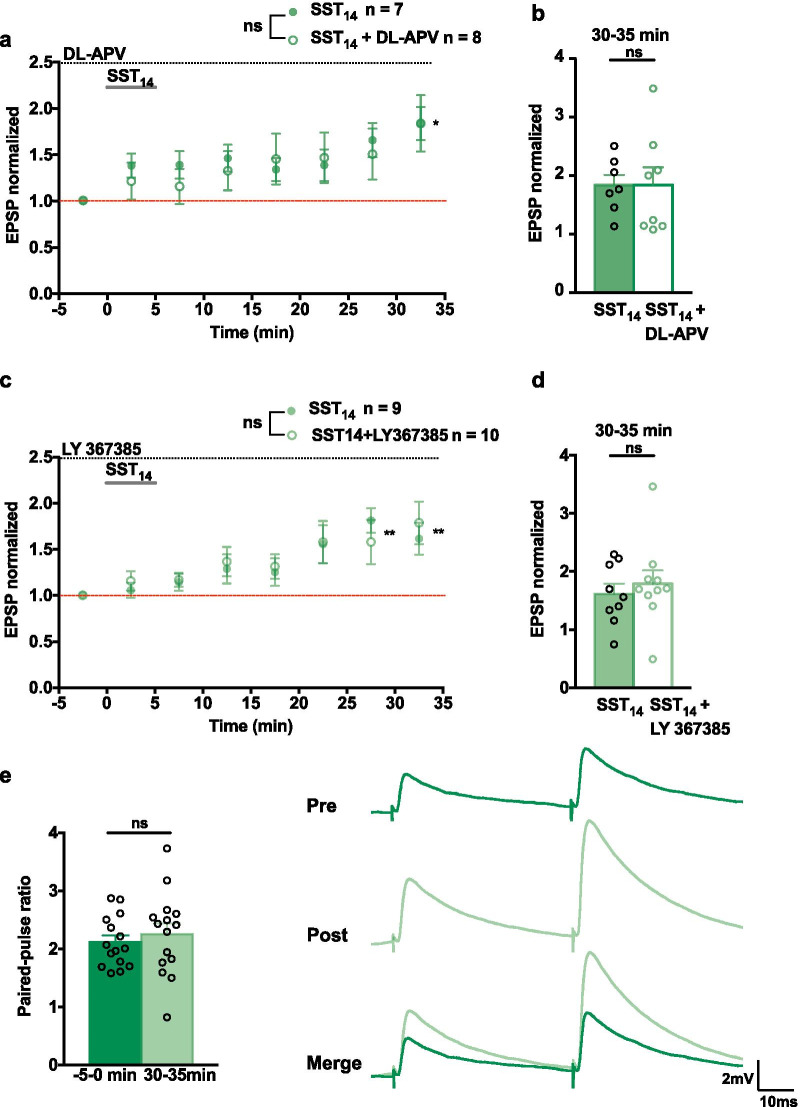
NMDA receptors (NMDAR) and metabotropic glutamate 1a receptors (mGluR1a) are involved in synaptic plasticity in hippocampal interneurons [12, 34]. We examined a possible implication of these receptors in SST14-induced LTP in SOM-INs. First, we examined if NMDARs were implicated by including the antagonist DL-APV (50 µM) in the ACSF for the duration of the experiment. Bath application of SST14 in presence of DL-APV, induced a gradual LTP of EPSPs (183.9 ± 30.5% of control at 30–35 min) that was similar to the LTP elicited by SST14 without DL-APV (183.8 ± 17.8% of control at 30–35 min) (Fig. 4a, b). Thus, SST14-induced LTP does not require NMDARs.
Fig. 4.
LTP induced by SST14 does not require NMDAR or mGluR1a. a Summary time plots of EPSP amplitude for experiments with application of SST14 in the presence (open green circle) and absence (filled green circle) of the NMDAR antagonist DL-APV (50 µM), indicating a similar slow onset LTP in both groups (SST14, n = 7 cells, 5 mice; SST14 + DL-APV, n = 8 cells, 6 mice; two-way mixed ANOVA p = 0.781, main effect of time p < 0.0001 with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons at 30–35 min p = 0.016). b Summary bar graph of EPSP amplitude, showing similar LTP at 30–35 min post application. c Summary time plots of EPSP amplitude for experiments with application of SST14 in the presence (open green circle) and absence (filled green circle) of the mGluR1a antagonist LY367385 (40 µM), showing similar LTP in both groups (SST14, n = 9 cells, 7 mice; SST14 + LY367385, n = 10 cells, 7 mice; two-way mixed ANOVA p = 0.613, main effect of time p < 0.0001 with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons at 25–30 min p = 0.004, 30–35 min p = 0.005). d Summary bar graph of EPSP amplitude indicating similar LTP at 30–35 min post application. e EPSPs from a representative cell receiving paired-pulse stimulation before and after SST14 application (right) and summary bar graph (left) showing similar paired-pulse ratio before (− 5 to 0 min) and after (30–35 min) SST14 application (n = 16 cells from SST14 groups in (a) and (c); paired t-test p = 0.531). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ns not significant
Similarly, we examined the possible role of mGluR1a by including the antagonist LY367385 (40 µM) in the ACSF. Application of SST14 in the presence of LY367385 elicited LTP of EPSPs (178.8 ± 23.1% of control at 30–35 min) that was not different from the LTP induced by SST14 in the absence of LY367385 (161.5 ± 17.4% of control at 30-35 min) (Fig. 4c, d). In both groups, LTP developed gradually (EPSP amplitude 169.7 ± 3.3% of control at 25–30 min and 170.1 ± 3.4% of control at 30–35 min). Therefore, SST14-induced LTP does not involve mGluR1a.
In the above series of experiments with DL-APV and LY367385, we used paired stimulation to measure the paired-pulse ratio of EPSPs in cells that received SST14 in the absence of antagonists. Paired-pulse facilitation was similar before (-5 to 0 min; 2.116 ± 0.113) and after (30 to 35 min; 2.254 ± 0.184) SST14 application (Fig. 4e). These results suggest an absence of presynaptic changes during SST14-induced LTP.
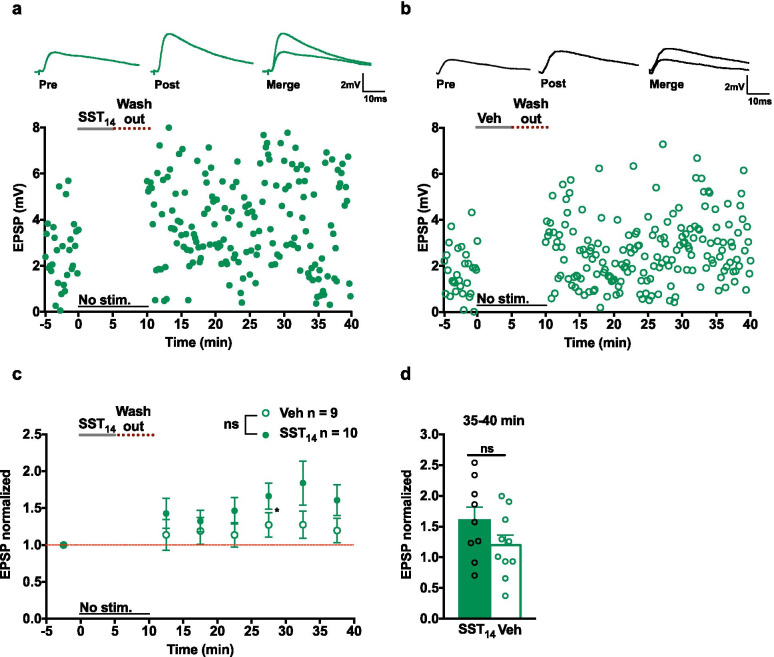
To shed further light on the mechanisms involved in the SST14-induced LTP, we examined if LTP is dependent on synaptic activity during SST14 application. EPSPs were recorded during a 5 min baseline period and stimulation was interrupted. SST14 was applied for 5 min and washed-out for another 5 min, without stimulation. Stimulation was resumed and EPSPs recorded for 30 min (Fig. 5a–c). Application of vehicle (127.2 ± 16.7% of control at 25–30 min) or SST14 (166.2 ± 17.8% of control at 25-30 min) produced similar effects with only a transient potentiation of EPSP amplitude (Fig. 5c). EPSP amplitude was not different at 35–40 min after application of vehicle (119.7 ± 16.6% of control) or SST14 (160.6 ± 21.1% of control) (Fig. 5c, d). These results suggest that, although interruption of stimulation induces a rebound potentiation in both groups, SST14-induced LTP of EPSPs may require synaptic stimulation in the presence of the peptide.
Fig. 5.
LTP of EPSPs is dependent on synaptic stimulation in the presence of SST14. a, b Examples of EPSPs (top) and summary time plots from representative cells receiving no synaptic stimulation during the 5 min SST14 (a) or vehicle (b) application and a 5 min wash-out. c Summary time plots of EPSPs for all cells showing a rebound potentiation of EPSP amplitude in both groups (Vehicle, n = 10 cells and 6 mice; SST14, n = 9 cells and 7 mice; two-way mixed ANOVA p = 0.258; main effect of time p = 0.004 with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons 25–30 min p = 0.029). d Summary bar graph showing no difference in EPSP amplitude at 35–40 min after SST14 or vehicle application. *p < 0.05; ns: not significant
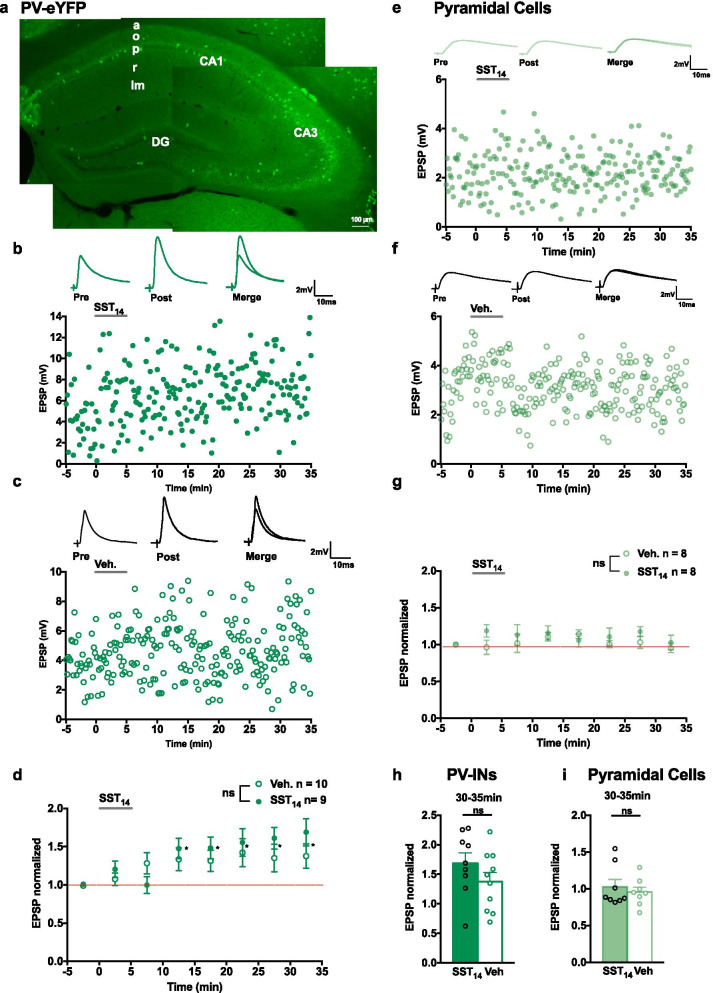
The mGluR1a-dependent Hebbian LTP found at excitatory synapses onto SOM-INs is not observed at synapses onto PV-INs [8]. Therefore, we examined if application of SST14 affects EPSPs of PV-INs using a similar recording paradigm from PV-INs of PV-eYFP mice (Fig. 6a). After bath application of vehicle or SST14, EPSP amplitude increased similarly in both groups (140.4 ± 10.0% of control at 10–15 min; 139.9 ± 9.8% of control at 15–20 min; 148.8 ± 12.5% of control at 20–25 min; 148.1 ± 11.7% of control at 25–30 min; 153.2 ± 12.1% of control at 30-35 min; Fig. 6b–d). These results suggest that, under our recording conditions, EPSPs of PV-INs show spontaneous run-up over time. Moreover, application of SST14 produced similar results as vehicle (Fig. 6h), suggesting that SST14-induced potentiation may not occur at excitatory synapses onto PV-INs.
Fig. 6.
SST14 does not affect EPSPs in PV-INs or PCs. a Montage of fluorescence images showing eYFP expression in hippocampal PV-INs from PV-eYFP mouse. b, c Examples of EPSPs (top) and time plots of EPSP amplitude (bottom) from representative PV-INs receiving 5 µM SST14 (b) or vehicle (c). d Summary time plots of EPSPs (normalized to baseline) for all cells, showing that with application of either SST14 (filled green circle) or vehicle (open green circle), EPSPs showed a gradual run-up with no difference between vehicle and SST14 (Vehicle, n = 10 cells and 6 mice; SST14, n = 9 cells and 6 mice; two-way mixed ANOVA p = 0.141, main effect of time p = 0.0001 with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons at 10–15 min p = 0.029, 15–20 min p = 0.027, 20–25 min p = 0.042, 25–30 min p = 0.021, 30–35 min p = 0.010). e–g Similar data presentation showing lack of effect of SST14 on EPSPs recorded in CA1 PCs. Examples of EPSPs (top) and time plots of EPSP amplitude (bottom) from representative cells receiving SST14 (e) or vehicle (f). Summary time plots of EPSPs for all cells (g), showing that SST14 (filled green square) or vehicle (open green circle) did not affect EPSPs in PCs. Two-way mixed ANOVA p = 0.506. h, i Bar graphs of EPSP amplitude in PV-INs (h) and PCs (i) at 30–35 min after SST14 or vehicle application showing no difference. *p < 0.05; ns not significant
Excitatory synapses onto SOM-INs originate mostly from CA1 pyramidal cells (PCs). The actions of SST14 on CA1 PCs are complex and both inhibitory and excitatory effects of SST14 have been reported [22, 28, 35]. As SST14 effects on SOM-IN EPSPs could arise from indirect effects on PCs, we examined if SST14 affects EPSPs in PCs. EPSPs were recorded from CA1 PCs in slices from SOM-eYFP mice and SST14 was applied under similar conditions. Application of either SST14 or vehicle did not affect EPSP amplitude in PCs (SST14 group, 102.8 ± 10.0% of control at 30–35 min; vehicle group, 95.6 ± 6.6% of control at 30–35 min; Fig. 6e–g, i), indicating a lack of SST14 effect on PC EPSPs. These results suggest that SST14-induced LTP of EPSPs in SOM-INs may not arise from a di-synaptic effect via CA1 PC excitatory synapses.
SST actions on SOM-IN excitatory synapses mediated by GABAA inhibition
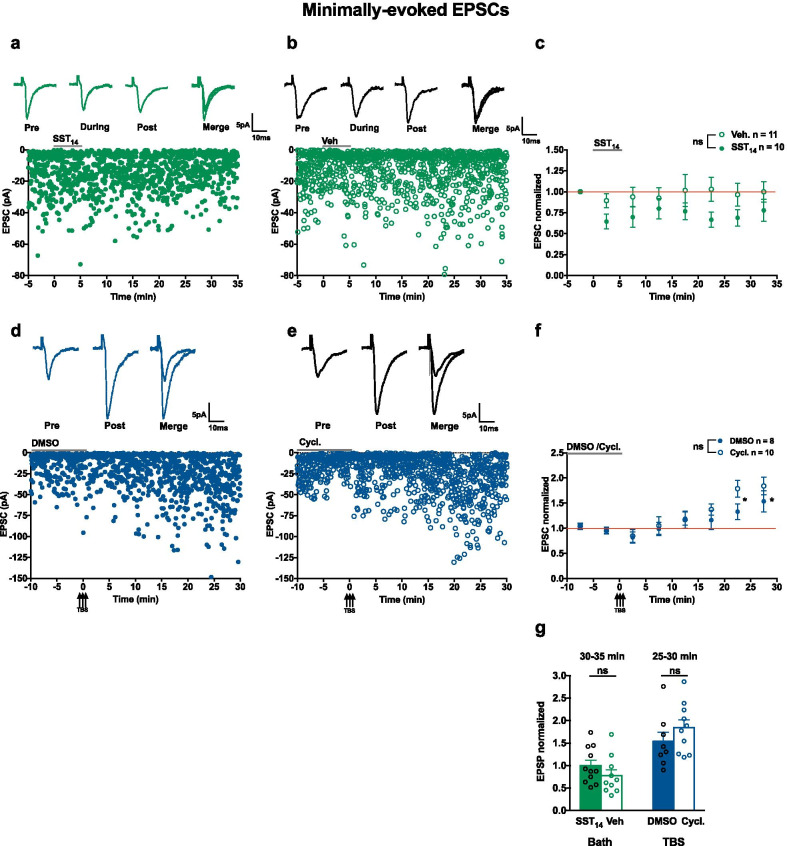
To gain more insight on the mechanisms of SST14-induced LTP, we investigated the effects of SST14 on putative single fiber excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) evoked by minimal stimulation [12, 36]. Non-NMDAR-mediated EPSCs were recorded in whole cell voltage clamp mode from SOM-INs in the presence of NMDA and GABAA receptor antagonists, DL-APV and gabazine respectively (Fig. 7a–c). EPSC amplitude was not affected by bath application of 5 µM SST14 (77.8 ± 13.3% of control at 30–35 min) or vehicle (99.9 ± 40.3% of control at 30-35 min) (Fig. 7c–g), suggesting a lack of lasting effect of SST14 on excitatory postsynaptic currents in these conditions.
Fig. 7.
SST14 and cyclosomatostatin fail to affect pharmacologically isolated non-NMDAR-mediated EPSCs. a, b Voltage clamp recording of EPSCs (top) and time plots of EPSC amplitude from representative SOM-INs receiving 5 µM SST14 (a) or vehicle (b). EPSCs shown are average for -5 to 0 min baseline period (pre) and 30 to 35 min post-application period (post). c Summary time plots of EPSCs (normalized to baseline), showing lack of lasting effects on EPSC amplitude after SST14 application (filled green circle) or vehicle application (open green circle) (vehicle, n = 11 cells and 7 mice; SST14, n = 10 cells and 6 mice; two-way mixed ANOVA p = 0.485). d, e EPSCs (top) and time plots of EPSC amplitude from representative SOM-INs receiving TBS in the presence of DMSO (d) or 1 µM cyclosomatostatin (e). EPSCs shown are average for − 10 to 0 min baseline period (pre) and 25 to 30 min post-TBS period (post). f Summary time plots of EPSCs (normalized to baseline), showing similar LTP of EPSC amplitude induced by TBS in DMSO (filled blue circle) and cyclosomatostatin (open blue circle). For DMSO group, n = 9 cells and 7 mice, Two-way mixed ANOVA p = 0.402, main effect of time p < 0.0001 with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons at 20–25 min p = 0.019, 25–30 min p = 0.017). g Summary bar graph showing no difference in EPSC amplitude at 30–35 min after SST14 or vehicle application (left), and increase in EPSC amplitude at 25–30 min after TBS showing similar LTP in DMSO and cyclosomatostatin (right). * p < 0.05; ns: no significant
Given this lack of effect of SST14 on EPSCs, we examined if the SST1-5R antagonist cyclosomatostatin affected TBS-induced LTP of EPSCs evoked by minimal stimulation. TBS given in the presence of DMSO elicited a slow onset LTP of EPSC amplitude (153.6 ± 20.9% of control at 30–35 min; Fig. 7d, f, g). Application of TBS in the presence of cyclosomatostatin produced LTP of EPSC amplitude that was not different from LTP elicited in DMSO (184.1 ± 17.6% of control at 30–35 min; Fig. 7e, f, g). These results indicate that blocking SST1-5Rs did not affect LTP of pharmacologically isolated non-NMDAR-mediated EPSCs.
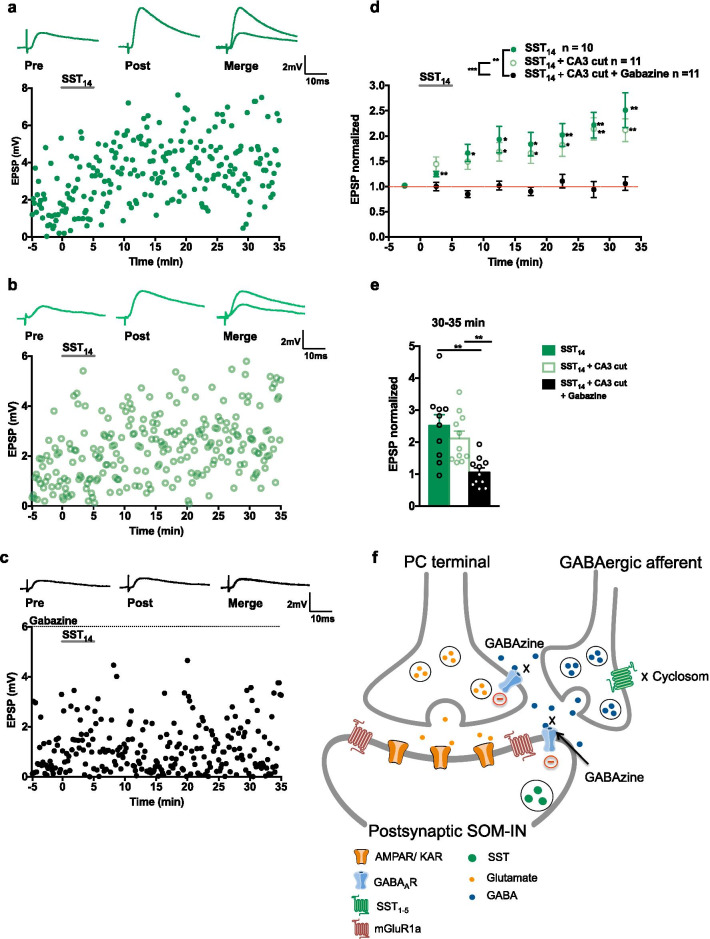
As the non-NMDAR-mediated EPSCs in the previous experiments were pharmacologically isolated in the presence of the GABAA receptor antagonist gabazine and in slices with CA3-CA1 surgical cuts, we examined if the long-lasting effects of SST14 on EPSPs was due to an indirect action via GABAA receptors. We tested the effects of SST14 on EPSPs of SOM-INs in normal slices, slices with a CA3-CA1 cut, or slices with a CA3-CA1 cut and gabazine (Fig. 8). Application of SST14 in normal slices evoked a gradual long-term increase in EPSP amplitude (124.4 ± 5.1% of control at 0–5 min, 166.3 ± 17.0% of control at 5–10 min, 193.3 ± 26.2% of control at 10–15 min, 187.3 ± 23.2% of control at 15–20 min, 202.0 ± 22.7 of control at 20–25 min, 221.8 ± 25.4% of control at 25–30 min, 251.2 ± 34.2% of control at 30–35 min; Fig. 8a, d, e). SST14 application in slices with a CA3-CA1 cut produced a similar long-lasting potentiation of EPSP amplitude (168.5 ± 18.4% of control at 10–15 min, 165.8 ± 19.8% of control at 15–20 min, 182.1 ± 22.5% of control at 20–25 min, 214.1 ± 22.1% of control at 25–30 min, 211.7 ± 22.8% of control at 30–35 min; Fig. 8b, d, e). In contrast, SST14 application in slices with a CA3-CA1 surgical cut and in the presence of gabazine did not affect EPSP amplitude (94.0 ± 15.6% of control at 25–30 min, 105.5 ± 13.4% of control at 30–35 min; Fig. 8c, d, e), indicating that antagonism of GABAA receptors blocked the SST14-induced potentiation of EPSPs. Thus, SST actions in LTP of excitatory synapses of SOM-INs may be indirectly mediated via GABAA inhibition (Fig. 8 f).
Fig. 8.
SST14-induced LTP of EPSPs is blocked by GABAAR antagonism. a–c EPSPs (top) and time plots of EPSP amplitude from representative SOM-INs receiving 5 µM SST14 in a normal slice (a), SST14 in a slice with a CA3-CA1 cut (b), or SST14 in a slice with a CA3-CA1 cut and the GABAA receptor antagonist gabazine (5 µM) (c). d Summary time plots of EPSPs (normalized to baseline) for all cells, showing LTP of EPSPs after SST14 application in normal slices (filled green circle) and in slices with a CA3-CA1 cut (open green circle), but not after SST14 application in the presence of gabazine in slices with a CA3-CA1 cut (black). For SST14 in normal slices; n = 10 cells and 7 mice; rmANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons (0–5 min p = 0.008, 5–10 min p = 0.023, 10–15 min p = 0.033, 15–20 min p = 0.033, 20–25 min p = 0.009, 25–30 min p = 0.007, 30–35 min p = 0.009). For SST14 in slices with CA3 cut; n = 11 cells and 6 mice; rmANOVA with Dunnett’s multiples comparisons (10–15 min p = 0.023, 15–20 min p = 0.046, 20–25 min p = 0.027, 25–35 min p = 0.003, 30–35 min p = 0.004). For SST14 in gabazine; n = 11 cells and 6 mice; rmANOVA p = 0.974. e Summary bar graph of EPSP amplitude at 30–35 min, showing absence of long-term changes in EPSP amplitude induced by SST14 in the presence of gabazine. SST14 vs SST14 in gabazine comparison, two-way mixed ANOVA, univariate analysis at 30–35 min p = 0.001. SST14 with CA3 cut vs SST14 with CA3 cut and gabazine comparison, two-way mixed ANOVA, univariate analysis at 30–35 min p = 0.001. f Model of the mechanism of SST actions in LTP of excitatory synapses onto SOM-INs (details in text). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01
Discussion
In the present work, we uncover a critical involvement of the peptide SST in long-term potentiation at excitatory synapses of hippocampal SOM-INs. We found that application of exogenous SST14 induces long-term potentiation of EPSPs in SOM-INs via somatostatin type 1–5 receptors (SST1-5Rs) (Fig. 1). Application of SST14 did not affect EPSPs in PCs or parvalbumin-expressing interneurons (Fig. 6). TBS-induced Hebbian LTP of EPSPs in SOM-INs was prevented by inhibition of SST1-5Rs (Fig. 2) and by depletion of hippocampal SST by cysteamine treatment (Fig. 3), suggesting a significant role of endogenous SST in LTP. LTP of SOM-IN EPSPs induced by SST14 did not involve changes in paired-pulse ratio of synaptic responses (Fig. 4), was independent of NMDAR and mGluR1a (Fig. 4) and was dependent on concomitant synaptic activity (Fig. 5). Importantly, we observed that SST14 did not affect non-NMDAR-mediated EPSCs recorded during GABAA receptor blockade, and that the SST1-5R antagonist cyclosomatostatin did not affect TBS-induced LTP of these EPSCs (Fig. 7). Finally, pharmacological block GABAA receptor function prevented SST14-induced potentiation of EPSPs (Fig. 8), indicating that SST14 long-term potentiation of excitatory synaptic responses is an indirect effect via GABAA inhibition.
Our results suggest the following model of the contribution of endogenous SST in Hebbian LTP at excitatory synapses of SOM-INs (Fig. 8f): theta burst stimulation of PC axons (i) releases glutamate at PC synapse onto SOM-IN, (ii) eliciting EPSP and action potential firing in SOM-IN, (iii) leading to SST release from SOM-IN, (iv) activation of SSTRs on GABAergic afferent, (v) inhibition of GABA release, (vi) disinhibition of pre- or postsynaptic compartment of the glutamatergic synapse, and (vii) potentiation of EPSP in SOM-IN. Our findings uncover a novel role for SST in long-term plasticity of excitatory synapses onto somatostatinergic cells by indirectly regulating GABAA inhibition.
SST14-induced LTP of SOM-INs excitatory synapses
The observed long-lasting potentiation of EPSPs in SOM-INs by SST14 contrasts with the previously described SST actions in hippocampal PCs. Bath-applied SST14 was reported to decrease evoked and spontaneous EPSCs in pyramidal cells [25]. These effects were acute, occurring within 2–4 min of application onset, and rapidly (2–4 min) reversible. Consistent with these previous observations, we did not find long-lasting effects of SST14 on EPSPs in PCs, suggesting that SST14 long-term effects on SOM-IN excitatory synapses do not arise from di-synaptic actions at PC afferent synapses, but are specific to synapses onto interneurons. Moreover, SST14 did not affect excitatory synaptic responses of PV-INs, indicating that SST14 long-term effects may be specific to excitatory synapses onto somatostatinergic cells. However, in experiments with recordings from PV-INs, the same basal recording and stimulating conditions that elicited stable synaptic responses in SOM-INs and pyramidal cells, resulted in a spontaneous run-up over time. Previous work has shown that excitatory synapses of PV-INs display an anti-Hebbian form of LTP mediated by Ca2+-permeable AMPARs [34]. Since in our recording conditions we maintained the postsynaptic PV-IN at hyperpolarized level during stimulation, the run-up over time may have been caused by anti-Hebbian plasticity. But anti-Hebbian plasticity is independent of GABAA inhibition [34], and, thus, unlikely to occlude SST14 actions via GABAA inhibition. Thus, it would be important to re-examine the SST14 effects on PV-INs excitatory synapses using different recording/stimulation conditions that elicit stable basal responses, to rule out a possible occlusion of SST14 effects by the response run-up over time. Hippocampal PCs are also hyperpolarized by bath application of SST14 via activation of postsynaptic K+ conductances [22–24]. These are also acute effects, reversible in minutes, that are unlikely to contribute to the slow onset and long-lasting potentiation of EPSPs in SOM-INs. Furthermore, SST14-induced hyperpolarization of PCs reduces action potential firing [22], and thus would be expected to reduce presynaptic activation of PCs and decrease EPSPs in SOM-INs. Although SST14 has been reported to depolarize and excite PCs [35], these effects are produced by local application of SST14 and are not observed with bath application [24]. Thus, these direct membrane effects of SST14 on PCs are distinct from the long-lasting actions of SST14 on SOM-IN excitatory synapses observed here.
SST14-induced potentiation is mediated by GABAA inhibition
SST14-induced potentiation of EPSPs was prevented by the GABAA antagonist gabazine, indicating that SST14 actions are mediated indirectly via GABAA inhibition. The mechanism by which SSTR activation acts via GABAA inhibition to increase synaptic excitation remains to be clarified. However, SSTRs are coupled to presynaptic inhibition via inhibition of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels and activation of K+ currents [17, 18]. Thus, via such mechanisms, activation of SSTRs could inhibit release from GABAergic terminals, blocking GABAA inhibition at the PC synapse onto SOM-IN, resulting in potentiation at this synapse via disinhibition. Inhibition of GABAergic synaptic transmission in PC was reported by local application of SST14 [28]. However, bath application of SST14 was reported to inhibit selectively synaptic excitation without affecting inhibition in PCs [25]. SST14 actions in hippocampal interneurons also appear complex with report of depolarization and hyperpolarization [35]. In other brain regions, SST was found to decrease GABA release [17].
Whether SST actions are mediated via GABAA inhibition acting pre- or post-synaptically at the PC to SOM-IN synapse remains unclear. Paired-pulse ratio was unchanged during and after SST14 application (Fig. 4), suggesting no presynaptic changes in transmitter release. However, the excitatory synapses from PC to SOM-INs are composed of calcium-permeable AMPA receptors, and paired stimulation of synaptic responses can be affected also by postsynaptic AMPAR mechanisms [36]. Thus, a lack of change in paired-pulse ratio may not be a reliable indication of a lack of pre-synaptic GABAA inhibition at these synapses. Further experimentation assessing additional parameters, such as coefficient of variation of synaptic currents [37], may be useful to help resolve this issue. Another possibility to assess if the SST-mediated indirect GABAA receptor inhibition occurs only at the presynaptic PC terminal would be to observe if the NMDA-component of synaptic responses recorded from SOM-INs is also potentiated by SST14.
SOM-INs receive postsynaptic GABAA mediated inhibition [13], notably from interneuron-selective interneurons expressing vasoactive intestinal peptide [38, 39], and these could be targeted by SST. However, we did not observe changes in cell input resistance during and after SST14 application (Fig. 1), suggesting no postsynaptic change. However, cell input resistance was measured at the soma and synaptic inhibition may occur at more remote dendritic sites [39]. Interestingly, local application of somatostatin depresses inhibitory postsynaptic potentials recorded in CA1 pyramidal cells, without affecting postsynaptic responses to exogenously applied GABA, indicating somatostatin-induced presynaptic inhibition of GABA synaptic responses in pyramidal cells [28]. Likewise, bath application of somatostatin presynaptically inhibits GABA synaptic transmission onto basal forebrain cholinergic neurons [29]. Similar experiments on inhibitory synaptic transmission onto SOM-INs would be important to clarify the mechanisms of SST14 actions via GABAA inhibition. Our results also raise the question of which type of GABAergic interneuron expresses SSTRs pre-synaptically? SST1-4R, and to a lesser extent SST5R, are present in CA1 hippocampus and in pyramidal cells [40–42]. Generally, SSTR subtypes preferentially occupy specific cell compartments. SST1R is mainly pre-synaptic, SST2,4,5R post-synaptic, and SST3R extra-synaptic (neuronal cilia) [43]. However, which inhibitory cell type in the hippocampus expresses the receptors and whether they are pre- or post-synaptic remains largely to be determined [42, 43]. Interestingly, SST5R and CB1 receptors co-localize in some CA1 interneurons [21]. CB1 receptors are highly expressed mostly in inhibitory interneurons that co-express the neuropeptide cholecystokinin (CCK) [44], suggesting that these interneuron subtypes may mediate SST actions on presynaptic GABAA inhibition. Further experiments will be required to elucidate the pre- and/or post-synaptic GABAA mechanisms involved in the disinhibitory actions of SST at SOM-IN excitatory synapses.
Our results with the antagonist cyclosomatostatin are also consistent with an effect of endogenous SST released after theta burst stimulation contributing to long-term potentiation at the PC to SOM-IN synapse indirectly via GABAA inhibition. Application of SST14 failed to modify non-NMDAR-mediated EPSCs recorded in the presence of gabazine (Fig. 7). In addition, the SSTR antagonist cyclosomatostatin did not affect TBS-induced LTP of non-NMDAR-mediated EPSCs recorded in the presence of gabazine (Fig. 7). However, SST14 and cyclosomatostatin showed effects on EPSPs recorded with GABAA inhibition intact (Figs. 1 and 2). These results suggest that, under physiologically relevant conditions, release of endogenous SST by theta burst stimulation contributes to long-term potentiation at PC to SOM-IN synapses indirectly via GABAA inhibition.
Mechanisms of SST-induced LTP
Although synaptic plasticity in some hippocampal interneurons involves NMDARs [34], mGluR1a-mediated Hebbian LTP in SOM-INs does not [12]. Consistent with this notion, our results indicate that SST14-induced LTP in SOM-INs is unaffected by the NMDAR antagonist DL-APV, and thus does not involve NMDARs.
Hebbian LTP requires mGluR1a activation [12] and our results indicate that SST14 actions that lead to LTP of EPSPs occur downstream of mGluR1a activation since the antagonist LY367385 does not prevent SST14-induced potentiation. Moreover, the long-lasting actions of SST14 are activity-dependent and require concomitant synaptic activity during application of SST14. In these experiments we observed that when synaptic stimulation was re-initiated after a period of interruption a rebound potentiation of synaptic responses was observed. Previous work in oriens-alveus interneurons has shown that, during recordings with intracellular BAPTA to buffer postsynaptic Ca2+ levels, LTP is blocked [37]. However, in addition, the injection of BAPTA induces a long-lasting depression of synaptic responses [37]. Thus, postsynaptic Ca2+ mechanisms are necessary for LTP induction and for maintenance of intact transmission at these synapses. Moreover, activation of excitatory synapses of SOM-INs involve calcium-permeable AMPARs [36] and Ca2+ influx [45]. These results suggest that inactivation and subsequent reactivation of synapses may influence postsynaptic Ca2+ homeostasis, resulting in rebound potentiation. Importantly, in comparison to SST-induced LTP, the magnitude of rebound potentiation was variable and transient, only reaching significance at 15–20 min after resuming stimulation, suggesting different mechanisms at play. Since SST-induced potentiation via GABAA inhibition occurs downstream of AMPAR- and mGluR1a-mediated Ca2+ signals, the mechanisms of rebound potentiation are unlikely to have interfered with, or occluded, the SST effects. Thus, SST14 actions on GABAA inhibition may require synaptic activity during SSTR activation to lead to long-lasting changes. Intriguingly, long-lasting reduction of synaptic inhibition by local application of SST was previously reported in PCs [28] but not with bath application [25]. Further experiments focusing on GABAA inhibition of SOM-INs will be necessary to explain the activity-dependent disinhibitory actions of SST14 in SOM-INs.
Endogenous SST contributes to mGluR1a-mediated Hebbian LTP
Our results with the SST1-5R antagonist cyclosomatostatin suggest that, under physiologically relevant conditions, theta burst stimulation causes release of endogenous SST which contributes to LTP at SOM-IN excitatory synapses via GABAA disinhibition. The release of endogenous SST is frequency-dependent, as EPSPs elicited at 0.1 Hz are unaffected by the antagonist (Fig. 1). During the LTP induction protocol, theta burst stimulation elicits EPSPs that cause action potential burst firing in SOM-INs [8], conditions that are sufficient to cause release of endogenous SST. Such an activity-dependent release of SST is consistent with recent evidence that release of endogenous SST in acute prefrontal cortex slices is induced by frequency-dependent (> 10 Hz) optogenetic stimulation of SOM-INs [46] and that release of endogenous somatostatin in cultured hippocampal neurons is stimulated by AMPA receptor activation [47].
Our results with SST depletion by cysteamine also support a role of endogenous SST in Hebbian LTP. We found that systemic injection of cysteamine or in vitro treatment of slices with cysteamine prevented TBS-induced Hebbian LTP, providing further support for a role of release of endogenous SST in LTP at SOM-IN excitatory synapses. We observed that TBS resulted in long-lasting depression of EPSPs after systemic cysteamine treatment. Since no lasting depression was observed after in vitro treatment of slices with cysteamine, the depression may be the result of extra-hippocampal effects of cysteamine treatment. In previous work during recordings with intracellular BAPTA to prevent postsynaptic Ca2+ rise, LTP was blocked in oriens-alveus interneurons and replaced by LTD [37]. Moreover, in this previous work, injection of BAPTA alone induced a long-lasting decrease in EPSC amplitude, indicating that postsynaptic Ca2+ mechanisms are necessary for LTP induction and for maintenance of intact transmission at these synapses [37]. Thus, extra-hippocampal effects of systemic cysteamine treatment may have interfered with Ca2+ homeostasis in SOM-INs and resulted in LTD.
SST was previously shown to be critical for hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity, as well as learning and memory. Depletion of SST by cysteamine treatment, or knock-out of the SST gene in transgenic mice, impairs hippocampus-dependent contextual fear memory but not hippocampus-independent auditory fear learning [30]. The memory impairment is associated with a decrease in LTP in CA1 PCs [30], as well as at mossy-fiber CA3 PC synapses [48]. SST-induced LTP in SOM-INs may be the link between the role of SST in regulation of hippocampal network plasticity and hippocampal memory. Firstly, contextual fear learning was shown to induce a persistent LTP at excitatory synapses of SOM interneurons mediated by mGluR1 and mTORC1 [9]. Our finding that SST contributes to mGluR1a-mediated Hebbian LTP in SOM-INs, suggests that SST-induced LTP may be induced by contextual learning. Secondly, SOM cell-specific transgenic mouse approaches have shown a functional role of LTP at SOM interneuron excitatory synapses in hippocampal learning and memory [9]. Genetic down-regulation of mTORC1 activity impaired, whereas up-regulation facilitated, mGluR1a-mediated LTP at SOM interneurons excitatory synapses [9]. At the network level, SOM interneurons, and most notably OLM cells, are dendrite projecting inhibitory interneurons that differentially regulate Schaffer collateral (SC) and temporo-ammonic (TA) pathways onto CA1 pyramidal cells [7]: they suppress the distal TA pathway and facilitate the more proximal SC pathway [7]. Thus, LTP at excitatory synapses onto SOM interneurons causes long-term changes in their output firing [36] and inhibition of pyramidal cells [37], resulting in differential long-term regulation of plasticity at SC and TA synapses onto pyramidal cells: up-regulation of plasticity of the SC pathway [8, 9] and down-regulation of plasticity of the TA pathway [11]. At the behavioral level, genetic loss of mTORC1 function specifically in SOM interneurons impaired contextual fear and spatial long-term memories, whereas genetic upregulation of mTORC1 augmented spatial and contextual fear memories [9]. Thus, learning-induced LTP at SOM-IN excitatory synapses is linked to regulation of CA1 network metaplasticity and hippocampal long-term memory consolidation [9]. Our findings that endogenous SST plays a critical role in LTP at SOM-IN excitatory synapses, suggest that impairments in LTP in CA1 pyramidal cells and deficits in contextual fear memory caused by SST depletion/knockout [30] may be due to loss of SST-mediated LTP at SOM-IN synapses [9]. Thus, the role of SST in long-term synaptic plasticity of SOM-INs uncovered here may be crucially implicated in SST regulation of hippocampal learning and memory.
Methods
Animals
All animal procedures and experiments were performed in accordance with Université de Montréal Animal Care Committee (Comité de déontologie de l'expérimentation sur les animaux, CDEA) and followed the guidelines of the Canadian Council on Animal Care. Experiments were carried out on mice (5–8 week-old males for electrophysiology, and from both sexes for immunofluorescence). Mice were housed 2–5 per cage and given ad libitum access to food and water, in temperature (~ 22 °C) and humidity (~ 55%) controlled rooms with a normal 12 h light/dark cycle.
Transgenic mice lines
Transgenic mice expressing Cre-dependent enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (eYFP) in SOM-INs (SOM-eYFP mice) were generated by crossing a knock-in mouse with an internal ribosome entry site (IRES)-linked Cre recombinase gene downstream of the Sst locus (Sstires−Cre; The Jackson laboratory, Bar Harbour, ME JAX #013044) with Rosa26lsl−EYFP reporter mice (Ai3; JAX #007903). Mice expressing eYFP in parvalbumin interneurons (PV-eYFP mice) were generated by crossing Pvalbires−Cre mice (JAX #008069) with Rosa26lsl−EYFP reporter mice (Ai3; JAX #007903).
Cysteamine injection
To study somatostatin depletion, SOM-eYFP mice were injected intraperitoneally (IP) with 150 mg/kg cysteamine (Sigma-Aldrich; M6500) diluted in bacteriostatic NaCl 0.9% (Hospira) or vehicle [49]. After 4 h, mice were anaesthetized with isoflurane inhalation and then decapitated to obtain acute hippocampal slices, as described below. Some mice were deeply anesthetized with sodium pentobarbital (MTC Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, Ontario, Canada) and were perfused transcardially, first with ice-cold 0.1 M phosphate buffer (PB), then with 4% para-formaldehyde in 0.1 M PB (PFA) and the brain isolated. Post-fixed brains were cryoprotected in 30% sucrose and coronal brain sections (50 µm thick) were obtained for immunofluorescence.
Acute hippocampal slice preparation
SOM-eYFP or PV-eYFP mice were anaesthetized with isoflurane inhalation and then decapitated. The brain was rapidly removed and placed in ice-cold sucrose-based solution containing (in mM): 75 sucrose, 87 NaCl, 2.5 KCl, 1.25 NaH2PO4, 7 MgSO4, 0.5 CaCl2, 11.6 ascorbic acid, 3.1 pyruvic acid, 25 D-glucose et 25 NaHCO3 (pH 7.3 ± 0.05; 300 ± 5 mOsmol/L). A block of tissue containing the hippocampus was obtained from each hemisphere and 300 µm thick transverse hippocampal slices were prepared with a Leica VT1000S vibratome. Slices were transferred for a 30 min recovery period in artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF) containing the following (in mM) 124 NaCl, 2.5 KCl, 1.25 NaH2PO4, 26 NaHCO3, 1.3 MgSO4,10 D-glucose, 2.5 CaCl2 (pH 7.3–7.4, 295–305 mOsmol/L) at 30 °C and subsequently maintained at room temperature (20 –22 °C) for at least 60 min, until use. Both cutting solution and ACSF were saturated with 95% O2/5% CO2.
Cysteamine treated acute hippocampal slices
Hippocampal slices were obtained as above and transferred in oxygenated ACSF containing cysteamine (200 µM) or ACSF alone, for 1 h at room temperature. Slices were then used for electrophysiological whole cell recording (as described below) or fixed overnight at 4 °C with 4% PFA, rinsed with PB 0.1 M, cryoprotected in 30% sucrose/PB 0.1 M and re-sectioned (50 µm) using a freezing microtome (Leica SM200R, Germany) for immunofluorescence.
Whole-cell current clamp recordings
Slices were transferred to a submersion chamber perfused with ACSF (3–4 ml/min) at 31 ± 0.5˚C. CA1 interneurons expressing eYFP, or pyramidal cells not expressing eYFP, were identified using an upright microscope (Zeiss Axioskop, Toronto, Canada) with a water-immersion long-working distance objective (40X N-Achroplan, Zeiss, Toronto, Canada), epifluorescence lamp (FluoArc N HBO 103, Zeiss, Toronto, Canada) and an infrared digital video camera (Infinity 3, Lumenera, Ottawa, Canada). Whole-cell current clamp recordings were obtained using borosilicate glass pipettes (2–5MΩ; WPI) filled with intracellular solution containing (in mM): 120 KMeSO4, 10 KCl, 10 HEPES, 0.5 EGTA, 10 Na2-phosphocreatine, 2.5 MgATP, 0.3 NaGTP (pH 7.4, 300 mOsmol/L). Data were acquired using a Multiclamp 700B amplifier (Molecular Devices), digitized at 20 kHz using Digidata 1440A and pClamp 10 (Molecular Devices). Recordings were low-pass filtered at 2 kHz. Access resistance was regularly monitored during experiments and data was included only if the holding current was stable and access resistance varied less than 20% of initial value. Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) were evoked using constant current pulses (50 µs duration) via a concentric bipolar Pt/Ir electrode (FHC) placed in stratum oriens near the alveus, 100 µm lateral from the recorded cell soma. Membrane potential was held at -60 mV by constant current injection. EPSPs were evoked during a hyperpolarizing current step (5–10 mV, 0.5–1 s duration) to avoid action potential generation. Paired stimulations (50 ms inter-event interval) were given at 0.1 Hz. LTP was induced by three episodes (at 30 s intervals) of theta-burst stimulation (TBS) of afferents (five bursts, each consisting of four pulses at 100 Hz, with a 250 ms interburst interval).
Whole-cell voltage clamp recordings
The protocol for slice preparation was as described above, except that CA1-CA3 regions were disconnected by a surgical cut. Glass pipettes were filled with intracellular solution containing (in mM): 120 CsMeSO3, 5 CsCl, 2 MgCl2, 10 HEPES, 0.5 EGTA, 10 Na2-phosphocreatine, 2 ATP-Tris, 0.4 GTP-Tris, 0.1 spermine, 2 QX314 (pH 7.2–7.3; 280 ± 5 mOsmol). Excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) were evoked using constant current pulses (50 µs duration) via an ACSF-filled bipolar theta-glass electrode (Harvard Apparatus) positioned 100 µm lateral to the recorded cell soma at the border between CA1 stratum oriens and the alveus. EPSCs were evoked at 0.5 Hz using minimal stimulation adjusted to obtain approximately 50% success events and 50% failures (paired stimulation with 50 ms interval). EPSCs were recorded in the presence of DL-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid (APV; 50 µM, abcam #120004) and SR-95531 (gabazine, 5 µM; abcam #120042) to block NMDA and GABAA receptors, respectively. For experiments with TBS-induced LTP of EPSCs, the ACSF contained 4 mM Mg2+ and Ca2+ to reduce spontaneous EPSC activity [12]. EPSCs and EPSPs were usually characterized in one cell per slice, and the different experimental conditions were interleaved. Responses were analyzed off-line using Clampfit (pClamp 10; Molecular Devices), GraphPad (Prism 7.2), SPSS 26 (IBM). Amplitude of EPSP and EPSC (average peak response; including failures for EPSCs) were averaged in 5 min bins over the total 35–40 min period of recordings.
Somatostatin immunofluorescence
Sections were permeabilized with 0.3% Triton X-100 in 0.1 M PB (15 min) and unspecific binding was blocked with 10% normal goat serum in 0.1% Triton X-100 and 0.1 M PB (1 h). Sections were incubated 24–48 h at 4ºC with mouse monoclonal somatostatin antibody (1/500; Santa Cruz Biotechnology; Dallas, TX), and subsequently at room temperature with Rhodamine-Red™ X-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG2b (1/200; 90 min; Jackson Immunoresearch Labs; West Grove, PA). Sections were mounted in ProLong™ Diamond (Life technologies; Carlsbad, CA) and images were acquired using a confocal microscope (LSM880; Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany) at excitation 488 and 543 nm. Images were acquired using the exact same parameters fixed on control slices (ACSF) or mice (saline). The intensity of the somatostatin immunofluorescence, in oriens-alveus region of the CA1 hippocampus was quantified using ImageJ software (National Institute of Health; https://github.com/imagej/imagej1) by comparing integrated density in cells corrected for background fluorescence. For experiments with cysteamine IP injection, cell fluorescence was measured typically in 44–63 fields of view per animal coming from 3–4 sections and averaged per animal. A total of 3 animals per group coming from 3 independent experiments were analyzed (total of 397 cells for saline; 441 cells for cysteamine). For acute slices, cell fluorescence was measured typically in 3–49 fields of view per slice coming from 2–4 sections and averaged per slice. A total of 3 animals coming from 3 independent experiments were analyzed (total of 714 cells for ACSF; 713 cells for cysteamine).
Pharmacology
The neuropeptide somatostatin (SST14; Abcam #141206) was diluted daily in ACSF at 5 µM and perfused for 5 min and then washed-out during whole cell recordings of EPSPs/EPSCs. In some experiments, cyclosomatostatin (Abcam #141211), a non-selective SST1-5R antagonist was dissolved in DMSO and applied at a final concentration of 1 µM in ACSF. It was perfused for 5 min before and during somatostatin application, and then washed out. In TBS LTP experiments, cyclostomatostatin was perfused for 10 min before and during TBS, and then washed out. In some experiments, 40 µM LY367385 (Tocris #1237), a mGluR1a selective antagonist, or 50 µM DL-APV (Abcam #120004), a NMDAR selective antagonist, were diluted in ACSF and perfused throughout the recording period (40 min).
Statistical analysis
No statistical methods were used to predetermine sample size but our sample sizes are comparable to those used generally in the field. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS statistics 26 (IBM). For experiments with two groups with repeated measures in each group, a two-way mixed ANOVA was performed. Outliers were removed if values of studentized residuals were greater than ± 3. Normality of data distribution was validated by Skewness and Kurtosis values. The assumption of homogeneity of variance was assessed by Levene’s test of equality of error variances. The assumption of sphericity was assessed by Mauchly’s test of sphericity. If the assumption of sphericity was violated, a Greenhouse–Geisser correction was applied. If two-way ANOVA showed a significant interaction between group and time, the interaction was decomposed with a univariate analysis of variance and one-way repeated measure ANOVA (rmANOVA). Univariate analysis of variance was used to compare between groups at each time point. rmANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons was used to compare each time point inside the same group to baseline. If no statistical interaction was found, only the main effect of group and time was reported with Bonferroni adjustment for multiple comparisons. In the figures, data are expressed as arithmetic mean ± SEM. Asterisks denote statistical significance as calculated by the specified statistical tests (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001; ns, not significant). Detailed results of all statistical tests referenced per figure are included in a supplemental table (Additional file 1).
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1. Statistical table. Description of data: results of all statistical tests referenced per figure.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Julie Pépin for technical support.
Abbreviations
- ACSF
Artificial cerebrospinal fluid
- AMPAR
α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor
- APV
DL-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid
- eIF2α
Eukaryotic initiation factor 2α
- EPSC
Excitatory postsynaptic current
- EPSP
Excitatory postsynaptic potential
- eYFP
Enhanced yellow fluorescent protein
- GABAA
γ-Aminobutyric acid type A
- IP
Intraperitoneal injection
- LTP
Long-term potentiation
- mGluR1a
Metabotropic glutamate receptors type 1a
- mTORC1
Mammalian/mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1
- NMDAR
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor
- O-LM
Oriens-lacunosum/moleculare
- PB
Phosphate buffer
- PC
Pyramidal cell
- PV-IN
Parvalbumin-expressing interneuron
- SOM-IN
Somatostatin-expressing interneuron
- SRIF
Somatotropin-release inhibitory factor
- SST
Somatostatin
- SST14
Somatostatin-14
- SST1-5R
Somatostatin type 1–5 receptor
- TBS
Theta-burst stimulation
Authors' contributions
JCL designed and supervised the project. ASR and JCL designed experiments. ASR, FXM and IL performed experiments and analysed data. ASR, IL and JCL wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by an operating grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR PJT-153311), a Research Centre grant (Centre Interdisciplinaire de Recherche sur le Cerveau et l'Apprentissage; CIRCA) from the Fonds de la Recherche du Québec – Santé (FRQS), and a Group grant from Université de Montréal (Groupe de recherche sur le système nerveux central; GRSNC) to JCL. JCL is the recipient of the Canada Research Chair in Cellular and Molecular Neurophysiology (CRC 950-231066). ASR was supported by a CIHR graduate bursary from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All animal procedures and experiments were performed in accordance with guidelines for maintenance and care of animals of the Canadian Council of Animal Care and in accordance with the Université de Montréal animal care committee regulations (Protocols: 18-002 and 18-003; 19-003 and 19-004; 20-001 and 20-002; 21-001 and 21-002).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Anne-Sophie Racine, Email: anne-sophie.racine@umontreal.ca.
François-Xavier Michon, Email: francois-xavier.michon@umontreal.ca.
Isabel Laplante, Email: isabel.laplante@umontreal.ca.
Jean-Claude Lacaille, Email: jean-claude.lacaille@umontreal.ca.
References
- 1.Tricoire L, Pelkey KA, Erkkila BE, Jeffries BW, Yuan X, McBain CJ. A blueprint for the spatiotemporal origins of mouse hippocampal interneuron diversity. J Neurosci. 2011;31(30):10948–10970. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0323-11.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Freund TF, Buzsaki G. Interneurons of the hippocampus. Hippocampus. 1996;6(4):347–470. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1063(1996)6:4<347::AID-HIPO1>3.0.CO;2-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pelkey KA, Chittajallu R, Craig MT, Tricoire L, Wester JC, McBain CJ. Hippocampal GABAergic Inhibitory Interneurons. Physiol Rev. 2017;97(4):1619–1747. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00007.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bezaire MJ, Soltesz I. Quantitative assessment of CA1 local circuits: knowledge base for interneuron-pyramidal cell connectivity. Hippocampus. 2013;23(9):751–785. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lovett-Barron M, Turi GF, Kaifosh P, Lee PH, Bolze F, Sun XH, Nicoud JF, Zemelman BV, Sternson SM, Losonczy A. Regulation of neuronal input transformations by tunable dendritic inhibition. Nat Neurosci. 2012 doi: 10.1038/nn.3024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Royer S, Zemelman BV, Losonczy A, Kim J, Chance F, Magee JC, Buzsaki G. Control of timing, rate and bursts of hippocampal place cells by dendritic and somatic inhibition. Nat Neurosci. 2012;15(5):769–775. doi: 10.1038/nn.3077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Leao RN, Mikulovic S, Leao KE, Munguba H, Gezelius H, Enjin A, Patra K, Eriksson A, Loew LM, Tort AB, et al. OLM interneurons differentially modulate CA3 and entorhinal inputs to hippocampal CA1 neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2012;15(11):1524–1530. doi: 10.1038/nn.3235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Vasuta C, Artinian J, Laplante I, Hebert-Seropian S, Elayoubi K, Lacaille JC. Metaplastic regulation of CA1 schaffer collateral pathway plasticity by hebbian MGluR1a-mediated plasticity at excitatory synapses onto somatostatin-expressing interneurons. eNeuro. 2015 doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0051-15.2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Artinian J, Jordan A, Khlaifia A, Honore E, La Fontaine A, Racine AS, Laplante I, Lacaille JC. Regulation of hippocampal memory by mTORC1 in somatostatin interneurons. J Neurosci. 2019;39(43):8439–8456. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0728-19.2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lovett-Barron M, Kaifosh P, Kheirbek MA, Danielson N, Zaremba JD, Reardon TR, Turi GF, Hen R, Zemelman BV, Losonczy A. Dendritic inhibition in the hippocampus supports fear learning. Science. 2014;343(6173):857–863. doi: 10.1126/science.1247485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sharma V, Sood R, Khlaifia A, Eslamizade MJ, Hung TY, Lou D, Asgarihafshejani A, Lalzar M, Kiniry SJ, Stokes MP, et al. eIF2alpha controls memory consolidation via excitatory and somatostatin neurons. Nature. 2020;586(7829):412–416. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2805-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Perez Y, Morin F, Lacaille JC. A hebbian form of long-term potentiation dependent on mGluR1a in hippocampal inhibitory interneurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(16):9401–9406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.161493498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Booker SA, Vida I. Morphological diversity and connectivity of hippocampal interneurons. Cell Tissue Res. 2018;373(3):619–641. doi: 10.1007/s00441-018-2882-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ran I, Laplante I, Bourgeois C, Pepin J, Lacaille P, Costa-Mattioli M, Pelletier J, Sonenberg N, Lacaille JC. Persistent transcription- and translation-dependent long-term potentiation induced by mGluR1 in hippocampal interneurons. J Neurosci. 2009;29(17):5605–5615. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5355-08.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ran I, Laplante I, Lacaille JC. CREB-dependent transcriptional control and quantal changes in persistent long-term potentiation in hippocampal interneurons. J Neurosci. 2012;32(18):6335–6350. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5463-11.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Brazeau P, Vale W, Burgus R, Ling N, Butcher M, Rivier J, Guillemin R. Hypothalamic polypeptide that inhibits the secretion of immunoreactive pituitary growth hormone. Science. 1973;179(4068):77–79. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4068.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Martel G, Dutar P, Epelbaum J, Viollet C. Somatostatinergic systems: an update on brain functions in normal and pathological aging. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2012;3:154. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2012.00154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gunther T, Tulipano G, Dournaud P, Bousquet C, Csaba Z, Kreienkamp HJ, Lupp A, Korbonits M, Castano JP, Wester HJ, et al. International union of basic and clinical pharmacology. CV. Somatostatin receptors: structure, function, ligands, and new nomenclature. Pharmacol Rev. 2018;70(4):763–835. doi: 10.1124/pr.117.015388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Schulz S, Handel M, Schreff M, Schmidt H, Hollt V. Localization of five somatostatin receptors in the rat central nervous system using subtype-specific antibodies. J Physiol Paris. 2000;94(3–4):259–264. doi: 10.1016/S0928-4257(00)00212-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Spary EJ, Maqbool A, Batten TF. Expression and localisation of somatostatin receptor subtypes sst1-sst5 in areas of the rat medulla oblongata involved in autonomic regulation. J Chem Neuroanat. 2008;35(1):49–66. doi: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2007.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Zou S, Somvanshi RK, Kumar U. Somatostatin receptor 5 is a prominent regulator of signaling pathways in cells with coexpression of Cannabinoid receptors 1. Neuroscience. 2017;340:218–231. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.10.056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pittman QJ, Siggins GR. Somatostatin hyperpolarizes hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. Brain Res. 1981;221(2):402–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90791-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Moore SD, Madamba SG, Joels M, Siggins GR. Somatostatin augments the M-current in hippocampal neurons. Science. 1988;239(4837):278–280. doi: 10.1126/science.2892268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Schweitzer P, Madamba SG, Siggins GR. Somatostatin increases a voltage-insensitive K+ conductance in rat CA1 hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1998;79(3):1230–1238. doi: 10.1152/jn.1998.79.3.1230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tallent MK, Siggins GR. Somatostatin depresses excitatory but not inhibitory neurotransmission in rat CA1 hippocampus. J Neurophysiol. 1997;78(6):3008–3018. doi: 10.1152/jn.1997.78.6.3008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ishibashi H, Akaike N. Somatostatin modulates high-voltage-activated Ca2+ channels in freshly dissociated rat hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1995;74(3):1028–1036. doi: 10.1152/jn.1995.74.3.1028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Baratta MV, Lamp T, Tallent MK. Somatostatin depresses long-term potentiation and Ca2+ signaling in mouse dentate gyrus. J Neurophysiol. 2002;88(6):3078–3086. doi: 10.1152/jn.00398.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Scharfman HE, Schwartzkroin PA. Selective depression of GABA-mediated IPSPs by somatostatin in area CA1 of rabbit hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1989;493(2):205–211. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91155-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Momiyama T, Zaborszky L. Somatostatin presynaptically inhibits both GABA and glutamate release onto rat basal forebrain cholinergic neurons. J Neurophysiol. 2006;96(2):686–694. doi: 10.1152/jn.00507.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kluge C, Stoppel C, Szinyei C, Stork O, Pape HC. Role of the somatostatin system in contextual fear memory and hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Learn Mem. 2008;15(4):252–260. doi: 10.1101/lm.793008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Fries JL, Murphy WA, Sueiras-Diaz J, Coy DH. Somatostatin antagonist analog increases GH, insulin, and glucagon release in the rat. Peptides. 1982;3(5):811–814. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(82)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Szabo S, Reichlin S. Somatostatin in rat tissues is depleted by cysteamine administration. Endocrinology. 1981;109(6):2255–2257. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-6-2255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sagar SM, Landry D, Millard WJ, Badger TM, Arnold MA, Martin JB. Depletion of somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system by cysteamine. J Neurosci. 1982;2(2):225–231. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-02-00225.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kullmann DM, Lamsa KP. Long-term synaptic plasticity in hippocampal interneurons. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8(9):687–699. doi: 10.1038/nrn2207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Scharfman HE, Schwartzkroin PA. Further studies of the effects of somatostatin and related peptides in area CA1 of rabbit hippocampus. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1988;8(4):411–429. doi: 10.1007/BF00711226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Croce A, Pelletier JG, Tartas M, Lacaille JC. Afferent-specific properties of interneuron synapses underlie selective long-term regulation of feedback inhibitory circuits in CA1 hippocampus. J Physiol. 2010;588(Pt 12):2091–2107. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.189316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lapointe V, Morin F, Ratte S, Croce A, Conquet F, Lacaille JC. Synapse-specific mGluR1-dependent long-term potentiation in interneurones regulates mouse hippocampal inhibition. J Physiol. 2004;555(Pt 1):125–135. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.053603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Acsady L, Gorcs TJ, Freund TF. Different populations of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-immunoreactive interneurons are specialized to control pyramidal cells or interneurons in the hippocampus. Neuroscience. 1996;73(2):317–334. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(95)00609-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Tyan L, Chamberland S, Magnin E, Camire O, Francavilla R, David LS, Deisseroth K, Topolnik L. Dendritic inhibition provided by interneuron-specific cells controls the firing rate and timing of the hippocampal feedback inhibitory circuitry. J Neurosci. 2014;34(13):4534–4547. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3813-13.2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Perez J, Rigo M, Kaupmann K, Bruns C, Yasuda K, Bell GI, Lubbert H, Hoyer D. Localization of somatostatin (SRIF) SSTR-1, SSTR-2 and SSTR-3 receptor mRNA in rat brain by in situ hybridization. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1994;349(2):145–160. doi: 10.1007/BF00169831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Perez J, Hoyer D. Co-expression of somatostatin SSTR-3 and SSTR-4 receptor messenger RNAs in the rat brain. Neuroscience. 1995;64(1):241–253. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)00364-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Cammalleri M, Bagnoli P, Bigiani A. Molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying somatostatin-based signaling in two model neural networks, the retina and the hippocampus. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(10):2506. doi: 10.3390/ijms20102506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Liguz-Lecznar M, Urban-Ciecko J, Kossut M. Somatostatin and somatostatin-containing neurons in shaping neuronal activity and plasticity. Front Neural Circuits. 2016;10:48. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2016.00048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Chevaleyre V, Takahashi KA, Castillo PE. Endocannabinoid-mediated synaptic plasticity in the CNS. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2006;29:37–76. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.29.051605.112834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Topolnik L, Congar P, Lacaille JC. Differential regulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor- and AMPA receptor-mediated dendritic Ca2+ signals by presynaptic and postsynaptic activity in hippocampal interneurons. J Neurosci. 2005;25(4):990–1001. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4388-04.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Dao NC, Brockway DF, Crowley NA. In vitro optogenetic characterization of neuropeptide release from prefrontal cortical somatostatin neurons. Neuroscience. 2019;419:1–4. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.08.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Fontana G, De Bernardi R, Ferro F, Gemignani A, Raiteri M. Characterization of the glutamate receptors mediating release of somatostatin from cultured hippocampal neurons. J Neurochem. 1996;66(1):161–168. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1996.66010161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Matsuoka N, Kaneko S, Satoh M. A facilitatory role of endogenous somatostatin in long-term potentiation of the mossy fiber-CA3 system in guinea-pig hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 1991;129(2):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90455-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Srikant CB, Patel YC. Cysteamine-induced depletion of brain somatostatin is associated with up-regulation of cerebrocortical somatostatin receptors. Endocrinology. 1984;115(3):990–995. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-3-990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1. Statistical table. Description of data: results of all statistical tests referenced per figure.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.