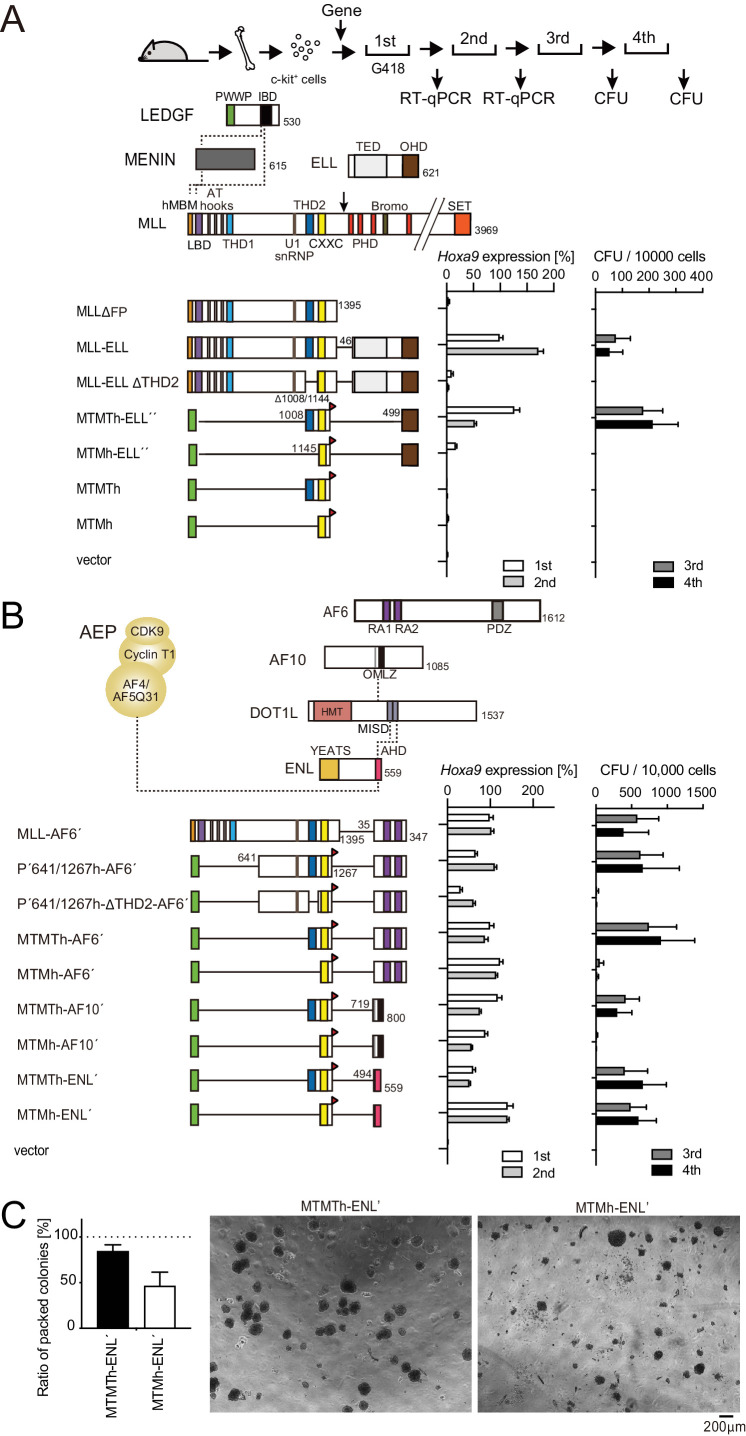
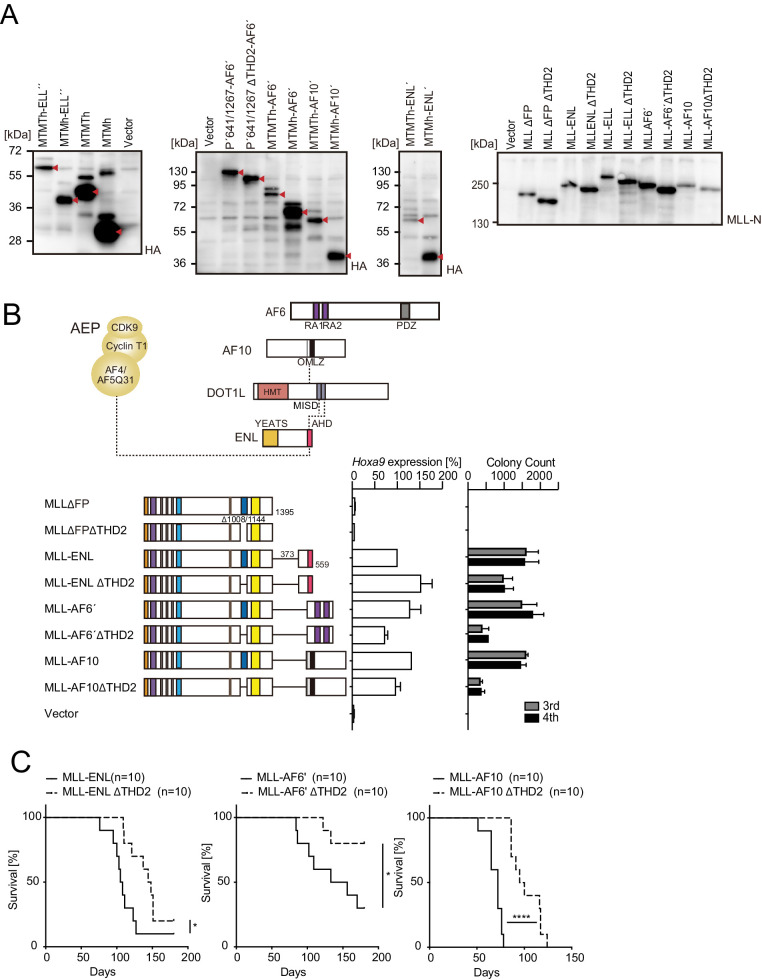
Figure 1. Trithorax homology domain 2 (THD2)-mediated functions promote MLL-fusion-dependent leukemic transformation.
(A) Structure/function analysis of MLL-ELL. Various MLL-ELL constructs were examined for the transformation of myeloid progenitors. HA-tag (h: indicated as a red triangle) was fused to MTM and MTMT constructs. A schema of myeloid progenitor transformation assay is shown on top. Hoxa9 expression normalized to Gapdh in first-round and second-round colonies (left) is shown as the relative value of MLL-ELL (arbitrarily set at 100%) with error bars (mean ± SD of PCR triplicates). Colony-forming ability at third- and fourth-round passages (right) is shown with error bars (mean ± SD of ≥3 biological replicates). IBD: integrase-binding domain; hMBM: high-affinity MENIN-binding motif; LBD: LEDGF-binding domain; THD1/2: trithorax homology domains 1 and 2; SET: Suver3-9/enhancer-of-zeste/trithorax motif; TED: transcription elongation domain; OHD: occludin homology domain. (B) Requirement of THD2 for various MLL fusion proteins in leukemic transformation. Various MLL fusion constructs were examined for the transformation of myeloid progenitors as in (A). RA1/2: RAS association domains 1/2; PDZ: PSD-95/Dlg/ZO-1 domain; OM: octapeptide motif; LZ: leucine zipper. MISD: minimum interaction site of DOT1L: YEATS: Yaf9 ENL AF9 Taf14 Sas5 domain; AHD: ANC1 homology domain. (C) Colony morphologies of MTMTh or MTMh-ENL′ transformed cells. The colonies on day 5 of fourth passage are shown with a scale bar. The ratio of compact colonies (≥100 total colonies were counted in each experiment) is shown on the left (mean ± SD of six biological replicates). Representative images are shown on the right.