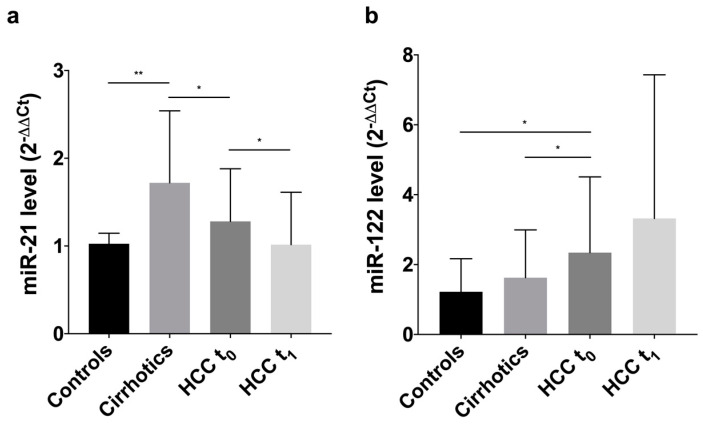
Figure 1.
Histograms showing circulating levels of miR-21 and miR-122 in controls, cirrhotics, HCC patients at t0 and t1 (representing median with error bar showing the third quartile). (a) The median of miR-21 circulating levels is 1.03 fc [0.74–1.15] in controls, 1.72 fc [1.13–2.54] in cirrhotics, and 1.28 fc [0.78–1.88] in patients with HCC at t0. There is a significant difference in the circulating level between controls and cirrhotics (p = 0.009) and between cirrhotics and HCC patients (p = 0.047). In HCC, the miR-21 levels at t0 are significantly higher than those measured at t1 (1.02 fc [0.69–1.66]; p = 0.03); (b) the median of miR-122 circulating levels is 1.22 fc [0.39–2.17] in controls, 1.63 fc [0.51–2.99] in cirrhotics, and 2.34 fc [1.36–4.51] in HCC patients at t0. There is a statistically significant difference in the levels of the miRNA comparing HCC patients with controls (p = 0.02) and cirrhotics (p = 0.04). In HCC patients, no significant differences are present in t0 and t1 levels of miR-122. * p < 0.05; ** p ≤ 0.01.