Abstract
Background
Tuta absoluta Meyrick 1917 (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) is an invasive, pesticide resistant, and a major treat of tomato production in the world. It needs effective management options that naturally infect the insect without causing any identified side effects. Entomopathogenic fungi (EPF) are the most important options. However, geographic origin and climatic condition apparently creates genetic variation among EPF strains that influence on their pathogenicity. Thus, screening of effective EPF strains from the local source is vital to develop environmental friendly pest control tactic for T. absoluta.
Results
In this study, 27 indigenous Beauveria were isolated from the various types of soil and 12 of the isolates were screened based on their biological efficiency index (BEI). These isolates scored 65.7–95.7% and 68.3–95% of mortality against second and third instar larvae of T. absoluta at concentration of 1 × 107spores·ml-1 in 7 days post inoculation, respectively. Out of these, five (18.5%) isolates scored above 90% mortality on both instar larvae with LT50 value of 3.33 to 5.33 days at the lowest (104 spores·ml-1) and 1.93 to 3.17 days at highest (108 spores·ml-1) spore concentrations and has LC50 value of 1.5 × 103 to 1.1× 105 spores·ml-1. Moreover, isolates exhibited the promising mortality better (1.5 × 106 to 3.5 × 107 spores·ml-1), sporulated over the larval cadavers, well grown at optimal temperature, and produced chitinolytic enzymes. Molecular analysis showed that isolates have nearly monophyletic characters and grouped under species of Beauveria bassiana.
Conclusion
Different types of soil in Ethiopia are an important source of B. bassiana, and these isolates showed promising pathogenicity against T. absoluta, which is crucial for ecofriendly biopesticide development. Although isolates were nearly monophyletic in phylogenetic study, five of them were highly effective in the laboratory bioassays against T. absoluta; however, further field evaluation is required for mass production.
Keywords: Biocontrol, Chitinolytic enzyme, Entomopathogenic fungi, Mycoinsecticides
Background
Insect pests are the major threats of vegetable production. The emergence of new invasive pests by global climate change is aggravating the problem by facilitating fast reproduction, easy adaptation, and rapid dissemination of insects [1]. Thus, invasive pests are becoming main challenges of food security against the continuously rising human population in the world.
Tuta absoluta Meyrick 1917 (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) is a native tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) leafminer pest in South America for more than 50 years [2]. Later on, it has become invasive with its notorious spread starting from Spain in 2006 [3], and is currently recognized as an economically important pest of solanaceous plants worldwide [4, 5]. It is estimated that T. absoluta has infested 41 out of 54 African countries [6]. In Ethiopia, the pest has been detected since 2012 [7] and is causing more than 78% loss of tomato production [8]. Although tomato is the main host for feeding and oviposition of T. absoluta, several cultivated and wild solanaceous plants are serving as alternative hosts [9]. T. absoluta can cause up to 100% of damage on the tomato production if it is not managed timely [10].
The control difficulty of the insect emanates from the enormous amount of eggs produced by the female that lays 250 up to 300 on the plant leaves, hatched to feeding stage larvae, which feed on leaf mesophyll, bore into fruits and stem, as well as expose plants for secondary infection [11]. The mean time controlling option of the insect is mainly dependent upon the application of synthetic insecticides as primary solution [12]. However, the insect is fast developing resistance to individual chemicals [13] that forces farmers to try a combination of several types of inappropriate chemicals to improve the control. Continuous application and flooding of huge doses of inappropriate chemicals on the cropland has been aggravating environmental pollution, food contamination, and human health problems [14]. Therefore, this multiple problem is calling for environmentally friendly pest management alternatives.
These days, the biocontrol method is given attention as a promising technology to control insect pests as part of the integrated pest management (IPM) strategy [15]. Entomopathogenic fungi (EPF) are the recognized part of mycoinsecticidal IPM agents against several insect pests [16]. The United States of Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) classified genus Beauveria as a biopesticide [17]. This insect pathogen is isolated from the soil [18, 19], insect cadavers [17], as well as plant tissues [20], and checked for their pathogenicity against several agriculturally important pests [21]. Out of these, Beauveria bassiana is highly pathogenic to many insect pests through the mechanism of spore germination, cuticle penetration, and mycelial dissemination mode of action inside the body [22], and is formulated and available in the market as biopesticides for many years.
Although this fungal species is commercialized as mycoinsecticides for more than decades and used for arthropod pest management [23], locally isolated strains showed better performance than formulated products. For instance, Wang and Zhang [24] identified virulent B. bassiana with 93% mortality against Frankliniella occidentalis Pergande from the local environment elsewhere indicating that the virulent strain can still be isolated from given environmental conditions with better adaptation. The geographic distance of origin apparently creates genetic variation among strains of B. bassiana [25]. This could possibly infer that distinct strains of B. bassiana might be found in different ecological zones of Ethiopia, which is imperative to explore entomopathogenically effective ones from the various locations to use for vegetable production by smallholder farmers with affordable economic return. Therefore, the objective of this study was isolation, molecular identification, and pathogenicity evaluation of local strains of B. bassiana against second and third instar larvae of T. absoluta, to validate and recommend for future biocontrol tactics.
Methods
Sample collection
The cropland and grassland soils were collected from the central rift valley area of Ethiopia. This area is potential for tomato production using irrigation system and known for T. absoluta infestation. The forest soil was collected from “Menagesha National Forest” that covers an altitude between 2574 and 2948 m above sea level (masl). Soil samples were taken from the tomato farm and undisturbed places of grassland and forest; each soil-sampling site was replicated three times; soils were pooled together, composited, and collected into 2-kg–capacity ethanol-sterilized (70%) polyethylene bags. A total of 43 soil samples were collected and brought into Applied Microbiology Laboratory, Addis Ababa University (AAU) for further work. For rearing the insect pest, T. absoluta–infected tomato leaves and fruits harboring larvae and pupae of the inset were collected from the same tomato-grown rift valley area.
Rearing of Tuta absoluta
The T. absoluta–infected tomato leaves and fruits harboring larvae and pupae collected from the central rift valley area were transferred into 5-week-old pot-grown “Awash” cultivar tomato plants, kept under zipped cages constructed from wooden poles and meshed cotton cloth. Pot-growing tomato plants supplemented in rearing cages once per 2 weeks to make insect egg-laying process is continuous and emerging larval feed. Infected tomato leaves in the rearing cages were periodically inspected for larval development until the suitable instar larvae were obtained and the third generation (F3) of T. absoluta was used for EPF pathogenicity bioassay.
Isolation of Beauveria species
The great wax moth (Galleria mellonella) reared in Ambo Plant Protection Research Centre (APPRC) according to the methods of Meyling [26] was used for EPF baiting. Beauveria were isolated from the soil using the G. mellonella baiting method [26]. Briefly, the third instar larvae of great wax moth were shocked for 10 s in hot (65 °C) water bath to reduce their fast movement within the soil and transferred into 1 1/2 L capacity of screw-caped glass jars filled with 1 kg of moisturized soil. The jars were inoculated with ten heat-shocked great wax moth larvae incubated at 30 °C for 10 days under complete dark condition.
The death of larvae in the soil was inspected every 3 days, and the moisture content of the soil was adjusted by gentle moistening with sterile water each time following the death inspection. Cadavers of dead larvae were carefully removed from the soil, surface sterilized by using sodium hypochlorite (3%) followed by ethanol (70%) for 3 min each, rinsed five times with sterile water, placed on the sterile plastic plates lined with UV serialized and moistened tissue paper, and incubated at room temperature under dark condition until fungal mycelia and spores outgrow. Then the spore was scraped using inoculating wire loop, transferred onto potato dextrose agar (PDA) medium supplemented with 0.03 g·l-1 of chloramphenicol and incubated at 28 °C for 20 days. Subculturing of isolates onto fresh PDA medium was used for purification, and pure cultures were maintained on agar slants at 4 °C for further work.
Morphological identification
Morphology of the isolated fungi was characterized by using methods of Rehner et al. [27]. The cultural characteristics such as colony size, mycelial color, colony reverse, and color of conidial mass were examined from the PDA culture plates. Spore morphology such as shape and size were inspected using light microscope (Fish Olympus phase contrast microscope). For microscopic spore characterization, slide culture technique and phenol staining were used.
Molecular identification
DNA extraction
The genomic DNA of the isolates was extracted from four days of old mycelial culture grown on PDA following a quick and safe fungal DNA extraction method [28] in the laboratory of molecular biology, University of Chile, Santiago. Approximately 400 mg of mycelia grown on the PDA were transferred to a 1.5-ml Eppendorf tube containing 0.5 ml of DNA extraction buffer (1 M KCl; 100 mM Tris-HCl; 10 mM EDTA) using sterile toothpick. Soon after mycelia transfer, mycelial tissue was pulverized by using sterile plastic pestle fitted with an instrument Black and Decker portable electronic drill (American manufacturer of power tools, Stanley Black & Decker, Inc.) for 2 to 3 s. The lysates were centrifuged at 12,000 g for 10 min in order to separate cell debris and contaminants from the supernatant. The DNA-containing supernatant was carefully transferred to another 1.5-ml Eppendorf tube containing 0.3 ml of 2-propanol and mixed through tube inverting and centrifuged at 13,000 g for 10 min. After discarding supernatant, pellet in the Eppendorf tube was gently washed with 0.7 ml of ethanol (70%) and allowed for ethanol evaporation at room temperature for 15 min. The pellet of DNA was dissolved by 100 μl of 20 mM Tris solution through gentle tapping. The amount of DNA in the suspension was quantified by transferring 2 μl aliquots on to nanodrop microplate in duplicate using an instrument, BioTek Synergy2TM Multi-mode Microplate Reader, controlled by Gen5TM Data analysis software, USA. Furthermore, the purity of DNA was checked by running the PCR products under agarose gel electrophoresis and stored at − 20 °C for further activities.
PCR amplification
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of DNA was performed by using ITS1 and ITS4 primers. ITS1 (TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG forward) and ITS4 (TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC reverse) were used to amplify the target regions [29]. The master mix was prepared from the components namely 6.8 μl of water, 4 μl of buffer, 1 μl (2.5 mM·μl-1) MgCl2, 1 μl (0.5 mM·μl-1) of dNTP, 0.2 μl (1 U·μl-1) of GoTaq polymerase, 2.5 μl (2.5 μM·μl-1) of each ITS1 (forward) and ITS4 (reverse) primers, and 1 μl (30 μg μl-1) of genomic DNA. The PCR reaction was conducted in a total volume of 20 μl. The thermo cycler settings were adjusted as 4-min initial denaturation at 94 °C followed by 35 cycles of 1-min denaturation at 94 °C, 1-min annealing at 56 °C, and 1-min extension at 72 °C with final extension for 5 min at 72 °C and storage temperature of 4 °C. The product was assayed by electrophoresis on a 2.5% agarose gel with TBE buffer (Tris; Borate; EDTA) at 100 V for 55 min. Then the gel was stained by shaking within 200 ml of TBE buffer supplemented with 10 μl (v/v) of noncarcinogenic dye “SafeViewTM Plus” for 50 min and photographed under UV light using eight-mega pixels canon pc1201 digital camera. The PCR products amplified at the volume of 50 μl was purified by using NucleoSpin® Gel and PCR Clean-up kits (Germany), checked for DNA purity using 2.5% of agarose gel electrophoresis and sent to Macrogen Inc. Seoul, South Korea, for sequencing.
Sequences were aligned using CLUSTALx program, edited by using Bioedit software, and the relationship of the isolates with other relatives were checked by sequence using the BLAST search method from NCBI database. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using MEGA4 program, the neighbor-joining method, the maximum composite likelihood model and 1000 bootstrap runs.
Screening of isolates
Spore germination potential of isolates
The conidial viability of the isolates were checked through germination test using procedures described by Habtegebriel et al. [30]. Spores were collected from the 3 weeks of old culture and transferred into a Falcon tube containing 10 ml of sterile distilled water supplemented with Tween 80 (0.1% v/v). A 100-μl spore suspension that adjusted to 1 × 106 conidia·ml-1 using an improved Neubauer hemocytometer was overspread on the fresh PDA and incubated at 25 °C for 24 h. Over germination of the spores on the medium was halted by dispensing 70% of ethanol. From which, 100 spores (both germinated and non-germinated ones) were counted using 40× magnifying light microscope and the experiment were repeated three times.
Spore production potential of isolates
The sporulation rates of the isolates on the medium were tested through the plate culture method by incubating at 28 °C under complete dark condition. The plate cultures grown on PDA were checked daily for sporulation initiation since 4 days after initial incubation. Sporulation initiation of each isolate was recorded for 20 consecutive days (day 20 is considered as experimental lasting date), and the experiment was undertaken in triplicates. To select fast-sporulating isolates, the relative sporulation rate (RSR) was calculated using the formula: where PCS (plate culture sporulation) date is the first date that the isolates were started to produce the spore on the PDA medium. Experimental lasting date is the final date of the experiment schedule, which is just at the 20th day of first inoculation.
Pathogenicity screening of isolates using Galleria mellonella
Pathogenic isolates were screened using third instar larvae of G. mellonella [30]. Spores from 3 weeks grown culture were collected and adjusted to conidial concentration of 1 × 107 ml-1 and suspended into Falcon tubes containing 10 ml of distilled water plus Tween 80 (0.1% v/v). Twenty of third instar larvae were dipped into spore suspensions for 15 s, air dried for 10 min under laminar airflow hood, and transferred into sterile small jars filled with a mixture of wheat bran (25 g), honey (40 g), and glycerol (90 ml), separately.
Inoculated jars with larvae were incubated at room temperature for 10 days under dark condition, from which dead larvae were collected every 3 days, surface sterilized, and transferred into sterilized plates lined with moistened tissue paper. Moisture content of the tissue paper was adjusted using sterile water spray to enhance mycelial outgrowth over the larval cadavers. Other twenty larvae were also dipped in sterilized water plus Tween 80 (0.1% v/v) and incubated at the same condition as a control, and the experiments were done in triplicates. Based on these screening procedures, the cumulative biological efficacy index (BEI) was computed by using formula stated by Sain et al. [31] with some modification; BEI (%) = 37 (SG) + 13 (RSR) + 50 ( LM), where SG means spore germination, RSR means relative sporulation rate, and LM means larval mortality of G. mellonella in 10 days post inoculation of spores.
Pathogencity bioassay of isolates against Tuta absoluta
Twelve of isolates, which were screened based on BEI values (isolates indicated by * in Table 1), were used for pathogenicity evaluation against second and third instar larvae of T. absoluta [32]. These isolates were grown on the PDA for 20 days, and their spore suspension were adjusted to 1 × 107 conidia·ml-1 consecration using sterile water plus Tween 80 (0.1% v/v) as before. The tomato leaves were surface sterilized using ethanol (70%) for 3 min and rinsed three times with sterile distilled water. The tomato leaf petioles were tied using UV-sterilized cotton wool to retain water and prevent leaf drying. The leaves were kept in sterile plastic plates (12 cm in diameter) and sprayed with 3 ml of the 1 × 107 spores·ml-1 concentration and air dried under laminar airflow hood for 3 min. Then twenty of each second and third instar larvae of T. absoluta were released over the spore-sprayed leaves, and the same number of larvae were released over surface-sterilized leaves that sprayed with Tween 80 (0.1% v/v) plus water as a control. All plates were incubated at room temperature for 7 days under dark condition. Mortality of larvae was checked daily, and dead larvae were surface-sterilized and transferred into other sterile plastic plates containing moistened tissue paper to see mycosis for 20 days and experiment was repeated three times. The data for larval mortality were calculated by using the Abbettos formula [33].
Table 1.
Percentage of spore germination, culture sporulation in 20 days, larval mortality of Galleria mellonella at 1 × 107 spores·ml-1 concentration within 10 days, and biological efficacy index of the isolates
| Isolates | Genera | Soil | SG (%) ± SE | DPCS ± SE | RSR | LM (%) ± SE | BEI (%) ± SE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAUB76* | Beauveria | Cropland | 94.0 ± 2.60 a | 10.7 ± 2.44a | 1.876 | 100 ± 0.00a | 85.0 ± 1.25a |
| AAUB28* | Beauveria | Cropland | 94.0 ± 1.87ab | 11.0 ± 1.60a | 1.818 | 100 ± 0.00a | 85.0 ± 0.75a |
| AAUB90* | Beauveria | Cropland | 90.7 ± 3.17b | 11.2 ± 2.02ab | 1.792 | 100 ± 0.00a | 83.8 ± 1.98ab |
| AAUB19* | Beauveria | Cropland | 93.3 ± 1.43ab | 11.5 ± 0.39a | 1.739 | 100 ± 0.00a | 84.8 ± 1.67a |
| AAUB39* | Beauveria | Cropland | 92.0 ± 3.23b | 12.7 ± 2.32ab | 1.580 | 100 ± 0.00a | 84.3 ± 2.12a |
| AAUB45 | Beauveria | Cropland | 81.3 ± 4.12ef | 14.0 ± 0.86c | 1.429 | 90.0 ± 3.23b | 75.3 ± 3.41bc |
| AAUB46 | Beauveria | Cropland | 90.7 ± 2.28b | 11.3 ± 2.43ab | 1.765 | 90.0 ± 3..32b | 78.7 ± 2.87b |
| AAUB22 | Beauveria | Cropland | 86.3 ± 2.45c | 15.0 ± 0.82d | 1.333 | 91.3 ± 1.67b | 77.8 ± 3.21b |
| AAUB49 | Beauveria | Cropland | 92.0 ± 4.00b | 15.0 ± 1.09d | 1.333 | 86.7 ± 1.67dc | 77.5 ± 2.45b |
| AAUB25 | Beauveria | Cropland | 89.0 ± 2.09bc | 12.2 ± 3.00ab | 1.645 | 86.7 ± 1.78dc | 76.5 ± 2.06b |
| AAUB70 | Beauveria | Cropland | 87.3 ± 3.18c | 11.2 ± 2.08ab | 1.792 | 89.0 ± 4.02bc | 77.1 ± 3.56b |
| AAUB08 | Beauveria | Cropland | 91.0 ± 2.06b | 14.8 ± 1.45bc | 1.349 | 83.3 ± 1.07d | 75.5 ± 1.12bc |
| AAUB60 | Beauveria | Cropland | 84.3 ± 1.65d | 12.7 ± 1.12ab | 1.580 | 86.7 ± 1.67de | 74.7 ± 1.89bc |
| AAUB85 | Beauveria | Cropland | 85.7 ± 4.23cd | 13.0 ± 2.09b | 1.538 | 80.0 ± 2.00de | 71.9 ± 3.80c |
| AAUB18 | Beauveria | Cropland | 85.7 ± 2.68cd | 13.0 ± 0.34b | 1.538 | 76.7 ± 2.78fg | 70.2 ± 4.56c |
| AAUB05* | Beauveria | Grassland | 94.0 ± 2.09a | 13.6 ± 0.64ab | 1.467 | 100 ± 0.00a | 85.0 ± 2.34a |
| AAUB03* | Beauveria | Grassland | 96.7 ± 3.06a | 10.8 ± 1.44a | 1.847 | 100 ± 0.00a | 86.0 ± 1.92a |
| AAUB06* | Beauveria | Grassland | 91.3 ± 1.10b | 14.3 ± 2.00c | 1.396 | 100 ± 0.00a | 84.0 ± 2.34ab |
| AAUB07 | Beauveria | Grassland | 43.3 ± 3.19gh | 14.0 ± 1.53c | 1.429 | 92.2 ± 4.08b | 62.3 ± 5.03d |
| AAUB59* | Beauveria | Forest | 92.3 ± 1.45ab | 11.2 ± 1.15ab | 1.792 | 100 ± 0.00a | 84.4 ± 2.57a |
| AAUB24* | Beauveria | Forest | 97.0 ± 4.20a | 12.0 ± 1.10ab | 1.667 | 100 ± 0.00a | 86.1 ± 1.56a |
| AAUB23* | Beauveria | Forest | 88.3 ± 2.45bc | 14.3 ± 1.27c | 1.397 | 100 ± 0.00a | 82.9 ± 3.67ab |
| AAUB29* | Beauveria | Forest | 91.7 ± 1.89b | 12.3 ± 0.72ab | 1.622 | 96.7 ± 3.67ab | 82.5 ± 2.56ab |
| AAUB26 | Beauveria | Forest | 91.0 ± 4.29b | 11.0 ± 2.10ab | 1.818 | 90.0 ± 2.70b | 78.9 ± 3.78b |
| AAUB69 | Beauveria | Forest | 90.7 ± 2.54b | 16.0 ± 1.78e | 1.250 | 86.7 ± 3.78cd | 77.0 ± 3.86b |
| AAUB09 | Beauveria | Forest | 90.7 ± 3.00b | 15.0 ± 1.60d | 1.333 | 86.7 ± 3.67cd | 77.1 ± 5.12b |
| AAUB20 | Beauveria | Forest | 94.7 ± 0.89ab | 14.7 ± 2.02cd | 1.364 | 83.3 ± 3.67cd | 76.9 ± 2.67bc |
Legends: DPCS, date of plate culture sporulation; SG, spore germination; LM, larval mortality; SE, standard error; * selected isolates; RSR, relative sporulation rating; BE, biological efficacy. The same letters in the columns (a, b, c, d, e, f, g, and h) showed the mean values without significant difference at p ≤ 0.05
Spore production potential of isolates over larval cadavers of Tuta absoluta
Plates with larval cadaver of third instar from the former experiment were incubated at room temperature under dark condition to determine spore concentration after 20 days of incubation. The spore concentration was checked by stirring sporulated larval cadaver within 1 ml of sterile water and Tween 80 (0.1% v/v) mixture from five folds of dilution under 40× magnifying microscope using a hemocytomere, and total spore was determined per volume of initial suspension concentration [34].
Dose response of isolates against Tuta absoluta
The most pathogenic eight isolates of Beauveria, which were selected based on their performance of pathogenicity bioassay (isolates indicated by # in Table 2), were evaluated for concentration (LC50 and LC90) mortality response and time taken to kill 50% (LT50) [35]. The stock spore suspension of each isolate was prepared and vortex mixed in sterile distilled water of Tween 80 (0.1% v/v) and adjusted to concentrations of 1 × 104, 1 × 105, 1 × 106, 1 × 107, and 1 × 108 spores·ml-1.
Table 2.
Pathogenicity percentage of isolates against second and third larval instars of Tuta absoluta at 1 × 107 spores·ml-1 concentration in 7 days post inoculation and sporulation potential over the cadavers
| Screened isolates | Species | Accession number | 2nd Instar LM ± SE |
3rd Instar LM ± SE |
Spore conc. per cadaver |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAUB03# | B. bassiana | MT588402 | 94.7 ± 3.08a | 93.3 ± 2.00a | 1.6 × 107 |
| AAUB29# | B. bassiana | MT588415 | 92.0 ± 1.20a | 95.0 ± 3.05a | 1.1 × 107 |
| AAUB28# | B. bassiana | MT588414 | 95.7 ± 2.67a | 95.0 ± 2.12a | 2.1 × 107 |
| AAUB76# | B. bassiana | MT588421 | 88.3 ± 1.09ab | 85.0 ± 3.10ab | 1.5 × 106 |
| AAUB24 | B. bassiana | MT588411 | 81.7 ± 3.62c | 84.0 ± 2.36ab | 8.3 × 106 |
| AAUB05 | B. bassiana | MT588403 | 71.0 ± 2.01de | 75.3 ± 3.76c | 4.6 × 106 |
| AAUB59# | B. bassiana | MT588419 | 85.0 ± 2.50b | 89.0 ± 2.24a | 1.2 × 107 |
| AAUB39# | B. bassiana | MT588416 | 86.7 ± 4.00b | 83.3 ± 3.98b | 1.2 × 107 |
| AAUB46 | B. bassiana | MT588417 | 73.0 ± 2.30d | 71.7 ± 3.61d | 7.3 × 106 |
| AAUB19# | B. bassiana | MT588408 | 94.7 ± 1.08a | 92.0 ± 4.10b | 3.5 × 107 |
| AAUB90# | B. bassiana | MT588422 | 92.0 ± 1.20a | 90.0 ± 3.02ab | 1.2 × 107 |
| AAUB06 | B. bassiana | MT588404 | 65.7 ± 2.67f | 68.3 ± 1.89d | 5.9 × 106 |
Legends: LM, larval mortality; SE, standard error; # reselected isolates for dose determination. The same letters in the columns (a, b, c, d, e, and f) showed the mean values without significant difference at p ≤ 0.05
This test was undertaken on third instar larvae of T. absoluta following the same procedure as before. Median lethal time (LT50) calculation was performed only for three intermediate concentrations (1 × 104, 1 × 106, and 1 × 108 spores·ml-1) to see the effects of low, medium, and high spore concentrations on times required to kill 50% of larvae, and all treatments were replicated three times. Median lethal concentration (LC50) was analyzed by using the probit analysis software of SPSS version 25, and the concentration responses of each replicates were checked for estimation of lethal time to kill 50% (LT50) of exposed larvae.
Chitinolytic enzyme production of isolates
Out of isolates evaluated for dose response, five (AAUB03, AAUB19, AAUB28, AAUB78, and AAUB90) isolates that scored relatively short LT50 and lowest LC50 values were tested for cuticle-degrading enzyme production on plate culture and determined by examination of clear zone formation. The 1% of olive oil for lipase, 0.5% of casein for protease, and 0.5% of colloidal chitin for chitinase productions were added into autoclaved and tempered PDA medium, separately. After trough mixing, the medium was poured into 12-cm diameter of Petri dish and allowed for solidification.
The spores from 20 days of old culture were collected by sterile spatula scraping and suspended into 10 ml of sterile distilled water supplemented with Tween 80 (0.1% v/v) and mixed through vortexing in a Falcon tube. The spore concentrations in the suspensions were adjusted to 1 × 107 conidia·ml-1 using improved Neubauer hemocytometer, and 1 ml of each suspension was transferred to Eppindorf tubes containing potato dextrose broth and incubated at 28 °C for 24 h to initiate spore germination. Growth-initiated spores of each isolates were spotted on PDA medium by impregnating UV-sterilized cotton buds (fohnsoni®). Inoculated plates sealed with laboratorial film (Parafilm®) and incubated at 28 °C in complete dark condition. The clear zone formation on the medium was checked, and if clear zone is formed, the isolate is considered as an enzyme producer, and the size of the clear zone directly correlates with the amount of enzyme produced.
Effect of temperature on the biology of the isolates
The effect of temperature on spore germination of these abovementioned five effective isolates were further evaluated as before by incubating at 15, 20, 28, 35, and 40 °C in complete dark conditions, whereas radial growth of the fungi was determined by using the mycelium disk plating method. The cork borer (6 mm in diameter)–excised mycelium from 72 h of old plate culture were placed on the center of fresh PDA medium, and incubated at 15, 20, 28, 35, and 40 °C under complete dark condition. The diameter of the growing colony was measured at the 12th day after initial inoculation using a ruler, and plates incubated at 28 °C were used as control. The sporulation rate of isolates on different temperature was determined from the culture plates used for radial growth. The starting date of sporulation on the plate was checked side by side with radial growth, and it is extended up to 25 days of first incubation. The date of the first start of sporulation was taken as sporulation beginning date for that specific isolate.
Statistical data analysis
Spore germination, sporulation date, screening test, and pathogenicity test results were analyzed by using one way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and SPSS software version 25 statistical programs. Mean separations were calculated using Tukey’s honestly significant difference (HSD) test when the values were significant at 푝 ≤ 0.05.
Results
Isolation and identification of Beauveria isolates
In this study, 43 soil samples were tested for the presence of the entomopathogenic Beauveria species, of which 27 (63%) were positive for the same (Table 1). Most of them (15 isolates) were isolated from cropland soil, followed by forest (8 isolates) and grassland (4 isolates) soils. All of these fungal isolates produced white conidial masses on the plate culture and had smooth plate reverses showing the distinct morphological features of Beauveria species. Microscopic spore morphology examination demonstrated that these isolates have circular and small-sized spores (data not shown). Although the cultural and morphological distinctiveness of Beauveria clearly gives inference for genus level identification, structural similarity and lack of typical phenotypic attributes at species level required genetically supported identification.
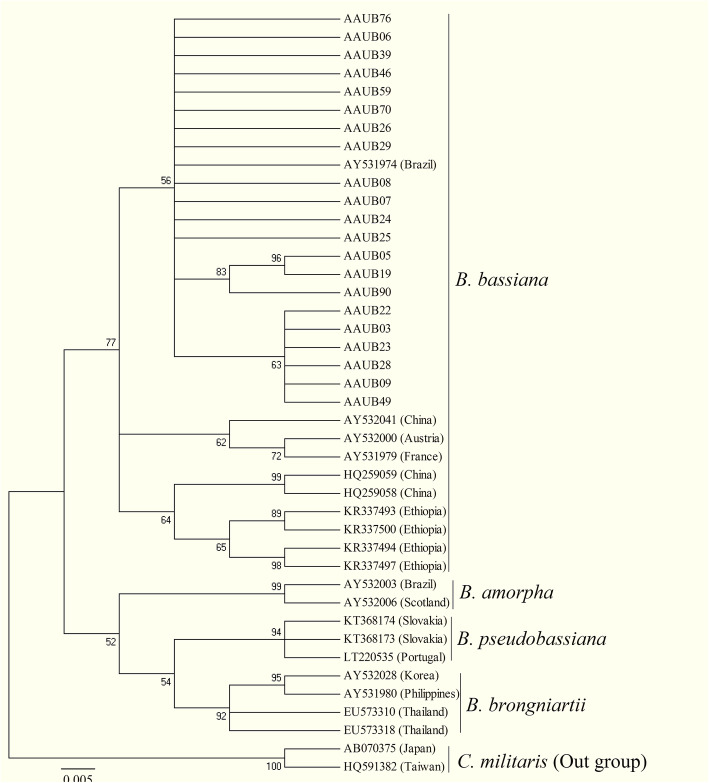
Therefore, the ribosomal internal transcribed spacer (ITS1-8.5S-ITS2) rDNA of all isolates were subjected to conventional PCR amplification, and out of these, 21 isolates showed clear and informative band formation with 554 bp (data not shown). The amplified genes of these 21 isolates were sequenced in both direction, and BLAST search results showed all the isolates had 99–100% similarity with previously documented B. bassiana. These sequences with other 20 (8 sequences obtained from Rehner and Buckley [36], 8 directly from Genbank, and 4 from Belay et al. [18]) ITS sequences of isolates retrieved from the database showed concordant topology (Fig. 1). The constructed phylogenetic tree showed the isolate category, and our isolates were grouped into three categories. Out of 21 isolates, twelve, three, and six isolates showed 56, 83, and 63% bootstrap support with each other, respectively. Two strains under the second category (AAUB05 and AAUB19) showed very distant evolutionary origin as compared with others with strong (96%) support with each other although they were isolated from different (grassland and cropland) sources of soil. Moreover, almost none of the isolates showed relation with previously identified strains, rather, one isolate from Brazil (B. bassiana-AY531974) matched our isolates with bootstrap support of 56% (Fig. 1), and therefore, this shows that our isolates were nearly monophyletic with each other and distinctive from the others.
Fig. 1.
Molecular phylogenic analysis of ITS region of Beauveria isolated from Ethiopian soil and other related sequences retrieved from GenBank. Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree (MEGA4.1) based on ITS sequences from Beauveria species using the neighbor-joining model to construct the tree and the Jukes–Cantor sequence evolution algorithm, with 1000 bootstrap replications. Bootstrap values above 50% are shown. The sequences of our isolates were deposited to NCBI database with accession numbers ranging between MT588402 and MT588422, whereas accession numbers of other previously identified strains were presented on the tree followed by countries in parenthesis
Screening of potential isolates
Morphologically and molecularly identified isolates of B. bassiana were first screened based on their spore viability, sporulation rate, and pathogenicity against their host insect (G. mellonella) through the computation of the biological efficiency index (BEI). All isolates displayed more than 80% of spore germination by showing the significant difference with one another at p ≤ 0.05, except isolate AAUB07 with a low spore germination of 43% (Table 1). They attained sporulation (DPCS) within 10 to12 days with relative sporulation ratings (RSR) of 1.2 to 1.8 on the culture plate and scored 76.7–100% of mortality on larvae of G. mellonella. The computed biological efficiency index (BEI) of isolates was reneged between 62 and 86%, defined on cumulative effect of all the above-working parameters combined (Table 1).
Out of the isolates explored in this study, 12 (44%) isolates scored BEI values of above 80% and screened for further work. These isolates were effective in larval mortality (LM) of 96.7 to 100% against G. mellonella in 10 days of post inoculation. From these, five (AAUB28, AAUB03, AAUB24, AAUB05, and AAUB76) isolates scored highest (85 to 86.1%) BEI values, and other seven isolates scored between 82 and 84.8% BEI values as indicated by asterisk (*) in Table 1. These twelve isolates were used for further pathogenicity bioassay against T. absoluta.
Pathogenicity bioassay against Tuta absoluta
It is interesting to note that most of the prescreened isolates were pathogenically effective against T. absoluta at 1 × 107spores·ml-1concentration in 7 days post inoculation (Table 2). Almost all of these isolates rated moderate (65.7%) to high (95.7%) mortality against both second and third instar larvae of T. absoluta. Five of the isolates (AAUB03, AAUB28, AAUB29, AAUB19, and AAUB90) were highly effective and scored 95, 95, 93.3, 92, and 94.7% of mortality against either of the instar larvae, respectively. The best isolate, AAUB28, was equally pathogenic against both second and third instar larvae, and scored 95.7 and 95% of mortality, respectively. However, the mean pathogenicity among isolates showed marked statistical difference with F (26, 52) = 8.97, p < 0.001 for second instar and F (14, 25) = 8.123, p < 0.001 for third instar larvae. The sporulation potential of these isolates was considerable and produced 4.6 × 106 to 3.5 × 107 spores·ml-1 over the larval cadavers (Table 2).
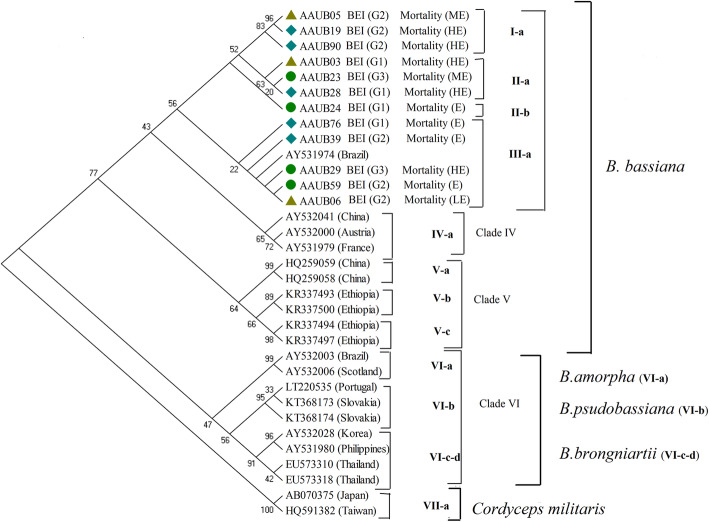
Furthermore, all of these selected isolates of B. bassiana were polyphyletic in source, biological efficiency, and pathogenicity (Fig. 2). For instance, AAUB19 and AAUB90 strains isolated from the cropland soil scored highly effective (HE) mortality against third instar larvae of T. absoluta, whereas AAUB05 isolated from the grassland soil scored moderate (ME) lethality, and all are categorized under G2 of BEI. Most G1 strains obtained from three soil types were scored moderate (ME) to high (HE) lethality against T. absoluta and distributed in different categories. The remaining five strains were isolated from different types of soil; have BEI of G1, G2, and G3; scored moderate (ME) lethality; and grouped in one category (III-a). In general, none of the isolates showed congruence with respect to sources, BEI, and pathogenicity, rather showed intermixed distribution in the tree (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
This cladogram showed the characteristics of twelve Ethiopian potent isolates. First sources of isolates, from grassland soil (▲), cropland soil (♦), and forest soil (●) followed by codes for each isolate and biological efficacy index showing that if BEI > 85 = G1, BEI: 83–85 = G2, BEI: 80–83 = G3. Finally, percentage of mortality against Tuta absoluta was indicated, such as if value is < 70% (less effective, LE), 70–80% (moderately effective, ME), 80–90% (highly effective, HE)
Virulence of isolates against Tuta absoluta
In this study, eight of the most pathogenic strains of B. bassiana were evaluated to determine the effect of the spore concentration against third instar larvae of T. absoluta. These strains scored median lethal time (LT50) values ranging between 3.3 and 5.67 days at 104 spores·ml-1 and 1.93 to 3.17 days at 108 spores·ml-1 concentrations (Table 3). Three strains, AAUB03, AAUB19, and AAUB28 attained the LT50 values at the same 3.33 days, whereas strain AAUB76 scored relatively extended (5.76 days) LT50 values. Similarly, corresponding LC50 values for all selected isolates ranged between 1.5 × 103 and 1.1 × 105 spores·ml-1and LC90 value of 2.8 × 105 and 1.8 × 107 spores·ml-1 (Table 3). The isolates AAUB03, AAUB28, AAUB19, and AAUB90 scored LC50 values of 5.3, 1.3, 1.8, and 2.6 × 103, and AAUB29, AAUB76, and AAUB39 scored 6.5, 9.3, and 1.8 × 104 spores·ml-1, respectively. The least LC50 value (1.1 × 105 spores·ml-1) was scored by isolate AAUB59. In general, concurrent larval mortality increase was recorded in all evaluated isolates as spore concentration and exposure time increased.
Table 3.
The LT50 determination and summary of probit analysis to determine LC50 and LC90 concentrations of Beauveria bassiana strains against the third instar of Tuta absoluta larvae in 10 days post incubation
| LT50 (mean ± SE) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAUB03 | AAUB29 | AAUB28 | AAUB76 | AAUB59 | AAUB39 | AAUB19 | AAUB90 | |
| Spores·ml-1 | ||||||||
| 104 | 3.33± 0.58a | 5.33 ± 0.58c | 3.33± 0.58a | 5.67 ± 0.58cd | 5.00 ± 1.00c | 3.67 ± 0.58ab | 3.33 ± 0.58a | 5.00 ± 1.00c |
| 106 | 2.33± 0.58a | 2.57 ± 0.51a | 2.50± 0.00a | 2.83 ± 0.29ab | 2.93 ± 0.12ab | 2.17 ± 0.29a | 2.33 ± 0.29a | 4.00 ± 0.00c |
| 108 | 1.93± 0.12a | 2.00 ± 0.00a | 2.20± 0.35a | 2.33 ± 0.29a | 2.50 ± 0.50ab | 2.00 ± 0.35a | 2.00 ± 0.62a | 3.17 ± 0.29c |
| Summary of probit analysis | ||||||||
| LC50 | 5.3 × 103 | 6.5 × 104 | 1.5 × 103 | 9.3 × 104 | 1.1 × 105 | 1.8 × 104 | 1.8 × 103 | 2.6 × 103 |
| 95% FL | 1.3 × 103 –7 × 104 | 2.2 × 104–1.5 × 105 | 8.6 × 102–4.9 × 103 | 9.9 × 103–1.3 × 104 | 2 × 104–3.3 × 105 | 3.9 × 103–6 × 104 | 1 × 103–6.1 × 104 | 1.2 × 103–3.1 × 104 |
| LC90 | 2.8 × 105 | 1.7 × 106 | 2.9 × 105 | 1.6 × 106 | 1.8 × 107 | 1.6 × 107 | 7.6 × 105 | 1.2 × 107 |
| 95% FL | 2.1 × 105 –6.3 × 106 | 6.3 × 105–1.1 × 107 | 1.9 × 104–2.9 × 106 | 1.8 × 105–2.7 × 107 | 4.2 × 106–2.8 × 108 | 2.2 × 106–3.1 × 108 | 7.1 × 104–2.1 × 107 | 1.5 × 106–7.3 × 108 |
| Int ± SE | 1.32 ± 0.91 | 4.33 ± 0.89 | 0.85 ± 0.83 | 1.16 ± 0.72 | 2.91 ± 0.66 | 1.54 ± 0.64 | 0.8 ± 0.75 | 1.19 ± 0.63 |
| S ± SE | 0.49 ± 0.18 | 0.9 ± 0.17 | 0.39 ± 0.16 | 0.39 ± 0.13 | 0.58 ± 0.11 | 0.39 ± 0.11 | 0.36 ± 0.14 | 0.35 ± 0.11 |
| p value | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | < 0.012 | < 0.003 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 |
Legends: FL, fiducial limit; SE, standard error; LT, lethal time taken to kill fifty of experimental organisms; LC, lethal concentration; Int, intercept; S, slope. The same letters in the columns (a, b, c, d, e, and f) showed the mean values without significant difference at p ≤ 0.05
Chitinolytic enzyme production of effective isolates
Out of eight potent isolates, five isolates that scored short LT50 and lowest LC50 values were evaluated about their pathogenicity-enhancing chitinolytic enzyme production potential using the clear zone determination method. The strains of B. bassiana which are capable to produce lipase, protease, and chitinase enzymes were highly pathogenic against their target pests. Therefore, five of our isolates were lipase, protease, and chitinase positive and showed clear zone formation on respective medium for each enzyme. However, the clear zone formation for each enzyme type varied among isolates (Table 4). Two isolates (AAUB03 and AAUB28) showed large (+++) clear zones on the PDA medium supplemented with casein as compared with other three isolates (Table 4). The large clear zone formation phenomenon may correlate with the amount of protease secreted by the fungal isolates. The remaining three (AAUB29, AAUB19, and AAUB90) isolates that scored 95, 92, and 90% of mortality against third instar larvae of T. absoluta formed intermediate (++) clear zones by protease (Table 4). The isolate AAUB03 continued production of better (++) clear zones on the medium supplemented with colloidal chitin than the others, those formed small (+) clear zones. Furthermore, isolates showed very small (+) clear zone formation on the medium supplemented with olive oil that correlates with less production of lipase enzyme (Table 4).
Table 4.
Extracellular enzyme production of five selected strains on agar culture medium
Effect of temperature on the biology of isolates
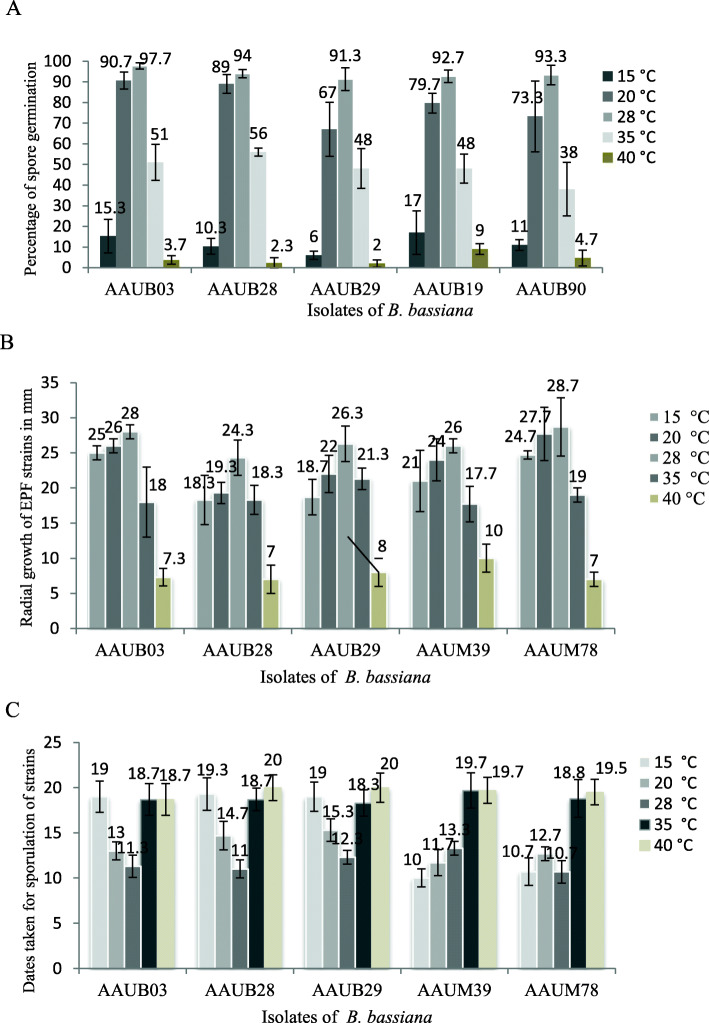
Temperature is the most important abiotic factor that influences the biology of EPF strains. Isolates that adapt temperatures ranging out of the optimum may be considered to be used in adverse conditions for pest control. Therefore, we have evaluated five of effective isolates for their spore germination, radial growth, and sporulation potential at different temperature classes (Fig. 3). Consequently, all tested isolates showed an effect on conidial germinations between 6 and 17%, and two of them (AAUB03 and AAUB90) showed better (15.3 and 17%) germination at 15 °C (Fig. 3A). All of the isolates showed almost better conidial germination ranging between 67 and 90.7% at 20 °C and above 90% of germination at 28 °C (Fig. 3A). The conidial germination of all the strains was highly affected at 35 °C that reduced almost between 38 and 55.3% germination, and almost none of the spores germinated at 40 °C temperature (Fig. 3A).
Fig. 3.
Effect of temperature on the spore germination (A) radial growth (B), and dates taken for sporulation (C) of B. bassiana isolates
Similarly, isolates showed normal radial growth at 20 and 30 °C; however, it was highly affected at 35 °C and 40 °C (Fig. 3B), while the radial growth of isolate AAUB28 was highly affected than the other isolates in all temperature ranges. Interestingly, AAUB03, AAUB19, and AAUB90 showed almost the same radial growth rate with positive control at 15 °C (Fig. 3B). In the same way, low and high temperature range, also affected the sporulation rates of the strains; however, temperature at 20 °C is better tolerated as compared with others (Fig. 3C).
Discussion
The first stage of infection of insects by entomopathogenic fungi (EPF) is the adhesion of the spore or conidia on the cuticle of the insect. The subsequent germination and generation of a macromolecular structure called appresorium, or the formation of a spore germ tube, induces the secretion of hydrolytic enzymes to begin the degradation of the insect’s integument [37–40]. Since the formation of appressorium in all B. bassiana strains is not yet clear [41], some strains of this fungus in contact with artificial surfaces generated an appressorial-like structure under laboratory conditions [42]. Literatures showed that the adherence of B. bassiana to the insect cuticle starts the secretion of hydrolytic enzymes, such as chitinase, protease, lipases, and glycosidase that play a crucial role on cuticle degradation [37, 38, 43]. Among these enzymes, the activity levels of chitinase, protease, and lipase have been shown to correlate with the degree of virulence of isolates [44–46].
As mentioned above, the virulence of EPF might be determined by the genetic makeup of the strains based on their adaptation of different geographical and ecological exposures to regulate expression of these hydrolytic enzymes [39, 40, 47]. Therefore, we have checked the production of lipase, protease, and chitinase enzymes by isolates of B. bassiana on the medium supplemented with respective substrates; however, the size of the clear zones formed for each types of enzymes vary from isolate to isolate. The variation of extracellular enzyme production within different EPF isolates was common phenomenon [45, 48]. This variation may be due to substrate quality, genetic variation, or adaptive attributes of enzyme-coding genes in the fungal isolates.
Literatures showed that lipase is an important lipolytic enzyme of EPF that facilitates the spore attachment on the integument of insect and starter of hydrolysis of the uppermost component, fatty acid of the cuticle [49–52]. Thus, our isolates formed small clamps around the colony on the medium supplemented with olive oil, showing that isolates were lipase positive, but the production is very low. On the other hand, protease has been identified as an important virulence factor of EPF isolates and is involved in the cleaving of peptide bonds of cuticle proteins and enhances the virulence against targeted insects [53]. Concordantly, the most potent isolates that scored 94 and 95% of mortality against T. absoluta showed large clear zone formation, and this implies that the amount of protease might be directly correlated with virulence of isolates. Therefore, their virulence could be associated with their ability of extracellular enzyme production. Other researchers reported high virulence of B. bassiana with their ability of producing large amounts of protease [45]. Furthermore, isolates were chitinase positive and formed clear zones on the medium supplemented with colloidal chitin; however, the clear zone formation is varying from isolate to isolate. This enzyme degrades chitin that is the main component of insect cuticle and finalizes the integument degradation following protease activity [54].
Thus, we have screened putative strains of B. bassiana from the different sources of local environment to obtain effective candidates for pest control. In this study, 27 isolates of B. bassiana were recovered from the cropland soil (55.6%), forest soil (29.6%), and grassland (14.8%) soil (Table 1), which is comparable with other reports on B. Bassiana (52.1%) from the soils of eastern Ethiopia, 80% of isolates from the natural forest, and 23% from cropland soils of Jimma Zone [18].
These isolates were analyzed for their genetic relations, and the resulted phylogenetic tree grouped isolates into three distinctive categories in which all are nearly monophyletic as similar to reports of others showing that the variations of most strains of B. bassiana are insignificant regardless of geographical locations [36, 55–57]. However, in the present study, isolates of B. bassiana showed different categorization and would correspond to new isolates, which is different from previously published Ethiopian isolates [18] because all the isolates previously described in Ethiopia appear in other clades (Fig. 1). This could give an important clue to investigate the most distinctive strains of B. bassiana from Ethiopian soil samples. Although isolates are unique from the other previously identified strains, all isolates showed less genetic variation among each other. This might lead to hypothesize that the soil type and sample location may not influence the genetic makeup of the isolates recovered.
In addition, biological characteristics such as spore viability, sporulation rate, and pathogenicity against their host insect are the vital attributes to screen effective strains of entomopathogens [31]. Therefore, we have screened our isolates based on the biological efficiency index determination (31), and 12 (44.4%) of the isolates were scored above 80% of BEI. These isolates achieved more than 90% of spore germination, 90–100% of larval mortality against G. mellonella, and sporulated within 10 to 12 days of culturing on the medium with relative sporulation rating (RSR) of 1.3 to 1.8. Similarly, different researchers screened effective EPFs for an agriculturally important pest control using these attributes [58, 59].
All of the screened isolates showed promising (65.7–95.7% and 68.3–95%) mortality rates against second and third instar larvae of T. absoluta, respectively. Interestingly, five (AAUB03, AAUB28, AAUB29, AAUB19, and AAUB90) of the isolates were scored 90–95.7% of mortality at 1 × 107 spores·ml-1 concentration. This is concurrent with other reports on B. bassiana that scored 90% of mortality against T. absoluta in Egypt [60]. In addition, recently explored Ethiopian isolate of B. bassiana displayed 95.8% of mortality against third instar larvae of T. absoluta at 2.5 × 109 spores·ml-1 [61]. In all cases, Ethiopian isolates of B. bassiana performed better than the commercially formulated products (Beauvitech® WP) that scored 60.8% of larval mortality against T. absoluta at 108 spores·ml-1 in Rwanda [62]. This could infer that locally screened isolates might be pathogenically effective than commercialized ones, and geographic origin of isolates may determine their pathogenicity.
Furthermore, these pathogenically valued isolates of B. bassiana showed almost equal efficacy against both second and third instar larvae of T. absoluta by scoring 95.7% and 95% of mortality, respectively, which is contradicting to reports of Tsownara and Port [63] which showed that third instar larvae of T. absoluta is more susceptible to B. bassiana than the second instar larvae. In addition, these isolates produced considerable (4.6 × 106 to 3.5 × 107 spores·ml-1) amount of spores over the dead larval cadavers. This makes that fungal spores are easily disseminated between insects through the process of auto-dissemination. Thus, high sporulation potential of EPF over the cadavers enhanced horizontal pest infection through the self-spore contamination process [64]. Besides, our isolates scored shortest (1.93 to 3.17 days) median lethal time (LT50) at 108 spores·ml-1, which were different from the two commercially formulated Beauveria (Beauvitech® WP and Botanigard® ES) that scored somewhat extended LT50 values of 5.2 and 6.6 days at the same spore concentration against T. absoluta, respectively [62]. This is at least twice the LT50 value of the Ethiopian isolates presented here. However, a former Ethiopian isolate of B. bassiana scored a LT50 value of 5.2 days at the spore concentration of 2.5 × 109 spores·ml-1 [61], which takes considerably longer time to kill 50% of third instar larvae of T. absoluta as compared with their spore concentration.
It is interesting to mention that effective isolates of B. bassiana in this study scored promising LC50 and LC90 (1.5 × 103 and 2.8 × 105 spores·ml-1) values against third instar larvae of T. absoluta, respectively. Similarly, other isolates of B. bassiana scored LC50 values of 4.5 × 105 and 3.6 × 105 spores·ml-1against second and third instar larvae of T. absoluta, respectively [65]. Usually, when the spore concentration and exposure time increases concurrently, larval mortality also increases in all evaluated strains of B. bassiana, which is comparable with other findings [61, 63, 65].
Although locally isolated EPF strains showed better performance on biocontrol activity, different abiotic factors might influence survival of the bioagents. Temperature is one of the abiotic factors that could influence spore germination, mycelial growth, and spore production of the fungal isolates [66]. We have checked both lower and upper temperature ranges against spore germination, radial growth, and sporulation rate of the some selected potent isolates and temperatures at 20 to 30 °C showed nil effect on spore germination, mycelial growth, and sporulation. Similarly, others reported that temperature ranging at 24–30 °C was optimum for spore germination, mycelial growth, and speculation [54]. However, temperature lower than 20 °C and above 30 °C was highly adverse for spore germination of B. bassiana [67], which is concurrent to our study.
Conclusion
This study explains the presence of more indigenous strains of B. bassiana in different soil types of Ethiopia with better entomopathogenic characteristics and that is crucial to develop ecofriendly biopesticides for sustainable agriculture. Molecular analysis of these isolates showed monophyletic attributes about genetic relationships and polyphyletic characters about sources, biological efficacy, and pathogenicity against the host insect. Among the isolates of B. bassiana, two (AAUB03 and AAUB28) isolates showed strong efficacy against T. absoluta with short LT50 and low LC50 values. These isolates were chitinolytic enzyme producers and better growers at optimum temperatures. Therefore, these indigenous B. bassiana were effective against T. absoluta under laboratory conditions; however, further investigation at the actual field is required for mass production.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the financial support of “The Healthy Seedling Project” granted by both the Ethiopian Biotechnology Institute (EBtI) and The Regional Project Supported by the Australian Development Agency (ADA).
Abbreviations
- AAU
Addis Ababa University
- ANOVA
Analysis of variance
- APPRC
Ambo Plant Protection Research Center
- BEI
Biological Efficiency Index
- BLAST
Basic Local Alignment Search Tool
- DPCS
Date of plate culture sporulation
- EDTA
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- EPF
Entomopathogenic fungi
- HE
Highly effective
- IPM
Integrated pest management
- ITS
Internal transcribed spacer
- JC
Jukes–Cantor
- LC
Lethal concentration
- LE
Less effective
- LM
Larval mortality
- LT
Lethal time
- NCBI
National Center for Biotechnology Information
- NJ
Neighbor-joining
- ME
Moderately effective
- MEGA
Molecular Evolutionary Genetic Analysis
- PCS
Plate culture sporulation
- PCR
Polymerase chain reaction
- PDA
Potato dextrose agar
- RSR
Relative sporulation rate
- SE
Standard error
- SG
Spore germination
- SPSS
Statistical Package for the Social Sciences
- TBE
Tris-borate-EDTA
- USEPA
United States of Environmental Protection Agency
Authors’ contributions
BA proposed the study, conducted experimental work, analyzed the data, and wrote manuscript draft. JV performed molecular work, processed DNA sequencing, and performed molecular data analysis. FA and DM read and edited the manuscript. The authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Healthy Seedling and the Australian Development Agency projects given to improve tomato production in Ethiopia and Fellowship program of the University of Chile.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used for this work are available with the corresponding author when legal request is presented.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Taylor JAR, Herms AD, Cardina J, Moore HR. Climate change and pest management: unanticipated consequences of trophic dislocation. Agronomy. 2018;8(7):1–23. doi: 10.3390/agronomy8010007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Biondi A, Wan F, Guedes CNR, Desneux N. Ecology, worldwide spread, and management of the invasive South American tomato pinworm, Tuta absoluta: past, present and future. Annu Rev Entomol. 2018;63:239–258. doi: 10.1146/annurev-ento-031616-034933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Urbaneja A, Vercher R, Navarro V, Garci´a F. Porcuna L. La polilla del tomate, Tuta absoluta. Phytoma Espan˜a. 2007;194:16–23. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tonnang ZEH, Mohamed FS, Khamis F, Ekesi S. Identification and risk assessment for worldwide invasion and spread of Tuta absoluta with a focus on Sub Saharan Africa: implications for phytosanitary measures and management. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0138319. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Santana AP, Kumar L, Da Silva SR, Picanço CM. Global geographic distribution of Tuta absoluta as affected by climate change. J Pest Sci. 2019;92:1373–1385. doi: 10.1007/s10340-018-1057-y. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rwomushana I, Beale T, Chipabika G, Day R, Gonzalez-Moreno P, Lamontagne-Godwin J, Makale F, Pratt C, Tambo J (2019) Evidence note: tomato leafminer (Tuta absoluta): impacts and coping strategies for Africa. CABI Working Paper:12–56. 10.1079/CABICOMM-62-8100
- 7.Retta NA, Berhe HD. Tomato leafminer, Tuta absoluta (Meyrick), a devastating pest of tomatoes in the highlands of Northern Ethiopia: a call for attention and action. Rev Res J Agric Environ Manage. 2015;4(6):264–269. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Shiberu T, Getu E. Determination of the economic threshold level of tomato leaf miner, Tuta absoluta Meyrick (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) on tomato plant under glasshouse conditions. J Horticulture Forestry. 2018;10(2):9–16. doi: 10.5897/JHF2018.0522. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Arnó J, Gabarra R, Molina P, Godfrey EK, Zalom GF. Tuta absoluta (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) success on common solanaceous species from California tomato production. Environ Entomol. 2019;48(6):1394–1400. doi: 10.1093/ee/nvz109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Desneux N, Wajnberg E, Wyckhuys GAK, Burgio G, Arpaia S, Narvaez-Vasquez AC, Gonzalez-Cabrera J, Ruescas CD, Tabone E, Frandon J, Pizzol J, Poncet C, Cabello T, Urbaneja A. Biological invasion of European tomato crops by Tuta absoluta: ecology, geographic expansion and prospects for biological control. J Pest Sci. 2010;83(3):197–215. doi: 10.1007/s10340-010-0321-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cherif A, Mansour R, Grissa-Lebdi K. Biological aspects of tomato leafminerTuta absoluta (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) in conditions of Northeastern Tunisia: possible implications for pest management. Environ Exp Biol. 2013;11:179–184. [Google Scholar]
- 12.De Smedt C, Van Damme V, De Clercq P, Spanoghe P. Insecticide effect of zeolites on the tomato leafminer Tuta absoluta (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) Insects. 2016;7(4):72–85. doi: 10.3390/insects7040072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Roditakis E, Grispou M, Nauen R, Vasakis E, Stavrakaki M, Gravouil M, Bassi A. First report of Tuta absoluta resistance to diamide insecticides. J Pest Sci. 2015;88(1):9–16. doi: 10.1007/s10340-015-0643-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Negatu B, Kromhout H, Mekonnen Y, Vermeulen R. Use of chemical pesticides in Ethiopia: a cross-sectional comparative study on knowledge attitude and practice of farmers and farm workers in three farming systems. Ann Occup Hyg. 2016;60(5):551–566. doi: 10.1093/annhyg/mew004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Naranjo ES, Ellsworth CP, Frisvold BG. Economic value of biological control in integrated pest management of managed plant systems. Annu Rev Entomol. 2015;60(1):621–645. doi: 10.1146/annurev-ento-010814-021005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Inglis DG, Goettel SM, Butt MT, Strasser H (2001) Use of hyphomycetous fungi for managing insect pests. Fungi as Biocontrol Agents(Butt TM, Jackson C, Magan N, eds):23–70
- 17.Jaber S, Mercier A, Knio K, Brun S, Kambris Z. Isolation of fungi from dead arthropods and identification of a new mosquito natural pathogen. Parasit Vectors. 2016;9(491):1–10. doi: 10.1186/s13071-016-1763-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Belay CY, Meressa HB, Alemu T, Hallmann J. Molecular detection of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana from soils of coffee growing areas in Ethiopia using rDNA-ITS. J Appl Biosci. 2017;119:11943–11953. [Google Scholar]
- 19.NiuX XW, Zhang J, Hu Q. Biodiversity of entomopathogenic fungi in the soils of South China. Microorganisms. 2019;7(311):1–14. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7090311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Allegrucci N, Velazquez SM, Russo LM, Perez E, Scorsetti CA. Endophytic colonization of tomato by the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana: the use of different inoculation techniques and their effects on the tomato leafminer Tuta absoluta (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) J Plant Protection Res. 2017;57(4):331–337. doi: 10.1515/jppr-2017-0045. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rohrlich C, Merle I, Hassani I, Verger M, Zuin M, Besse S. Variation in physiological host range in three strains of two species of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria. PLoS One. 2018;13(7):e0199199. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mora EAM, Castilho CMA, Fraga EM. Classification and infection mechanism of entomopathogenic fungi (Review) Agric Microbiol Review Article. 2017;84(0):1–10. doi: 10.1590/1808-1657000552015. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Faria MR, Wraight SP. Mycoinsecticides and mycoacaricides: a comprehensive list with worldwide coverage and international classification of formulation types. Biol Control. 2007;43(3):237–256. doi: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2007.08.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wang J, Zheng C. Characterization of a newly discovered Beauveria bassiana isolate to Franklimiella occidentalis Perganda, a non-native invasive species in China. Microbiol Res. 2012;167(2):116–120. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2011.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fernandes ÉKK, Moraes ÁML, Pacheco RS, Rangel DEN, Miller MP, Bittencourt VREP, Roberts DW. Genetic diversity among Brazilian isolates of Beauveria bassiana: comparisons with non-Brazilian isolates and other Beauveria species. J Appl Microbiol. 2009;107(3):760–774. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Meyling VN (2007) Methods for isolation of entomopathogenic fungi from the soil environment. Thorval dsensvej 40, DK-1871 Frederiksberg C, Denmark, pp1-19.
- 27.Rehner SA, Minnis AM, Sung GH, Luangsa-ard JJ, Devotto L, Humber RA. Phylogeny and systematics of the anamorphic, entomopathogenic genus Beauveria. Mycologia. 2011;103(5):1055–1073. doi: 10.3852/10-302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Chi M, Park S, Lee Y. A quick and safe method for fungal DNA extraction. Plant Pathol J. 2009;25(1):108–111. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.2009.25.1.108. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor JW. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ, editors. PCR Protocols: a guide to methods and applications. New York pp: Academic Press Inc; 1990. pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Habtegebriel B, Getu E, Dawd M, Seyoum E, Atnafu G, Khamis F, Hilbur Y, Ekesi S, Larsson CM. Molecular characterization and evaluation of indigenous entomopathogenic fungal isolates against Sorghum Chafer, Pachnoda interrupta (Olivier) in Ethiopia. J Entomol Nematol. 2016;8(5):34–45. doi: 10.5897/JEN2016.0159. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sain KS, Monga D, Kumar R, Nagrale TD, Hiremani SN, Kranthi S. Compatibility of entomopathogenic fungi with insecticides and their efficacy for IPM of Bemisia tabaci in cotton. J Pestic Sci. 2019;44(2):97–105. doi: 10.1584/jpestics.D18-067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sabbour MM, Singer SM (2014) Evaluations of two Metarhizium varieties against Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) in Egypt. IJSR3:1983–1987
- 33.Abbott WS. A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J Econ Entomol. 1925;18(2):265–267. doi: 10.1093/jee/18.2.265a. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Tefera T, Pringle LK. Effect of exposure method to Beauveria bassiana and conidia concentration on mortality, mycosis, and sporulation in cadavers of Chilo partell (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) J Invertebr Pathol. 2003;84(2):90–95. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2003.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tefera T, Pringle LK. Evaluation of Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae for controlling Chilo partellus (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) in Maize. Biocontrol Sci Tech. 2004;14(8):849–853. doi: 10.1080/0958315041000172707. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Rehner AS, Buckley E. A Beauveria phylogeny inferred from nuclear ITS and EF1-a sequences: evidence for cryptic diversification and links to Cordyceps teleomorphs. Mycologia. 2005;97(1):84–98. doi: 10.1080/15572536.2006.11832842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Binod P, Sukumaran RK, Shirke SV, Rajput JC, Pandey A. Evaluation of fungal culture fíltrate containing chitinase as a biocontrol agent against Helicoverpa armigera. J Appl Microbiol. 2007;103(5):1845–1852. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03428.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Esparza MA, Conteiro CAM, Fraga ME. Classification and infection mechanism of entomopathogenic fungi. Arq Inst Biol. 2017;84:1–10. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Pinnamaneni R, Kalidas p, Rao S. Cloning and expression of Bbchit1 gene of Beauveria bassiana. Open Entomol J. 2010;4(1):30–35. doi: 10.2174/1874407901004010030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Mondal S, Baksi S, Koris A, Vatai G. Journey of enzymes in entomopathogenic fungi. Pacific Sci Rev A Nat Sci Eng. 2016;18(2):85–99. doi: 10.1016/j.psra.2016.10.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Guerri-Agulloo B, Gomez-Vidal S, Asensio L, Barranco P, Lopez-Llorca LV. Infection of the red palm weevil (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus) by the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana: a SEM study. Microsc Res Tech. 2010;73:714–725. doi: 10.1002/jemt.20812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Zhang S, Xia XY, Kim B, Keyhani ON. Two hydrophobins are involved in fungal spore coat rodlet layer assembly and each play distinct roles in surface interactions, development and pathogenesis in the entomopathogenic fungus, Beauveria bassiana. Mol Microbiol. 2010;80(3):811–826. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07613.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Holder DJ, Kirkland BH, Lewis MW, Keyhani NO. Surface characteristics of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. Microbiology. 2007;153(10):3448–3457. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/008524-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Cho EM, Boucias D, Keyhani NO (2006) EST analysis of cDNA libraries from the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana II. Fungal cells sporulating on chitin and producing oosporein. Microbiology.152:2855–2864. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 45.Dhawan M, Joshi N. Enzymatic comparison and mortality of Beauveria bassiana against cabbage caterpillar Pieris brassicae. Braz J Microbiol. 2017;48(3):522–529. doi: 10.1016/j.bjm.2016.08.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Khosravi R, Sendi JJ, Zibaee A, Shokrgozar MA. Virulence of four Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo) (Asc., Hypocreales) isolates on rose sawfly, Argerosae under laboratory condition. J. King Saud. Univ Sci. 2015;27:49–53. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Arruda W, Lubeck I, Schrank A, Vainstein HM. Morphological alterations of Metarhizium anisopliae during penetration of Boophilus microplus ticks. Exp Appl Acarol. 2005;37(4):231–244. doi: 10.1007/s10493-005-3818-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Mustafa U, Kaur G. Extracellular enzyme production in Metarhizium anisopliae isolates. Folia Microbiol. 2009;54(6):499–504. doi: 10.1007/s12223-009-0071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Keyhani ON. Lipid biology in fungal stress and virulence: entomopathogenic fungi. Review Fungal Biology XXX. 2017;122(6):1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.funbio.2017.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Charnley KA. Fungal pathogens of insects: cuticle degrading enzymes and toxins. Adv Bot Res. 2003;40:241–321. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2296(05)40006-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Fernandes EG, Valerio HM, Feltrin T, Van der Sand ST. Variability in the production of extracellular enzymes by entomopathogenic fungi grown on different substrates. Braz J Microbiol. 2012;43(2):827–833. doi: 10.1590/S1517-83822012000200049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Rodrigues CJBC, Perinotto WMD, da Silva WOB, Santi L, Berger M, Marciano AF, de Sa FA, Nogueira MRD, QuinelatoS,Bittencourt VREP Virulence, proteolytic and lipolytic activities of Brazilian Beauveria bassiana s.l. isolates (Hypocreales: Clavicipitaceae) to Rhipicephalus microplus ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) Biocontrol Sci Tech. 2016;26(2):239–249. doi: 10.1080/09583157.2015.1091876. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 53.St Leger R. The role of cuticle-degrading proteases in fungal pathogenesis of insects. Can J Bot. 2011;73(1):1119–1125. doi: 10.1139/b95-367. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.St Leger JR, Cooper MR, Charnley KA. Cuticle-degrading enzymes of entomopathogenic fungi: regulation of production of chitinolytic enzymes. J Gen Microbiol. 1986;132(6):1509–1517. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-6-1509. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Muro MA, Elliott S, Moore D, Parker BL, Skinner M, Reid W, El Bouhssini M. Molecular characterization of Beauveria bassiana isolates obtained from overwintering sites of Sunn pests (Eurygaster and Aelia species) Mycol Res. 2005;109(3):294–306. doi: 10.1017/S0953756204001832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Sayed MS, Ali FE, El-Arnaouty AS, Mahmoud FS, Amer AS. Isolation, identification, and molecular diversity of indigenous isolates of Beauveria bassiana from Taif region, Saudi Arabia. Egyptian J Biological Pest Control. 2018;28:1–6. doi: 10.1186/s41938-017-0002-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Garrido-Jurado I, Márquez M, Ortiz-Urquiza A, Santiago-Álvarez C, Iturriaga AE, Quesada-Moraga E, Enrique Monte E, Hermosa R. Genetic analyses place most Spanish isolates of Beauveria bassiana in a molecular group with word-wide distribution. BMC Microbiol. 2011;11(1):1–12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Mar TT, Lumyong S, Suwannarach N. Isolation of entomopathogenic fungi from Northern Thailand and their production in cereal grains. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012;28(12):3281–3291. doi: 10.1007/s11274-012-1139-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Saleh MME, Abdel-Raheem AM, Ebadah MI, Elbehery HH. Natural abundance of entomopathogenic fungi in fruit orchards and their virulence against Galleria mellonella larvae. Egyptian J Biological Pest Control. 2016;26(2):203–207. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Youssef AN. Efficacy of the entomopathogenic nematodes and fungi for controlling the tomato leaf miner, Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) Arab Univ J Agri Sci. 2015;23(2):591–598. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Tadele S, Emana G. Entomopathogenic effect of Beauveriabassiana (Bals.) and Metarrhizium anisopliae (Metschn.) on Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) larvae under laboratory and glasshouse conditions in Ethiopia. J Plant Pathol Microbiol. 2017;8(5):411–414. doi: 10.4172/2157-7471.1000411. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Ndereyimana A, Nyalala S, Murerwa P, Gaidashova S. Pathogenicity of some commercial formulations of entomopathogenic fungi on the tomato leaf miner, Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) Egyptian J Biological Pest Control. 2019;29(70):1–5. doi: 10.1186/s41938-019-0184-y. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Tsowlnara D, Port G. Efficacy of Beauveria bassiana strain, Bacillus thuringiensis and their combination against the tomato leafminer Tuta absoluta. Entomologia Hellenica. 2016;25(2):23–30. doi: 10.12681/eh.11548. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Conceschi RM, Moral AR, D’Alessandr PC, Demetri BGC, Junior DI. Transmission potential of the entomopathogenic fungi Isaria fumosorosea and Beauveria bassiana from sporulated cadavers of Diaphorin acitri and Toxopter acitricida to uninfected D. citri adults. BioControl. 2016;61(5):567–577. doi: 10.1007/s10526-016-9733-4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Shalaby HH, Faragalla FH, El-Saadany HM, Ibrahim AA. Efficacy of three entomopathogenic agents for control the tomato borer, Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) Nat Sci. 2013;11:63–72. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Pelizza SA, Medina H, Ferreri NA, Elíades LA, Pocco ME, Stenglein SA, Lange CE. Virulence and enzymatic activity of three new isolates of Beauveria bassiana (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) from the South American locust Schistocerca cancellata (Orthoptera: Acrididae) J King Saud Univ Sci. 2020;32(1):44–47. doi: 10.1016/j.jksus.2017.11.006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Kiewnick S. Effect of temperature on growth, germination, germ-tube extension and survival of Paecilomy ceslilacinus strain 251. Biocontrol Sci Tech. 2006;16(5):535–546. doi: 10.1080/09583150500532766. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used for this work are available with the corresponding author when legal request is presented.