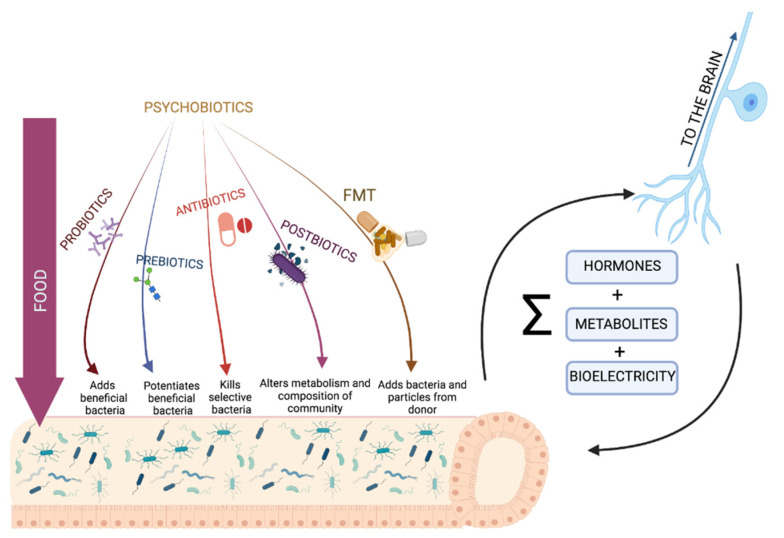
Figure 2.
Microbiota–gut–brain–axis-targeted approaches. Food and psychobiotics [114] are the main exogenous factors whose impacts on the brain are mediated through gut bacteria. The pathways for bacteria–brain bidirectional communication, although still largely unknown, could involve hormones; metabolites; and, as recently proposed, bioelectrical signals [39,40]. FMT, fecal microbiota transplantation. Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 25 July 2021).