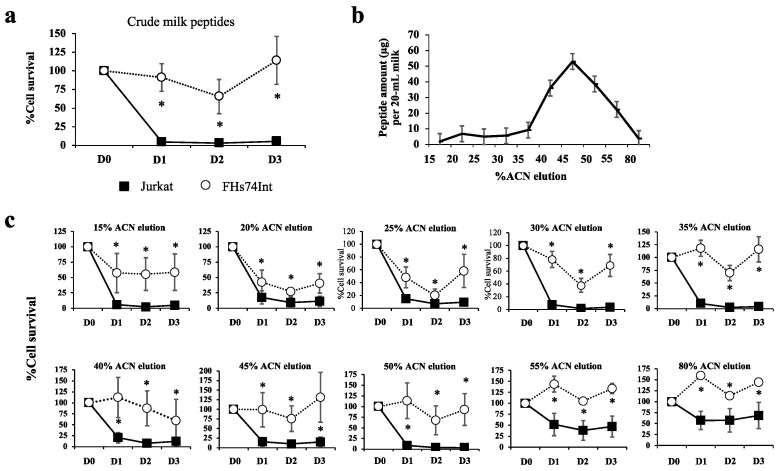
Figure 2.
Fractionation of peptides from human milk and cytotoxicity of fractions towards leukemic and normal cells. Ten samples of human milk were divided into 3 pools. Twenty milliliters of each pool were centrifuged at 4 °C to remove cells, lipid, and extracellular vesicles. The crude milk peptides obtained from each pool were separately eluted through a cut-off column of <3 kDa, and the eluate was loaded to a C18 SPE column. Milk peptides bound to the C18 SPE column were eluted with various concentrations of acetonitrile (ACN) from 15% ACN to 80% ACN (1 mL each). Eluted fractions of milk peptides were dried using a SpeedVac concentrator, resuspended in a culture medium and then used to treat Jurkat (black square) and FHs74Int cells (white circle), using 3 biological replicates. WST-1 assay was applied to measure cell viability. (a) % cell survival (mean ± SEM) after the treatment of cells with crude milk peptides for 1 (D1), 2 (D2), or 3 (D3) days, compared to those of the untreated control (D0); (b) amounts of peptides eluted from the C18 SPE column eluted in a stepwise manner using 1 mL each of increasing ACN concentrations of 15%, 20%, 25%, 30%, 35%, 40%, 45%, 50%, 55%, and 80% ACN. Peptides were quantitated by the Bradford method and shown as mean ± SEM; (c) % cell survival (mean ± SEM) after the treatment of cells with eluates obtained at different %ACN concentration, for 1 day (D1), 2 days (D2), or 3 (D3) days, compared to those of the untreated controls (D0). * p < 0.05 comparing to the untreated condition.