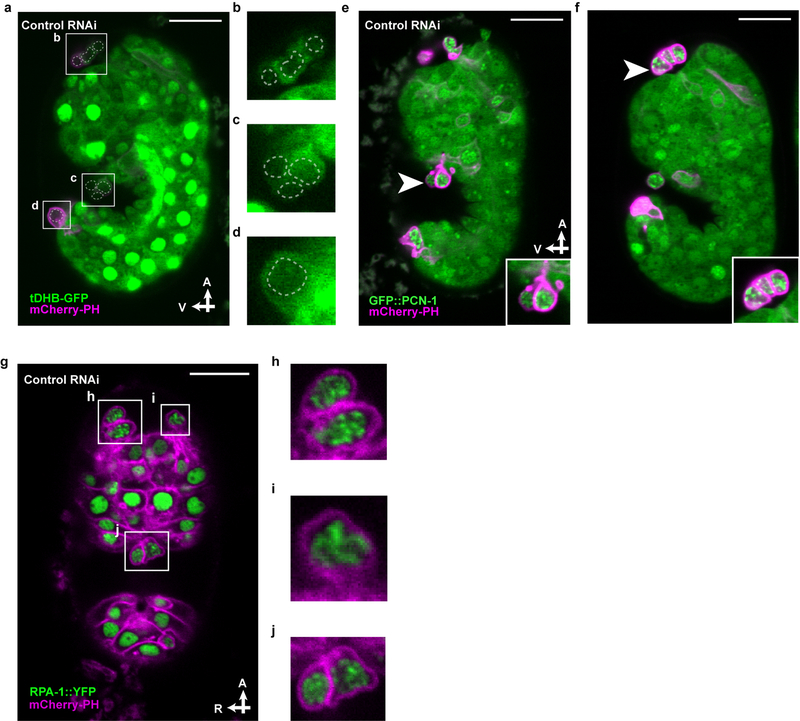
Extended Data Figure 4. All extruded cells display features of cell cycle entry, S-phase arrest, and replication stress.
a-d, tDHB-GFP fluorescence in unidentified extruded cells from (b) the anterior sensory depression, (c) the ventral pocket, and (d) the posterior tip of a comma stage embryo of the genotype heSi192[Peft-3::tDHB-GFP]; ced-3(lf); nIs861[Pegl-1::mCherry::PH] after RNAi against empty vector control. Nuclei of extruded cells, as identified by Nomarski optics, are marked by dotted lines. e, f, micrographs of GFP::PCN-1 fluorescence in unidentified extruded cells (arrowhead) at (e) the ventral pocket or (f) the anterior sensory depression from ced-3(lf); isIs17[Ppie-1::GFP::pcn-1]; nIs861 embryos after (e) RNAi against empty vector control or (f) no RNAi. Insets, extruded cells marked by arrowhead in micrograph. g-j, RPA-1::YFP fluorescence in unidentified extruded cells from (h, i) the anterior sensory depression and (j) ventral pocket from a in a ced-3(lf); ltIs44[Ppie-1::mCherry::PH]; opIs263[Prpa-1::rpa-1::YFP] embryos after RNAi against empty vector control. A, anterior; R, right; V, ventral. Scale bars, 10 μm.