FIG 4.
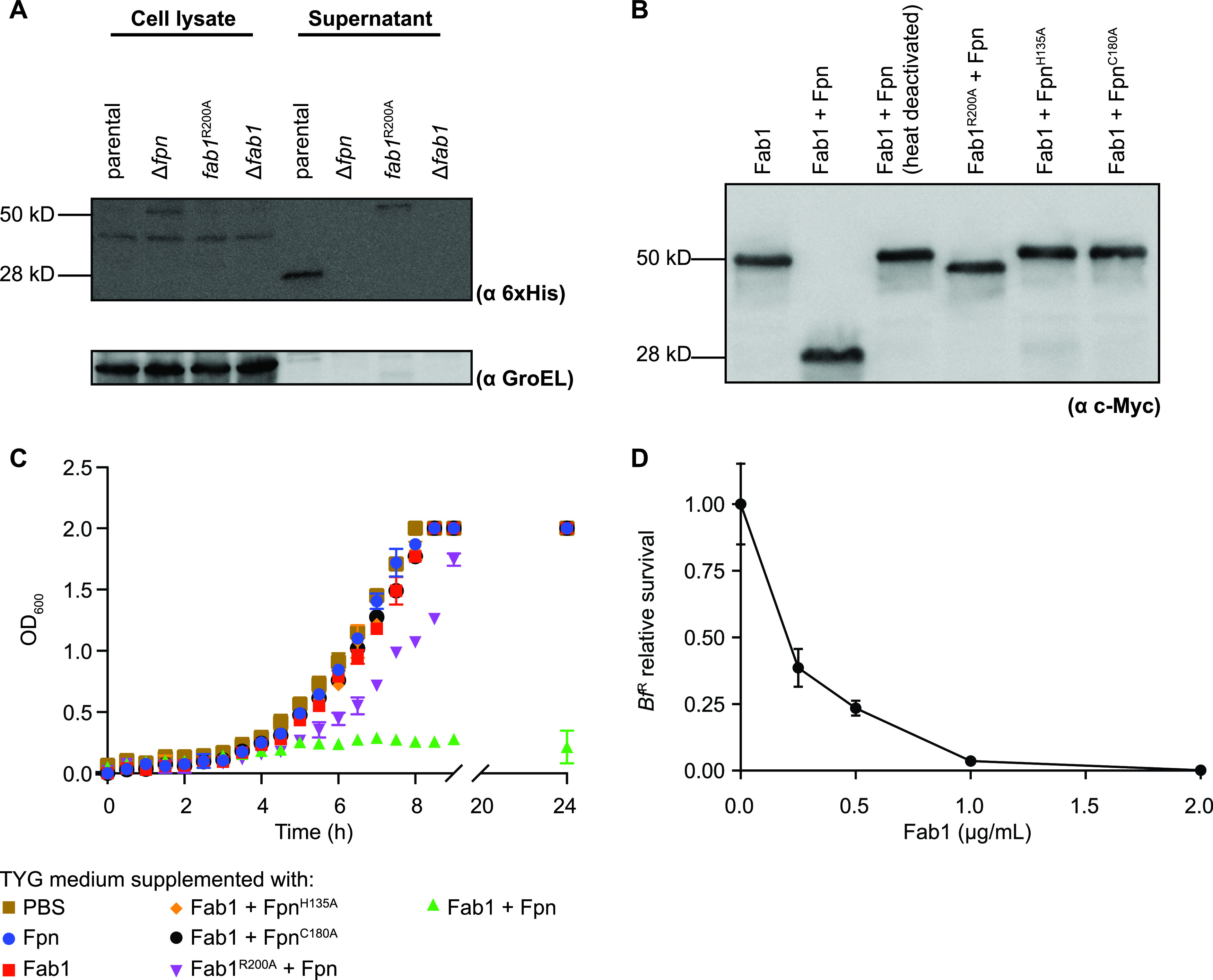
Fpn cleaves Fab1 to activate its antimicrobial function. (A) Western blot analysis of BfN parental and mutant strains carrying Fab1-His6 in the native genomic location and probed with anti-6×His. (B) Western blot analysis of Fab1 products generated following incubation of purified Fpn (wild type or catalytic residue mutants) with purified Fab1 (wild type or cleavage site mutant). Fab1 carries a C-terminal c-Myc tag; Western blots were probed with anti-c-Myc. (C) Growth of the susceptible BfR parental strain in TYG medium supplemented with combinations of purified Fpn (wild type or catalytic residue mutants) and purified Fab1 (wild type or cleavage site mutant). Error bars indicate SD (n = 2; representative of three independent experiments). (D) Concentration dependence of Fab1 activity on BfR viability. Fpn is included at 2 μg/ml under all conditions. Cell viability (CFU/ml) is normalized to the mean viability of cultures incubated in the absence of Fab1. Error bars indicate SD (n = 2; representative of three independent experiments).
