Fig 4.
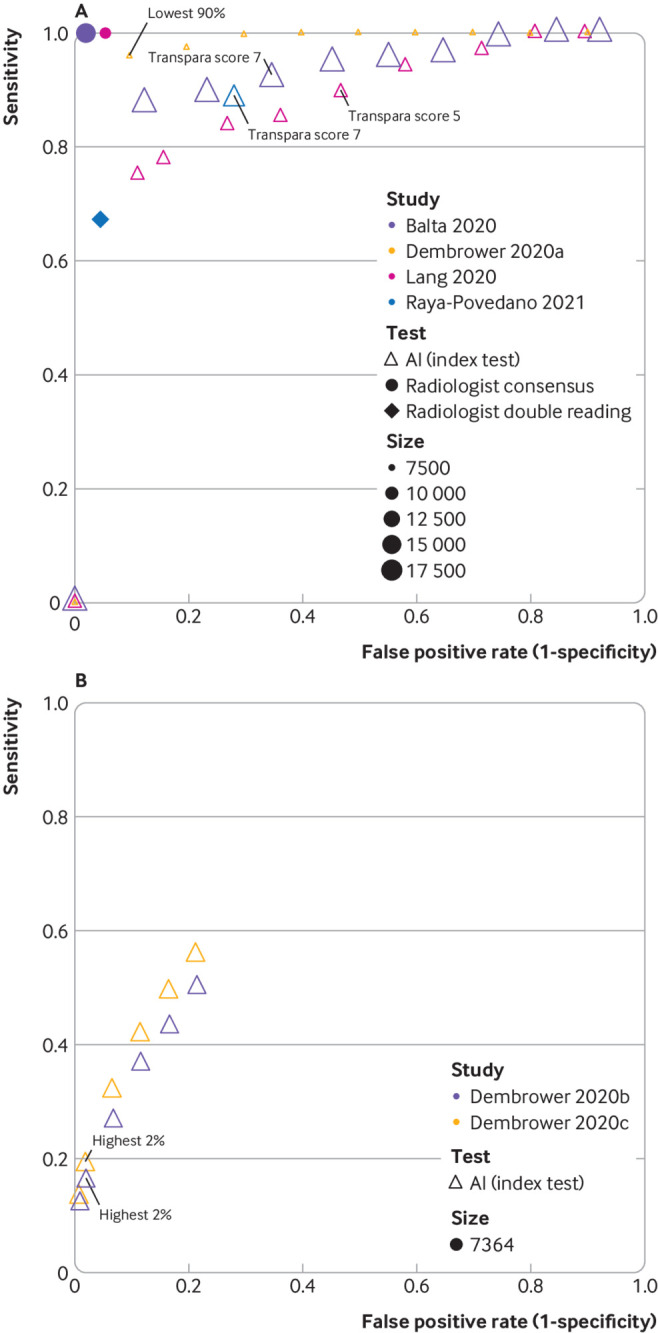
Study estimates of sensitivity and false positive rate (1−specificity) in receiver operating characteristic space for studies of artificial intelligence (AI) as a pre-screen (A) or post-screen (B). Pre-screen requires very high sensitivity, but can have modest specificity, post-screen requires very high specificity, but can have modest sensitivity. Reference standard for test negatives was double reading not follow-up. (A) Dembrower 2020a: retrospective study using AI (Lunit version 5.5.0.16) for pre-screen (point estimates not based on exact numbers). Reference standard includes only screen detected cancers. No data reported for radiologists.26 Balta 2020 (Transpara version 1.6.0),25 Raya-Povedano 2021 (Transpara version 1.6.0),31 and Lång 2020 (Transpara version 1.4.0)27: retrospective studies using AI as pre-screen. Reference standard includes only screen detected cancers. (B) Dembrower 2020b: retrospective study using AI (Lunit version 5.5.0.16) for post-screen detection of interval cancers,26 Dembrower 2020c: retrospective study using AI (Lunit version 5.5.0.16) for post-screen detection of interval cancers and next round screen detected cancers.26 Thresholds highlighted represent thresholds specified in studies. Radiologist double reading for this cohort would be 100% specificity and 0% sensitivity as this was only in a cohort of women with screen (true and false) negative mammograms
