Key Points
Question
What is the longer-term association of surgery with quality of life in young breast cancer survivors?
Findings
In this cross-sectional study of a prospective cohort, unilateral or bilateral mastectomy with radiotherapy (vs breast-conserving therapy) was associated with decreased breast satisfaction and psychosocial and sexual well-being.
Meaning
These findings suggest that more extensive surgery is associated with poorer quality-of-life outcomes in young breast cancer survivors, particularly those treated with mastectomy and radiotherapy, irrespective of reconstruction.
Abstract
Importance
Increasing rates of bilateral mastectomy have been most pronounced in young women with breast cancer, but the association of surgery with long-term quality of life (QOL) remains largely unknown.
Objective
To examine the association of surgery with longer-term satisfaction and QOL in young breast cancer survivors.
Design, Setting, and Participants
This multicenter cross-sectional study of a prospective cohort was conducted from October 2016 to November 2017, at academic and community hospitals in North America. Women 40 years or younger enrolled in the Young Women’s Breast Cancer Study were assessed. Data analysis was performed from during a 1- to 2-year period after conclusion of the study.
Exposures
Primary breast surgery, reconstruction, and radiotherapy.
Main Outcomes and Measures
Mean BREAST-Q breast satisfaction and physical, psychosocial, and sexual well-being scores were compared by type of surgery; higher BREAST-Q scores (range, 0-100) indicate better QOL. Linear regression was used to identify demographic and clinical factors associated with BREAST-Q scores for each domain.
Results
A total of 560 women with stage 0 to III breast cancer (median age at diagnosis, 36 years; range, 17-40 years; 484 [86%] with stage 0-II disease) completed the BREAST-Q a median of 5.8 years (range, 1.9-10.4 years) from diagnosis. A total of 290 patients (52%) of patients underwent bilateral mastectomy, 110 patients (20%) underwent unilateral mastectomy, and 160 patients (28%) received breast-conserving therapy. Among mastectomy patients, 357 (89%) had reconstruction and 181 (45%) received radiotherapy. In multivariate analyses, implant-based reconstruction (vs autologous) was associated with decreased breast satisfaction (β = −7.4; 95% CI, −12.8 to −2.1; P = .007) and complex reconstruction (vs autologous) with worse physical well-being (β = −14.0; 95% CI, −22.2 to −5.7; P < .001).
Conclusions and Relevance
These results suggest that local therapy in young breast cancer survivors is persistently associated with poorer scores in multiple QOL domains, particularly among those treated with mastectomy and radiotherapy, irrespective of breast reconstruction. Socioeconomic stressors also appear to play a role.
This cross-sectional study of young breast cancer survivors assesses whether mastectomy is associated with poor quality-of-life outcomes.
Introduction
Breast cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in women younger than 40 years, accounting for 7% of all cancers diagnosed in the US annually.1 It is widely established that choice of surgery (ie, breast conservation vs mastectomy) is not associated with overall survival, even among young women.2,3 Historically, there has been concern that young women may experience higher rates of locoregional recurrence if electing to undergo breast conservation. More recent data have demonstrated excellent local control in young women undergoing both breast conservation and mastectomy, with local recurrence rates of 1% to 12% even in the absence of optimal systemic therapy.4,5,6,7 Despite this finding, rates of mastectomy, and particularly bilateral mastectomy, have continued to increase in young women and have been reported to be as high as 35% to 40% in the US.8,9
Given equivalent oncologic outcomes after breast cancer surgery in young women, quality of life (QOL) outcomes are of critical importance. Older studies10,11 found small differences that favored breast conservation over mastectomy with regard to QOL in women of all ages. More recent data suggest that patients undergoing contralateral prophylactic mastectomy may experience higher satisfaction with the appearance of their breast(s) vs unilateral mastectomy.12 Younger women are increasingly likely to pursue bilateral mastectomy for treatment of a unilateral breast cancer and are more likely to undergo breast reconstruction.9 They also experience higher levels of distress and are at increased risk for poorer psychosocial outcomes after a breast cancer diagnosis.13 Compounding this, young women have a higher likelihood of receiving adjuvant therapies, such as chemotherapy and postmastectomy radiotherapy, which have also been demonstrated to be negatively associated with QOL.14,15
Data are limited regarding the association of surgery with longer-term satisfaction and QOL in young breast cancer survivors, particularly in the era of increasing bilateral mastectomy. To promote shared decision-making and choices that align with patients’ values and preferences, information about long-term outcomes after breast surgery in young women is needed. Using a multicenter, prospective cohort of young women with breast cancer, we sought to compare QOL among women who received breast-conserving therapy (BCT), unilateral mastectomy, and bilateral mastectomy as well as to evaluate differences by type of reconstruction among women who pursued unilateral mastectomy or bilateral mastectomy. We also sought to identify demographic and other treatment-related factors associated with QOL after breast cancer treatment.
Methods
Study Design and Population
The Young Women’s Breast Cancer Study (YWS) is a multicenter, prospective cohort study conducted from October 10, 2016, to November 31, 2017, to examine biological, medical, and QOL issues in women diagnosed with primary invasive breast cancer or ductal carcinoma in situ at 40 years or younger. Participating sites include academic and community hospitals in the Massachusetts region and 3 additional sites in Toronto, Canada; Colorado; and Minnesota. During a 10-year period (October 10, 2006, to June 30, 2016), 2162 eligible women were identified through pathology record review or review of clinic lists at participating hospitals and invited to participate in the YWS. A total of 1302 patients provided written informed consent, of whom 4 were found to be ineligible after enrollment and 1 withdrew consent after enrollment. Participants are sent a survey at study baseline (median of 5 months after diagnosis) followed by additional surveys twice a year for the first 3 years after diagnosis and annually thereafter. All data were deidentified. Data analysis was performed from during a 1- to 2-year period after conclusion of the study. The YWS is approved by the institutional review board at the Dana Farber-Harvard Cancer Care Center and other participating sites. Study design details have been previously reported.16 The study followed the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) reporting guideline.
BREAST-Q Substudy
Beginning in 2016, the BREAST-Q, a well-validated breast surgery–specific instrument focused on satisfaction with outcomes and health-related QOL,17 was sent to a subset of 743 YWS participants as a part of their 10-year follow-up or as a stand-alone survey. We excluded from the substudy population those participants who filled out only a short-form survey (eg, all patients enrolled in Toronto, n = 91), those who were deceased or lost to follow-up (n = 411), and those with confirmed recurrence or who presented with de novo stage IV disease (n = 52).
The BREAST-Q includes separate modules for BCT, mastectomy without reconstruction, and mastectomy with reconstruction and evaluates the following 6 different domains: satisfaction with breasts (breast appearance in terms of size, texture, and appearance in and out of clothes), psychosocial well-being (body image, confidence in social settings, emotional health, and self-esteem), physical well-being (pain or tightness in the breast area and difficulty with mobility or activities), sexual well-being (feelings of attractiveness and confidence as related to breasts and comfort during sexual activity), satisfaction with overall outcome, and satisfaction with care (information, medical team, surgeon, and office staff). We elected not to use satisfaction with overall outcome and satisfaction with care given time elapsed between surgery and completion of the questionnaires. Each domain is scored independently on a scale of 0 to 100, with higher scores representing a more favorable outcome. Minimally important differences in BREAST-Q scores are noted as the following: small, 2 to 3 points; moderate, 4 to 7 points; and large, 8 to 10 points.18
Patient, Disease, and Treatment Characteristics
Patient characteristics collected through the baseline survey included race and ethnicity (supplemented by medical record review if not reported or if baseline survey data were not available), employment status, perceived financial comfort level,19,20 and body mass index (BMI; calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared) at diagnosis. Given the small numbers of patients who were races other than White (2 [0.4%] American Indian or Alaska Native; 32 [6%] Asian; 17 [3%] Black, Haitian, or African American; and 3 [1%] unknown), race and ethnicity were dichotomized (White vs other race), allowing us to explore potential differences between White women and women from other racial and ethnic groups. Pathology and medical records of all patients were reviewed for stage of disease, hormone receptor, and ERBB2 (formerly HER2 or HER2/neu) status. We used 1-year survey data together with medical record review to determine genetic testing status and results. Surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy information (yes/no) was also obtained by self-report in combination with medical record review. Reconstruction was defined as implant, autologous, or complex (combination of implant and autologous). Endocrine therapy use was based on self-report on any survey completed. Self-reported lymphedema at 1 year was assessed with a question about experiencing arm swelling from the Breast Cancer Prevention Trial Symptom Checklist.21
Statistical Analysis
We calculated numbers (percentages) for categorical covariates and means (ranges) for continuous covariates. Unadjusted mean BREAST-Q scores for each domain were compared using analysis of variance between the following local therapy groups: BCT, unilateral mastectomy with and without radiotherapy, and bilateral mastectomy with and without radiotherapy. Among the subset of women who had mastectomy with reconstruction, we compared unadjusted mean BREAST-Q scores between women undergoing implant-based reconstruction with and without radiotherapy, autologous tissue reconstruction with and without radiotherapy, and complex reconstruction. Univariate and multivariate linear regression was used to identify independent factors associated with BREAST-Q scores for each domain. Variables with a 2-tailed P ≤ .20 in univariate analyses were entered into the multivariate model, and stepwise model selection based on Akaike Information Criterion was used to create the final multivariate model. All analyses were conducted using R software, version 4.0.4 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing).
Results
Patient and Treatment Characteristics
Of the 743 participants sent the BREAST-Q, 584 completed the survey (response rate, 79%) as a part of their 10-year follow-up (n = 59) or as a stand-alone survey (n = 525). After excluding patients who completed a version of the BREAST-Q that did not match the surgery received (n = 3) and patients who had confirmation of a recurrence (n = 16) or new primary tumor (n = 5) after the BREAST-Q was sent, 560 patients (median age at diagnosis, 36 years; range, 17-40 years; 484 [86%] with stage 0-II disease) were included in the analytic cohort (eFigure in the Supplement). The median time from diagnosis to BREAST-Q completion was 5.8 years (range, 1.9-10.4 years). Patient characteristics are detailed in the Table. Most patients were White, were married, reported being financially comfortable, and had a college education. At study baseline, 336 (60%) had a BMI in the normal range (18.5 to 24.9), and 179 patients (32%) had a BMI of 25 or higher. Sixty-four patients (11%) tested positive for a BRCA (OMIM 113705) or p53 (OMIM 191170) mutation; test results were negative for 418 patients (75%). A total of 214 patients (38%) had stage I breast cancer, and 216 (39%) had stage II breast cancer. A total of 407 patients (73%) received chemotherapy, and 372 patients (66%) reported current or past use of endocrine therapy.
Table. Patient and Treatment Characteristics.
| Characteristic | No. (%) (N = 560) |
|---|---|
| BMI at first survey | |
| <18.5 | 25 (4) |
| 18.5-24.9 | 336 (60) |
| ≥25 | 179 (32) |
| Missing | 20 (4) |
| Race or ethnicity | |
| White | 506 (90) |
| Other | 54 (10) |
| American Indian or Alaska Native | 2 (0.4) |
| Asian | 32 (6) |
| Black, Haitian, or African American | 17 (3) |
| Unknown | 3 (1) |
| Marital status | |
| Married or living as married | 429 (77) |
| Single, divorced or widowed | 113 (20) |
| Missing | 18 (3) |
| Financial status | |
| Comfortable | 445 (79) |
| Uncomfortable | 90(16) |
| Missing | 25 (5) |
| Work status | |
| Work full time | 344 (62) |
| Other | 19 (3) |
| Missing | 197 (35) |
| Educational level | |
| Some college, college graduate, or postcollege work | 479 (86) |
| Other (grade school/junior high and some high school, high school graduate, and technical/vocational school) | 64 (11) |
| Missing | 17 (3) |
| Genetic testing for BRCA and p53 | |
| Negative result | 418 (75) |
| Positive result | 64 (11) |
| No record of testing | 78 (14) |
| Stage | |
| 0 | 54 (10) |
| I | 214 (38) |
| II | 216 (39) |
| III | 76 (13) |
| Chemotherapy | |
| Yes | 407 (73) |
| No | 153 (27) |
| Endocrine therapy | |
| Yes | 372 (66) |
| No | 188 (34) |
| Time since surgery, y | |
| 1-5 | 218 (39) |
| >5 | 342 (61) |
| Surgery | |
| Breast-conserving therapya | 160 (28) |
| Mastectomy | |
| Unilateral | 110 (20) |
| Bilateral | 290 (52) |
| Axillary surgery | |
| Sentinel node biopsy | 336 (60) |
| Sentinel node biopsy and axillary dissection | 123 (22) |
| Axillary lymph node dissection | 86 (15) |
| No axillary surgery | 13 (2) |
| Missing | 2 (0) |
| Postmastectomy radiotherapy (n = 399) | 181 (45) |
| Lymphedema at 1 y | |
| Yes | 163 (29) |
| No | 397 (71) |
| Reconstruction (among patients undergoing mastectomy) (n = 400) | |
| No reconstruction | 42 (11) |
| Implant-based reconstruction | 288 (72) |
| Autologous reconstruction | 56 (14) |
| Complex reconstruction | 13 (3) |
| Unknown | 1 (0) |
Abbreviation: BMI, body mass index (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared).
Only 1 patient who received breast-conserving therapy did not receive radiotherapy.
Details related to local therapy, including surgery, radiotherapy, and lymphedema are described in the Table. A total of 290 patients (52%) underwent bilateral mastectomy, 110 patients (20%) underwent unilateral mastectomy, and 160 patients (28%) received BCT. A total of 181 patients (45%) who had mastectomy received radiotherapy. Most patients had axillary surgery performed, with 336 (60%) receiving sentinel lymph node biopsy only, 123 patients (22%) having sentinel lymph node biopsy and completion axillary lymph node dissection, and 86 patients (15%) having axillary lymph node dissection. Lymphedema was self-reported by 163 patients (29%) at 1 year.
Of patients undergoing mastectomy, 357 (89%) also underwent reconstruction (eTable 1 in the Supplement). In this group, 56 patients (16%) had autologous reconstruction, 288 patients (81%) had implant reconstruction, and 13 patients (3%) had complex reconstruction. A total of 17 patients reported reconstruction after lumpectomy, but these patients were excluded from the reconstruction subset analysis.
Local Therapy BREAST-Q Outcomes
Unadjusted mean BREAST-Q scores by local therapy strategy are shown in Figure 1. Satisfaction with breasts, psychosocial well-being, and sexual well-being all differed by local therapy strategy (global P < .001), with scores across these domains highest in women who had BCT (breast satisfaction score, 65.5; psychosocial well-being score, 75.9; and sexual well-being score, 57.4) and lowest among women who had unilateral or bilateral mastectomy with radiotherapy (breast satisfaction score, 54.6 unilateral and 55.8 bilateral; psychosocial well-being score, 66.1 unilateral and 65.1 bilateral; and sexual well-being score, 50.4 unilateral and 46.2 bilateral) vs those without radiotherapy (breast satisfaction: 64.3 unilateral and 64.0 bilateral; physical well-being: 80.5 unilateral and 80.2 bilateral; psychosocial well-being: 75.2 unilateral and 71.3 bilateral; and sexual well-being: 56.6 unilateral and 51.4 bilateral). No significant differences were found by local therapy strategy in physical well-being scores (BCT, 78.9; bilateral mastectomy without radiotherapy, 80.2; bilateral mastectomy with radiotherapy, 76.8; unilateral mastectomy without radiotherapy, 80.5; unilateral mastectomy with radiotherapy, 77.4; P = .31).
Figure 1. Unadjusted BREAST-Q Mean Scores by Local Therapy Strategy.
BCT indicates breast-conserving therapy; BMx, bilateral mastectomy; RT, radiation therapy; UMx, unilateral mastectomy.
Breast Satisfaction
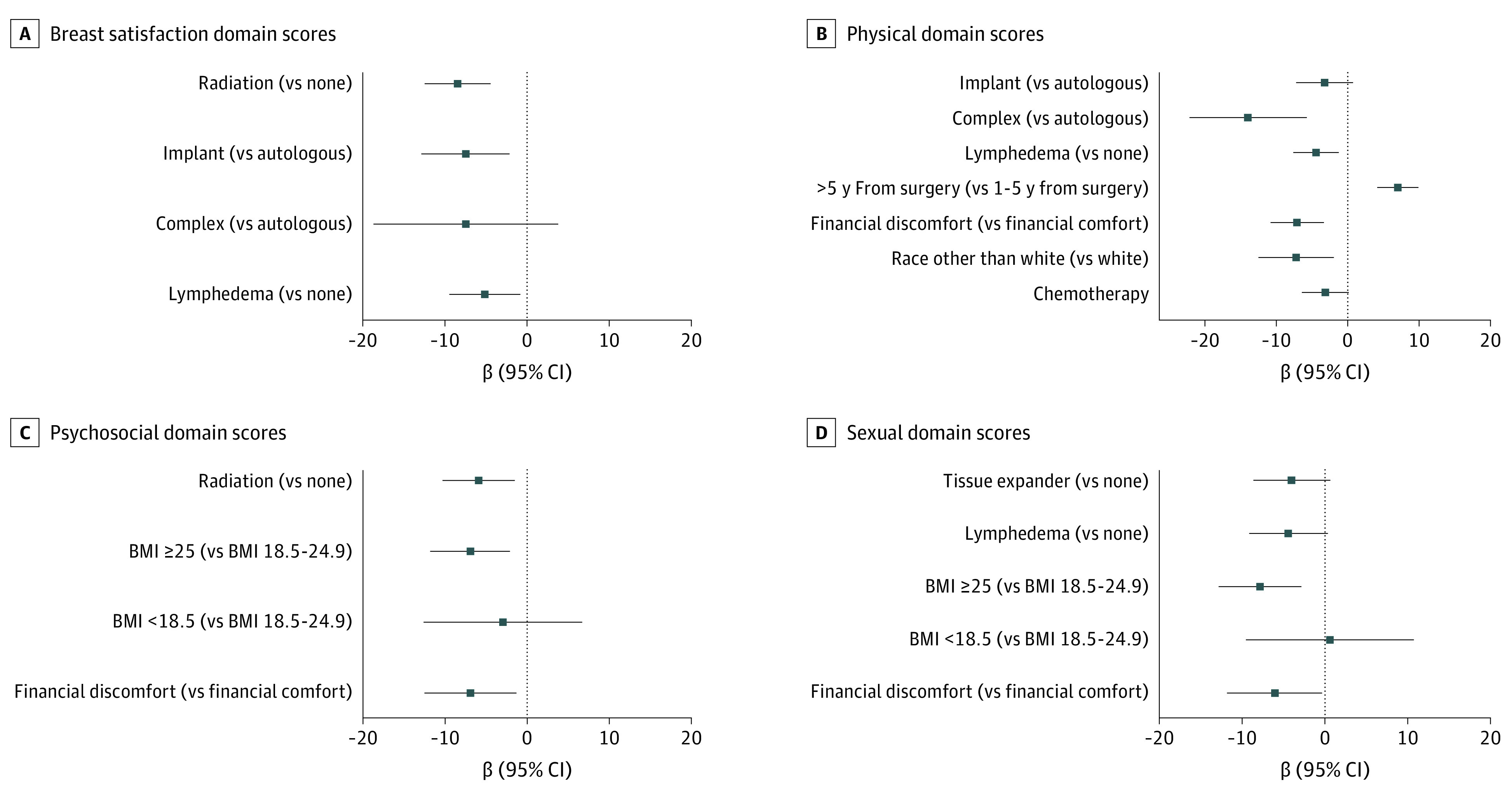
Factors independently associated with lower breast satisfaction (Figure 2A) on multivariate analysis included financial discomfort (β = −5.1; 95% CI, −9.5 to −0.7; P = .02), unilateral mastectomy with radiotherapy (vs BCT; β = −9.8; 95% CI, −15.8 to −3.9; P = .001), and bilateral mastectomy with radiotherapy (vs BCT; β = −8.8; 95% CI, −13.4 to −4.2; P < .001). Stage III (vs stage I) and presence of lymphedema were associated with lower breast satisfaction only in univariate analyses. Other demographic, clinical, and treatment covariates were not associated with breast satisfaction (eTable 2 in the Supplement).
Figure 2. Patient and Treatment Factors Associated With BREAST-Q Scores.

Error bars indicate 95% CIs. BCT indicates breast-conserving therapy; BMI, body mass index (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared); RT, radiation therapy.
Physical Well-being
Longer time since surgery (>5 vs ≤5 years) was independently associated with better physical well-being (β = 6.1; 95% CI, 3.6-8.6; P < .001), whereas financial discomfort (β = −4.9; 95% CI −8.1 to −1.6; P = .004) and presence of lymphedema (β = −6.1; 95% CI, −8.8 to −3.5; P < .001) were independently associated with worse physical well-being (Figure 2B). Other demographic, clinical, and treatment covariates were not associated with physical well-being (eTable 3 in the Supplement).
Psychosocial Well-being
Factors independently associated with worse psychosocial well-being (Figure 2C) included financial discomfort (β = −7.0; 95% CI, −11.6 to −2.4; P = .003), BMI of 25 or higher (vs BMI of 18.5-24.9; β = −4.2; 95% CI, −8.0 to −0.52; P = .03), unilateral mastectomy with radiotherapy (β = −9.5; 95% CI, −15.7 to −3.3; P = .003), bilateral mastectomy without radiotherapy (β = −4.8; 95% CI, −9.3 to −0.32; P = .04), and bilateral mastectomy with radiotherapy (β = −10.5; 95% CI, −15.1 to −5.5; P < .001). Lymphedema and time since surgery were associated with worse psychosocial well-being only in univariate analyses. Other demographic, clinical, and treatment covariates were not associated with psychological well-being (eTable 4 in the Supplement).
Sexual Well-being
Factors independently associated with worse sexual well-being (Figure 2D) included BMI of 25 or higher (vs BMI of 18.5-24.9; β = −5.1; 95% CI, −8.9 to −1.4; P = .008), financial discomfort (β = −6.7; 95% CI, −11.3 to −2.0; P = .005), unilateral mastectomy with radiotherapy (β = −6.4; 95% CI −12.8 to −0.1; P = .05), bilateral mastectomy without radiotherapy (β = −6.4; 95% CI, −10.9 to −1.8; P = .006), and bilateral mastectomy with radiotherapy (β = −10.4; 95% CI, −15.3 to −5.5; P < .001). Lymphedema was associated with worse sexual well-being only on univariate analyses. Other demographic, clinical, and treatment covariates were not associated with sexual well-being (eTable 5 in the Supplement).
BREAST-Q Outcomes After Reconstruction
To understand whether there were differences in QOL among women who had mastectomy with breast reconstruction, we performed similar analyses among this subgroup. Unadjusted mean BREAST-Q scores by reconstruction type among women who had mastectomy with reconstruction (n = 357) are shown in Figure 3. Satisfaction with breasts, physical well-being, and psychosocial well-being all differed by local therapy strategy, with scores across these domains highest in women who had autologous reconstruction without radiotherapy and lowest among women who had implant reconstruction with radiotherapy or complex reconstruction. No significant differences were found by reconstruction type seen in sexual well-being scores (autologous without radiotherapy, 54.2; autologous with radiotherapy, 49.6; implant without radiotherapy, 51.9; implant without radiotherapy, 46.7; complex, 47.7; P = .26).
Figure 3. Unadjusted BREAST-Q Mean Scores by Reconstruction Type.
RT indicates radiation therapy.
In multivariate analyses (Figure 4), implant-based reconstruction (vs autologous) was associated with decreased breast satisfaction (β = −7.4; 95% CI, −12.8 to −2.1; P = .007) and complex reconstruction (vs autologous) with worse physical well-being (β = −14.0; 95% CI, −22.2 to −5.7; P < .001). Reconstruction type was not associated with psychosocial or sexual well-being, and bilateral mastectomy, delayed vs immediate reconstruction, use of tissue expander, and use of symmetry procedure were not associated with BREAST-Q scores on univariate or multivariate analysis. Other statistically significant factors associated with BREAST-Q scores (across all domains) among the subset of women who had reconstruction were largely consistent with results of the local therapy models (eTable 6 in the Supplement).
Figure 4. Patient and Treatment Factors Associated With BREAST-Q Score Among Women Who Underwent Mastectomy With Reconstruction.
Error bars indicate 95% CIs. BMI indicates body mass index.
Discussion
In this multicenter prospective cross-sectional study of a cohort of young women diagnosed with breast cancer, moderate to large QOL differences by local therapy strategy were apparent several years after surgery, with women who underwent more extensive surgery, particularly when combined with radiotherapy, having lower QOL largely driven by inferior satisfaction with breasts and psychosocial and sexual well-being. These findings are all the more striking considering the recent trends toward bilateral mastectomy for unilateral breast cancer and the fact that most of these women underwent reconstruction.
Several prior studies,12,22 inclusive of women of all ages, have used the BREAST-Q to evaluate health-related QOL after breast cancer surgery. Findings from a cross-sectional analysis22 of 7619 women of all ages recruited through the Army of Women research registry an average of 6.7 years after surgery were similar to those of our study, with higher scores indicating better QOL among women who underwent BCT or mastectomy with autologous reconstruction and lower scores among women having implant-based reconstruction, complex reconstruction, or mastectomy with no reconstruction. This study22 reported slightly larger differences in breast satisfaction scores, which were a mean of 8.6 points lower among women who had implant-based reconstruction than among those who had BCT; we found a more modest difference (5.6 points lower) in women who underwent mastectomy with implant-based reconstruction compared with women who underwent BCT. Findings of decreased breast satisfaction for women who undergo mastectomy, particularly for those receiving postmastectomy radiotherapy after implant-based reconstruction, are concerning given the large numbers of young women who choose bilateral mastectomy for a unilateral early breast cancer in combination with the recent trend of increasing rates of postmastectomy radiotherapy for young patients with breast cancer.15
For certain BREAST-Q domains, mean scores in our study were lower than those reported in other studies,12,23 supporting previous data demonstrating poorer psychosocial outcomes in younger patients. In a recently published single-institution study23 that followed up 3233 women (median age, 53 years) with early-stage breast cancer, psychosocial and sexual well-being scores improved in both the BCT and mastectomy groups during the follow-up period and were higher at all time points, indicating better QOL, when compared with the scores in our study. Similarly, compared with BREAST-Q scores of 3977 women from the Army of Women study12 (mean age, 57 years) who underwent mastectomy, psychosocial well-being in our study was slightly lower among women who underwent unilateral mastectomy (73.9 vs 70.6) and bilateral mastectomy (71.7 vs 68.4). In contrast, sexual well-being scores were similar after bilateral mastectomy (48.6 vs 49.0) and modestly better in our study after unilateral mastectomy (50.0 vs 53.4).12 Physical well-being scores were also slightly higher for patients in our study after unilateral mastectomy (76.8 vs 78.9) and bilateral mastectomy (74.5 vs 78.7),12 perhaps attributable to the younger age of women in our cohort and a decreased likelihood of experiencing age-related comorbidities that may affect physical functioning.24
In addition to surgical type, it is not surprising that other clinical factors, such as weight and lymphedema, are negatively associated with QOL as well. Identification of these risk factors may enable intervention at an early stage, ultimately decreasing the potential for long-term QOL sequelae after breast cancer. Perhaps most profound was the association with perceived financial status, which was associated with lower QOL across all domains. Others25,26 have similarly documented an association between financial hardship and QOL and speak to the need to further address issues of financial toxicity among young patients, as well as challenges experienced by patients from socioeconomically disadvantaged backgrounds.
Limitations
This study has limitations. This was a cross-sectional, 1-time survey of a prospective cohort; thus, we do not have these particular measures over time, including true prediagnosis or preoperative baseline. Baseline QOL may drive surgical choices as well as postoperative QOL. In addition, we did not examine candidacy for BCT compared with definitive surgical procedure, although previous work27 has demonstrated that factors associated with undergoing bilateral mastectomy vs lumpectomy are similar even when restricted to patients who reported that their physician said that lumpectomy was an option or was recommended to them. It is possible that women who chose mastectomy because of personal preference may perceive their QOL differently than women who underwent mastectomy because they were not candidates for BCT. The generalizability of these findings may also be limited because our cohort is mostly White and of higher socioeconomic status. Nevertheless, patient-reported outcomes can provide essential QOL information and help identify potential areas of need for intervention during survivorship.
Conclusions
Although most young women report satisfaction with their treatment decisions, some women have regrets,28 underscoring the relevance of data that reflect the long-term, patient-reported, postoperative experience. The current study identified a negative association between more extensive surgery, particularly when radiotherapy is indicated, and QOL for young women with breast cancer several years after surgery. Consideration should be given to including QOL data as part of decision support tools for young women with newly diagnosed breast cancer as well as in physician discussions with patients to ensure young women understand the long-term impacts of surgery with and without radiotherapy, which is of particular importance given the extended survivorship period most young patients experience after breast cancer surgery.
eFigure. Study Flow Diagram
eTable 1. Local Therapy Characteristics for Reconstruction Patients (N = 357a)
eTable 2. Univariate and Multivariate Analysis: Association of Patient and Treatment Factors With BREAST-Q Breast Satisfaction Domain Score
eTable 3. Univariate and Multivariate Analysis: Association of Patient and Treatment Factors With BREAST-Q Physical Domain Score
eTable 4. Univariate and Multivariate Analysis: Association of Patient and Treatment Factors With BREAST-Q Psychosocial Domain Score
eTable 5. Univariate and Multivariate Analysis: Association of Patient and Treatment Factors With BREAST-Q Sexual Domain Score
eTable 6. Multivariate Analysis of Patient and Treatment Factors Associated With BREAST-Q Domain Scores Among Patients Who Had Mastectomy With Reconstruction
References
- 1.American Cancer Society . Breast cancer facts and figures, 2015-2016. Accessed March 26, 2021. https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/breast-cancer-facts-and-figures/breast-cancer-facts-and-figures-2015-2016.pdf
- 2.Ye JC, Yan W, Christos PJ, Nori D, Ravi A. Equivalent survival with mastectomy or breast-conserving surgery plus radiation in young women aged < 40 years with early-stage breast cancer: a national registry-based stage-by-stage comparison. Clin Breast Cancer. 2015;15(5):390-397. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2015.03.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vila J, Gandini S, Gentilini O. Overall survival according to type of surgery in young (≤40 years) early breast cancer patients: a systematic meta-analysis comparing breast-conserving surgery versus mastectomy. Breast. 2015;24(3):175-181. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2015.02.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Aalders KC, van Bommel AC, van Dalen T, et al. Contemporary risks of local and regional recurrence and contralateral breast cancer in patients treated for primary breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2016;63:118-126. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2016.05.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Aalders KC, Postma EL, Strobbe LJ, et al. Contemporary locoregional recurrence rates in young patients with early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(18):2107-2114. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.64.3536 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Braunstein LZ, Taghian AG, Niemierko A, et al. Breast-cancer subtype, age, and lymph node status as predictors of local recurrence following breast-conserving therapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017;161(1):173-179. doi: 10.1007/s10549-016-4031-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Truong PT, Sadek BT, Lesperance MF, et al. Is biological subtype prognostic of locoregional recurrence risk in women with pT1-2N0 breast cancer treated with mastectomy? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014;88(1):57-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.09.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Nash R, Goodman M, Lin CC, et al. State variation in the receipt of a contralateral prophylactic mastectomy among women who received a diagnosis of invasive unilateral early-stage breast cancer in the United States, 2004-2012. JAMA Surg. 2017;152(7):648-657. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.0115 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kurian AW, Lichtensztajn DY, Keegan TH, Nelson DO, Clarke CA, Gomez SL. Use of and mortality after bilateral mastectomy compared with other surgical treatments for breast cancer in California, 1998-2011. JAMA. 2014;312(9):902-914. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.10707 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ganz PA, Schag AC, Lee JJ, Polinsky ML, Tan SJ. Breast conservation versus mastectomy: is there a difference in psychological adjustment or quality of life in the year after surgery? Cancer. 1992;69(7):1729-1738. doi: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rowland JH, Desmond KA, Meyerowitz BE, Belin TR, Wyatt GE, Ganz PA. Role of breast reconstructive surgery in physical and emotional outcomes among breast cancer survivors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92(17):1422-1429. doi: 10.1093/jnci/92.17.1422 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hwang ES, Locklear TD, Rushing CN, et al. Patient-reported outcomes after choice for contralateral prophylactic mastectomy. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(13):1518-1527. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.61.5427 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Howard-Anderson J, Ganz PA, Bower JE, Stanton AL. Quality of life, fertility concerns, and behavioral health outcomes in younger breast cancer survivors: a systematic review. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012;104(5):386-405. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djr541 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kroman N, Jensen MB, Wohlfahrt J, Mouridsen HT, Andersen PK, Melbye M. Factors influencing the effect of age on prognosis in breast cancer: population based study. BMJ. 2000;320(7233):474-478. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7233.474 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ohri N, Sittig MP, Tsai CJ, et al. Trends and variations in postmastectomy radiation therapy for breast cancer in patients with 1 to 3 positive lymph nodes: a National Cancer Data Base analysis. Cancer. 2018;124(3):482-490. doi: 10.1002/cncr.31080 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rosenberg SM, Ruddy KJ, Tamimi RM, et al. BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation testing in young women with breast cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2016;2(6):730-736. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.5941 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Pusic AL, Klassen AF, Scott AM, Klok JA, Cordeiro PG, Cano SJ. Development of a new patient-reported outcome measure for breast surgery: the BREAST-Q. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;124(2):345-353. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181aee807 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Voineskos SH, Klassen AF, Cano SJ, Pusic AL, Gibbons CJ. Giving meaning to differences in BREAST-Q scores: minimal important difference for breast reconstruction patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020;145(1):11e-20e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000006317 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gierisch JM, Earp JA, Brewer NT, Rimer BK. Longitudinal predictors of nonadherence to maintenance of mammography. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2010;19(4):1103-1111. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-09-1120 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Williams RB, Barefoot JC, Califf RM, et al. Prognostic importance of social and economic resources among medically treated patients with angiographically documented coronary artery disease. JAMA. 1992;267(4):520-524. doi: 10.1001/jama.1992.03480040068032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Stanton AL, Bernaards CA, Ganz PA. The BCPT symptom scales: a measure of physical symptoms for women diagnosed with or at risk for breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97(6):448-456. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dji069 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Atisha DM, Rushing CN, Samsa GP, et al. A national snapshot of satisfaction with breast cancer procedures. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22(2):361-369. doi: 10.1245/s10434-014-4246-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Flanagan MR, Zabor EC, Romanoff A, et al. A comparison of patient-reported outcomes after breast-conserving surgery and mastectomy with implant breast reconstruction. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019;26(10):3133-3140. doi: 10.1245/s10434-019-07548-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ganz PA, Guadagnoli E, Landrum MB, Lash TL, Rakowski W, Silliman RA. Breast cancer in older women: quality of life and psychosocial adjustment in the 15 months after diagnosis. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21(21):4027-4033. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.08.097 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bowen DJ, Alfano CM, McGregor BA, et al. Possible socioeconomic and ethnic disparities in quality of life in a cohort of breast cancer survivors. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007;106(1):85-95. doi: 10.1007/s10549-006-9479-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lathan CS, Cronin A, Tucker-Seeley R, Zafar SY, Ayanian JZ, Schrag D. Association of financial strain with symptom burden and quality of life for patients with lung or colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(15):1732-1740. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.63.2232 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Rosenberg SM, Sepucha K, Ruddy KJ, et al. Local therapy decision-making and contralateral prophylactic mastectomy in young women with early-stage breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22(12):3809-3815. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4572-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fernandes-Taylor S, Bloom JR. Post-treatment regret among young breast cancer survivors. Psychooncology. 2011;20(5):506-516. doi: 10.1002/pon.1749 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
eFigure. Study Flow Diagram
eTable 1. Local Therapy Characteristics for Reconstruction Patients (N = 357a)
eTable 2. Univariate and Multivariate Analysis: Association of Patient and Treatment Factors With BREAST-Q Breast Satisfaction Domain Score
eTable 3. Univariate and Multivariate Analysis: Association of Patient and Treatment Factors With BREAST-Q Physical Domain Score
eTable 4. Univariate and Multivariate Analysis: Association of Patient and Treatment Factors With BREAST-Q Psychosocial Domain Score
eTable 5. Univariate and Multivariate Analysis: Association of Patient and Treatment Factors With BREAST-Q Sexual Domain Score
eTable 6. Multivariate Analysis of Patient and Treatment Factors Associated With BREAST-Q Domain Scores Among Patients Who Had Mastectomy With Reconstruction




