Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory dermatological disorder having complex pathophysiology with autoimmune and genetic factors being the major players. Despite the availability of a gamut of therapeutic strategies, systemic toxicity, poor efficacy, and treatment tolerance due to genetic variability among patients remain the major challenges. This calls for effective intervention with the superior pharmacological profile. Nimbolide (NIM), a major limonoid is an active chemical constituent found in the leaves of the Indian Neem tre, Azadirachta indica. It has gained immense limelight in the past decades for the treatment of various diseases owing to its anti-proliferative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer potentials.
OBJECTIVE:
The present study was centered around evaluating the anti-psoriatic effect of NIM in the experimental model of Imiquimod (IMQ)-induced psoriasis-like inflammation model.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
Application of IMQ topically on the dorsum of Balb/c mice from day 0-6 prompted psoriasis-like inflammatory symptoms. Treatment groups included topical administration of NIM incorporated carbopol gel formulation and NIM free drug given through subcutaneous route. Protein expression studies such as immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and ELISA were employed.
RESULTS:
It was clearly observed from our results that NIM significantly ameliorated the expression of inflammatory and proliferation mediators. Further, NIM in the treatment groups significantly improved classic Psoriasis Area Severity Index scoring when compared to IMQ administered group.
CONCLUSION:
It is noteworthy that NIM showed a predominant therapeutic effect as compared to other treatment group. To recapitulate, NIM has shown promising activity as an anti-psoriatic agent by remarkably ameliorating inflammation and associated proliferation.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory, Imiquimod, Nimbolide, psoriasis, topical therapy
Introduction
Psoriasis or skin inflammation is a chronic autoimmune disease with strong genetic susceptibility. It accounts for approximately 2%–3% of the world population affected by it (Rendon, 2019 #1). Clinical manifestations include well-demarcated red and scaly papules and plagues, but it can also be characterized by lesions with erythema, squamae, and epidermal thickening with round, oval, and descriptive polycyclic borders along with leukocyte infiltration and augmented leaky vessels in the dermis.[1] Psoriasis entails complex crosstalk between genetic, environmental factors, and immune system dysfunction.[2] The exact molecular mechanism for psoriasis has not yet been unraveled but there are various reports suggesting cross-talk between epidermal and immune cells. Genome-wide analysis has pointed towards a significant role of genes involved in the production of inflammatory mediators.[3] Keratinocytes serve as principal cells in cytokine release and targeting.[4]
Homeostasis of dermal tissue is governed by signaling between various types of dermal cells as well as cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors which is often altered due to various genetic factors or some unrecognized stimuli, thus initiating psoriatic changes.[5] Despite much research, the cause and pathogenesis of psoriasis in not well elucidated. However, two hypotheses have been proposed. One of them considers it as a disorder of epidermal keratinocytes with deregulated inflammatory changes, while the other hypothesis emphasizes on the immune facet proposing it to be majorly an immune-mediated disorder with upregulated production of various growth factors, chemokines, and cytokines epidermis leading to inflammation-mediated hyperproliferation in epidermis. On T-cells activation by various known/unknown stimuli, they migrate toward dermis and kindle the release of cytokines which induce rapid production of dermal cells.[6]
The treatment of Psoriasis involves long-term medication. Topical therapy with glucocorticoid, Vitamin D, and phototherapy is preferred for mild forms, whereas moderate to severe cases require systemic therapy. Drugs such as methotrexate, cyclosporin A, monoclonal antibodies such as adalimumab, certolizumab, secukinumab, infliximab are used for clinical management.[7] The emergence of natural products for effective management of psoriasis has come a long way. Till date, many of them have proved their finesse with better efficacy and safety profile compared to conventional therapies like Indirubin, Berberine, Capsaicin, and water processed rosin have demonstrated potent activity in this regard.[8,9,10,11] In line with the current use of natural compounds as potential candidates in treating psoriasis, we hereby propose the use of Nimbolide (NIM) which is an active constituent isolated from the leaves of Indian Neem or Azadirachta indica. It possess potential anti-inflammatory,[12] anti-proliferative,[13] and anticancer[14] activity. However, its effect in psoriatic conditions has not been exemplified yet. The current study has been designed and performed with the objective to evaluate the anti-psoriatic effect of NIM as topical gel and upon subcutaneous (SC) administration in murine model of Imiquimod (IMQ) induced-psoriatic like inflammation.
Materials and Methods
Chemicals and antibodies
NIM was purchased from Aptus Therapeutics Pvt Ltd. (Hyderabad, India). IMQ (5% w/w IMQ cream) was procured from Glenmark Pharmaceuticals (Mumbai, India). Bovine serum albumin (BSA), 2-thiobarbituric acid, tissue protein extraction reagent (T-PER) lysis buffer, bicinchoninic acid kit, and Bradford reagents were obtained from Sigma Aldrich. Carbopol was obtained from Loba Chemie (Mumbai, India). Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1, interleukin (IL)-22, IL-17, IL-1 β, and IL-6 ELISA kits were from eBiosciences (USA). Anti-NF-κB, anti-COX-2, anti-intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1, anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, anti-Ki-67, anti-proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), and anti-IL-6 antibodies were obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (USA), anti-pNF-κB was procured from cell signaling technology (USA). All the reagents and chemicals utilized in this study were of analytical grade and were commercially available.
Preparation of Nimbolide gel formulation
Topical application of NIM gel was employed in the current study. Carbopol of grade 934 was accurately weighed and mixed with sufficient quantity of distilled water for 2 h. NIM was weighed as needed and incorporated into the Carbopol gel with uninterrupted agitation. The pH of the resulting gel was adjusted to 6.8 with triethanolamine with constant stirring to allow the formation of the homogenous gel.
Animal experimentation and study design
Balb/c mice with weights approximately around 22–25 g (Teena labs, Hyderabad) were employed for the current study. Animals were randomly divided based on weights into four groups (n = 6 in each group) as follows: (1) Normal control (2) IMQ control (62.5 mg/mice) (3) IMQ + NIM (subcutaneous NIM-3 mg/kg) (4) IMQ + NIM (topical gel-75 μg/mice). The dorsum of the animals was clipped before study commencement. 62.5 mg of IMQ cream per mice was applied daily to the shaved dorsum starting from day 0 to day 6 of the study was followed. Treatment group animals were given NIM from day 3 to day 6, once daily after 8 h of IMQ induction. The study was terminated on day 7; spleen and dorsum skin of all the mice were collected and stored for further experimental studies. All the animal studies and procedures were executed with the approval of the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee, NIPER-Hyderabad (NIP/08/2017/RT/253).
Psoriasis Area Severity Index scoring
To determine the graveness of inflammation and psoriasis, objective scoring methodology of Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI) was used. In short, relevant parameters of skin, namely erythema, skin thickness, and scaling were scored by an independent blinded observer on day 0, 2, 4, and 6 of the study. Each parameter was scored distinctly on a scale ranging from 0 to 4 (0-none; 1-mild; 2-moderate; 3-severe; 4-very severe) as per the magnitude of severity.
Spleen to body weight index
While terminating the study, animal body weights were recorded. Before sacrifice, pictures of the dorsum of mice from all experimental groups were captured from a constant height using a digital camera. After necropsy, spleen from all the animals of each group was gathered, cleaned, and weighed. Spleen to bodyweight index was calculated as the ratio of spleen weight to body weight. In addition, representative spleen images from all study groups were captured.
Quantifying inflammatory cytokines by ELISA
Skin tissues were weighed followed by their homogenization using ELISA extraction buffer containing protease and phosphatase inhibitors, and centrifugation at 4°C for performing ELISA. The acquired tissue supernatants were utilized to estimate cytokine levels including IL-17, IL-22, TGF-β1, IL-1 β, and IL-6 using commercially available ELISA kits (eBioscience, USA).
Estimation of nitric oxide levels
Griess reagent was employed to estimate levels of NO in skin tissue supernatants. Supernatants obtained after homogenization of skin tissues were mixed with equal proportion of Griess reagent which was incubated in dark for 10 min. Absorbance was taken at 548 nm and results were indicated as μM/mg of skin protein.[15] Sodium nitrite was used as standard.
Histopathology
Skin tissues were fixed in 10% formal saline followed by embedding in paraffin. Sections with 5 μm thickness were made using microtome and were stained with H and E to examine pathologic histological changes in the tissue sections of all experimental groups under the light microscope.
Immunohistochemistry
Skin tissue sections fixed on slides were deparaffinized in xylene followed by rehydration in gradient alcohol and afterward, antigen retrieval. Then, 3% H2O2 was employed to remove all the endogenous peroxidases. Further incubation of skin sections with 3% BSA containing anti-Ki-67, anti-TNF-α, and anti-ICAM-1 primary antibodies (1:100) was performed for 1 h at room temperature. HRP-linked polymer/DAB detection system was utilized to develop antigen-antibody reaction the other day. Then, counterstaining of sections with hematoxylin was performed followed by mounting with coverslips using the resinous mounting solution. Sections were visualized for immunoreactivity under light microscope.
Western blot
Homogenization of skin tissues was performed with T-PER lysis buffer containing protease and phosphatase inhibitors. The obtained lysates were centrifuged at 4°C and supernatants were collected. Then, Bicinchonic acid kit was employed to determine the protein concentrations in all the lysates. An equal protein quantity from all the experimental groups were separated on sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gels and the protein bands were transferred onto nitrocellulose membrane. 3% BSA was used to block non-specific binding of the protein of interest. Membranes were incubated overnight with corresponding primary antibodies at 4°C. The next day, three washings of TBST were given to the blots followed by secondary antibody incubation at room temperature for 1 h. The visualization of protein bands was done using enhanced chemiluminescence reagents by chemdoc (Vilber fusion Fx) followed by their densitometric analysis using Image J software. β-actin was employed as an internal control.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis of data was carried out using one-way analysis of variance ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. The software employed was GraphPad Prism® Version 8. Values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation.
Results
Nimbolide reduces Psoriasis Area Severity Index scoring and splenomegaly
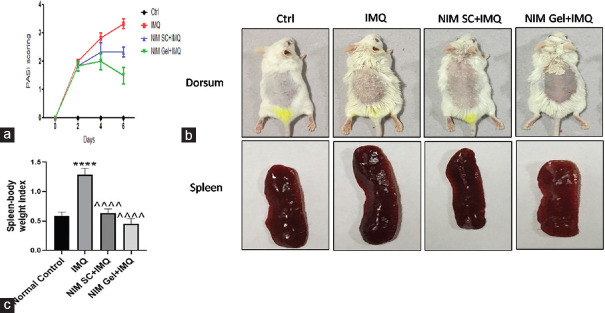
The PASI scoring is a quantitative rating score to evaluate the graveness of psoriasis taking into account the area coverage and plaque attributes such as scaling, erythema, and thickness. It was taken on a scale of 0–4. Application of the inducer, IMQ elevated PASI scoring taking it to the range of 3–4 compared to the control group with zero score. NIM given through SC route and in topical gel form reduced PASI scoring significantly taking it to 2.16 and 1.77, respectively, as shown in Figure 1a. This explains the superior effect of topical application of NIM gel in alleviating psoriasis symptoms. Morphologically, NIM prominently improved plaque appearance which was visualized as decreased scaling, thickness, and erythema in both the treatment routes. Dorsum skin of mice after application of NIM showed a significant decrease in skin thickness and scaly appearance compared to IMQ exposed group with dense scaly skin as reflected in Figure 1b.
Figure 1.
Effect of NIM on PASI scoring, IMQ induced skin epidermal thickness, and splenomegaly. Objective scoring accounting for redness (erythema), skin thickness, and scaling on a scale of 0 to 4, where 0 represents none, 1 represents mild, 2 represents moderate, 3 represents severe and 4 represents very severe. (a) Representative graph of PASI scoring, (b) Morphological representation of skin epidermis of mice dorsum and spleen of all experimental groups on termination day, (c) Graphical presentation of spleen body weight index. ****P< 0.0001 of IMQ versus Normal Control; ^^^^P< 0.0001 of NIM versus IMQ. IMQ=Imiquimod, PASI=Psoriasis Area Severity Index, NIM=Nimbolide
IMQ caused a noteworthy elevation in spleen weight compared to the control group with the normal spleen. Treatment with NIM, both via SC route and topical administration caused near to 2-fold reduction in spleen weights with the topical treatment taking it to almost the same level as the control group as depicted in Figure 1c.
Nimbolide alleviated psoriasis-related inflammation
Protein expression study, like western blotting was done to evaluate inflammatory markers like COX-2, NF-kB, and IL-6. Compared to control group, abnormal expression of all the aforementioned inflammatory mediators was observed in IMQ treated group. SC administered NIM caused a decrease in all types of inflammatory markers. However, treatment with topically applied NIM produced pronounced reduction in expression levels of all the mediators with IL-6 showing highly reduced expression and NF-kB level was comparable to the control group [Figure 2a-e].
Figure 2.
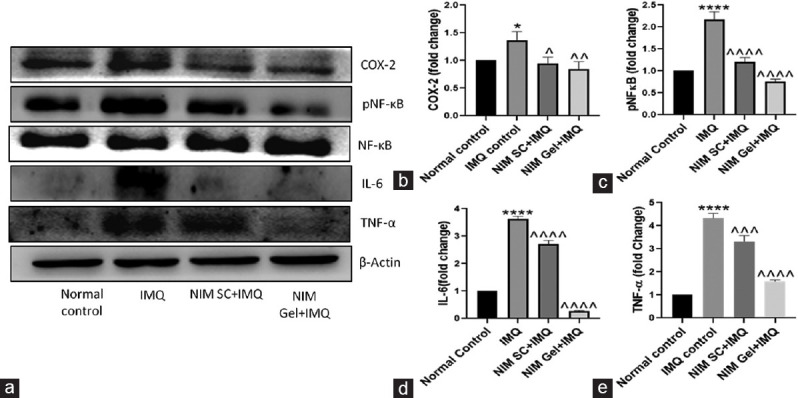
Immunoblot analysis demonstrating the effect of NIM on expression of various proteins involved in inflammatory signaling cascade. (a) Representation of immunoblots of COX 2, pNF κB, NF κB, IL 6 and TNF α, (b-e) Quantification of immunoblots of COX 2, pNF κB, IL 6 and TNF α respectively. ****P < 0.0001, *P < 0.05 of IMQ versus Normal Control; ^^^^P < 0.0001, ^^^P < 0.001, ^^P < 0.01, ^P < 0.05 of NIM versus IMQ. IMQ = Imiquimod, NIM = Nimbolide, TNF = Tumor necrosis factor, IL = Interleukin
IMQ treated group reflected aberrantly elevated levels of all these pro-inflammatory cytokines as evident from ELISA. Subcutaneously administered and topically applied NIM significantly downregulated the expression levels of all the markers with topical treatment showing superior effect as portrayed in Figure 3a-f.
Figure 3.
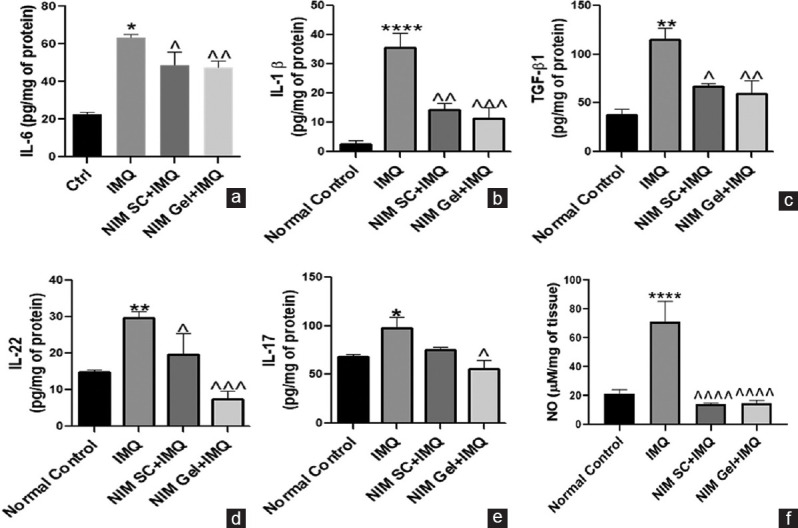
Anti-inflammatory role of NIM in reducing the progression of IMQ induced psoriasis like inflammation. (a-f) ELISA and Griess assay analysis for determining expression of various inflammatory cytokines including IL-6, IL-1β, TGF-β1, IL-22, IL-17 and NO respectively. ****P< 0.0001, **P< 0.01, *P< 0.05 of IMQ versus Normal Control; ^^^^P< 0.0001, ^^^P< 0.001,^^P< 0.01, ^P< 0.05 of NIM versus IMQ. TGF = Transforming growth factor, IMQ = Imiquimod, NIM = Nimbolide, IL = Interleukin, NO = Nitric oxide
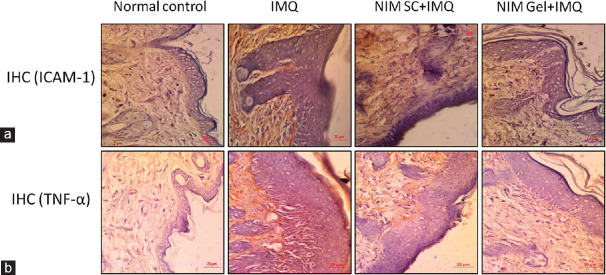
Immunohistochemical analysis of skin sections for expression levels of pro-inflammatory mediator TNF-α and adhesion marker ICAM-1 was performed. Pronounced expression of both TNF-α and ICAM-1 was observed in IMQ induced group which was remarkably attenuated in both the treatment groups and the expression in of these proteins in the NIM topically treated group was comparable to that of the control group as illustrated in Figure 4a and b.
Figure 4.
Effect of NIM in abridging psoriasis-like inflammation (a) representative images of immunohistochemical analysis of adhesion marker ICAM-1 protein expression of all experimental groups (b) Representative images of immunohistochemical analysis of pro-inflammatory protein TNF-α expression of all experimental groups (×40). TNF = Tumor necrosis factor, ICAM = Intercellular adhesion molecule
Nimbolide mitigates nitrative stress in Imiquimod-induced psoriasis
Quantification of NO levels in psoriatic lesions of all experimental groups represented the extent of nitrative stress. As expected, there was a remarkable increase in NO levels in IMQ exposed group. Treatment with NIM through topical and subcutaneous administration showed a similar decrease in NO levels. This demonstrates the strong anti-nitrative stress effect of NIM in psoriasis.
Nimbolide counter-balanced epidermal hyperproliferation and improved skin architecture
Evaluation of skin architecture and epidermal thickness was done by histopathological analysis of skin sections using H and E staining. The inducer group showed an elevated skin thickness, whereas subcutaneous administration of NIM reflected a marked decrease in the thickness [Figure 5a and b. Topical administration further reduced the degree of thickness compared to SC treatment strategy, coming out as a better therapeutic option in the treatment of psoriasis.
Figure 5.
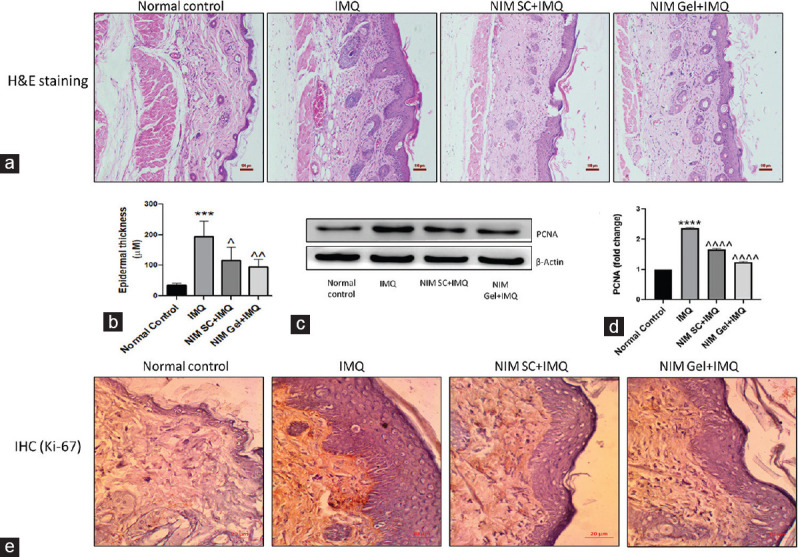
(a) Representative microphotographs of H and E staining of all experimental groups for evaluating histological changes in skin tissue sections (×10), (b) Graphical representation of epidermal thickness in μM as measured from microphotographs of H and E staining, (c) Western blotting analysis of proliferative protein marker PCNA, (d) Graphical representation of quantified PCNA, (e) Immunohistochemical analysis of another proliferative marker, Ki-67. ****P< 0.0001, ***P< 0.001 of IMQ versus Normal Control; ^^^^P< 0.0001, ^^P< 0.01, ^P< 0.05 of NIM versus IMQ. IMQ = Imiquimod, NIM = Nimbolide, PCNA = Proliferating cell nuclear antigen
Analysis of proliferative markers like PCNA and Ki-67 was done to further strengthen the previous finding. Protein expression studies, like immunohistochemistry and western blotting, were done to evaluate the expression of Ki 67 [Figure 5e and PCNA, respectively. In line with the above observations, abnormally high expression of both the markers was visible in IMQ administered group as delineated in Figure 5c and d. Treatment with NIM by either SC or topical route showed noteworthy reduction in these proliferative markers with latter administration bringing down the expression similar to control group.
Discussion
Psoriasis is an enervating chronic skin condition, driven by excessive infiltration of the inflammatory cell leading to hyperactivation of immune cells. Clinically, it is characterized by acanthosis, erythematous plaques, and epidermal hyperplasia due to enhanced mitosis in keratinocytes.[16] Although there are several theories governing the pathogenesis of this disease, there remains a need to connect the dots and formulate a theory with all the alterations considered. Since the last few decades, there has been a shift in trend with propensity toward employing natural products for treating chronic diseases due to their diversity of pharmacological actions. Due to their anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative and anti-angiogenic actions, natural products are apt as potential intervention in treating psoriasis. NIM is an active ingredient found in the leaves of plant A. indica (Indian Neem). It is well-explored drug in cancer treatment due to its strong anti-proliferative, anti-angiogenic, and anti-inflammatory characteristics. It is a potent deregulator of the NF-ΚB pathway which is the cornerstone in driving psoriatic inflammation.[14]
The current study is based on the hypothesis that the application of NIM may alleviate psoriasis effectively. It is a 7 days study performed in IMQ induced psoriasis-like inflammation model in Balb/C mice. IMQ is a specific agonist of TLR7/8 receptors present on dendritic cells. Activations of dendritic cells by IMQ lead to the huge influx of immune cells to skin tissue resulting in the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines by the IL-23/IL-17 axis which is externally visible as erythema, scale formation, and epidermal thickness.[17]
We found that NIM reduced the skin thickness and associated inflammation more effectively in gel formulation compared to subcutaneous administration as apparent by PASI scoring. Photographs of mice dorsum also supported this finding with more pronounced decrease in scaly epidermis and redness in animals treated with NIM gel formulation compared to their counterparts receiving SC administration. H and E staining to histologically evaluate the effect of NIM in improving skin architecture and epidermal thickness by abridging inflammation further strengthened the finding.
A complex role of differentially expressed genes in T-cells is strongly associated with keratinocytes hyperproliferation as evident from altered protein expression of proliferative markers in keratinocytes and reduction in epidermal turnover time from 50 days in healthy tissue to 5 days in psoriatic lesion condition.[18] In line with the existing literature, we observed an altered expression of these proliferative markers like Ki-67 and PCNA in the IMQ group. However, treatment with NIM was effective in decreasing the proliferation of keratinocytes which was evident from reduced expression of Ki-67 and PCNA in the groups treated with NIM, both gel formulation, and SC administration.
IL-10 cytokine produced from B-cells, matured in spleen plays a major role in the regulation of immune system function.[19] Assessment of spleen weight and spleen body weight index in NIM administered group, both topical and subcutaneous showed significant improvement in these two parameters which was comparable to control group.
Keratinocytes harbor two isoforms of NO synthase enzyme, constitution and inducible which are responsible for the formation of NO. Activation of these enzymes by various stimuli results in excess production of NO causing nitrative stress in keratinocytes. At higher concentrations, NO acts as cytotoxic agent and aids in disease progression by augmenting cell proliferation.[20] Topical and subcutaneous administration of NIM brought down the NO to equal levels.
There have been many theories and hypothesis predicting the role of various molecular alterations in driving psoriasis. However, the role of inflammation with the plethora of cytokines are cornerstone of the pathogenesis of psoriasis and can be underscored as major partakers in disease progression. IL-6 cytokine which is synthesized in keratinocytes is significantly increased in psoriatic skin. It is responsible for the progression of inflammation and enhancing skin cell proliferation.[21] IL-1 β is a potent inducer of dermal T-cell proliferation and IL-17 production. It triggers keratinocytes to maintain Th17 cells in the skin dermis via secretion of chemokines for amplification of inflammatory cascade.[22] Another very important inflammatory mediator, TGF-β1 mediates the formation of psoriatic lesions as reported by Zhang et al.[23] Differentiation of Th17 cells by various inflammatory cytokines leads to the subsequent production of IL-17 and IL-22 chemokines which are cornerstones in promoting skin cell hyperproliferation and maintenance of vicious inflammatory loop.[24] We found that NIM substantially reduced the levels of all the aforementioned inflammatory cytokines to a great extent with topical therapy once again showing a superior effect over subcutaneous administration. NIM has proven effect on abrogating the activation of the NF-κB pathway also. NF-κB signaling is crucial for the synthesis of various inflammatory cytokines implicated in psoriasis progression.[25] Consistent with the previous literature, we observed the expression of NF-κB to be significantly reduced upon treatment with NIM. Further, immunohistochemical analysis to evaluate the expression of another cytokine, TNF-α underscored the potent anti-inflammatory effect of NIM with topical therapy showing outstanding results. COX-2 is a major player in inflammation which positively correlated with the expression of NF-κB. As reported by Bakry et al., NF-κB and COX-2 are two concordant players in the pathogenesis of psoriasis.[26] Further, nosediving expression of master inflammatory proteins like NF-κB, COX-2, and IL-6 favored the anti-inflammatory effect of NIM gel to a large extent.
ICAM-1 is required for the migration of T lymphocytes and other mononuclear inflammatory cells to the dermis. ICAM-1 expression is directly correlated to the severity of psoriasis.[27] It has been reported that upon stimulation by inflammatory cytokines, which are aberrantly released in psoriasis, epidermal keratinocytes express ICAM-1. Upregulated expression of ICAM-1 on the surface of keratinocytes augments infiltration of lymphocytes into inflamed areas. Increased infiltration is known to be one of the most crucial steps in the pathogenesis of psoriasis and thus making it a potential target.[28] Given its key role, we looked into the outcome of NIM treatment on modulation of ICAM-1 expression. NIM treated groups demonstrated reduced adhesion marker.
Conclusion
Concluding the findings of the current study, we demonstrate the potential of NIM as an anti-psoriatic compound by demonstrating its protective effect in IMQ induced murine model of psoriasis-like inflammation. Our study also reiterates that topical application of NIM in a suitable formulation in treating psoriasis, as in gel here, would be more beneficial and patient compliant thus emphasizing the probable clinical translation of this compound.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Casciano F, Pigatto PD, Secchiero P, Gambari R, Reali E. T cell hierarchy in the pathogenesis of psoriasis and associated cardiovascular comorbidities. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1390. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chandran V, Raychaudhuri SP. Geoepidemiology and environmental factors of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. J Autoimmun. 2010;34:J314–21. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2009.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schleicher SM. Psoriasis: Pathogenesis, assessment, and therapeutic update. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2016;33:355–66. doi: 10.1016/j.cpm.2016.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gröne A. Keratinocytes and cytokines. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2002;88:1–12. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2427(02)00136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Blanpain C, Fuchs E. Epidermal homeostasis: A balancing act of stem cells in the skin. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10:207–17. doi: 10.1038/nrm2636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ryu S, Broussard L, Youn C, Song B, Norris D, Armstrong CA, et al. Therapeutic effects of synthetic antimicrobial peptides, TRAIL and NRP1 blocking peptides in psoriatic keratinocytes. Chonnam Med J. 2019;55:75–85. doi: 10.4068/cmj.2019.55.2.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rendon A, Schäkel K. Psoriasis pathogenesis and treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:1475. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lin YK, See LC, Huang YH, Chi CC, Hui RY. Comparison of indirubin concentrations in indigo naturalis ointment for psoriasis treatment: A randomized, double-blind, dosage-controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:124–31. doi: 10.1111/bjd.15894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bernstein S, Donsky H, Gulliver W, Hamilton D, Nobel S, Norman R. Treatment of mild to moderate psoriasis with Reliéva, a Mahonia aquifolium extract – A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Am J Ther. 2006;13:121–6. doi: 10.1097/00045391-200603000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Li XQ, Chen Y, Zhou HM, Shi HL, Yan XN, Lin LP, et al. Anti-psoriasis effect of water-processed rosin in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019;242:112073. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ellis CN, Berberian B, Sulica VI, Dodd WA, Jarratt MT, Katz HI, et al. A double-blind evaluation of topical capsaicin in pruritic psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;29:438–42. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(93)70208-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Diddi S, Bale S, Pulivendala G, Godugu C. Nimbolide ameliorates fibrosis and inflammation in experimental murine model of bleomycin-induced scleroderma. Inflammopharmacology. 2019;27:139–49. doi: 10.1007/s10787-018-0527-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Raja Singh P, Arunkumar R, Sivakamasundari V, Sharmila G, Elumalai P, Suganthapriya E, et al. Anti-proliferative and apoptosis inducing effect of nimbolide by altering molecules involved in apoptosis and IGF signalling via PI3K/Akt in prostate cancer (PC-3) cell line. Cell Biochem Funct. 2014;32:217–28. doi: 10.1002/cbf.2993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wang L, Phan DD, Zhang J, Ong PS, Thuya WL, Soo R, et al. Anticancer properties of nimbolide and pharmacokinetic considerations to accelerate its development. Oncotarget. 2016;7:44790–802. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sunkari S, Thatikonda S, Pooladanda V, Challa VS, Godugu C. Protective effects of ambroxol in psoriasis like skin inflammation: Exploration of possible mechanisms. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;71:301–12. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.03.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Nestle F, Kaplan D, Schon M, Barker J. Psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:496–509. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0804595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.van der Fits L, Mourits S, Voerman JS, Kant M, Boon L, Laman JD, et al. Imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice is mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. J Immunol. 2009;182:5836–45. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Li J, Li X, Hou R, Liu R, Zhao X, Dong F, et al. Psoriatic T cells reduce epidermal turnover time and affect cell proliferation contributed from differential gene expression. J Dermatol. 2015;42:874–80. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.12961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pestka S, Krause CD, Sarkar D, Walter MR, Shi Y, Fisher PB. Interleukin-10 and related cytokines and receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:929–79. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.22.012703.104622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ghosh A, Tiwari GJ. Role of nitric oxide-scavenging activity of Karanjin and Pongapin in the treatment of Psoriasis. 3 Biotech. 2018;8:338. doi: 10.1007/s13205-018-1337-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Miao X, Xiang Y, Mao W, Chen Y, Li Q, Fan B. TRIM27 promotes IL-6-induced proliferation and inflammation factor production by activating STAT3 signaling in HaCaT cells. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology. 2020 doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00314.2019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cai Y, Xue F, Quan C, Qu M, Liu N, Zhang Y, et al. A critical role of the IL-1β–IL-1R signaling pathway in skin inflammation and psoriasis pathogenesis. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:146–56. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2018.07.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhang Y, Meng XM, Huang XR, Wang XJ, Yang L, Lan HY. Transforming growth factor-β1 mediates psoriasis-like lesions via a Smad3-dependent mechanism in mice. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2014;41:921–32. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mease PJ. Inhibition of interleukin-17, interleukin-23 and the TH17 cell pathway in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015;27:127–33. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Dou R, Liu Z, Yuan X, Xiangfei D, Bai R, Bi Z, et al. PAMs ameliorates the imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin disease in mice by inhibition of translocation of NF-κB and production of inflammatory cytokines. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0176823. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bakry OA, Samaka RM, Shoeib MA, Abdel Aal SM. Nuclear factor kappa B and cyclo-oxygenase-2: Two concordant players in psoriasis pathogenesis. Ultrastruct Pathol. 2015;39:49–61. doi: 10.3109/01913123.2014.952470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Elias A, Goodman M, Rohan M. Serum ICAM-1 concentrations in patients with psoriasis treated with antithyroid thioureylenes. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1993;18:526–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.1993.tb01022.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Xiong H, Xu Y, Tan G, Han Y, Tang Z, Xu W, et al. Glycyrrhizin ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in BALB/c mice and inhibits TNF-a-induced ICAM-1 expression via NF-κB/MAPK in HaCaT cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35:1335–46. doi: 10.1159/000373955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]