Abstract
The vertebrate cerebellum arises at the dorsal part of rhombomere 1, induced by signals from the isthmic organizer. Two major cerebellar neuronal subtypes, granule cells (excitatory) and Purkinje cells (inhibitory), are generated from the anterior rhombic lip and the ventricular zone, respectively. This regionalization and the way it develops are shared in all extant jawed vertebrates (gnathostomes). However, very little is known about early evolution of the cerebellum. The lamprey, an extant jawless vertebrate lineage or cyclostome, possesses an undifferentiated, plate-like cerebellum, whereas the hagfish, another cyclostome lineage, is thought to lack a cerebellum proper. In this study, we found that hagfish Atoh1 and Wnt1 genes are co-expressed in the rhombic lip, and Ptf1a is expressed ventrally to them, confirming the existence of r1’s rhombic lip and the ventricular zone in cyclostomes. In later stages, lamprey Atoh1 is downregulated in the posterior r1, in which the NeuroD increases, similar to the differentiation process of cerebellar granule cells in gnathostomes. Also, a continuous Atoh1-positive domain in the rostral r1 is reminiscent of the primordium of valvula cerebelli of ray-finned fishes. Lastly, we detected a GAD-positive domain adjacent to the Ptf1a-positive ventricular zone in lampreys, suggesting that the Ptf1a-positive cells differentiate into some GABAergic inhibitory neurons such as Purkinje and other inhibitory neurons like in gnathostomes. Altogether, we conclude that the ancestral genetic programs for the formation of a distinct cerebellum were established in the last common ancestor of vertebrates.
Keywords: cerebellum evolution, cyclostome, lamprey, hagfish, evolutionary developmental biology (EvoDevo), rhombic lip, Purkinje cells, granule cells of cerebellum
Introduction
During development, the cerebellum arises from the dorsal part of rhombomere 1 (r1), just posterior to the midbrain-hindbrain boundary (MHB or isthmic organizer). R1 is defined as an Otx- and Hox-negative region and this molecular state is critical for cerebellar development (Broccoli et al., 1999; Katahira et al., 2000; Butts et al., 2014a; Figure 1B). In addition, FGF8, a secreted molecular signal from the MHB, plays an important role for the induction of the cerebellum (Reifers et al., 1998; Sato et al., 2001). Wnt1, which is expressed in the most caudal part of the midbrain, is also known to encode an important signaling molecule. Although not directly involved in the induction of the cerebellum, Wnt1-knockout mice lack the cerebellum. This, however, might be a secondary effect as a result of the disruption of the specification of the midbrain and hindbrain (McMahon and Bradley, 1990).
FIGURE 1.
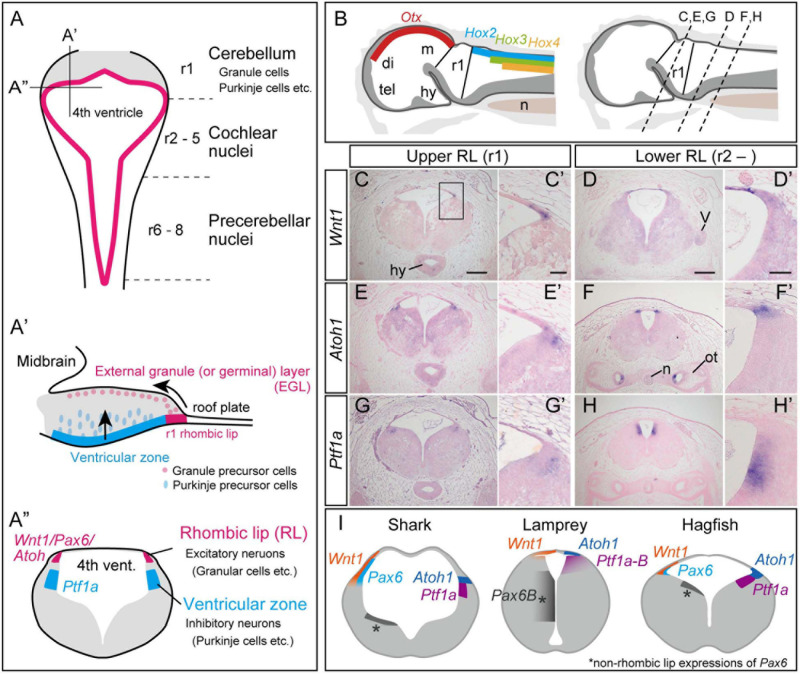
Development of the cerebellum in mammals, based on Fujiyama et al., 2009 (A). (A) Dorsal view of the rhombomeres. The rhombomere 1 (r1) gives rise to the cerebellum, while r2–8 generates the cochlear nuclei and precerebellar nuclei. (A’) Sagittal view of the rhombomere 1. Granule precursor cells, generated in the r1 rhombic lip, migrate tangentially to form the external germinal layer (EGL). The Purkinje precursor cells originating from the ventricular zone secrete Shh, which is involved in the proliferation of the granule cells. The granule cells in EGL then migrate ventrally to form the granular layer. (A”) Transverse view of rhombomere 1 showing the rhombic lip as the source for excitatory neurons, and the ventricular zone where the inhibitory neurons arise. (B–H) Upper and lower rhombic lip gene expression patterns in the hagfish, E. burgeri. (B) Illustration of a sagittal section of the anterior part of a stage 53 embryo. (left) Rhombomere 1 (Upper rhombic lip) is identified as a negative region of both Otx and Hox genes (Oisi et al., 2013; Pascual-Anaya et al., 2018). (right) Anterior-posterior level of transverse sections shown in (C–H) are indicated in a sagittal illustration. (C–H) Section in situ hybridizations for hagfish Wnt1, Atoh1 and Ptf1a genes showing their expression patterns in r1 (C,E,G) and posterior to r1 (D,F,H). (C’–H’) Higher magnification images of the rhombic lip expression patterns shown in (C–H). (I) Comparison of the upper rhombic lip gene expression patterns in the shark (S. torazame), lamprey (L. camtschaticum), and hagfish (E. burgeri) based on Sugahara et al. (2017) and the present study. di, diencephalon; hy, hypothalamus; m, mesencephalon; n, notochord; ot, otic capsule; tel, telencephalon; r1, rhombomere 1; V, trigeminal nerve. Scale bars: 200 μm (C–H), 50 μm (C’–H’).
Excitatory granule neurons (glutamatergic), and inhibitory Purkinje cells (GABAergic) play a major role in the processing of the cerebellar cortex. These cerebellar neurons arise from two distinct embryonic domains: the rhombic lip and the ventricular zone (Figures 1A–A”). The rhombic lip is the rostrodorsal edge of the hindbrain formed just below the roof plate (Wullimann et al., 2011). The rhombic lip can be divided into the anterior part that arises from r1 and the rest, the posterior part comprised between r2 and 8. In gnathostomes, Wnt1 and Pax6 are co-expressed throughout the rhombic lip. Also, Atoh1 (a bHLH transcription factor; Math1 in mice)-positive neuron precursors specifically arise from the upper (anterior) rhombic lip, differentiating into cerebellar granule cells, while the cells in the lower (posterior) rhombic lip differentiate into excitatory neurons in the cochlear nuclei and the precerebellar nuclei and give rise to mossy fibers (Fujiyama et al., 2009). In amniotes, Atoh1-positive precursors migrate secondarily from the upper rhombic lip to cover the surface of the cerebellar cortex, forming the external granule cell layer (EGL) (Wullimann et al., 2011; Figures 1A–A”). The proliferative activity of EGL cells is stimulated transiently by Shh signaling from Purkinje cells (Martí and Bovolenta, 2002). Subsequently, the EGL cells start to express a proneural gene, NeuroD1, and stop expressing Atoh1, then shifting toward a postmitotic state. Finally, the granule cells migrate ventrally to generate an internal granular layer (Wullimann et al., 2011). This proliferative EGL may have been acquired in the amniote lineage, because frogs have only non-proliferative EGL (Gona, 1972; Butts et al., 2014b) and no EGL has been identified in zebrafish, paddlefish (Polyodon spathula), and sharks (Scylliorhinus canicula) (Chaplin et al., 2010; Butts et al., 2014c; Hibi et al., 2017). However, there are reports of cell migration and genetic mechanisms similar to the amniote EGL in zebrafish (Biechl et al., 2016), although this remains controversial. The internal migration of the granule cells is also reported in frogs and teleosts, but not in sharks and paddlefish (Chaplin et al., 2010; Butts et al., 2014c; Hibi et al., 2017).
The ventricular zone, another source of cerebellar neurons, occupies the ventromedial position to the rhombic lip (Figure 1A”). This domain is characterized by the expression of the bHLH transcription factor coding gene Ptf1a, and gives rise to GABAergic inhibitory neurons including Purkinje, basket, stellate, and Golgi cells in the cerebellar cortex (Leto et al., 2016). A Ptf1a knockout mouse, cerebelles, lacks the entire cerebellar cortex together with Purkinje cells and other GABAergic interneurons, indicating that Ptf1a is essential for the development of GABAergic inhibitory neurons in the cerebellum (Hoshino et al., 2005; Hoshino, 2006). The caudal area (r2-r8) of the ventricular zone produces inhibitory neurons in the cochlear nuclei and neurons that generate climbing fibers in the precerebellar nuclei (Yamada et al., 2007; Fujiyama et al., 2009).
Cyclostomes that include lampreys and hagfish, are the only living jawless vertebrates and diverged from gnathostomes over 500 million years ago (Kuraku and Kuratani, 2006). The lamprey possesses only a small, plate-like cerebellum in the rostrodorsal part of the hindbrain, in which small granule-like cells are present (Striedter and Northcutt, 2020). Therefore, the lamprey cerebellum is considered to be homologous to the corpus cerebelli (the central lobe of the cerebellum) of gnathostomes (Nieuwenhuys, 1967). However, the lamprey lacks a layered cerebellar cortex. The presence of the Purkinje cells is still ambiguous in lamprey (Lannoo and Hawkes, 1997). On the other hand, the hagfish, the other group of cyclostomes, does not possess a morphologically distinct cerebellum, showing only the vestibulo-lateral commissure reported at the midbrain-hindbrain boundary (Larsell, 1947; Nieuwenhuys et al., 1998; Sugahara et al., 2016).
Previous studies have shown that lamprey embryos exhibit Otx- and Hox1-negative rhombomere 1 region (Ueki et al., 1998; Takio et al., 2004), while Gbx is expressed in the entire hindbrain (Takio et al., 2007). As in gnathostomes, the lamprey MHB expresses FGF8 and Wnt1 (Shigetani et al., 2002; Sugahara et al., 2016; Supplementary Figure 1), suggesting that a certain regionalization and inductive signals for the cerebellum are shared at least by lampreys. Regarding the development of cerebellar neurons, we previously reported that Atoh1 is expressed in the lamprey in dorsal rhombomeres, including r1, and one of two orthologous genes of Ptf1a expressed in the ventral part (Sugahara et al., 2016). However, it is still unclear whether cerebellar neuron subtypes are differentiated from these domains or not. Much less is known about the presence or absence of this regionalization in the hagfish, the involved induction signals or the genetic program for the specification of cerebellar neurons subtypes. We previously reported that Pax6 and Atoh1 are expressed in the rhombic lip of the hagfish but could not identify exactly if it was in r1 only or also in more caudal rhombomeres, because we could use only sectioned samples due to the limitation of embryonic material (Ota et al., 2007). Here, we further investigated the molecular basis underlying the cerebellum regionalization and the cerebellar neuron specification in lamprey and hagfish embryos. Also, by comparing gnathostomes and cyclostomes, we tried to depict the molecular and morphological ground patterns of the cerebellum of the last common ancestor of crown vertebrates, and to infer the evolutionary changes in its developmental mechanisms in the different vertebrate lineages.
Materials and Methods
Animals
Matured arctic lamprey, Lethenteron camtschaticum were collected in Hokkaido, Japan. Embryos were obtained by artificial fertilization and staged as described previously (Tahara, 1988; Sugahara et al., 2015) and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde. Matured Japanese inshore hagfish, Eptatretus burgeri were caught from the Japan Sea off Shimane Prefecture. The embryos of E. burgeri were obtained by keeping adults in cages and placed in the sea bottom as described previously (Oisi et al., 2015). The staging of hagfish embryos followed Dean (1899) and Oisi et al. (2013) and fixed with Serra’s fixative (6:3:1 mixture of ethanol, formalin, and glacial acetic acid).
Gene Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis
Sequence of hagfish Wnt1 and Ptf1a genes were obtained from a previously published transcriptome assembly (Pascual-Anaya et al., 2018) by means of TBLASTN v2.2.31 + searches (Altschul et al., 1997) and using gnathostome counterparts as queries. Ptf1a sequence was completed on the 3′ end by manual cloning and sequence following standard protocols. For the lamprey GAD gene, the sequence was obtained from transcriptome data reported previously (Pascual-Anaya et al., 2018), based on the sequence of Petromyzon marinus GAD1 (XM_032965485). Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT–PCR) was performed to amplify fragments of each gene with specific primers from total RNA of lamprey embryos or hagfish juvenile (sequences of primers used are listed in Supplementary Table 1). The sequences identified here have been deposited in GenBank under accession numbers LC60429-31. Hagfish Atoh1 (KT897935), lamprey Atoh1 (KT897930), Ptf1a-B (KT897934), NeuroD (LC424505) were reported previously (Sugahara et al., 2016; Higuchi et al., 2019).
Molecular phylogenetic tree inference of the Wnt1 and Ptf1a genes were performed as previously described (Hara et al., 2018) using homolog sequences retrieved via the aLeaves webserver (Kuraku et al., 2013).
In situ Hybridization of the Hagfish and Lamprey Embryos
In situ hybridization on paraffin sections of E. burgeri was performed as described (Oisi et al., 2015). Whole-mount in situ hybridization on lamprey embryos was performed according to Sugahara et al., 2015. Some stained specimens were made transparent by 1:2 mixture of Benzyl-alcohol and Benzyl-benzoate after dehydration. Staining specimens were embedded in tissue tek® O.C.T.TM compound and sectioned (12 μm) by CryoStar NX50 (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
Results
Isthmic Gene Expressions in Cyclostomes
Previously, we have identified the expression of FGF8/17 and Wnt1 in a sharp domain, of the lamprey brain and corresponding to the MHB (Shigetani et al., 2002; Sugahara et al., 2016; Supplementary Figures 1B,D). However, the presence of this expression domain in the hagfish is so far unknown. We newly identified a hagfish Wnt1 orthologous gene (Supplementary Figure 3A) and investigated its expression pattern in the hagfish brain. At mid-pharyngula stage (Dean stage 45), hagfish Wnt1 expression was observed as a sharp transverse band corresponding to the MHB (Supplementary Figure 1A). Also, hagfish FGF8/17 was expressed around the MHB, but in a relatively broader domain than that of lamprey and gnathostomes (Supplementary Figure 1C).
Expression Patterns of Upper- and Lower-Rhombic Lip Marker Genes in Hagfish
Next, we investigated whether the genetic machinery for r1-neuronal differentiation is present in cyclostomes or not. Generally, when looked from a dorsal view, the gnathostome hindbrain appears as a rhomboid shape with a thin roof plate over the fourth ventricle. The most expanded region corresponds to the boundary between r1 and r2 (Wingate, 2001). In hagfish, the anterior border of the Hox2 expression was seen in the lateral edge of the fourth ventricle (Pascual-Anaya et al., 2018). We therefore defined this region as the posterior limit of the anterior rhombic lip (Figure 1B). At late pharyngular stage (Dean stage 53), Atoh1 was expressed in the bilateral dorsal-most edges of the hindbrain, the “rhombic lip,” in the upper and lower rhombomeres. Wnt1 expression overlaps with Atoh1 in the rhombic lip but extends to the roof plate (Figures 1C–F’). We newly identified a Ptf1a ortholog gene in hagfish (Supplementary Figure 3B). Hagfish Ptf1a is expressed at the surface of the fourth ventricle ventral to the Atoh1/Wnt1 expressing region in both lower and upper rhombomeres (Figures 1G,H). These results indicate that the regionalization of the rhombic lip and the ventricular zone are present in hagfish r1 (Figure 1I).
Spatio-Temporal Atoh1 Expression in the Lamprey Hindbrain
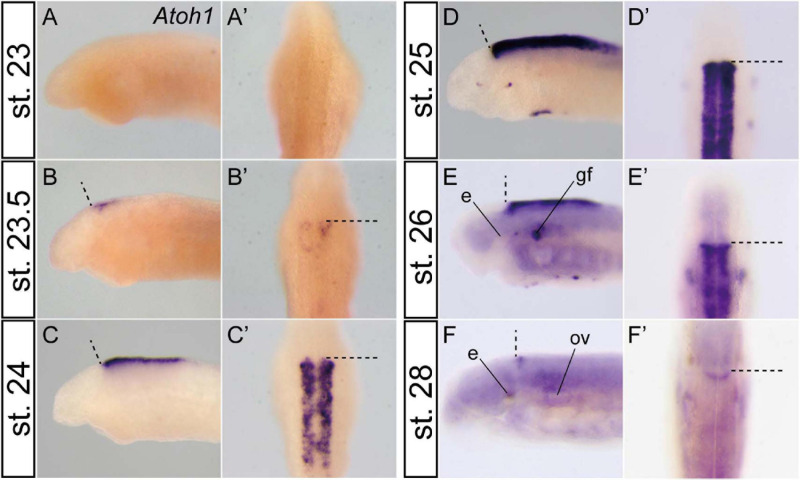
In zebrafish and paddlefish, granule neuron precursors are reported to express Atoh1 in early embryonic stages, but Atoh1 is later downregulated in the lateral cerebellar rhombic lip. Subsequently, post-mitotic granule precursor cells express NeuroD and differentiate into matured granule cells. Meanwhile, proliferation of the precursor cells, which express Atoh1, is selectively maintained in the rostromedial rhombic lip until late development (Kani et al., 2010; Butts et al., 2014c). To investigate whether the same or a similar genetic mechanism for the differentiation of the cerebellar granule cells is present in the lamprey or not, we observed the spatio-temporal expression pattern of Atoh1 in lamprey embryos. Atoh1 expression starts at stage 23.5 in the rostral half of the rhombic lip (Figure 2B) and then expands throughout the upper and lower rhombic lip during stages 24–26 (Figures 2C–E). Subsequently, this Atoh1 expression is downregulated in the caudal half of r1 and lower rhombic lip, whereas its expression is maintained in the rostral tip of r1. This continuous expression of Atoh1 is observed at least until respiration stage (stage 28) (Figure 2F). Like ray-finned fish, the rostral area of lamprey r1 is apparently regulated differently from the other rhombic lip (Kani et al., 2010; Butts et al., 2014c). In birds and mammals, Atoh1-positive granule precursor cells migrate from the rhombic lip to cover the surface of the cerebellum to form the EGL. Subsequently, EGL cells migrate ventrally and form the internal granule layer (Butts et al., 2014a). In the lamprey, however, we could not observe the expansion or migration of Atoh1-positive cells as is the case in the shark and paddlefish (Chaplin et al., 2010; Butts et al., 2014c).
FIGURE 2.
Temporal Atoh1 expression pattern in the lamprey hindbrain. Lateral (A–F) and dorsal views (A’–F’). Dashed lines indicate the MHB. Atoh1 expression starts at stage 23.5 in the rostral half of the rhombic lip (B) and subsequently expands throughout the rhombic lip during stages 24–26 (C–E). After stage 27 (not shown), the expression is restricted only to the rostral border of the rhombomere 1 (F). Note that the apparent asymmetrical staining in (B) does not reflect the actual difference in expression, but is caused by the staining process. e, eye; gf, complex of facial/lateral line ganglion; ov, otic vesicle.
Differentiation of Atoh1–Positive Cells in the Lamprey Late Development
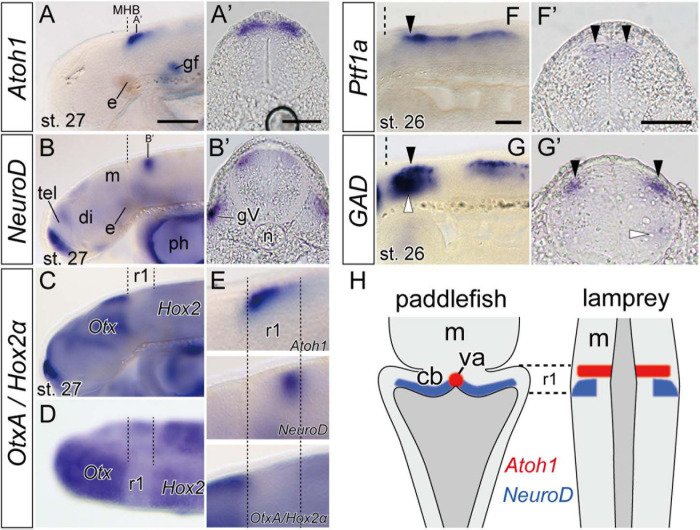
As mentioned above, lamprey Atoh1 is downregulated at late stages except in the rostral area of the r1 (Figure 2F). In accordance with the decrease of Atoh1 expression, the NeuroD expression become apparent slightly caudal to the Atoh1-positive area (Figures 3A,B and Supplementary Figure 2). To distinguish whether the NeuroD-positive region is included within r1 or not, we conducted double in situ hybridization with OtxA and Hox2α (Figures 3C,D). Since OtxA and Hox2α are expressed in the midbrain and r2, respectively (Ueki et al., 1998; Takio et al., 2004), we could identify r1 as the OtxA/Hox2α-negative region in between. By comparing NeuroD expression with Otx–Hox2 expression, we identified the NeuroD–positive region located in the posterior part of r1 (Figure 3E). Transverse sections showed that NeuroD expression was located lateral to, but slightly overlapping the Atoh1 expression domain (Figures 3A’,B’). The topological location of these two Atoh1 and NeuroD expression domains suggests that precursors migrate from more anterior/medial (Atoh1-positive) areas to more posterior/lateral (NeuroD-positive) zones during their differentiation process. At the same time, however, neuron precursors in the rostral r1 retain Atoh1 expression. This positional relationship is comparable to the development of cerebellar granule neurons in some gnathostome fishes as discussed below.
FIGURE 3.
Expression of genes involved in neuron differentiation during lamprey late embryonic stages. (A,A’) Atoh1 expression is restricted to the anterior r1 in stage 27 embryo (arrow heads). Dashed lines indicate the MHB. (B,B’) NeuroD expression is observed behind the Atoh1 expression domain (arrowheads). Note that (A’,B’) are not at the same rostrocaudal positions in r1. The apparent asymmetrical staining in (B’) does not reflect the actual difference in expression, but is caused by the slightly oblique cutting of the sections. (C,D) In situ hybridization of both OtxA and Hox2α probes in stage 27 in lateral view (C) and dorsal view (D). OtxA is expressed only anterior to the midbrain, whereas Hox2α is expressed caudally from r2. Dashed lines indicate the borders of r1 identified as “Otx–Hox free” domain. (E) High magnifications of the panel (A–C) in r1 region. (F,F’) Ptf1a-B expression at the ventricular zone at stage 26 (arrowheads). (G,G’) GAD is expressed in the hindbrain at the same dorsal level than –but lateral to– the Ptf1a expression domains (black arrowheads) and also in a ventral domain (white arrowheads). (H) Comparison of Atoh1 and NeuroD expression patterns in the hindbrain between paddlefish, Polyodon spathula (stage 42, based on Butts et al., 2014c), and lamprey. Note that although the lamprey hindbrain does not show a ‘diamond shape’ of the rhombic lip during embryonic stages, the topological relationship of these gene expression patterns is comparable in both species. cb, cerebellum primordium; gV, trigeminal ganglion; ph, pharynx; va, valvula cerebelli. See Figures 1,2 for other abbreviations. Scale bars, 100 μm (A–D), 50 μm (A’,B’,F,F’,G,G’).
Ptf1a Expression and GAD–Positive Inhibitory Neurons
In mammals, Ptf1a–positive cells in r1 ventricular zone differentiate into GABA-releasing inhibitory neurons such as Purkinje cells and several other types of interneurons (basket, stellate, and Golgi cells) (Hoshino et al., 2005). Presence of Ptf1a–positive cells in r1 ventricular zone in both lampreys and hagfish suggests that an active and probably homologous genetic mechanism for GABAergic inhibitory neuron production exist in cyclostomes. We therefore observed the expression of glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) gene, which encodes an enzyme to catalyze the synthesis of GABA. In lamprey, at stage 26, GAD expression domain overlaps the Ptf1a expression domain in the anterior part of the rhombencephalon (including r1) (arrowheads in Figures 3F,G). Transverse sections showed that GAD expression localizes relatively lateral to the Ptf1a–positive ventricular zone (Figures 3F’,G’). Since Ptf1a is expressed only in undifferentiated neurons in the neuroepithelium (Hoshino et al., 2005), this may possibly reflect that Ptf1a-positive precursor cells in lamprey are generated in the ventricular zone, then migrate radially, and finally differentiate into inhibitory GABAergic neurons.
Discussion
Presence of MHB Signals in Cyclostomes
Signaling factors from the MHB are essential for the induction and development of the gnathostome cerebellum (Leto et al., 2016). In this study, we identified both FGF8/17 and Wnt1 expression around the MHB region in the hagfish embryo similar to gnathostomes and the lamprey (Supplementary Figure 1), suggesting that these signals are conserved through all extant vertebrates. Curiously, hagfish FGF8/17 expression showed a broader pattern than in other vertebrates (Supplementary Figure 1C). This unique FGF8/17 expression pattern in the hagfish might be related to the absence of a distinct cerebellum in adult hagfish. Alternatively, FGF8 signaling might have a limited effect on cerebellar development, since some reports have indicated that conditional mutant mice with reduced FGF8 expression in the MHB shows only loss of the cerebellar vermis region (Basson et al., 2008; Yu et al., 2011, 2013). Further experiments would be needed to explain this unusual FGF8/17 expression pattern in the hagfish.
Upper and Lower Rhombic Lip and Ventricular Zone in Cyclostomes
We morphologically defined the domain of r1 in paraffin sections of a hagfish embryo and found that Wnt1 and Atoh1 are expressed not only in r1, but also in the more caudal rhombomeres. Expression of Pax6, another rhombic lip gene, was previously reported (see Figure 4C in Sugahara et al., 2016). In addition, we identified Ptf1a expression in the ventral side of the Wnt1/Atoh1 expression domain (Figures 1G,H). Together with previous studies in the lamprey, we conclude that the regionalization into the upper/lower rhombic lip and the accompanying ventricular zone is shared between cyclostomes and gnathostomes (Figure 1I).
Presence of a Differentiation Mechanism for Granule Cells and a Continuous Atoh1-Expression Domain
Lamprey Atoh1 is initially expressed in the entire rhombic lip, but subsequently gets downregulated in the caudal half of r1 and the lower rhombic lip (Figure 2). Concomitantly with this downregulation, NeuroD becomes upregulated in the caudal part of r1 (Supplementary Figure 2 and Figure 3B). This transition is consistent with the differentiation process of granule cells in zebrafish, paddlefish and amniotes (Kani et al., 2010; Butts et al., 2014c). Therefore, the genetic mechanism for the differentiation of the cerebellar granule cells might be present in the lamprey as well.
We found a continuous expression domain of the Atoh1 in the rostral r1, topologically comparable to the rostromedial domain of the paddlefish and zebrafish r1 (Kani et al., 2010; Butts et al., 2014c; Figure 3H). In the zebrafish, this region differentiates into valvula cerebelli, a unique cerebellar structure in ray-finned fishes but not in cartilaginous fish and lobe-finned fish including tetrapods (Nieuwenhuys et al., 1998). Although the valvula cerebelli has not been identified anatomically in adult lampreys, it is possible that a homologous genetic domain might be present in the embryonic lamprey r1.
Presence of GAD-Positive Inhibitory Neurons in Lamprey r1
In mice, all cerebellar inhibitory neurons arise from the Ptfa1-positive ventricular zone (Hoshino et al., 2005). Also, inhibitory neurons in the cochlear nucleus arise from r2–5, and the climbing fibers originate from the inferior olivary nucleus arise from r6–8 (Yamada et al., 2007; Fujiyama et al., 2009). In this study, orthologous Ptf1a genes were expressed in the ventricular zone in lamprey and hagfish r1 and more posterior rhombomeres (Figures 1, 3). In addition, lamprey GAD and Ptf1a expression domains were observed at the same anterior-posterior level in the rhombomeres with a distinct dorso-ventral pattern (Figure 3G). If GAD-positive inhibitory neurons are derived from the Ptf1a-positive ventricular zone, GABAergic inhibitory neurons in the lamprey may be formed by a similar developmental mechanism to that of gnathostome Purkinje cells. However, so far, Purkinje cells have not been identified in the adult lamprey cerebellum (Nieuwenhuys et al., 1998; Striedter and Northcutt, 2020). Further studies are necessary to determine whether these GABAergic neuron precursors in the lamprey embryo are homologous to Purkinje cells or any other inhibitory interneurons in gnathostomes or not (e.g., basket, stellate, and Golgi cells). In mice, small GABAergic neurons in the deep cerebellar nuclei (DCN) arise from the Ptf1a-positive ventricular zone and migrate ventrally (Hoshino et al., 2005). It is necessary to confirm whether the ventral population of GAD-expressing cells in the lamprey (white arrowheads in Figure 3G) originate from the ventricular zone and migrate ventrally like DCN neurons in amniotes. In mice, a subpopulation of Ptf1a-positive cells in the ventricular zone expressing Gsx1 differentiates into interneurons in the DCN (Seto et al., 2014). Two Gsx1 homolog genes have been identified in the lamprey and one of them was amplified from the brain tissue by RT-PCR (Zhang et al., 2017). However, further research is needed to determine whether a similar neurodevelopmental mechanism for the differentiation of Ptf1a-expressing cells in the ventricular zone is present in the lamprey.
Developmental Evolution in the Vertebrate Cerebellum
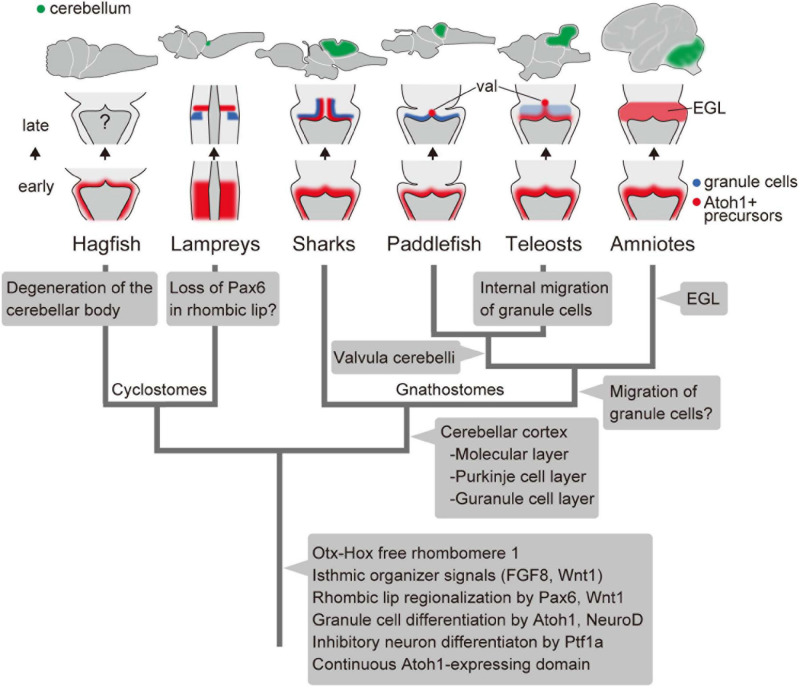
By comparing both cyclostomes and gnathostomes, we can depict a hypothetical evolutionary scenario of the vertebrate cerebellum, as shown in Figure 4. The developing brain of the last common ancestor of extant vertebrates already had Otx-Hox free r1, with isthmic organizer signals such as FGF8 and Wnt1. Given the presence of similar expression field with conserved function in the hemichordate larvae, the isthmic FGF signaling may date back to deep deuterostome ancestry (Pani et al., 2012). In the r1 rhombic lip, Pax6 and Wnt1 specify a domain, from which the granule cells differentiate as the result of Atoh1 and NeuroD expression. Also, Ptf1a-positive ventricular zone generates some GABAergic inhibitory neurons.
FIGURE 4.
An evolutionary scenario for the vertebrate cerebellum, based on Chaplin et al. (2010) and Butts et al. (2014c) and the present study. Note that the internal migration of postmitotic granule cells has been observed in teleosts but not in the paddlefish. Therefore, it is equally possible that this migration of granule cells was acquired after the divergence of chondrichthyans and osteichthyans, with paddlefish losing this ability secondarily. Alternatively, it is possible that teleosts acquired the migration independently from amniotes. val, valvula cerebelli; EGL, external granule cell layer.
We can also trace lineage-specific evolutionary modifications to this ancestral state of the cerebellum. In the hagfish, although the rhombic lip and ventricular zone are present in the embryo, most structures and neurons were degenerated developmentally in the adult brain.
Unlike in gnathostomes and hagfish, lamprey Pax6a and 6b are not expressed in the rhombic lip (Murakami et al., 2001; Sugahara et al., 2016). In Pax6 knockout mice, proliferation and initial differentiation of granule cells are unaffected, while cell migration to form the EGL is disrupted (Engelkamp et al., 1999). So far, migration of granule cells has not been observed in the lamprey as in cartilaginous fish and paddle fish. It is possible that the lamprey lost this Pax6 expression domain in the rhombic lip secondarily. Subsequently, Pax6 may have become involved in the migration of granule cells and the formation of the EGL at a certain period of gnathostome evolution (Figure 4). Recently, a third lamprey Pax6 gene was identified (Ravi et al., 2019). Future experiments will be necessary to determine whether this Pax6 paralog is expressed in the lamprey rhombic lip or not, which eventually could change this evolutionary scenario (Figure 4).
The cerebellar cortex was established in gnathostomes before the divergence of chondrichthyans and osteichthyans. At this period, Purkinje cells started expressing Shh, which is not seen in the lampreys (Sugahara et al., 2011). Finally, the proliferative activity of EGL cells by SHH signaling was acquired in the course of amniote evolution. In conclusion, we suggest that the Atoh1/NeuroD axis for granule cell fate and Ptf1a role in inhibitory neuronal specification are genetic programs involved in cerebellar development that were already established in the last common ancestor of living vertebrates. Subsequently, the developmental program of the cerebellum has evolved to adapt to complex environments especially in gnathostomes, presumably related to the acquisition of balancing organs such as paired appendages and inner ear with three semicircular canals.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Ethics Statement
The animal study was reviewed and approved by the Animal Experiment Committee of Hyogo College of Medicine.
Author Contributions
FS, JP-A, SKurat, and YM conceived the project, designed the experiments, and wrote the manuscript. FS performed animal sampling and gene cloning and gene expression analyses. JP-A searched gene sequences from NGS databases. SKurak performed the gene phylogenetic analysis. All authors analyzed and discussed the data, and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
We thank O. Kakitani, K. Ota, Y. Oisi, W. Takagi, and S. Higuchi for hagfish sampling; R. Kusakabe, Noboru Sato, H. Nagashima, and Naohiro Sato for lamprey sampling; S. Shibuya, K. Yamamoto, and Y. Yamamoto for maintenance of hagfish aquarium tanks; M. Kawaguchi for discussions. We are grateful to the past and current members of the Evolutionary Morphology Laboratory at RIKEN for their technical advice, animal sampling and maintenance.
Footnotes
Funding. This project has been supported by the RIKEN, Kobe, Japan, the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS; grant no. 19K06794 to FS, 20K06892 to YM) and Brain Science Foundation.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcell.2021.700860/full#supplementary-material
Expression of genes involved signaling pathways of the isthmic organizer. Wnt1 (A,B) and FGF8/17 (C,D) in hagfish stage 45 (A,C) and lamprey stage 26 (B,D). Arrowheads mark the isthmic organizer region in the most caudal part of the midbrain. lv, lateral ventricle; 4v, fourth ventricle; ph, pharynx.
Temporal expression of the NeuorD in the rhombomere 1. Dorsal views of the head region of the lamprey stages 25 (A), 26 (B), and 27 (C). Arrowheads in (B,C) indicate the expression in the rhombomere 1. gV1, ophthalmic ganglion; gV2,3, maxillomandibular ganglion.
Phylogenetic trees of Wnt1 (A) and Ptf1a (B) genes. The trees were inferred with the maximum-likelihood method using 355 and 153 aligned amino acid sites, respectively. The support values at nodes indicate bootstrap values and posterior probabilities based on the maximum-likelihood method and Bayesian inference in order, respectively. See the section “Materials and Methods” for details.
Primers used for gene cloning and probe synthesis.
References
- Altschul S. F., Madden T. L., Schaffer A. A., Zhang J., Zhang Z., Miller W., et al. (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 25 3389–3402. 10.1093/nar/25.17.3389 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basson M. A., Echevarria D., Ahn C. P., Sudarov A., Joyner A. L., Mason I. J., et al. (2008). Specific regions within the embryonic midbrain and cerebellum require different levels of FGF signaling during development. Development 135 889–898. 10.1242/dev.011569 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biechl D., Dorigo A., Koster R. W., Grothe B., Wullimann M. F. (2016). Eppur Si Muove: evidence for an external granular layer and possibly transit amplification in the teleostean cerebellum. Front. Neuroanat. 10:49. 10.3389/fnana.2016.00049 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broccoli V., Boncinelli E., Wurst W. (1999). The caudal limit of Otx2 expression positions the isthmic organizer. Nature 401 164–168. 10.1038/43670 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butts T., Green M. J., Wingate R. J. (2014a). Development of the cerebellum: simple steps to make a ‘little brain’. Development 141 4031–4041. 10.1242/dev.106559 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butts T., Hanzel M., Wingate R. J. (2014b). Transit amplification in the amniote cerebellum evolved via a heterochronic shift in NeuroD1 expression. Development 141 2791–2795. 10.1242/dev.101758 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butts T., Modrell M. S., Baker C. V., Wingate R. J. (2014c). The evolution of the vertebrate cerebellum: absence of a proliferative external granule layer in a non-teleost ray-finned fish. Evol. Dev. 16 92–100. 10.1111/ede.12067 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin N., Tendeng C., Wingate R. J. (2010). Absence of an external germinal layer in zebrafish and shark reveals a distinct, anamniote ground plan of cerebellum development. J. Neurosci. 30 3048–3057. 10.1523/jneurosci.6201-09.2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean B. (1899). On the Embryology of Bdellostoma stouti. A General Account of Myxinoid Development from the Egg and Segmentation to Hatching. Festschrift zum 70ten Geburststag Carl von Kupffer. Jena: Verlag von Gustav Fischer in Jena, 220–276. [Google Scholar]
- Engelkamp D., Rashbass P., Seawright A., van Heyningen V. (1999). Role of Pax6 in development of the cerebellar system. Development 126 3585–3596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyama T., Yamada M., Terao M., Terashima T., Hioki H., Inoue Y. U., et al. (2009). Inhibitory and excitatory subtypes of cochlear nucleus neurons are defined by distinct bHLH transcription factors, Ptf1a and Atoh1. Development 136 2049–2058. 10.1242/dev.033480 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gona A. G. (1972). Morphogenesis of the cerebellum of the frog tadpole during spontaneous metamorphosis. J. Comp. Neurol. 146 133–142. 10.1002/cne.901460202 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara Y., Yamaguchi K., Onimaru K., Kadota M., Koyanagi M., Keeley S. D., et al. (2018). Shark genomes provide insights into elasmobranch evolution and the origin of vertebrates. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2 1761–1771. 10.1038/s41559-018-0673-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibi M., Matsuda K., Takeuchi M., Shimizu T., Murakami Y. (2017). Evolutionary mechanisms that generate morphology and neural-circuit diversity of the cerebellum. Dev. Growth Differ. 59 228–243. 10.1111/dgd.12349 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi S., Sugahara F., Pascual-Anaya J., Takagi W., Oisi Y., Kuratani S. (2019). Inner ear development in cyclostomes and evolution of the vertebrate semicircular canals. Nature 565 347–350. 10.1038/s41586-018-0782-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino M. (2006). Molecular machinery governing GABAergic neuron specification in the cerebellum. Cerebellum 5 193–198. 10.1080/14734220600589202 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino M., Nakamura S., Mori K., Kawauchi T., Terao M., Nishimura Y. V., et al. (2005). Ptf1a, a bHLH transcriptional gene, defines GABAergic neuronal fates in cerebellum. Neuron 47 201–213. 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.06.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kani S., Bae Y. K., Shimizu T., Tanabe K., Satou C., Parsons M. J., et al. (2010). Proneural gene-linked neurogenesis in zebrafish cerebellum. Dev. Biol. 343 1–17. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.03.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katahira T., Sato T., Sugiyama S., Okafuji T., Araki I., Funahashi J., et al. (2000). Interaction between Otx2 and Gbx2 defines the organizing center for the optic tectum. Mech. Dev. 91 43–52. 10.1016/s0925-4773(99)00262-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuraku S., Kuratani S. (2006). Time scale for cyclostome evolution inferred with a phylogenetic diagnosis of hagfish and lamprey cDNA sequences. Zoolog. Sci. 23 1053–1064. 10.2108/zsj.23.1053 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuraku S., Zmasek C. M., Nishimura O., Katoh K. (2013). aLeaves facilitates on-demand exploration of metazoan gene family trees on MAFFT sequence alignment server with enhanced interactivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 41 W22–W28. 10.1093/nar/gkt389 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lannoo M. J., Hawkes R. (1997). A search for primitive Purkinje cells: zebrin II expression in sea lampreys (Petromyzon marinus). Neurosci. Lett. 237 53–55. 10.1016/s0304-3940(97)00802-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsell O. (1947). The cerebellum of myxinoids and petromyzonts including developmental stages in the lampreys. J. Comp. Neurol. 86 395–445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leto K., Arancillo M., Becker E. B., Buffo A., Chiang C., Ding B., et al. (2016). Consensus paper: cerebellar development. Cerebellum 15 789–828. 10.1007/s12311-015-0724-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martí E., Bovolenta P. (2002). Sonic hedgehog in CNS development: one signal, multiple outputs. Trends Neurosci. 25 89–96. 10.1016/s0166-2236(02)02062-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon A. P., Bradley A. (1990). The Wnt-1 (int-1) proto-oncogene is required for development of a large region of the mouse brain. Cell 62 1073–1085. 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90385-r [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Ogasawara M., Sugahara F., Hirano S., Satoh N., Kuratani S. (2001). Identification and expression of the lamprey Pax6 gene: evolutionary origin of the segmented brain of vertebrates. Development 128 3521–3531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwenhuys R. (1967). Comparative anatomy of the cerebellum. Prog. Brain Res. 25 1–93. 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60962-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwenhuys R., Donkelaar H. J. T., Nicholson C. (1998). The Central Nervous System of Vertebrates. Berlin: Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Oisi Y., Kakitani O., Kuratani S., Ota K. G. (2015). “Analysis of embryonic gene expression patterns in the hagfish,” in Situ Hybridization Methods. Neuromethods, Vol. 99 ed. Hauptmann G. (New York, NY: Humana Press; ), 249–262. [Google Scholar]
- Oisi Y., Ota K. G., Kuraku S., Fujimoto S., Kuratani S. (2013). Craniofacial development of hagfishes and the evolution of vertebrates. Nature 493 175–180. 10.1038/nature11794 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ota K. G., Kuraku S., Kuratani S. (2007). Hagfish embryology with reference to the evolution of the neural crest. Nature 446 672–675. 10.1038/nature05633 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pani A. M., Mullarkey E. E., Aronowicz J., Assimacopoulos S., Grove E. A., Lowe C. J. (2012). Ancient deuterostome origins of vertebrate brain signalling centres. Nature 483 289–294. 10.1038/Nature10838 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascual-Anaya J., Sato I., Sugahara F., Higuchi S., Paps J., Ren Y., et al. (2018). Hagfish and lamprey Hox genes reveal conservation of temporal colinearity in vertebrates. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2 859–866. 10.1038/s41559-018-0526-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravi V., Bhatia S., Shingate P., Tay B. H., Venkatesh B., Kleinjan D. A. (2019). Lampreys, the jawless vertebrates, contain three Pax6 genes with distinct expression in eye, brain and pancreas. Sci. Rep. 9:19559. 10.1038/s41598-019-56085-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reifers F., Bohli H., Walsh E. C., Crossley P. H., Stainier D. Y., Brand M. (1998). Fgf8 is mutated in zebrafish acerebellar (ace) mutants and is required for maintenance of midbrain-hindbrain boundary development and somitogenesis. Development 125 2381–2395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Araki I., Nakamura H. (2001). Inductive signal and tissue responsiveness defining the tectum and the cerebellum. Development 128 2461–2469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto Y., Nakatani T., Masuyama N., Taya S., Kumai M., Minaki Y., et al. (2014). Temporal identity transition from Purkinje cell progenitors to GABAergic interneuron progenitors in the cerebellum. Nat. Commun. 5:3337. 10.1038/ncomms4337 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigetani Y., Sugahara F., Kawakami Y., Murakami Y., Hirano S., Kuratani S. (2002). Heterotopic shift of epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in vertebrate jaw evolution. Science 296 1316–1319. 10.1126/science.1068310 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Striedter G. F., Northcutt R. G. (2020). Brains Through Time: A Natural History of Vertebrates. Oxford: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Sugahara F., Aota S., Kuraku S., Murakami Y., Takio-Ogawa Y., Hirano S., et al. (2011). Involvement of Hedgehog and FGF signalling in the lamprey telencephalon: evolution of regionalization and dorsoventral patterning of the vertebrate forebrain. Development 138 1217–1226. 10.1242/dev.059360 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugahara F., Murakami Y., Kuratani S. (2015). “Gene expression analysis of lamprey embryos,” in In Situ Hybridization Methods. Neuromethods, Vol. 99 ed. Hauptmann G. (Cham: Springer; ), 263–278. [Google Scholar]
- Sugahara F., Pascual-Anaya J., Oisi Y., Kuraku S., Aota S., Adachi N., et al. (2016). Evidence from cyclostomes for complex regionalization of the ancestral vertebrate brain. Nature 531 97–100. 10.1038/nature16518 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugahara F., Murakami Y., Pascual-Anaya J., Kuratani S. (2017). Reconstructing the ancestral vertebrate brain. Dev. Growth Differ 59 163–174. 10.1111/dgd.12347 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahara Y. (1988). Normal stages of development in the lamprey, lampetra-reissneri (Dybowski). Zoolog. Sci. 5 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Takio Y., Kuraku S., Murakami Y., Pasqualetti M., Rijli F. M., Narita Y., et al. (2007). Hox gene expression patterns in Lethenteron japonicum embryos–insights into the evolution of the vertebrate Hox code. Dev. Biol. 308 606–620. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.05.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takio Y., Pasqualetti M., Kuraku S., Hirano S., Rijli F. M., Kuratani S. (2004). Evolutionary biology: lamprey Hox genes and the evolution of jaws. Nature 429:1 p following 262. 10.1038/nature02616 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueki T., Kuratani S., Hirano S., Aizawa S. (1998). Otx cognates in a lamprey, Lampetra japonica. Dev. Genes Evol. 208 223–228. 10.1007/s004270050176 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingate R. J. (2001). The rhombic lip and early cerebellar development. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 11 82–88. 10.1016/s0959-4388(00)00177-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wullimann M. F., Mueller T., Distel M., Babaryka A., Grothe B., Köster R. W. (2011). The long adventurous journey of rhombic lip cells in jawed vertebrates: a comparative developmental analysis. Front. Neuroanat. 5:27. 10.3389/fnana.2011.00027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada M., Terao M., Terashima T., Fujiyama T., Kawaguchi Y., Nabeshima Y., et al. (2007). Origin of climbing fiber neurons and their developmental dependence on Ptf1a. J. Neurosci. 27 10924–10934. 10.1523/jneurosci.1423-07.2007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu T., Meiners L. C., Danielsen K., Wong M. T., Bowler T., Reinberg D., et al. (2013). Deregulated FGF and homeotic gene expression underlies cerebellar vermis hypoplasia in CHARGE syndrome. Elife 2:e01305. 10.7554/eLife.01305 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu T., Yaguchi Y., Echevarria D., Martinez S., Basson M. A. (2011). Sprouty genes prevent excessive FGF signalling in multiple cell types throughout development of the cerebellum. Development 138 2957–2968. 10.1242/dev.063784 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Ravi V., Tay B. H., Tohari S., Pillai N. E., Prasad A., et al. (2017). Lampreys, the jawless vertebrates, contain only two ParaHox gene clusters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 114 9146–9151. 10.1073/pnas.1704457114 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Expression of genes involved signaling pathways of the isthmic organizer. Wnt1 (A,B) and FGF8/17 (C,D) in hagfish stage 45 (A,C) and lamprey stage 26 (B,D). Arrowheads mark the isthmic organizer region in the most caudal part of the midbrain. lv, lateral ventricle; 4v, fourth ventricle; ph, pharynx.
Temporal expression of the NeuorD in the rhombomere 1. Dorsal views of the head region of the lamprey stages 25 (A), 26 (B), and 27 (C). Arrowheads in (B,C) indicate the expression in the rhombomere 1. gV1, ophthalmic ganglion; gV2,3, maxillomandibular ganglion.
Phylogenetic trees of Wnt1 (A) and Ptf1a (B) genes. The trees were inferred with the maximum-likelihood method using 355 and 153 aligned amino acid sites, respectively. The support values at nodes indicate bootstrap values and posterior probabilities based on the maximum-likelihood method and Bayesian inference in order, respectively. See the section “Materials and Methods” for details.
Primers used for gene cloning and probe synthesis.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.