Abstract
Vaccine‐induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT) has caused global concern. VITT is characterized by thrombosis and thrombocytopenia following COVID‐19 vaccinations with the AstraZeneca ChAdOx1 nCov‐19 and the Janssen Ad26.COV2.S vaccines. Patients present with thrombosis, severe thrombocytopenia developing 5–24 days following first dose of vaccine, with elevated D‐dimer, and PF4 antibodies, signifying platelet activation. As of June 1, 2021, more than 1.93 billion COVID‐19 vaccine doses had been administered worldwide. Currently, 467 VITT cases (0.000024%) have been reported across the UK, Europe, Canada, and Australia. Guidance on diagnosis and management of VITT has been reported but the pathogenic mechanism is yet to be fully elucidated. Here, we propose and discuss potential mechanisms in relation to adenovirus induction of VITT. We provide insights and clues into areas warranting investigation into the mechanistic basis of VITT, highlighting the unanswered questions. Further research is required to help solidify a pathogenic model for this condition.
Keywords: adenovirus, COVID‐19 vaccine, platelet activation, thrombocytopenia, thrombosis
1. INTRODUCTION: WHAT IS KNOWN ABOUT VACCINE‐INDUCED IMMUNE THROMBOTIC THROMBOCYTOPENIA?
The novel, and rare, syndrome termed vaccine‐induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT), or thrombotic thrombocytopenic syndrome (TTS), has caused global concern among physicians, researchers, and the public. VITT is characterized by thrombosis and thrombocytopenia occurring following COVID‐19 vaccinations and, so far, only reported following treatment with the AstraZeneca ChAdOx1 nCov‐19 and the Janssen Ad26.COV2.S vaccines. The clinical features of VITT include thrombosis, commonly cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST; but many patients had other non‐CVST thromboses with several exhibiting concurrent thromboses at other sites), 1 , 2 and severe thrombocytopenia (median platelet counts 20,000–30,000) developing 5 to 24 days following the first dose of the vaccine, together with elevated D‐dimer. A hallmark of VITT patients is the presence of antibodies specific to platelet factor 4 (PF4), signifying platelet activation. This autoimmune element in VITT mimics autoimmune heparin‐induced thrombocytopenia (aHIT), 3 also known as HIT/T 4 or HIT, a thrombocytopenic disorder caused by the formation of immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies against PF4 upon exposure to heparin 5 , 6 or more precisely “spontaneous/autoimmune HIT” where there is no prior heparin exposure. 7 , 8
Previous work has shown that aHIT patients express several classes of anti‐PF4 antibodies. Group 1 only weakly binds to the PF4/heparin complex and is not capable of causing aggregation and activation of platelets. Group 2 can aggregate PF4 in complex with heparin, leading to platelet activation via Fcγ‐receptor IIA (FcγRIIa). Group 3 binds most strongly and can aggregate PF4 in the absence of heparin or other polyanions. 9 It has been observed that non–platelet‐activating anti‐PF4/heparin antibodies occur in COVID‐19 patients despite no prior heparin treatment. 10 However, VITT patients reported to date all tested positive for a particularly strong antibody type capable of binding to PF4 in the absence of heparin, mimicking aHIT. 10 The kinetics of PF4 antibodies in VITT compared to HITT is currently unknown and requires further studies. Thus far, the suggested treatment paradigm has been to treat VITT similarly to HIT. This involves discontinuing heparin‐based therapies and switching to an alternative, non–heparin‐based, anti‐thrombin inhibitor. Treatment with high dose intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), which acts as a competitive inhibitor of IgG associated with FcγRIIa on the platelet surface, has also been used in VITT patients, with positive outcomes, reducing platelet activation and coagulation. ISTH guidance on diagnosis and management of VITT has been reported. 11
It is difficult to determine the exact incidence of this adverse effect but thus far it remains extremely low. As of June 1, 2021, more than 1.93 billion COVID‐19 vaccine doses had been administered worldwide. 12 Currently, a total of 467 VITT cases (0.000024%) have been reported across the United Kingdom (UK), Northern Europe, Canada, and Australia; however, more cases are continuing to be reported. 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 As of June 1, 2021, the estimated incidence rate of VITT, based on the total number of first‐dose vaccinations (not exclusively AstraZeneca), is approximately 0.00086%, 0.000127%, 0.00028%, and 0.000087% in the UK, Canada, Australia, and central Europe, respectively. 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 Recent work has shown, robustly, that that incidence rate of VITT in recipients of the ChAdOx1 vaccine is in excess of the general population, and that similar effects are not seen in recipients of the BioNTech mRNA vaccine, 20 although thrombocytopenia (without thrombosis) has been shown with BNT162b2. 21 Whether similar incidence rates are observed in other populations with different genetic backgrounds remains to be seen.
The pathogenic mechanism of VITT remains to be verified, but thus far all evidence suggests a role for the vaccine material. Experimentation has demonstrated that the IgG antibodies that recognize PF4 activate platelets through FcγRIIA. This has been validated by ELISA testing. 5 , 6 , 13 However, it remains unclear what triggers production of these antibodies. The fact that VITT, so far, has been described only in association with adenoviral vector‐‐based DNA virus vaccines, but not mRNA/lipid‐based vaccines, raises the question of whether the syndrome is linked to the vector or other constituents in the vaccine preparation.
Herein, we discuss and analyze adenovirus immunogenicity and its interaction with platelets and other host proteins. We review aspects of the respective adenoviruses to provide clues on areas warranting investigation into the mechanistic basis of VITT, highlight several unanswered questions, and discuss the potential pathogenic mechanisms involved.
2. ADENOVIRUS AS A POPULAR CANDIDATE FOR COVID‐19 VACCINATION
Adenovirus has been a popular and powerful therapeutic as a gene delivery vehicle. However, its value is restricted by the limited duration of transgene expression, typically 7 to 10 days. The intense overexpression of transgene, resulting in robust antigen‐specific responses 22 ; ease of manipulation of their double stranded DNA genome compared to RNA viruses; and the ability to scale up capacity to high titers 23 make it an attractive candidate as a vaccine platform.
Despite the broad phylogenetic tree of human adenoviruses, preclinical and clinical development of adenoviruses have focused, largely, on just one serotype—the species C serotype 5 (Ad5). Ad5 is known to induce potent antigen‐specific T cell responses against the delivered transgenes, which makes it a compelling candidate as a vaccine. 24 However, clinical trials of Ad5‐based vaccines have a checkered history with limited evidence that their use results in protective immunity. 25 , 26 The results of the Ad5‐based human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) STEP trial indicated that widespread pre‐existing anti‐Ad5 immunity in the population, among other variables, was associated with lack of efficacy from the vaccine. 27 These studies indicate how high seroprevalence hampers efficacy of Ad5‐based vaccines. This prompted a switch toward exploring the diversity within the human adenovirus phylogenetic tree, as well as adenoviruses of non‐human origin, to develop efficacious adenovirus‐based vaccines with low or zero seroprevalence rates in the human population.
From the diverse phylogenetic tree, encompassing >100 human adenoviruses, and >100 closely related members including those of simian origin (http://hadvwg.gmu.edu/), two have emerged as leading candidates, critical in curtailing the 2019 SARS‐CoV‐2 pandemic—namely that based on species D human adenovirus serotype 26 (Ad26, developed by Janssen Ltd) and that derived from the chimpanzee adenovirus isolate Y25 (developed by the Jenner Institute), also termed ChAdOx1, which is phylogenetically close to Ad4, though the hexon and fiber proteins display homology to their counterparts in species D and C, respectively. Both vaccine platforms have been widely clinically evaluated, for several indications, prior to the 2019 SARS‐CoV‐2 pandemic and demonstrated a robust ability to induce T cell and antibody responses against a wide range of antigens. 28 , 29 In terms of side effects, early phase clinical trials of both viral vector backbones have generally shown mild/moderate adverse events (AEs), limited to transient local and systemic events, with no serious vaccine‐related AEs reported. 30 , 31
This positive safety profile coupled with their ability to induce durable and robust antibody and T cell responses have made both Ad26 and ChAdOx1 obvious front runners in the race to develop SARS‐CoV‐2 vaccines to mitigate the COVID‐19 pandemic.
3. ADENOVIRUS TRIGGERS PLATELET ACTIVATION AND PROMOTES BLOOD CLOTTING
Adenovirus‐‐platelet interactions deserve close attention due to the thrombocytopenia consistently reported following intravenous administration, while noting that thromboembolic events have not been observed previously and that COVID‐19 vaccine is administered intramuscularly. 32 , 33 , 34 Experimental data show that thrombocytopenia occurs 5 to 24 h following intravenous administration of adenovirus to mice. 35 Thrombocytopenia is a well‐known complication of various viral infections in humans. Multiple mechanisms have been proposed. These include increased nonspecific destruction of platelets caused by the deposition of circulating immune complexes on their surface, the appearance of specific antiplatelet antibodies, a decrease in platelet production, a direct effect of viruses on megakaryopoiesis, or a direct interaction between platelets and viruses. 36 , 37 These interactions may be a part of platelets’ complex role in host defense processes. It is plausible the host defense role requires platelets to be activated to remove microbes, because activated platelets are cleared from circulation by the reticuloendothelial system. 38 , 39 The addition of adenovirus to platelet rich plasma (PRP) in vitro leads to spontaneous ADP‐ and ristocetin‐induced platelet aggregation, and P‐selectin and CD41a expression on the platelet surface. The latter are two markers of platelet activation. 40 , 41
Increased P‐selectin in platelet and leukocyte‐derived microparticle release is also observed following intravenous adenovirus (Ad5) injection in mice. This in turn triggers the formation of platelet‐‐leukocyte aggregates that adhere and roll on the endothelium. 35 A crucial role of von Willebrand factor (VWF) in mediating thrombocytopenia was shown during in vivo experiments. This role is based on the high levels of VWF seen in the plasma and the appearance of ultra‐large molecular weight VWF multimer (UL‐VWF) following adenovirus injection in mice 35 and in Rhesus macaques. 34 This is further supported by the fact that thrombocytopenia was not significant when the virus was injected into VWF knock‐out mice. 35
Adenovirus infection can stimulate a series of platelet responses, including platelet binding and internalization. However, the kinetics of the platelet activation and which components of platelets are involved in the internalization process remain unclear. Virus particles were found in association with the cell surface and are localized to the open canalicular system as shown by electron microscopy. 40 Ad5 attachment to the cell surface requires binding of the fiber knob protein to Coxsackie and adenovirus receptor (CAR) 42 but it is unclear if this is a requirement for platelet attachment. One study indicated that ~3.5 ± 1.9% of resting human platelets express CAR, which is dominantly localized within intracellular aggregates at sites of cell‐‐cell contacts. 43 This indicates that CAR expression might be upregulated in response to platelet activation. 43 In addition to CAR, adenoviruses use a number of proteins and adhesion molecules that act as “co‐receptors” and facilitate cell internalization. It has been shown that Ad5 interacts with members of the αV‐integrin family—αVβ3 44 and αVβ5 45 —via the RGD‐motif containing penton base protein. 46 Dual inhibition of αIIbβ3 and αVβ3 by Kistrin, a potent protein inhibitor of platelet aggregation and fibrinogen endocytosis, does not prevent adenovirus platelet coupling or virus internalization in vitro, 40 indicating additional receptor binding partners may be able to facilitate internalization. 47 Despite unchanged internalization, the use of Kistrin leads to a decrease in platelet activation. A possible explanation is the existence of two independent processes, one leads to platelet activation following adenovirus administration and the other to virus uptake. One can speculate that adenovirus‐‐platelet binding does not always result in virus internalization with its subsequent clearance from the bloodstream. This hypothesis is supported by the fact that very little platelet‐associated virus was found in vivo in the blood of cancer patients treated intravenously with oncolytic adenovirus, and in vitro experiments in which whole blood was incubated with the studied adenoviruses. 48 It is possible that activation is a prerequisite for platelets to play their role in the host defense process.
It is important to note the above effects apply to blood‐borne, replicating, viruses, rather than replication‐incompetent vectors such as in the vaccines. While adenovirus‐based vaccinations are generally delivered intramuscularly, rather than intravenously, it would seem likely that small quantities of vector will enter the blood via leaky vasculature or capillary injuries at the injection site. Therefore, it is plausible that some adenovirus vector might be able to interact with blood and endothelial cells.
4. ADENOVIRUS INTERACTIONS WITH HOST PROTEINS
The chimpanzee Y25 isolate, now known commonly as the ChAdOx1 vector, maps phylogenetically as closely related to the human adenovirus species E. 49 The sole human adenovirus member of this species, Ad4, is highly homologous to ChAdOx1, and is thought to have crossed over from chimps in a zoonotic event in the past. 50 , 51 Adenovirus zoonosis events appear to be exceptionally rare, though they do have precedent. Cross‐species transmission of Titi monkey adenovirus was observed to cause infection in at least two humans, of which one was an animal handler. 52 Adenovirus, especially Ad4, has been associated with occasional but serious outbreaks among military recruits, 53 and as such an unattenuated, replication competent, Ad4 vaccine has been delivered orally—a non‐pathogenic route of delivery for this vector. 54 , 55 Replication competent Ad4 vectors have also been evaluated in Phase 1 clinical testing as oral/intranasal vaccine vectors for influenza virus, 56 , 57 , 58 oral vaccine vectors for anthrax 59 and intramuscular/intranasal vaccine vectors for HIV. 60 , 61 , 62 Ad4 has been shown to utilize CAR receptors to gain cell entry. 63 Previous studies had hinted at this as an entry receptor for ChAdOx1 also, 64 but a recent preprint demonstrates, using biological and structural studies, that ChAdOx1 can engage CAR as a primary cell attachment receptor, with a binding affinity similar to that of Ad5. 65 In the same study, CD46, a receptor used extensively by species B1 adenoviruses, was observed to be unable to interact with ChAdOx1 fiber knob protein. Interactions involving other major entry receptors such as Desmoglein‐2 (DSG‐2) or sialic acid bearing glycans have not yet been excluded as possible receptors. In the future it will also be important to investigate ChAdOx1’s co‐receptor usage, such as integrins.
The major receptor usage of Ad26, a species D adenovirus, was clouded in controversy for many years. Initial infectivity studies using peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from mice and humans suggested that CD46 was the major receptor used by Ad26. 66 However, these conclusions were based upon data drawn from the transduction of a small number of cells, yielding infection in only a fraction of cells even at high multiplicities of infection.
Recent structural and biological studies have ruled out CD46 as an entry receptor engaged by the fiber knob protein of Ad26 (although a novel mechanism involving CD46 binding to the hexon protein has recently been proposed 67 ). These studies demonstrate CAR is a receptor for Ad26, though the affinity of this interaction is reduced, compared to Ad5, by the presence of an extended loop in the fiber knob protein, which sterically inhibits CAR engagement. 68 Biologically, it is estimated that this steric clash reduces CAR affinity by approximately 15‐fold compared to Ad5. Ad26 appears to have evolved a second receptor binding mechanism, attaching to sialic acid bearing glycans with high affinity. 69 This mechanism is tightly conserved by adenoviruses, like Ad26, that cause epidemic keratoconjunctivitis (EKC). 70 An alternative mechanism of cell entry, involving αvβ3 integrin engagement, has also been proposed, 71 though engagement of integrins as co‐receptors by the adenovirus penton base protein is well documented across all adenovirus species, with the exception of enteric species F adenoviruses (Ad40, Ad41). 72
As well as their interactions with cellular receptors and co‐receptors, adenoviruses are well documented to interact with a variety of proteins in the blood. One such interaction involves a high affinity interaction between the major adenovirus capsid protein, hexon, and circulating blood clotting factor, FX. 73 , 74 , 75 For Ad5, this is documented as a high affinity, Ca2+ dependent interaction, which is responsible for efficient hepatic gene transfer of adenovirus, which transduces hepatocytes via heparan sulphate proteoglycan receptors (HSPGs). 74 , 76 This interaction can occur independently of factor X (FX) activation status (i.e., FXa interacts with Ad5 equally as efficiently as FX), but does not result in the conversion of FX to FXa—either alone or in the presence of factor VII (FVII) and cells presenting tissue factor (Figure S1 in supporting information). Furthermore, while the ability of ChAdOx1 to bind FX has not been assessed at the time of writing, it is known that Ad26 does not bind FX by the same mechanism. 74 , 77 Ad5 hexon was shown to bind FVII in a subtly different way. 78 We previously demonstrated that protein C, FVII, factor IX (FIX), and FX (homologous domains) might bind and promote Ad5 uptake. 79 Prothrombin (factor II) may also bind and compete with FX for hexon binding sites, though it lacks an SP domain, thus preventing interaction with HSPGs, which, for FX, is known to be mediated by a stretch of basic amino acids within the FX serine protease (SP) domain, 80 which form a putative heparan binding exosite. FX appears to be the major player in hepatic gene transfer. It is worth mentioning that FVII and FX may influence innate immunity and fibrosis in hepatic cells. 81 In addition to the well‐characterized interactions with blood clotting factors, interactions of adenovirus with complement proteins C3. 82 and CR1, 83 as well as VWF and P‐selectin. 33 have all been described in the literature.
5. VITT—WHICH VACCINE?
VITT has been observed following vaccination by both AstraZeneca’s ChAdOx1 nCoV‐19 vaccine and the Janssen Ad26.COV2.S vaccine. At the time of writing, it has not been associated with non‐adenoviral vector vaccinations, such as mRNA vaccines, as confirmed in a recent comparison of thrombotic events in recipients of ChAdOx1 and Pfizer/BioNTech vaccines. 20 Information is currently lacking on whether VITT is observed in recipients of other adenovirus vectored vaccines, such as the Sputnik V Ad5/Ad26 vaccine regimen administered, primarily, in Russia, or in recipients of the Ad5 vectored CanSino vaccine.
6. PROPOSED MECHANISMS FOR VITT
The primary and downstream mechanisms underpinning VITT are not currently understood, but the fact that this side effect is clearly observed in the adenovirus‐based formulations warrants careful consideration and specific investigation. We herein discuss the potential “smoking guns” in relation to adenovirus induction of VITT. We provide an illustration of the proposed mechanisms in Figure 1.
FIGURE 1.
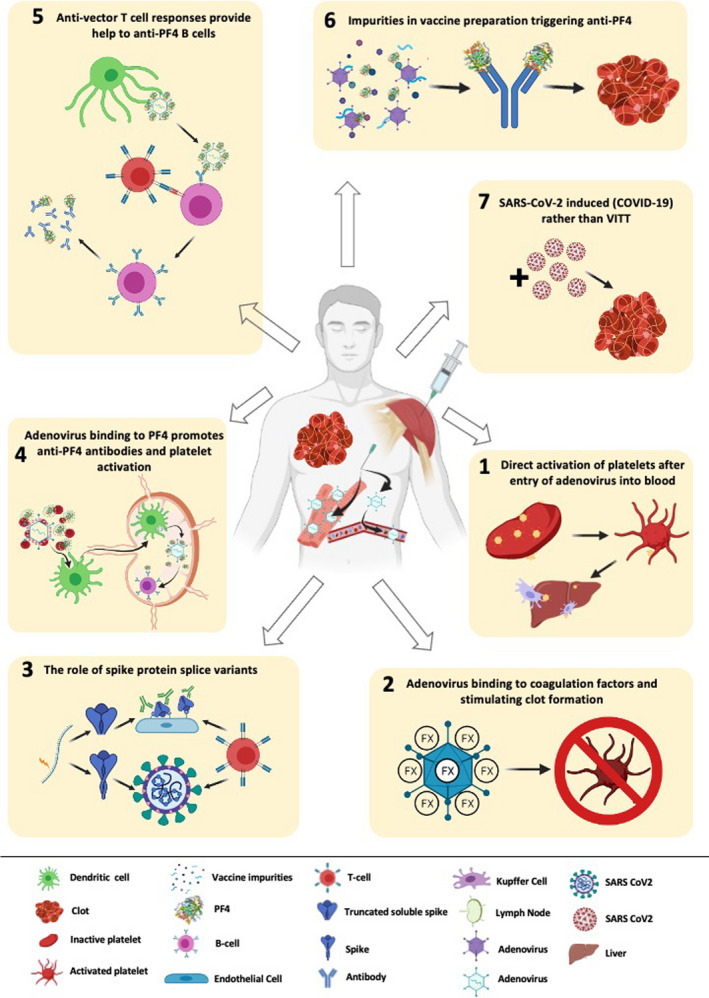
The seven “smoking guns” of vaccine‐induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT). Possible mechanisms of how adenoviral vectors may cause rare VITT. 1: Adenovirus leaks into bloodstream following intramuscular injection of the vaccine, directly binds to platelet via Coxsackie and adenovirus receptor (CAR), and/or secondary receptors present on platelets, inducing platelet activation and triggering coagulation as well as liver clearance of activated platelets and thrombocytopenia. 2. The binding of adenovirus to coagulation factors such as factor X (FX), their potential activation thus triggering clot formation. 3. “Vaccine induced COVID mimicry” resulting from vaccine induced secretion of mis‐spliced, C‐terminal truncated spike protein into the blood, activating endothelial cells through ACE2. This initiates vascular inflammation and damage with consequent platelet activation, thrombotic events and platelet factor 4 (PF4) release. 4. Binding of adenovirus capsid to PF4. The adenovirus/PF4 complex stimulates pre‐existing memory B cells against PF4, the IgG/PF4 complex then binds to Fcγ‐receptor IIA (FcγRIIa) and stimulates platelet activation, and clot formation. 5. PF4‐adenovirus complexes are internalized by B cells that recognize PF4. These B cells present adenoviral peptides via major histocompatibility complex class II, which are recognized pre‐existing anti‐vector CD4+ T cells that in turn provide T cell help to B cells, and drive their production of anti‐PF4 antibodies that can stimulate platelets via FcγRIIa. 6. Impurities of human or non‐structural viral proteins in vaccine preparation triggering autoantibodies such as anti‐PF4m which stimulates platelet activation and clot formation. 7. Acute infection with SARS‐CoV‐2 following vaccine administration, modified/atypical COVID‐19, presented with thrombosis and thrombocytopenia.
6.1. Direct activation of platelets following entry of adenovirus into the blood?
It is likely that small amounts of the adenovirus may enter the bloodstream through capillary injuries resulting from the injection or leaky vasculature due to the inflammatory state induced by vaccination. CAR is an attachment receptor for both ChAdOx1 and Ad26. 42 and has been shown to be expressed on the platelet surface. 35 , 38 , 43 The αVβ3, and other integrins, are key secondary cell entry receptors to which adenoviruses can attach and are also present on the platelet surface. 84 Similarly, surface glycans have a strong negative charge that may be able to passively facilitate adenovirus localization to the platelet surface. 85 Adenovirus binding has been demonstrated to drive platelet activation, platelet‐‐leukocyte aggregate formation, and endothelial activation. It is tempting, therefore, to conclude that this is strong circumstantial evidence for a role of direct adenovirus binding to platelets in the formation of clots. However, it is known that once bound by adenoviruses, these platelets are cleared by liver Kupffer cells. 86 This has been observed to result in thrombocytopenia in a study of mice treated with intravenous adenovirus at a dose >7000X higher than the equivalent doses, by body weight, given in the vaccine. 35 , 38 It should be noted that none of these animals developed blood clots despite the considerable level of adenovirus in the blood. A further study performed in Rhesus macaques also observed thrombocytopenia, but not clotting, and noted that the adenovirus therapy resulted in longer clotting times. 32 , 87
Nevertheless, if direct binding to platelets resulted in their activation and triggered a pro‐thrombotic milieu, we might expect patients to present very shortly following vaccination, rather than after days to weeks as has been reported. It is well established that replication‐incompetent adenoviruses, such as ChAdOx1 nCoV‐19 and Ad26.COV2.S, are rapidly cleared from the body, as are adenovirus‐bound platelets. 35 The earliest VITT event reported so far was 5 days post vaccination. Therefore, this is an unlikely direct explanation for VITT based on currently available evidence.
6.2. Adenovirus binding to coagulation factors and stimulate clot formation?
It is well established that certain adenoviruses, such as Ad5, bind to FX 73 , 74 , 75 This has been shown to facilitate an alternative mechanism of adenovirus infection via binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans. 74 , 75 , 76 Previously unpublished data (now presented in Figure S1) demonstrate that despite strong binding to the adenovirus, FX does not become activated. It has also previously been demonstrated that Ad26 does not engage FX, and ChAdOx1 does not share any of the key adenovirus/FX binding residues. 74 , 77 , 88 and is thus unlikely to sequester FX. Also, as discussed above, a mechanism for VITT that is driven by the presence of adenovirus in the blood would present shortly following vaccination, rather than >5 days later.
6.3. “Vaccine induced COVID‐19 mimicry”—The role of spike protein splice variants?
It was recently proposed that trace amounts of spike splice variant transcripts are produced via alternative splicing, resulting in C‐terminally deleted mRNAs. These C‐terminally deleted mRNAs could, if translated, result in soluble alternative spike isoforms being secreted into the extracellular space and leaked into the bloodstream. 89 As alternative splicing is a DNA‐specific phenomenon, this presents an alternative explanation as to why VITT is observed with adenovirus vectored vaccines, which encode the transgene as DNA, and not the lipid vector mRNA vaccines. In this model, the authors propose that spike protein binding ACE2 on endothelial cells may initiate vascular inflammation and damage with consequent platelet activation, initiating thrombotic events and PF4 release, characteristic of VITT. 90 The authors term this effect “Vaccine induced COVID‐19 mimicry.” Because mRNA‐based vaccines would, by definition, not require splicing, this would explain why this side effect is mediated specifically by adenoviral vectors and not mRNA‐based vaccines. However, a previous study evaluating the transcriptome of ChAdOx1 nCoV‐19 infected A549 and MRC‐5 lung cells failed to show any detectable levels of such a transcript, and it remains to be clarified whether this alternative transcript is translated into functional, secreted protein. 91 This proposed mechanism could be easily tested in mouse models using either intravenous delivery of SARS‐CoV‐2 free spike protein, and/or intramuscular delivery of viral vectors engineered to only express soluble spike protein isoforms, to evaluate whether such treatments result in a VITT‐like syndrome in human ACE2 transgenic animals. This proposed mechanism may account for some of the delay observed in the induction of VITT, as it would take 24 to 48 h for the vaccination to begin producing maximal quantities of spike protein and the supposed soluble variant. Presumably the rest of the delay might be accounted for by rarity of soluble spike being presented on the cell surface long enough to encounter enough anti‐spike antibodies and remain presented long enough to result in antibody dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC), as the study’s authors propose. 89 Further studies should also assess how long such a C‐terminal truncated spike protein can remain attached to the surface of the ACE2 expressing cell, and at what rate it becomes internalized or degraded. A short half‐life on the cell surface would reduce the probability of a pathogenic ADCC response. This mechanism would presuppose that VITT patients have pre‐existing anti‐spike antibodies to trigger ADCC in as early as 5 days post vaccination, as it would take longer to raise novel anti‐spike antibodies without existing B‐memory cells. 92 However, as previously discussed, an earlier study failed to demonstrate transcription of soluble SARS‐CoV‐2 spike from cells transduced with the vaccine. 91 Also, this mechanism fails to account for why all tested VITT patients are expressing anti‐PF4 antibodies. 5 Finally, if this mechanism can induce clotting it might be expected to be more common than is observed as it would not seem to require any risk factors and could occur with equal likelihood in any member of the population.
6.4. Does adenovirus binding to PF4 promote misplaced anti‐PF4 antibodies leading to (heparin independent) platelet activation?
Given that patients presenting with VITT appear to also present with significant anti‐PF4 responses, an obvious start would be to investigate whether there are any interactions between PF4 and ChAdOx1/Ad26, which might prime a misplaced anti‐PF4 response. Indeed, such a mechanism has been proposed by Greinacher and colleagues, whose recent transmission electron microscopy experiments suggest a direct interaction between ChAdOx1 and PF4. 93 More recently still, Baker et al. pre‐printed the ~4 angstrom resolution structure of the ChAdOx1 viral capsid, and demonstrated putative binding of tetrameric PF4 between ChAdOx1 hexon proteins using computational simulations. 65 The authors suggest that ChAdOx1 capsid retains PF4 when the virus is taken up by monocytes and trafficked to the lymph nodes. They suggest that upon release of the adenovirus/PF4 complex into the lymph this may stimulate proliferation of pre‐existing memory B cells against PF4, which have been previously observed in a minority of the population, contributing to instances of aHIT. 8 These strong antibodies, if released at a sufficient titer, could then aggregate PF4 in a ligand‐independent manner, as shown previously. 9 These IgG/PF4 complexes could then bind to FcγRIIa and stimulate platelet activation, and the clotting cascade, in a mechanism similar to aHIT. 3 In support of this idea is that VITT patients are known to present with strong, heparin independent, anti‐PF4 antibodies. 5 If trafficked by association with the adenovirus there would not be any polyanions, such as heparin, present during B‐cell stimulation. Therefore, the only memory B‐cells stimulated would be heparin independent, as observed. Further, this mechanism pre‐supposes the existence of anti‐PF4 antibodies, a known phenomenon. This proposal, which remains to be tested, also accounts for the timing of VITT, as 5 days post antigen exposure is within the timeframe for secondary antibody responses. One unanswered question is: Why does VITT seem to occur only after the first dose and not the second? Further, a definite association between the adenovirus capsid and PF4 remains to be conclusively established via surface plasmon resonance and microscopy studies. Finally, additional experiments would be required to prove that an adenovirus/PF4 complex could be trafficked to the lymph nodes where it could stimulate memory B cell proliferation and secondary immunity.
6.5. Do anti‐vector T cell responses play a role?
ChAdOx1 and Ad26 were selected based on their very low seroprevalence rates in the community. However, it is feasible that pre‐existing, cross‐reactive T cell responses against prior adenovirus infections may provide help to B cells in the generation of anti‐PF4 responses, following the formation of PF4‐‐adenovirus complexes. To provide such helper functions, these T cell responses would be CD4+. Indeed, CD4+ T cells against species E chimpanzee adenovirus 63 (ChAd63) were measured at low pre‐vaccination frequencies during clinical evaluation of ChAd63 as a malaria vaccine candidate and were boosted by vaccination. 94 Research into HIT suggests T cells could play such a helper role, with T cells to PF4‐‐heparin complexes measured in HIT patients, 95 and mouse studies demonstrating a necessary role for CD4+ T cells in the generation of PF4/heparin‐specific antibodies in murine HIT. 96
The strong proinflammatory T cell responses induced by vaccination could also advantage the anti‐PF4 antibody response in VITT, as IL‐10–producing regulatory T cells have been demonstrated to suppress PF4/heparin‐specific antibody responses during HIT in mice. 97 Research suggests HIT in humans has characteristics of both T‐dependent and T‐independent antibody production pathways, 98 , 99 with the role of T cells in VITT remaining to be elucidated. Future studies should aim to examine T cell responses against ChAdOx1: (1) addressing the extent to which cross‐reactive T cell responses from other adenovirus infections exist in the community, (2) examining whether they are boosted by vaccination, and (3) evaluating how they might contribute to VITT. One difficulty in addressing the latter is the lack of pre‐vaccination PBMC specifically from VITT patients. Importantly, the timing of the T helper contribution fits with the onset of VITT, with pre‐existing anti‐vector T cells able to provide early help to B cells in the generation of anti‐PF4 antibodies. Expanded populations of antigen‐specific T cells are also measured within the first 7 days of vaccination. 100 The potential role of anti‐vector T cells in VITT, however, does not explain why VITT predominantly occurs after the first vaccination.
6.6. Impurities in vaccine preparations?
Another proposition states that it is possible that impurities of human proteins in vaccine preparation trigger autoantibodies. Biochemical and proteomic analysis of the ChAdOx1 nCov‐19 showed both human and non‐structural viral proteins such as heat‐shock proteins and cytoskeletal proteins. 100 This proposal suggests that adenovirus acts as an adjuvant for the ~50% of human protein in the preparation, and autoantibodies against human membrane proteins from HEK293 cell contaminants during the process of adenovirus manufacture might be the source. Hence, it is possible that the differing frequencies with which VITT is observed might relate to the relative purities of the preparations in question. Recent work has shown that SARS‐CoV‐2 infection itself can also induce a diverse array of functional autoantibodies in the host. 101 though their clinical implications are unclear. While in VITT the cause for platelet activation seems to be the PF4/IgG complexes, theoretically, any circulating autoantibody can do if in sufficient amounts. Thromboembolism remains an extremely rare side effect of COVID‐19 vaccination. In the future, it will be important to profile autoantibody production resulting from SARS‐CoV‐2 infection and the proposed autoantibodies resulting from vaccination to establish any possible links between the presence of autoantibodies and thromboembolic events.
6.7. SARS‐CoV‐2 induced (COVID‐19) rather than VITT?
Is it possible that some VITT patients would have been infected with SARS‐CoV‐2 immediately after adenoviral vectored vaccine administration and that the immune thrombosis in VITT is an atypical COVID‐19 immune thrombosis? While this theory currently lacks evidence and is a somewhat remote possibility, it is worth the discussion. Both SARS‐CoV‐2 infection and VITT appear to have several features in common, with some differences (Table 1). They both feature platelet activation, thrombocytopenia—although in VITT, this is much more severe—and thrombosis, with the presence of PF4 antibodies, at least in some COVID‐19 patients. VITT presents more strongly than regular COVID‐19. Thrombocytopenia has been documented in varying levels in COVID‐19 and severe thrombocytopenia was considered a marker of severity of disease and mortality. 46 , 102 The concept of COVID‐19–induced coagulopathy (CAC) has helped understand the pathology and diagnosis of the predominantly procoagulant state in COVID‐19. 103 , 104 , 105 but the pathological focus was on thrombin generation—rather than primarily platelet activation—as a trigger for thrombosis. But perhaps COVID coagulopathy is primarily triggered by platelet activation that then stimulates thrombin generation. It is possible that SARS‐CoV‐2 spike protein binds to the ACE2 receptor on platelets although it is debatable whether platelets have the ACE2 receptor. 106 There is also the potential that adenovirus binds to αIIbβ3 via its RGD domain. Antibodies to spike protein can induce platelet activation in COVID‐19 patients in a FcγRIIA‐dependent manner. 107 and blocking of this by COVID‐19 plasma prevented this activation in vitro. 108 Activated platelets release ADP and PF4 microparticles in COVID‐19 patients. 2 We know all VITT patients have anti‐PF4 antibodies despite no history of heparin exposure. 109 , 110 We also know 0.3% to 5% of the normal population have anti‐PF4 antibodies. High levels of PF4 and anti‐PF4 antibodies were reported in COVID‐19 patients. 111 An important treatment for both HIT and for VITT is intravenous IgG (IVIg), a known inhibitor of FcγRIIA. PCR testing has shown negative SARS CoV2 infection in many but not all VITT patients. Whether VITT is an atypical form of COVID‐19 requires further studies.
TABLE 1.
Comparison between COVID‐19 and VITT
| VITT | COVID−19 | |
|---|---|---|
| Presentation |
|
|
| Platelet activation | Yes | Yes |
| Thrombosis |
|
|
| PF4 ELISA | Positive (all) | Some are positive |
| Thrombocytopenia |
|
|
| D‐dimer | Markedly elevated | Markedly elevated in severe cases, ARDS, or those with poor prognosis |
| Fibrinogen | Reduced |
|
| DIC | Has not been reported | Has been reported |
| Multiple organ failure | No | Yes |
| Heparin exposure |
|
|
| IVIg use | Yes, first line of treatment | Not likely |
Abbreviations: ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome; CVS, cerebral venous sinus; DIC, disseminated intravascular coagulation; DVT, deep vein thrombosis; IVIg, intravenous immunoglobulin G; PE, pulmonary embolism; PF4, platelet factor 4; VITT, vaccine‐induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia.
7. CONCLUDING REMARKS
The primary and downstream mechanisms underlying the VITT phenomenon remain to be completely elucidated. Here, we have discussed and critiqued the potential mechanisms in relation to adenovirus induction of VITT. While it is not possible yet to pinpoint the direct pathogenic mechanism(s) underpinning VITT, it is worthwhile to explore the possible evidence in relation to what is known around adenovirus immunogenicity and interactions with platelets and other host proteins, as well as the role of PF4 and platelet activation. We overviewed these proposed “smoking guns” that could underlie VITT in Figure 1. While it is challenging to agree on a singular model at this point, we have attempted to provide clues on areas warranting further investigation into the mechanistic basis of VITT and to highlight the unanswered questions. We appeal for immediate and urgent further investigation into each of these questions to solidify a pathogenic model for this condition. This understanding will facilitate condition‐specific clinical guidance for the treatment of this condition and will inform how adenovirus‐based vaccines might be further developed and improved to enhance their otherwise impressive safety profile.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
All authors have no conflicts of interest.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
MO and AP developed the concept and synthesized the plan for the manuscript. All authors contributed intellectually to the manuscript, critiqued the mechanisms presented, wrote various sections, reviewed, and approved the manuscript.
Supporting information
Fig S1
Othman M, Baker AT, Gupalo E, et al. To clot or not to clot? Ad is the question—Insights on mechanisms related to vaccine‐induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia. J Thromb Haemost. 2021;19:2845–2856. 10.1111/jth.15485
REFERENCES
- 1. See I, Su JR, Lale A et al. US case reports of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis with thrombocytopenia after Ad26.COV2.S vaccination, March 2 to April 21, 2021. JAMA 2021; 325: 2448–2456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Scully M, Singh D, Lown R, et al. Pathologic antibodies to platelet factor 4 after ChAdOx1 nCoV‐19 vaccination. N Engl J Med Massachusetts Med Soc. 2021;384:2202‐2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Greinacher A, Selleng K, Warkentin TE. Autoimmune heparin‐induced thrombocytopenia. J Thromb Haemost. 2017;15:2099‐2114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Baglin TP. Heparin induced thrombocytopenia thrombosis (HIT/T) syndrome: diagnosis and treatment. J Clin Pathol. 2001;54:272‐274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Greinacher A, Thiele T, Warkentin TE, Weisser K, Kyrle PA, Eichinger S. Thrombotic thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCov‐19 vaccination. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:2092‐2101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Schultz NH, Sørvoll IH, Michelsen AE, et al. Thrombosis and thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCoV‐19 vaccination. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:2124‐2130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Mohanty E, Nazir S, Sheppard J‐AI, Forman DA, Warkentin TE. High‐dose intravenous immunoglobulin to treat spontaneous heparin‐induced thrombocytopenia syndrome. J Thromb Haemost. 2019;17:841‐844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Warkentin TE, Makris M, Jay RM, Kelton JG. A spontaneous prothrombotic disorder resembling heparin‐induced thrombocytopenia. Am J Med. 2008;121:632‐636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Nguyen T‐H, Medvedev N, Delcea M, Greinacher A. Anti‐platelet factor 4/polyanion antibodies mediate a new mechanism of autoimmunity. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Brodard J, Hovinga JAK, Fontana P, Studt J‐D, Gruel Y, Greinacher A. COVID‐19 patients often show high‐titer non‐platelet‐activating anti‐PF4/heparin IgG antibodies. J Thromb Haemost. 2021;19:1294‐1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Interim IMGISTH . Guidance for the diagnosis and treatment on… by. ISTH academy. 2021.
- 12. Holder J Tracking coronavirus vaccinations around the world. The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2021/world/covid‐vaccinations‐tracker.html. Accessed August 16, 2021.
- 13. Cines DB, Bussel JB. SARS‐CoV‐2 vaccine–induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(23):2254–2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Italy Reported Four Clot Deaths After AstraZeneca Shots, Data Shows | World News | US News. US News & World Report.
- 15. Administration AGD of HTG . COVID‐19 vaccine weekly safety report ‐ 20‐05‐2021. Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). Australian Government Department of Health; 2021.
- 16. News JPT·C . Canada reports 28 cases of rare blood clots following AstraZeneca vaccinations | CBC News. CBC. 2021.
- 17. Chan B, Odutayo A & Juni P et al. Risk of vaccine‐induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT) following the AstraZeneca/COVISHIELD adenovirus vector COVID‐19 vaccines. Ontario COVID‐19 Science Advisory Table. 2021. https://covid19‐sciencetable.ca/sciencebrief/risk‐of‐vaccine‐induced‐thrombotic‐thrombocytopenia‐vitt‐following‐the‐astrazeneca‐covishield‐adenovirus‐vector‐covid‐19‐vaccines/. Accessed August 16, 2021.
- 18. Coronavirus vaccine ‐ weekly summary of Yellow Card reporting. GOV.UK.
- 19. Coronavirus (COVID‐19) Vaccinations ‐ Statistics and Research. Our World in Data .
- 20. Simpson CR, Shi T, Vasileiou E, et al. First‐dose ChAdOx1 and BNT162b2 COVID‐19 vaccines and thrombocytopenic, thromboembolic and hemorrhagic events in Scotland. Nat Med. 2021;27(7):1290–1297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Lee E, Cines DB, Gernsheimer T, et al. Thrombocytopenia following Pfizer and Moderna SARS‐CoV‐2 vaccination. Am J Hematol. 2021;96(5):534–537. 10.1002/ajh.26132 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Coughlan L. Factors which contribute to the immunogenicity of non‐replicating adenoviral vectored vaccines. Front Immunol. 2020;11:909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Kallel H, Kamen AA. Large‐scale adenovirus and poxvirus‐vectored vaccine manufacturing to enable clinical trials. Biotechnol J. 2015;10(5):741‐747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Krause A, Worgall S. Delivery of antigens by viral vectors for vaccination. Ther Deliv. 2011;2(1):51‐70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Watkins DI, Burton DR, Kallas EG et al. Nonhuman primate models and the failure of the Merck HIV‐1 vaccine in humans. Nat Med. 2008;14(6):617‐621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Patterson LJ. The “STEP‐wise” future of adenovirus‐based HIV vaccines. Curr Med Chem. 2011;18(26):3981‐3986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Koblin BA, Mayer KH, Noonan E et al. Sexual risk behaviors, circumcision status, and preexisting immunity to adenovirus type 5 among men who have sex with men participating in a randomized HIV‐1 vaccine efficacy trial: step study. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2012;60(4):405‐413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Matz KM, Marzi A, Feldmann H. Ebola vaccine trials: progress in vaccine safety and immunogenicity. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2019;18(12):1229‐1242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Morris SJ, Sebastian S, Spencer AJ, Gilbert SC. Simian adenoviruses as vaccine vectors. Future Virol. 2016;11(9):649‐659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Antrobus RD, Coughlan L, Berthoud TK et al. Clinical assessment of a novel recombinant simian adenovirus ChAdOx1 as a vectored vaccine expressing conserved Influenza A antigens. Mol Ther. 2014;22(3):668‐674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Mutua G, Anzala O, Luhn K et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of a 2‐Dose Heterologous Vaccine Regimen With Ad26.ZEBOV and MVA‐BN‐Filo Ebola Vaccines: 12‐month data from a phase 1 randomized clinical trial in Nairobi, Kenya. J Infect Dis. 2019;220(1):57‐67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Lozier JN, Csako G, Mondoro TH, et al. Toxicity of a first‐generation adenoviral vector in rhesus macaques. Human Gene Therapy Mary Ann. 2002;13:113‐124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Cichon G, Schmidt HH, Benhidjeb T, et al. Intravenous administration of recombinant adenoviruses causes thrombocytopenia, anemia and erythroblastosis in rabbits. J Gene Med. 1999;1:360‐371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Varnavski AN, Calcedo R, Bove M, Gao G, Wilson JM. Evaluation of toxicity from high‐dose systemic administration of recombinant adenovirus vector in vector‐naïve and pre‐immunized mice. Gene Ther. 2005;12(5):427–436. 10.1038/sj.gt.3302347 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Othman M, Labelle A, Mazzetti I, Elbatarny HS, Lillicrap D. Adenovirus‐induced thrombocytopenia: the role of von Willebrand factor and P‐selectin in mediating accelerated platelet clearance. Blood. 2006;109(7):2832‐2839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Assinger A. Platelets and infection – an emerging role of platelets in viral infection. Front Immunol. 2014;5:649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Raadsen M, Du Toit J, Langerak T, van Bussel B, van Gorp E, Goeijenbier M. Thrombocytopenia in virus infections. J Clin Med. 2021;10:877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Stone D, Liu Y, Shayakhmetov D, Li Z‐Y, Ni S, Lieber A. Adenovirus‐platelet interaction in blood causes virus sequestration to the reticuloendothelial system of the liver. J Virol. 2007;81:4866‐4871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Furie B, Furie BC, Flaumenhaft R. A journey with platelet P‐selectin: the molecular basis of granule secretion, signalling and cell adhesion. Thromb Haemost. 2001;86:214‐221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Gupalo E, Kuk C, Qadura M, Buriachkovskaia L, Othman M. Platelet‐adenovirus vs. inert particles interaction: effect on aggregation and the role of platelet membrane receptors. Platelets. 2013;24:383‐391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Jin Y‐Y, Yu X‐N, Qu Z‐Y, et al. Adenovirus type 3 induces platelet activation in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2014;9(1):370–374. 10.3892/mmr.2013.1805 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Bergelson JM, Cunningham JA, Droguett G, et al. Isolation of a common receptor for coxsackie B viruses and adenoviruses 2 and 5. Sci Am Assoc Adv Sci. 1997;275:1320‐1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Gupalo E, Buriachkovskaia L, Othman M. Human platelets express CAR with localization at the sites of intercellular interaction. Virol J. 2011;8:456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Wickham TJ, Mathias P, Cheresh DA, Nemerow GR. Integrins αvβ3 and αvβ5 promote adenovirus internalization but not virus attachment. Cell. 1993;73(2):309–319. 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90231-e [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Wickham TJ, Filardo EJ, Cheresh DA, Nemerow GR. Integrin alpha v beta 5 selectively promotes adenovirus mediated cell membrane permeabilization. J Cell Biol. 1994;127:257‐264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Amgalan A, Othman M. Hemostatic laboratory derangements in COVID‐19 with a focus on platelet count. Platelets. 2020;31:740‐745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Zhang Y, Bergelson JM. Adenovirus receptors. J Virol Am Soc Microbiol. 2005;79:12125‐12131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Escutenaire S, Cerullo V, Diaconu I, et al. In vivo and in vitro distribution of type 5 and fiber‐modified oncolytic adenoviruses in human blood compartments. Ann Med. 2011;43:151‐163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Dicks MD, Spencer AJ, Edwards NJ et al. A novel chimpanzee adenovirus vector with low human seroprevalence: improved systems for vector derivation and comparative immunogenicity. PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e40385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Graham FL, Prevec L. Adenovirus‐based expression vectors and recombinant vaccines. Biotechnology. 1992;20:363‐390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Borkenhagen LK, Fieldhouse JK, Seto D, Gray GC. Are adenoviruses zoonotic? A systematic review of the evidence. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2019;8:1679‐1687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Chen EC, Yagi S, Kelly KR, et al. Cross‐species transmission of a novel adenovirus associated with a fulminant pneumonia outbreak in a new world monkey colony. PLoS Pathog. 2011;7(7):e1002155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Ludwig SL, Brundage JF, Kelley PW et al. Prevalence of antibodies to adenovirus serotypes 4 and 7 among unimmunized US Army trainees: results of a retrospective nationwide seroprevalence survey. J Infect Dis. 1998;178(6):1776‐1778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Gooch WM 3rd, Mogabgab WJ. Simultaneous oral administration of live adenovirus types 4 and 7 vaccines. Protection and lack of emergence of other types. Arch Environ Health. 1972;25(6):388‐394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. van der Veen J, Abarbanel MF, Oei KG. Vaccination with live type 4 adenovirus: evaluation of antibody response and protective efficacy. J Hyg. 1968;66(4):499‐511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Gurwith M, Lock M, Taylor EM et al. Safety and immunogenicity of an oral, replicating adenovirus serotype 4 vector vaccine for H5N1 influenza: a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, phase 1 study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13(3):238‐250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. BioSolutions E . Phase 1 Evaluation of the Safety and Immunogenicity of a Replication‐Competent Adenovirus Serotype 4‐vectored H5N1 Influenza Candidate Vaccine ‐ Ad4‐H5‐Vtn. clinicaltrials.gov; 2020 Mar. Report No.: NCT01006798.
- 58. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) . Phase 1 study of safety and immunogenicity of intranasal Ad4‐H5‐VTN in Ad4 seronegative and seropositive volunteers. clinicaltrials.gov; 2019 Oct. Report No.: NCT01806909.
- 59. BioSolutions E . A Phase 1 Randomized Double‐Blind Positive‐Controlled Ascending Dose Study to Evaluate the Safety and Immunogenicity of a Replication‐Competent Adenovirus Serotype 4 Anthrax Vector Candidate Vaccines ‐ Ad4‐PA (Protective Antigen) and Ad4‐PA‐GPI (Glycosylphosphatidylinositol). clinicaltrials.gov; 2020 Mar. Report No.: NCT01979406.
- 60. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) . Phase I Open‐Label Study of Safety and Immunogenicity of AD4‐HIV Envelope Vaccine Vectors in Healthy Volunteers. clinicaltrials.gov; 2020. Dec. Report No.: NCT03878121.
- 61. BioSolutions E . A Phase 1 Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Safety and Immunogenicity of Orally‐administered Replication‐competent Adenovirus Type‐4 HIV Vaccine Regimens in Combination With an AIDSVAX® B/E Boost in Healthy, HIV‐uninfected Adult Participants. clinicaltrials.gov; 2018. Jul. Report No.: NCT02771730.
- 62. Imperial College London . A phase I single‐blind randomised trial investigating immunisation strategies using Ad4‐EnvCN54, MVA‐CN54 and CN54gp140/MPLA combinations in order to maximise antibody responses to human immunodeficiency virus. clinicaltrials.gov; 2020. Feb. Report No.: NCT03408262.
- 63. Martino TA, Petric M, Weingartl H et al. The coxsackie‐adenovirus receptor (CAR) is used by reference strains and clinical isolates representing all six serotypes of coxsackievirus group B and by swine vesicular disease virus. Virology. 2000;271(1):99‐108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Dicks MD, Spencer AJ, Coughlan L et al. Differential immunogenicity between HAdV‐5 and chimpanzee adenovirus vector ChAdOx1 is independent of fiber and penton RGD loop sequences in mice. Sci Rep. 2015;5:16756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Baker AT, et al. The structure of ChAdOx1/AZD‐1222 reveals interactions with CAR and PF4 with implications for vaccine‐induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia. bioRxiv. 2021; 2021.05.19.444882. [Google Scholar]
- 66. Li H, Rhee EG, Masek‐Hammerman K et al. Adenovirus serotype 26 utilizes CD46 as a primary cellular receptor and only transiently activates T lymphocytes following vaccination of rhesus monkeys. J Virol. 2012;86(19):10862‐10865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Persson BD, John L, Rafie K, et al. Human species D adenovirus hexon capsid protein mediates cell entry through a direct interaction with CD46. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2021;118:e2020732118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Baker AT, Greenshields‐Watson A, Coughlan L et al. Diversity within the adenovirus fiber knob hypervariable loops influences primary receptor interactions. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Baker AT, Mundy RM, Davies JA et al. Human adenovirus type 26 uses sialic acid‐bearing glycans as a primary cell entry receptor. Sci Adv. 2019;5(9): eaax3567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Chandra N, Frängsmyr L, Imhof S et al. Sialic acid‐containing glycans as cellular receptors for ocular human adenoviruses: implications for tropism and treatment. Viruses. 2019;11(5):395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Nestić D, Uil TG, Ma J et al. αvβ3 integrin is required for efficient infection of epithelial cells with human adenovirus type 26. J Virol. 2019;93(1):01474‐18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Albinsson B, Kidd AH. Adenovirus type 41 lacks an RGD alpha(v)‐integrin binding motif on the penton base and undergoes delayed uptake in A549 cells. Virus Res. 1999;64(2):125‐136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Parker AL, Waddington SN, Nicol CG et al. Multiple vitamin K‐dependent coagulation zymogens promote adenovirus‐mediated gene delivery to hepatocytes. Blood. 2006;108(8):2554‐2561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Waddington SN, McVey JH, Bhella D et al. Adenovirus serotype 5 hexon mediates liver gene transfer. Cell. 2008;132(3):397‐409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Kalyuzhniy O, Di Paolo NC, Silvestry M et al. Adenovirus serotype 5 hexon is critical for virus infection of hepatocytes in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105(14):5483‐5488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Parker AL, Waddington SN, Buckley SMK et al. Effect of neutralizing sera on factor x‐mediated adenovirus serotype 5 gene transfer. J Virol. 2009;83(1):479‐483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Alba R, Bradshaw AC, Parker AL et al. Identification of coagulation factor (F)X binding sites on the adenovirus serotype 5 hexon: effect of mutagenesis on FX interactions and gene transfer. Blood. 2009;114(5):965‐971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Irons EE, Flatt JW, Doronin K, et al. Coagulation factor binding orientation and dimerization may influence infectivity of adenovirus‐coagulation factor complexes. J Virol. 2013;87:9610‐9619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Parker AL, Waddington SN, Nicol CG, et al. Multiple vitamin K‐dependent coagulation zymogens promote adenovirus‐mediated gene delivery to hepatocytes. Blood. 2006;108:2554‐2561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Duffy MR, Bradshaw AC, Parker AL, McVey JH, Baker AH. A cluster of basic amino acids in the factor X serine protease mediates surface attachment of adenovirus/FX complexes. J Virol. 2011;85:10914‐10919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. Shiri A, Sarvari J, Firoozi Ghahestani S, et al. The inflammatory and fibrotic patterns of hepatic stellate cells following coagulation factors (VII or X)‐shielded adenovirus infection. Curr Microbiol. 2021;78:718‐726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82. Jiang H, Wang Z, Serra D, Frank MM, Amalfitano A. Recombinant adenovirus vectors activate the alternative complement pathway, leading to the binding of human complement protein C3 independent of anti‐ad antibodies. Mol Ther. 2004;10(6):1140‐1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Carlisle RC, Di Y, Cerny AM et al. Human erythrocytes bind and inactivate type 5 adenovirus by presenting Coxsackie virus‐adenovirus receptor and complement receptor 1. Blood. 2009;113(9):1909‐1918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Huang J, Li X, Shi X et al. Platelet integrin αIIbβ3: signal transduction, regulation, and its therapeutic targeting. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12(1):26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85. Trimaille A, Curtiaud A, Marchandot B, et al. Venous thromboembolism in non‐critically ill patients with COVID‐19 infection. Thromb Res. 2020;193:166‐169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86. Alemany R, Suzuki K, Curiel DT. Blood clearance rates of adenovirus type 5 in mice. J Gen Virol. 2000;81:2605‐2609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87. Bradshaw AC, Parker AL, Duffy MR, et al. Requirements for receptor engagement during infection by adenovirus complexed with blood coagulation factor X. PLoS Pathog. 2010;6(10):e1001142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88. Alba R, Bradshaw AC, Coughlan L, et al. Biodistribution and retargeting of FX‐binding ablated adenovirus serotype 5 vectors. Blood. 2010;116:2656‐2664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89. Kowarz E, Krutzke L, Reis J, Bracharz S, Kochanek S & Marschalek R “Vaccine‐Induced Covid‐19 Mimicry” Syndrome:Splice reactions within the SARS‐CoV‐2 Spike open reading frame result in Spike protein variants that may cause thromboembolic events in patients immunized with vector‐based vaccines. In Review; 2021 May.
- 90. Krutzke L, Roesler R, Wiese S & Kochanek S Process‐related impurities in the ChAdOx1 nCov‐19 vaccine. In Review; 2021 May. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 91. Almuqrin A, Davidson AD, Williamson MK, et al. SARS‐CoV‐2 vaccine ChAdOx1 nCoV‐19 infection of human cell lines reveals low levels of viral backbone gene transcription alongside very high levels of SARS‐CoV‐2 S glycoprotein gene transcription. Genome Med. 2021;13:43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92. Weaver C, Mowat A, Berg L, Chaplin D, Janeway CA, Travers P & Walport M. Janeway’s immunobiology. 9th ed. New York: W.W. Norton & Company; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 93. Greinacher A, Selleng K, Wesche J, Handtke S, Palankar R, Aurich K & Lalk M Towards Understanding ChAdOx1 nCov‐19 Vaccine‐induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia (VITT). 13.
- 94. Bliss CM, Bowyer G, Anagnostou NA, et al. Assessment of novel vaccination regimens using viral vectored liver stage malaria vaccines encoding ME‐TRAP. Sci Rep. 2018;8:3390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95. Bacsi S, Geoffrey R, Visentin G, De Palma R, Aster R, Gorski J. Identification of T cells responding to a self‐protein modified by an external agent. Hum Immunol. 2001;62:113‐124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96. Zheng Y, Yu M, Padmanabhan A, et al. Critical role of CD4 T cells in PF4/heparin antibody production in mice. Blood. 2015;125:1826‐1829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97. Zheng Y, Zhu W, Haribhai D et al. Regulatory T cells control PF4/Heparin antibody production in mice. J Immunol. 2019;203(7):1786‐1792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98. Khandelwal S, Arepally GM. Immune pathogenesis of heparin‐induced thrombocytopenia. Thromb Haemost. 2016;116(5):792‐798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99. Staibano P, Arnold DM, Bowdish DME, Nazy I et al. The unique immunological features of heparin‐induced thrombocytopenia. Br J Haematol. 2017;177(2):198‐207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100. Ewer KJ, Barrett JR, Belij‐Rammerstorfer S, et al. T cell and antibody responses induced by a single dose of ChAdOx1 nCoV‐19 (AZD1222) vaccine in a phase 1/2 clinical trial. Nat Med. 2021;27(2):270‐278. 10.1038/s41591-020-01194-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101. Wang EY, Mao T, Klein J et al. Diverse functional autoantibodies in patients with COVID‐19. Nature. 2021;595(7866):283–288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102. Bomhof G, Mutsaers PGNJ, Leebeek FWG, et al. COVID‐19‐associated immune thrombocytopenia. Br J Haematol. 2020;190:e61‐e64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103. Iba T, Levy JH, Connors JM, Warkentin TE, Thachil J, Levi M. The unique characteristics of COVID‐19 coagulopathy. Crit Care. 2020;24:360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104. Chen B, Jiang C, Han B, et al. High prevalence of occult thrombosis in cases of mild/moderate COVID‐19. Int J Infect Dis. 2021;104:77‐82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105. Tang N, Bai H, Chen X, Gong J, Li D, Sun Z. Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients with coagulopathy. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18:1094‐1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106. Campbell RA, Boilard E, Rondina MT. Is there a role for the ACE2 receptor in SARS‐CoV‐2 interactions with platelets? J Thromb Haemost. 2021;19:46‐50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107. Apostolidis SA, Sarkar A & Giannini HM et al. Signaling through FcγRIIA and the C5a‐C5aR pathway mediates platelet hyperactivation in COVID‐19. bioRxiv Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 2021. 2021.05.01.442279. 10.1101/2021.05.01.442279 [DOI]
- 108. Cappellano G, Raineri D, Rolla R, et al. Circulating platelet‐derived extracellular vesicles are a hallmark of Sars‐Cov‐2 infection. Cells. 2021;10:85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109. Muir K‐L, Kallam A, Koepsell SA, Gundabolu K. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia after Ad26.COV2.S Vaccination. N Engla J Med. 2021;384(20):1964–1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110. Cai Z, Greene MI, Zhu Z, Zhang H. Structural features and PF4 functions that occur in heparin‐induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) complicated by COVID‐19. Antibodies. 2020;9:52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111. Ladner JT, Henson SN, Boyle AS, et al. Epitope‐resolved profiling of the SARS‐CoV‐2 antibody response identifies cross‐reactivity with endemic human coronaviruses. CR Med. 2021;2(1):100189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Fig S1


