Abstract
Nanoparticles are used in the clinic to treat cancer, resolve mineral deficiencies, image tissues, and facilitate vaccination. As a modular technology, nanoparticles combine diagnostic agents or therapeutics (e.g., elements, small molecules, biologics), synthetic materials (e.g., polymers), and biological molecules (e.g., antibodies, peptides, lipids). Leveraging these parameters, nanoparticles can be designed and tuned to navigate biological microenvironments, negotiate biological barriers, and deliver therapeutics or diagnostic agents to specific cells and tissues in the body. Recently, with the Emergency Use Authorization of the COVID‐19 lipid nanoparticle vaccines, the advantages and potential of nanoparticles as a delivery vehicle have been displayed at the forefront of biotechnology. Here, we provide a 5‐year status update on our original “Nanoparticles in the Clinic” review (also a 2‐year update on our second “Nanoparticles in the Clinic” review) by discussing recent nanoparticle delivery system approvals, highlighting new clinical trials, and providing an update on the previously highlighted clinical trials.
Keywords: clinic, clinical translation, clinical trials, drug delivery, nanomedicine, nanoparticles, translational medicine
1. INTRODUCTION
Over the past 2 years, the nanomedicine landscape has evolved rapidly, driven by the worldwide clinical introduction of the Moderna and Pfizer‐BioNTech COVID‐19 lipid nanoparticle mRNA vaccines.1 Given this sudden expansion of nanoparticle use in the clinic, we are updating our “Nanoparticles in the Clinic” review and providing an update on the clinical landscape of nanomedicines. Our original review was published in 2016 and highlighted >25 approved nanomedicines and >45 unapproved nanoparticles that were being evaluated clinical trials.2 In 2019, our second review included three new nanoparticle approvals, added >75 new clinicals trials for the previously highlighted unapproved nanoparticles, and added >15 new nanoparticles that entered clinical trials.3 In this 2021 update, we provide a broad overview of the current clinical landscape by adding two nanoparticles that recently received Emergency Use Authorization (both in 2020), >30 new trials that have started for previously tabulated unapproved nanoparticles, and >35 new nanoparticle technologies (associated with >55 new trials) that have recently entered clinical trials.
2. UPDATES ON CURRENTLY APPROVED NANOPARTICLES AND NEW ADDITIONS
Over the past 2 years, the nanomedicine landscape has evolved rapidly, driven by the global need for new technologies to provide prophylactic and therapeutic approaches against the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19),4, 5, 6 which is caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‐CoV‐2).7 Of the technologies that have emerged to combat COVID‐19, lipid nanoparticles are the delivery vehicle used in the Moderna and Pfizer‐BioNTech COVID‐19 vaccines, both of which were granted Emergency Use Authorization in the United States in 2020.8
The Moderna vaccine, mRNA‐1273, is a lipid nanoparticle consisting of the ionizable cationic lipid SM‐102 (heptadecan‐9‐yl 8 ((2 hydroxyethyl) (6 oxo 6‐(undecyloxy) hexyl) amino) octanoate), DSPC (1,2‐distearoyl‐snglycero‐3 phosphocholine), cholesterol, and PEG‐DMG (1 monomethoxypolyethyleneglycol‐2,3‐dimyristylglycerol with polyethylene glycol).9 mRNA‐1273 was granted Emergency Use Authorization by the U.S. FDA on December 18th, 2020,10 based on a number of clinical trials, including one that demonstrated anti‐SARS‐CoV‐2 immune responses in participants without trial‐limiting safety concerns11 and another clinical trial with 30,420 participants that demonstrated 94.1% efficacy at preventing COVID‐19 illness.12 The Pfizer‐BioNTech vaccine, BNT162b2, is also a lipid nanoparticle and consists of the ionizable cationic lipid ALC‐0315 ((4‐hydroxybutyl)azanediyl)bis(hexane‐6,1‐diyl)bis(2‐hexyldecanoate), DSPC (1,2‐distearoyl‐sn‐glycero‐3‐phosphocholine), cholesterol, and PEG‐DMA (2 [(polyethylene glycol)‐2000]‐N,N‐ditetradecylacetamide).9 BNT162b2 was granted Emergency Use Authorization by the U.S. FDA on December 11th, 2020,10 based on a number of clinical trials, including one that demonstrated both safety and immunogenicity of BNT162b2,13 and another clinical trial with 43,548 participants that demonstrated BNT162b2 was 95% effective in preventing COVID‐19.14 Both lipid nanoparticle formulations are administered intramuscularly in two separate doses and are used to encapsulate mRNA that encodes for the SARS‐CoV‐2 spike glycoprotein, which mediates attachment to host cells and thus enables viral entry.11 By encoding for this spike glycoprotein, the host generates an immune response to the presented antigenic proteins; thus, a neutralizing antibody response against SARS‐CoV‐2 is generated.15 In both formulations, lipid nanoparticles enable delivery of the sensitive mRNA cargo into the cytoplasm,16 which has been the major obstacle in translation of mRNA technologies.17 By overcoming the challenges of intracellular delivery using lipid nanoparticles, antigen presentation could occur and the neutralizing antibody response against SARS‐CoV‐2 was achieved. Collectively, mRNA‐1273 and BNT162b2 are used in >35 countries10 with an estimated 3 billion (2 billion for BNT162b2 and 1 billion for mRNA‐1273) doses to be manufactured throughout 2021.18
Table 1 has been updated to list FDA/EMA approved injectable nanomedicines up to 2021, including the lipid nanoparticle mRNA vaccines against COVID‐19. Figures 1 and 2 highlight key aspects of these tabulated findings. Figure 1 shows the chronological approvals of nanoparticles based on particle type. Lipid‐based and inorganic nanoparticles comprise the majority of clinically‐approved nanoparticles. Interestingly, the first (1989) and most recent (2020) clinically approved/authorized particles highlight how lipid‐based nanoparticles, as a platform technology, enable controlled interactions between encapsulated therapeutics and complex microenvironments within patients. While the majority of lipid‐based nanoparticles are approved and clinically‐used for intravenous applications, lipid‐based nanoparticles are also used to protect sensitive cargos (e.g., mRNA) after manufacturing, during storage, and during intramuscular muscular injection and throughout their action within the host. Figure 2 shows the chronological approvals of nanoparticles based on indication, with the dominant applications being cancer, anemia, and imaging.
TABLE 1.
Clinically approved nanoparticle therapies and diagnostics, grouped by their broad indication
| Name | Particle type | Payload | Approved application/indication | Approval (year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| New additions | ||||
| mRNA‐1273 (Moderna) | Lipid nanoparticle | mRNA | COVID‐19 vaccine | FDA, Emergency Use Authorization (2020) |
| Tozinameran/BNT162b2 (Pfizer‐BioNTech) | Lipid nanoparticle | mRNA | COVID‐19 vaccine | FDA, Emergency Use Authorization (2020) |
| Cancer | ||||
|
Doxil Caelyx (Janssen) |
PEGylated liposome | Doxorubicin | Ovarian cancer, HIV‐associated Kaposi's sarcoma, Multiple myeloma |
FDA (1995) EMA (1996) |
| DaunoXome (Galen) | Liposome (non‐PEGylated) | Daunorubicin | HIV‐associated Kaposi's sarcoma | FDA (1996) |
| Myocet (Teva UK) | Liposome (non‐PEGylated) | Doxorubicin | Breast cancer |
EMA (2000) |
| Abraxane (Celgene) | Albumin‐particle | Paclitaxel | Advanced non‐small cell lung cancer, Metastatic pancreatic cancer, Metastatic breast cancer |
FDA (2005) EMA (2008) |
| Marqibo (Spectrum) | Liposome (non‐PEGylated) | Vincristine | Philadelphia chromosome‐negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia | FDA (2012) |
| MEPACT (Millennium) | Liposome (non‐PEGylated) | Mifamurtide | Osteosarcoma | EMA (2009) |
|
NBTXR3 Hensify (Nanobiotix) |
Hafnium oxide nanoparticles | Stimulated with external radiation to enhance tumor cell death via electron production | Squamous cell carcinoma | CE Mark (2019) |
|
Onivyde MM‐398 (Merrimack) |
PEGylated liposome | Irinotecan | Metastatic pancreatic cancer | FDA (2015) |
|
VYXEOS CPX‐351 (Jazz Pharmaceuticals) |
Liposome | Cytarabine:daunorubicin (5:1 molar ratio) | Acute myeloid leukemia |
FDA (2017) EMA (2018) |
| Iron‐replacement | ||||
|
CosmoFer INFeD Ferrisat (Pharmacosmos) |
Iron dextran colloid | Iron | Iron deficient anemia |
FDA (1992) Some of Europe |
|
DexFerrum DexIron (American Regent) |
Iron dextran colloid | Iron | Iron deficient anemia | FDA (1996) |
| Ferrlecit (Sanofi) | Iron gluconate colloid | Iron | Iron replacement for anemia treatment in patients with chronic kidney disease | FDA (1999) |
| Venofer (American Regent) | Iron sucrose colloid | Iron | Iron replacement for anemia treatment in patients with chronic kidney disease | FDA (2000) |
|
Feraheme (AMAG) Rienso (Takeda) Ferumoxytol |
Iron polyglucose sorbitol carboxymethylether colloid | Iron | Iron deficiency in patients with chronic kidney disease | FDA (2009) |
|
Injectafer Ferinject (Vifor) |
Iron carboxymaltose colloid | Iron | Iron deficient anemia | FDA (2013) |
| Monofer (Pharmacosmos) | 10% iron isomaltoside 1000 colloid | Iron | Treating iron deficiency and anemia when oral methods do not work or when iron delivery is required immediately | Some of Europe (2009) |
| Diafer (Pharmacosmos) | 5% iron isomaltoside 1000 colloid | Iron | Iron deficient anemia |
Some of Europe (2013) |
| Imaging agents | ||||
| Definity (Lantheus Medical Imaging) | Lipid microspheres | Perflutren | Ultrasound contrast agent | FDA (2001) |
|
Feridex I.V. (AMAG) Endorem |
Iron dextran colloid | Iron | Imaging of liver lesions |
FDA (1996) Discontinued (2008) |
|
Ferumoxtran‐10 Combidex Sinerem (AMAG) |
Iron dextran colloid | Iron | Imaging lymph node metastases | Only available in the Netherlands (2013) |
| Optison (GE Healthcare) | Human serum albumin stabilized microspheres | Perflutren | Ultrasound contrast agent |
FDA (1997) EMA (1998) |
| SonoVue (Bracco Imaging) | Phospholipid stabilized microbubble | Hexafluoride | Ultrasound contrast agent | EMA (2001) |
|
Resovist (Bayer Schering Pharma) Cliavist |
Iron carboxydextran colloid | Iron | Imaging of liver lesions |
Some of Europe (2001) Discontinued (2009) |
| Vaccines | ||||
| Epaxal (Crucell) | Liposome | Inactivated hepatitis A virus | Hepatitis A vaccine | Some of Europe (2003; Now discontinued) |
| Inflexal V (Crucell) | Liposome | Trivalent‐influenza virus surface antigens | Influenza vaccine | Some of Europe (1997; Now discontinued) |
| Anesthetics | ||||
| Diprivan | Liposome | Propofol | Induction and maintenance of sedation or anesthesia | FDA (1989) |
| Amyloidosis | ||||
|
ONPATTRO Patisiran ALN‐TTR02 (Alnylam Pharmaceuticals) |
Lipid nanoparticle | RNAi for the knockdown of disease‐causing TTR protein | Transthyretin (TTR)‐mediated amyloidosis |
FDA (2018) EMA (2018) |
| Fungal infections | ||||
| AmBisome (Gilead Sciences) | Liposome | Amphotericin B |
Cryptococcal Meningitis in HIV‐infected patients Aspergillus, Candida and/or Cryptococcus species infections (secondary) Visceral leishmaniasis parasite in immunocompromised patients |
FDA (1997) Most of Europe |
| Macular degradation | ||||
| Visudyne (Bausch and Lomb) | Liposomal | Verteporfin | Treatment of subfoveal choroidal neovascularization from age‐related macular degeneration, pathologic, or ocular histoplasmosis |
FDA (2000) EMA (2000) |
FIGURE 1.
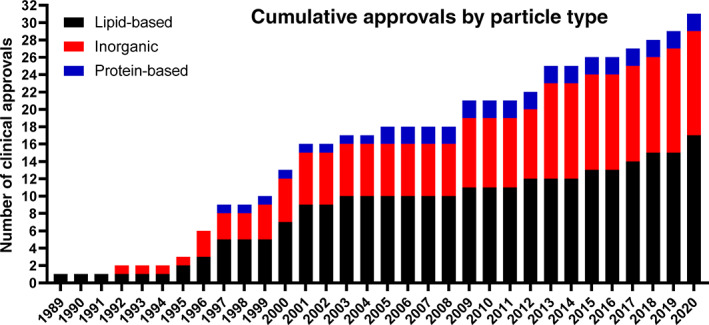
Chronological nanoparticle approvals based on particle type
FIGURE 2.
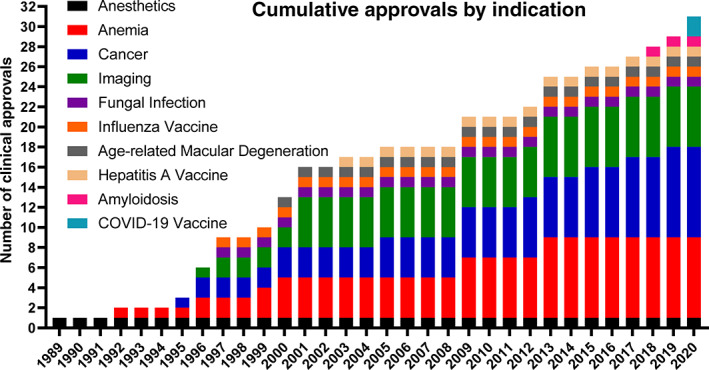
Chronological nanoparticle approvals based on indication
In addition to this updated Table 1, we also report an update on the number of clinical trials for approved nanoparticles that have appeared since our previous two articles in 2016 and 20192, 3: Figure 3 shows the number of clinical trials for each of the approved nanoparticles (see Table S1 for detailed summary) from 2016 (red) to 2019 (blue) to 2021 (green). Of particular note, we observe: (i) an increase in the number of clinical trials for 21 of the 29 approved nanoparticles in Table 1 (excluding the newly‐added mRNA‐1723 and BNT162b2), and (ii) an increase in the total number of clinical trials for approved nanoparticles from 1220 (in 2016), to 1716 (in 2019), and to 1935 (in 2021). Together, this demonstrates the continued success of nanoparticles that are being introduced into the clinic and the continued investigation of already‐approved nanoparticles toward expanding or improving their clinical use.
FIGURE 3.
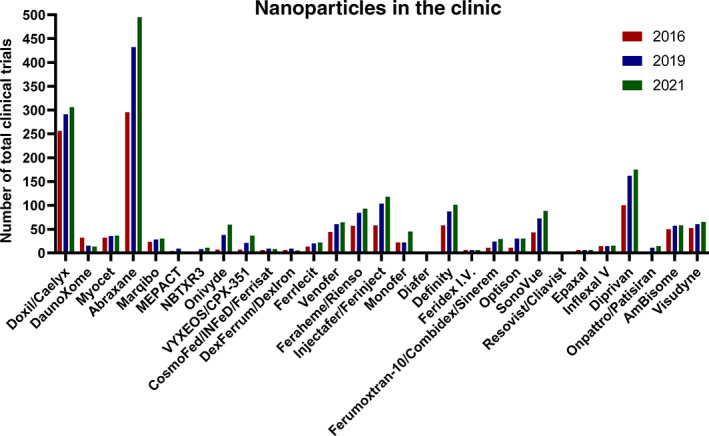
Chronological update on the number of clinical trials for each nanoparticle, based on the number of identified trials in our previous “Nanoparticles in the Clinic” reviews in 20162 and 2019.3 These trials and nanoparticles have appeared on the ClinicalTrial.gov databaseSource: Modified with permissions from References 2 and 3
3. UPDATE ON PREVIOUS CLINICAL TRIALS FOR UNAPPROVED NANOPARTICLES
In our previous article,3 >60 different non‐approved nanoparticles were listed as active in >100 clinical trials. Here, we are updating the current clinical landscape for each of these clinically investigated nanoparticles (Table 2). In this update, >40 new trials have been added. Regarding previous clinical trials that were available before 2019,3 11 have been updated to active status, 5 have been updated to recruiting status, 5 have been terminated, 8 have been updated to unknown status, 12 have been completed, 3 have been withdrawn, and 12 have posted results that are viewable on ClinicalTrials.gov (Table 2). Of particular note: (i) 10 new trials began for a mitoxantrone hydrochloride liposome, used for the treatment of various cancers, (ii) 11 new trials began for Sonazoid, which is a lipid‐encapsulated formulation of F‐butane for ultrasound imaging, and (iii) results have been posted for PNT2258, DCR‐MYC, SGT‐53, NK105, CRLX101, CRLX301, AuroLase, and Halaven. Table 2 provides a detailed tabulation of these recent updates.
TABLE 2.
Updates on previously reported nanoparticle clinical trials that are not clinically approved or authorized and are currently active in clinical trials
| Name (company) | Particle type | Payload | Investigated application/indication | ClinicalTrials.gov identifiers (phase) | Updates since 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lipid‐based (cancer) | |||||
|
PROMITIL (Lipomedix Pharmaceuticals) |
PEGylated liposome | Mitomycin‐C | Solid tumors |
2016: NCT01705002 (Ph I): Completed 2019: NCT03823989 (Ph Ib): Recruiting (Active as of 2021) 2021 additions: NCT04729205 (Ph I): Recruiting |
2021: One new trial One trial updated to active 2019: One new trial One trial updated to completed |
|
ThermoDox® (Celsion) |
Lyso‐thermosensitive liposome | Doxorubicin | Various cancers |
2016: NCT02536183 (Ph I): Recruiting NCT00826085 (Ph I/II): Completed NCT02112656 (Ph III): Completed NCT02181075 (Ph I): Completed 2019 additions: NCT03749850 (Ph I): Not yet recruiting (Recruiting as of 2021) 2021 additions: NCT04852367 (Ph I): Not yet recruiting NCT04791228 (Ph II): Not yet recruiting |
2021: Two new trials One trial updated to recruiting 2019: One new trial Three trials updated to completed |
|
Oncoprex/GPX‐001 (Genprex) |
Liposome | FUS1 (TUSC2) | Lung cancer |
2016: NCT01455389 (Ph I/II): Active, not recruiting 2021 additions: NCT04486833 (Ph I/II): Not yet recruiting |
2021: One new trial 2019: No updates |
|
Halaven E7389‐LF (Eisai) |
Liposome | Eribulin mesylate | Solid tumors |
2016: NCT01945710 (Ph I): Completed 2019 additions: NCT03207672 (Ph I): Recruiting (Active as of 2021) 2021 additions: NCT04078295 (Ph I/II): Recruiting |
2021: One new trial One trial updated to recruiting Results posted and viewable on ClinicalTrials.gov for NCT01945710 2019: One new trial One trial updated to completed |
| 188Re‐BMEDA‐liposome | Pegylated liposome | 188Re‐N,N‐bis (2‐mercaptoethyl)‐N′,N′‐diethylethylenediamine | Advanced solid tumors |
2016: NCT02271516 (Ph I): Unknown (Terminated as of 2021 due to concerns of accumulation of radioactivity in both the liver and spleen) |
2021: One trial updated to terminated 2019: Zero new trials |
|
Mitoxantrone Hydrochloride Liposome (CSPC ZhongQi Pharmaceutical Technology) |
Liposome | Mitoxantrone | Various cancers |
2016: NCT02131688 (Ph I): Unknown NCT02596373 (Ph II): Recruiting (Unknown status as of 2021) NCT02597387 (Ph II): Recruiting (Unknown status as of 2021) NCT02595242 (Ph I): Withdrawn NCT02597153 (Ph II): Terminated (Only one subject enrolled in 1.5 years) 2019 additions: NCT03776279 (Ph I): Recruiting (Unknown status as of 2021) 2021 additions: NCT04668690 (Ph III): Not yet recruiting NCT04718402 (Ph I): Recruiting NCT04902027 (Ph I): Not yet recruiting NCT04719065 (Ph I): Recruiting NCT04718376 (Ph I): Recruiting NCT04900766 (Ph I): Not yet recruiting NCT04548700 (Ph I): Not yet recruiting NCT04509466 (Ph I): Not yet recruiting NCT04331743 (Ph I): Not yet recruiting NCT04352413 (Ph II): Recruiting |
2021: 10 new trials Three trials updated to unknown status 2019: One new trial One trial updated to withdrawn One trial updated to terminated |
| JVRS‐100 | Cationic liposome | Plasmid DNA complex for immune system stimulation | Leukemia |
2016: NCT00860522 (Ph I): Completed |
2021: No updates 2019: Zero new trials One trial updated to completed |
|
Lipocurc (SignPath Pharma) |
Liposome | Curcumin | Solid tumors |
2016: NCT02138955 (Ph I/II): Unknown |
2021: No updates 2019: Zero new trials One trial updated to unknown status |
|
LiPlaCis (LiPlasome Pharma) |
Liposome with specific degradation‐controlled drug release via phospholipase A2 (PLA2) | Cisplatin | Advanced or refractory tumors |
2016: NCT01861496 (Ph I): Recruiting (Active as of 2021) |
2021: One trial updated to active 2019: No updates |
|
MM‐302 (Merrimack Pharmaceuticals) |
HER2‐targeted PEGylated liposome | Doxorubicin | Breast cancer |
2016: NCT01304797 (Ph I): Unknown NCT02213744 (Ph II/III): Terminated (Felt not to show benefit over control per DMC and confirmed via futility analysis) 2019 additions: NCT02735798 (Ph I): Withdrawn (The study was not started due to the sponsor choosing to not fund the trial) |
2021: No updates 2019: One new trial (withdrawn) One trial updated to terminated One trial updated to unknown status |
|
LIPUSU® (Nanjing Luye Sike Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.) |
Liposome | Paclitaxel | Advanced solid tumors, or gastric, breast cancer |
2016: NCT01994031 (Ph IV): Unknown NCT02142790 (Ph IV): Unknown NCT02163291 (Ph II): Unknown NCT02142010 (Not Provided): Unknown 2019 additions: NCT02996214 (Ph IV): Not yet recruiting (Active as of 2021) |
2021: One trial updated to active 2019: One new trial |
|
TKM‐080301 (Arbutus Biopharma) |
Lipid particle targeting polo‐like kinase 1 (PLK1) | siRNA | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
2016: NCT02191878 (Ph I/II): Completed |
2021: No updates 2019: Zero new trials One trial updated to completed |
| siRNA‐EphA2‐DOPC | Liposome | siRNA for EphA2 knockdown | Solid tumors |
2016: NCT01591356 (Ph I): Recruiting (Active as of 2021) |
2021: One trial updated to active 2019: Zero new trials |
|
PNT2258 (ProNAi Therapeutics) |
Lipid nanoparticle | Proprietary single‐stranded DNAi (PNT100) | Lymphomas |
2016: NCT02378038 (Ph II): Terminated NCT02226965 (Ph II): Unknown (Completed as of 2021) NCT01733238 (Ph II): Completed |
2021: Results posted and viewable on ClinicalTrials.gov for NCT02378038, NCT02226965, and NCT01733238 2019: Zero new trials One trial updated to completed One trial updated to terminated One trial updated to unknown status |
|
BP1001/Prexigebersen (Bio‐Path Holdings) |
Neutral liposomes | Growth factor receptor bound protein‐2 (Grb‐2) antisense oligonucleotide | Leukemias and solid tumors |
2016: NCT01159028 (Ph I): Active, not recruiting (Updated to completed) 2019 additions: NCT02923986 (Ph I): Recruiting (Withdrawn as of 2021 due to no enrollment) NCT02781883 (Ph II): Recruiting 2021 additions: NCT04196257 (Ph I): Not yet recruiting |
2021: One new trial One trial updated to completed One trial updated to withdrawn 2019: Two new trials |
|
DCR‐MYC (Dicerna Pharmaceuticals) |
Lipid nanoparticle | DsiRNA for NYC oncogene silencing | Solid tumors, multiple myeloma, lymphoma, or hepatocellular carcinoma |
2016: NCT02110563 (Ph I): Terminated (Sponsor Decision) NCT02314052 (Ph I/II) Terminated (Sponsor Decision) |
2021: Results posted and viewable on ClinicalTrials.gov for NCT02314052 2019: Zero new trials Two trials updated to terminated |
|
Atu027 (Silence Therapeutics GmbH) |
Liposome | AtuRNAi for PKN3 knockdown in vascular endothelium | Pancreatic cancer |
2016: NCT01808638 (Ph I/II): Completed |
2021: No updates 2019: Zero new trials One trial completed |
|
SGT‐53 (SynerGene Therapeutics) |
Cationic liposome with anti‐transferrin receptor antibody | Wildtype p53 sequence | Glioblastoma, solid tumors, or pancreatic cancer |
2016: NCT02354547 (Ph I): Recruiting (Active as of 2021) NCT02340156 (Ph II): Recruiting (Terminated as of 2021) NCT00470613 (Ph I): Completed 2019 additions: NCT03554707 (Ph I): Not yet recruiting 2021 additions: NCT02340117 (Ph II): Recruiting |
2021: One new trial Results posted and viewable on ClinicalTrials.gov for NCT02340156 2019: One new trial One trial updated to completed |
|
SGT‐94 (SynerGene Therapeutics) |
Liposome with anti‐transferrin receptor antibody | RB94 plasmid DNA | Solid tumors |
2016: NCT01517464 (Ph I): Completed |
2021: No updates 2019: Zero new trials One trial updated to completed |
|
MRX34 (Mirna Therapeutics) |
Liposome | Double‐stranded RNA mimic of miR‐34 |
Liver cancer |
2016: NCT01829971 (Ph I): Terminated (Five immune related serious adverse events) 2019 additions: NCT02862145 (Ph I): Withdrawn (five immune related serious adverse events in Phase 1 study) |
2021: No updates 2019: One new trial (withdrawn) One trial updated to terminated |
|
TargomiRs (EnGeneIC) |
Anti‐EGFR bispecific antibody minicells (bacteria derived nanoparticles) | miR‐16 based microRNA | Mesothelioma and non‐small cell lung cancer |
2016: NCT02369198 (Ph I): Completed |
2021: No updates 2019: Zero new trials One trial updated to completed |
|
MM‐310 (Merrimack Pharmaceuticals) |
Liposome functionalized with antibodies targeted to the EphA2 receptor | Docetaxel | Solid tumors |
2019: NCT03076372 (Ph I): Recruiting (Unknown as of 2021) |
2021: No updates |
|
EGFR(V)‐EDV‐Dox (EnGeneIC) |
Bacterially derived minicell | Doxorubicin | Recurrent glioblastoma |
2019: NCT02766699 (Ph I): Recruiting |
2021: No updates |
|
Alprostadil liposome (CSPC ZhongQi Pharmaceutical Technology) |
Liposome |
Alprostadil | Safety and tolerability |
2019: NCT03669562 (Ph I): Recruiting (Unknown as of 2021) 2021 additions: NCT04197323 (Ph II): Recruiting |
2021: One trial updated to active One trial updated to unknown status |
|
Liposomal Annamycin (Moleculin Biotech) |
Liposome | Annamycin | Acute myeloid leukemia |
2019: NCT03388749 (Ph II): Recruiting NCT03315039 (Ph II): Recruiting (Active as of 2021) 2021 additions: NCT04887298 (Ph I/II): Not yet recruiting |
2021: One new trial One trial updated to active |
|
FF‐10832 (Fujifilm Pharmaceuticals) |
Liposome | Gemcitabine | Advanced solid tumors |
2019: NCT03440450 (Ph I): Recruiting |
2021: No updates |
|
Anti‐EGFR‐IL‐dox (Swiss Group for Clinical Cancer Research; University Hospital, Basel, Switzerland) |
Anti‐EGFR immunoliposome | Doxorubicin |
Advanced triple negative EGFR positive breast cancer High grade gliomas |
2019: NCT02833766 (Ph II): Recruiting (Active as of 2021) NCT03603379 (Ph I): Recruiting (Completed as of 2021) |
2021: One trial updated to active One trial updated to completed |
|
TLD‐1/Talidox (Swiss Group for Clinical Cancer Research) |
Liposome | Doxorubicin | Advanced solid tumors |
2019: NCT03387917 (Ph I): Recruiting |
2021: No updates |
|
NC‐6300 (NanoCarrier) |
Micelle | Epirubicin | Advanced solid tumors or soft tissue sarcoma |
2019: NCT03168061 (Ph II): Recruiting |
2021: No updates |
|
MRT5201 (Translate Bio) |
PEGylated liposomes | mRNA | Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency |
2019: NCT03767270 (Ph I): Not yet recruiting (Withdrawn as of 2021 due to program discontinuation) |
2021: One trial updated to withdrawn |
|
Lipo‐MERIT (BioNTech SE) |
Liposome | Four naked ribonucleic acid (RNA)‐drug products | Cancer vaccine for advanced melanoma |
2019: NCT02410733 (Ph I): Recruiting (Active as of 2021) |
2021: One trial updated to active |
|
BNT114/IVAC_W_bre1_uID (BioNTech SE) |
Patient‐specific liposome (specificity for antigen‐expression on a patient's tumor) | Complexed RNA | Triple negative breast cancer |
2019: NCT02316457 (Ph I): Recruiting (Active as of 2021) |
2021: One trial updated to active |
| Lipid‐based (other) | |||||
|
ND‐L02‐s0201 (Nitto Denko) |
Lipid nanoparticle conjugated to Vitamin A | siRNA |
Hepatic fibrosis and pulmonary fibrosis |
2016: NCT02227459 (Ph I): Completed 2019 additions: NCT01858935 (Ph I): Completed NCT03241264 (Ph I): Completed NCT03538301 (Ph II): Recruiting |
2021: No updates 2019: Three new trials (two completed) One trial updated to completed |
|
ARB‐001467 TKM‐HBV (Arbutus Biopharma) |
Lipid particle | Three RNAi therapeutics that target three sites on the HBV genome | Hepatitis B |
2016: NCT02631096 (Ph II): Completed |
2021: No updates 2019: Zero new trials One trial updated to completed |
|
CAL02 (Combioxin SA) |
Cholesterol liposomes for toxin neutralization | Sphingomyelin | Pneumonia |
2016: NCT02583373 (Ph I): Completed |
2021: No updates 2019: Zero new trials One trial updated to completed |
|
Nanocort/Sunpharma1505 (Enceladus in collaboration with Sun Pharma Global) |
PEGylated liposome | Prednisolone | Rheumatoid arthritis and hemodialysis fistula maturation |
2016: NCT02495662 (Ph II): Terminated (Slow inclusion) NCT02534896 (Ph III): Terminated |
2021: No updates 2019: Zero new trials Two trials updated to terminated |
|
RGI‐2001 (Regimmune) |
Liposome | α‐GalCer | Mitigating graft versus host disease following stem cell transplant |
2016: NCT01379209 (Ph I/II): Unknown (Completed as of 2021) 2019 additions: NCT04014790 (Ph II): Not yet recruiting (Recruiting as of 2021) 2021 additions: NCT04473911 (Ph I): Recruiting |
2021: One new trial One trial updated to completed One trial updated to recruiting 2019: One new trial |
| Sonazoid | Lipid shell | F‐butane | Contrast enhanced ultrasound for imaging hepatocellular carcinoma, skeletal muscle perfusion, or for estimating portal hypertension |
2016: NCT00822991 (Not Provided): Recruiting (Unknown status as of 2021) NCT02398266 (Ph II): Unknown NCT02188901 (Not Provided): Completed NCT02489045 (Ph IV): Recruiting (Completed as of 2021) 2021 additions: In 2021, there are 28 total studies |
2021: 28 trials total (11 active trials were added after 2019) 2019: Zero new trials One trial updated to unknown status One trial completed |
|
mRNA‐1944 (Moderna) |
Moderna's proprietary lipid nanoparticle technology | Two mRNAs that encode heavy and light chains of anti‐Chikungunya antibody | Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics toward the prevention of Chikungunya virus infection |
2019: NCT03829384 (Ph I): Recruiting (Active as of 2021) |
2021: One trial updated to active |
| Polymeric and micelles (cancer) | |||||
|
AZD2811 (AstraZeneca with BIND Therapeutics) |
BIND therapeutics polymer particle accruing platform | Aurora B kinase inhibitor | Advanced solid tumors |
2016: NCT02579226 (Ph I): Recruiting (Completed as of 2021) 2019 additions: NCT03366675 (Ph II): Terminated (Early detection of the purpose of the study) NCT03217838 (Ph I): Recruiting (Completed as of 2021) 2021 additions: NCT04525391 (Ph II): Recruiting NCT04745689 (Ph II): Recruiting |
2021: Two new trials Two trials updated to completed 2019: Two new trials (one terminated) |
|
BIND‐014 (BIND Therapeutics) |
PSMA targeted (via ACUPA) PEG‐PLGA or PLA–PEG particle | Docetaxel | Prostate, metastatic, non‐small cell lung, cervical, head and neck, or KRAS positive lung cancers |
2016: NCT02479178 (Ph II): Terminated NCT02283320 (Ph II): Completed NCT01812746 (Ph II): Completed NCT01792479 (Ph II): Completed NCT01300533 (Ph I): Completed |
2021: No updates 2019: Zero new trials Four trials updated to completed |
|
Cynviloq IG‐001 (Sorrento) |
Polymeric micelle | Paclitaxel | Breast cancer |
2016: NCT02064829 (Not Provided): Completed |
2021: No updates 2019: Zero new trials One trial updated to completed |
|
Genexol‐PM (Samyang Biopharmaceuticals) |
Polymeric micelle | Paclitaxel | Head and neck or breast cancer |
2016: NCT01689194 (Ph II): Unknown (Completed as of 2021) NCT02263495 (Ph II): Completed NCT00912639 (Ph IV): Unknown 2019 additions: NCT02739633 (Ph II): Recruiting (Unknown as of 2021) NCT03008512 (Ph II): Recruiting (Terminated as of 2021, due to poor accrual) |
2021: One trial updated to unknown status One trial updated to terminated 2019: Two new trials One trial updated to completed One trial updated to unknown status |
|
NC‐6004 Nanoplatin (Nanocarrier) |
Polyamino acid and PEG micellar nanoparticle | Cisplatin | Advanced solid tumors, lung, biliary, bladder, or pancreatic cancers |
2016: NCT02240238 (Ph I/II): Active, not recruiting (Completed as of 2021) NCT02043288 (Ph III): Unknown (Completed as of 2021) 2019 additions: NCT03771820 (Ph II): Not yet recruiting (Recruiting as of 2021) NCT03109158 (Ph I): Completed NCT02817113 (Ph I): Unknown (Terminated as of 2021 due to strategy change) |
2021: Two trials updated to completed One trial updated to recruiting One trial updated to terminated 2019: Three new trials One trial updated to unknown status |
|
NC‐4016 DACH‐Platin micelle (Nanocarrier) |
Polyamino acid and PEG micellar nanoparticle | Oxaliplatin | Advanced solid tumors or lymphomas |
2016: NCT01999491 (Ph I): Completed |
2021: No updates 2019: Zero new trials |
|
NK105 (Nippon Kayaku) |
Micelle | Paclitaxel | Breast cancer |
2016: NCT01644890 (Ph III): Completed |
2021: Results posted and viewable on ClinicalTrials.gov for NCT01644890 2019: Zero new trials One trial completed |
|
Docetaxel‐PM DOPNP201 (Samyang Biopharmaceuticals) |
Micelle | Docetaxel | Head and neck cancer and advanced solid tumors |
2016: NCT02639858 (Ph II): Recruiting (Unknown as of 2021) NCT02274610 (Ph I): Completed 2019 additions: NCT03585673 (Ph II): Recruiting (Unknown as of 2021) 2021 additions: NCT04066335: Recruiting |
2021: One new trial Two trials updated to unknown 2019: One new trial One trial updated to completed |
|
CriPec (Cristal Therapeutics) |
Micelle | Docetaxel | Solid tumors, ovarian cancer |
2016: NCT02442531 (Ph I): Completed 2019 additions: NCT03712423 (Ph I): Recruiting (Completed as of 2021) NCT03742713 (Ph II): Recruiting (Completed as of 2021) |
2021: Two trials updated to completed 2019: Two new trials One trial updated to completed |
|
CRLX101 (Cerulean) |
Cyclodextrin based nanoparticle | Camptothecin | Ovarian, renal cell, small cell lung, or rectal cancers |
2016: NCT02187302 (Ph II): Completed NCT02010567 (Ph I/II): Active, not recruiting (Terminated as of 2021 due to funding partner's request) NCT02389985 (Ph I): Terminated (Company decision) NCT01803269 (Ph II): Terminated (Due to lack of activity and slow accrual) NCT01652079 (Ph II): Completed 2019 additions: NCT02769962 (Ph I): Recruiting NCT03531827 (Ph II): Recruiting NCT02648711(Ph I): Terminated (Company decision) NCT01380769 (Ph II): Completed NCT01612546 (Ph II): Completed NCT00333502 (Ph II): Completed NCT01625936 (Ph I): Completed NCT00753740 (Ph II): Withdrawn (Poor trial recruitment) NCT00163319 (Ph III): Completed |
2021: One trial updated to terminated Results posted and viewable on ClinicalTrials.gov for NCT01380769, NCT01803269, and NCT02010567 2019: Nine new trials (one terminated, one withdrawn, five completed) Two trials updated to completed Two trials updated to terminated |
|
CRLX301 (Cerulean) |
Cyclodextrin based nanoparticle | Docetaxel | Dose escalation study in advanced solid tumors |
2016: NCT02380677 (Ph I/II): Terminated (Company decision) |
2021: Results posted and viewable on ClinicalTrials.gov for NCT02380677 2019: Zero new trials One trial updated to terminated |
|
MTL‐CEBPA (Mina Alpha) |
SMARTICLES (amphoteric liposomes) | Double stranded RNA | Advanced liver cancer and solid tumors |
2019: NCT02716012 (Ph I): Recruiting (Active as of 2021) 2021 additions: NCT04105335 (Ph I): Recruiting NCT04710641 (Ph II): Not yet recruiting |
2021: Two new trials One trial updated to active |
|
Imx‐110 (Immix Biopharma Australia) |
Micelle | Stat3/NF‐kB/poly‐tyrosine kinase inhibitor and low‐dose doxorubicin | Advanced solid tumors |
2019: NCT03382340 (Ph I/II): Recruiting |
2021: No updates |
|
IT‐141 (Intezyne Technologies) |
Micelle | SN‐38 | Advanced cancer |
2019: NCT03096340 (Ph I): Recruiting (terminated as of 2021) |
2021: One trial updated to terminated |
| Polymeric and micelles (other) | |||||
|
RadProtect (Original BioMedicals) |
PEG, iron, and amifostine micelle Transferrin‐mediated chelation for amifostine release |
Amifostine | Dose escalation and safety for acute radiation syndrome |
2016: NCT02587442 (Ph I): Unknown |
2021: No updates 2019: Zero new trials |
| Albumin‐bound (cancer) | |||||
|
ABI‐009 (Aadi with Celgene) |
Albumin‐bound drug nanoparticle | Rapamycin | Bladder cancer, PEComa, or pulmonary arterial hypertension |
2016: NCT02009332 (Ph I/II): Recruiting (Completed as of 2021) NCT02587325 (Ph I): Recruiting NCT02494570 (Ph II): Active not recruiting 2019 additions: NCT03747328 (Ph II): Not yet recruiting NCT03657420 (Ph I): Not yet recruiting (Withdrawn as of 2021) NCT03670030 (Ph II): Recruiting (Completed as of 2021) NCT03646240 (Ph I): Recruiting NCT03190174 (Ph I): Recruiting NCT00635284 (Ph I): Completed NCT03817515: Expanded Access Status: Available NCT03439462 (Ph II): Recruiting NCT03463265 (Ph II): Recruiting NCT03660930 (Ph I): Recruiting NCT02975882 (Ph I): Recruiting NCT02646319 (Ph I): Completed |
2021: Two trials updated to completed 2019: 12 new trials (two completed) |
|
ABI‐011 (NantBioScience) |
Albumin‐bound drug nanoparticle | Thiocolchicine analog (IDN 5405) | Solid tumors or lymphomas |
2016: NCT02582827 (Ph I): Recruiting (Withdrawn as of 2021 due to enrollment not initiated) |
2021: One trial updated to withdrawn 2019: Zero new trials |
| Inorganic (cancer) | |||||
|
AuroLase (Nanospectra Biosciences) |
PEG‐coated silica‐gold nanoshells | Thermal ablation from near infrared light stimulation | Thermal ablation of solid primary and/or metastatic lung tumors |
2016: NCT01679470: Terminated 2019 additions: NCT02680535: Recruiting (Completed as of 2021) NCT00848042: Completed 2021 additions: NCT04240639: Recruiting |
2021: One new trial One trial updated to completed Results posted and viewable on ClinicalTrials.gov for NCT00848042 2019: Two new trials One trial updated to terminated |
| Cornell Dots | Silica nanoparticles with a NIR fluorophore, PEG coating, and a 124I radiolabeled cRGDY targeting peptide | NIR fluorophore | Imaging of melanoma and malignant brain tumors |
2016: NCT01266096: Active, not recruiting 2019 additions: NCT03465618 (Ph I): Recruiting NCT02106598 (Ph II): Recruiting 2021 additions: NCT04167969 (Ph I): Recruiting |
2021: One new trial 2019: Two new trials |
| Magnablate | Iron nanoparticles | Iron | Thermal ablation for prostate cancer |
2016: NCT02033447 (Ph I): Completed |
2021: No updates 2019: Zero new trials One trial updated to completed |
|
NU‐0129 (Northwestern) |
Spherical nucleic acid platform consisting of nucleic acids arranged on the surface of a spherical gold nanoparticle | Nucleic acids | Glioblastoma |
2019: NCT03020017 (Ph I): Active, not recruiting (Completed as of 2021) |
2021: No updates |
| Imaging | |||||
|
AGuIX (National Cancer Institute, France) |
Polysiloxane gadolinium chelates based nanoparticles | Gadolinium chelates | Various cancers |
2019: NCT03308604 (Ph I): Recruiting (Unknown as of 2021) 2021 additions: NCT04881032 (Ph I/II): Not yet recruiting NCT03818386 (Ph II): Recruiting NCT04899908 (Ph II): Not yet recruiting NCT04094077 (Ph II): Active, not recruiting NCT04789486 (Ph I/II): Not yet recruiting NCT04784221 (Ph II): Not yet recruiting |
2021: Six new trials One trial updated to unknown status |
|
ONM‐100 (OncoNano Medicine) |
Micelle covalently conjugated to indocyanine green | Indocyanine green | Intraoperative detection of cancer |
2019: NCT03735680 (Ph II): Not yet recruiting (Recruiting as of 2021) |
2021: One trial updated to recruiting |
4. NEW NANOPARTICLE TECHNOLOGIES IN CLINICAL TRIALS
Since our 2019 article,3 >35 new nanoparticle technologies have begun clinical trials. Of these new additions, 28 are lipid‐based (25 of which are for mRNA‐based vaccines). The remaining new nanoparticle technologies are indicated for cancer treatment (two pure‐drug nanoparticles are being studied in five different clinical trials), imaging applications (three trials are investigating carbon nanoparticles for imaging lymph nodes), and non‐mRNA vaccines (three protein‐based nanoparticles are being investigated as vaccines). Table 3 summarizes these new additions.
TABLE 3.
Nanoparticle vaccines, therapies, and diagnostics which are not clinically approved and are currently active clinical trials that have appeared on the ClinicalTrial.gov database since 2019
| Name (company) | Particle type | Payload | Investigated application/indication | Current ClinicalTrials.gov identifiers (phase) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lipid‐based | ||||
|
mRNA‐1283 (Moderna) |
Lipid nanoparticle | mRNA | COVID‐19 vaccine | NCT04813796 (Ph I): Recruiting |
|
mRNA‐1345 (Moderna) |
Lipid nanoparticle | mRNA | Respiratory syncytial virus vaccine | NCT04528719 (Ph I): Recruiting |
|
mRNA‐1647 (Moderna) |
Lipid nanoparticle | mRNA | Cytomegalovirus vaccine | NCT04232280 (Ph II): Recruiting |
|
mRNA‐1653 (Moderna) |
Lipid nanoparticle | mRNA | Combined human metapneumovirus and parainfluenza virus type 3 vaccine | NCT04144348 (Ph I): Recruiting |
|
mRNA‐2416 (Moderna) |
Lipid nanoparticle | mRNA | Advanced solid tumor malignancies | NCT03323398 (Ph I/II): Recruiting |
|
mRNA‐2752 (Moderna) |
Lipid nanoparticle | mRNA | Advanced solid tumor malignancies |
NCT03739931 (Ph I): Recruiting NCT02872025 (Ph I): Recruiting |
|
mRNA‐4157 (Moderna) |
Lipid nanoparticle | mRNA | Personalized cancer vaccine |
NCT03313778 (Ph I): Recruiting NCT03897881 (Ph II): Recruiting |
|
mRNA‐5671/V941 (Merck) |
Lipid nanoparticle | mRNA | KRAS vaccine | NCT03948763 (Ph I): Recruiting |
|
AZD8601 (AstraZeneca) |
Lipid nanoparticle | mRNA | Personalized cancer vaccine |
NCT03313778 (Ph I): Recruiting NCT03897881 (Ph II): Recruiting |
|
MEDI1191 (MedImmune) |
Lipid nanoparticle | mRNA | Advanced solid tumors | NCT03946800 (Ph I): Recruiting |
|
DS‐5670a (Daiichi Sankyo) |
Lipid nanoparticle | mRNA | COVID‐19 Vaccine | NCT04821674 (Ph I/II): Recruiting |
|
BNT111 (BioNTech) |
Size‐ and charge‐based RNA‐lipoplex nanoparticles for targeting dendritic cells | RNA that elicits immune response against four antigens | Metastatic melanoma vaccine | NCT04526899 (Ph II): Recruiting |
|
BNT112 (BioNTech) |
Size‐ and charge‐based RNA‐lipoplex nanoparticles for targeting dendritic cells | RNA that enables expression of five antigens | Prostate cancer vaccine | NCT04382898 (Ph I/II): Recruiting |
|
BNT113 (BioNTech) |
Size‐ and charge‐based RNA‐lipoplex nanoparticles for targeting dendritic cells | RNA that elicits immune response against oncoproteins E6 and E7 | Head and neck cancer vaccine | NCT04534205 (Ph II): Recruiting |
|
BNT115 (BioNTech) |
mRNA‐lipoplex nanoparticles | mRNA that increases tumor associated antigen expression | Ovarian cancer | NCT04163094 (Ph I): Recruiting |
|
BNT122/RO7198457 (BioNTech and Genentech) |
Size‐ and charge‐based RNA‐lipoplex nanoparticles for targeting dendritic cells | RNA that encodes neoantigens | Colorectal cancer, melanoma, lung cancer, bladder cancer |
NCT04486378 (Ph II): Recruiting NCT03815058 (Ph II): Recruiting NCT03289962 (Ph I): Recruiting |
|
BNT141 (BioNTech) |
Liver‐targeting lipid nanoparticle | mRNA that enables systemic production of IgG antibodies | Solid tumors | NCT04710043 (Ph I): Not yet recruiting |
|
BNT151 (BioNTech) |
Liver‐targeting lipid nanoparticle | mRNA that enables systemic production of IL‐2 | Solid tumors | NCT04455620 (Ph I/II): Recruiting |
|
BNT152 + BNT153 (BioNTech) |
Liver‐targeting lipid nanoparticle | mRNA that enables systemic production of IL‐7 and IL‐2 | Multiple solid tumors | NCT04710043 (Ph I): Not yet recruiting |
|
CLDN6 RNA‐LPX (BioNTech) |
Size‐ and charge‐based RNA‐lipoplex nanoparticles for targeting dendritic cells | RNA that encodes a receptor against CLDN6 | Solid tumor | NCT04503278 (Ph I/II): Recruiting |
|
CVnCoV (CureVac) |
Lipid nanoparticle | mRNA | COVID‐19 vaccine |
NCT04860258 (Ph III): Recruiting NCT04838847 (Ph III): Recruiting NCT04674189 (Ph III): Recruiting NCT04652102 (Ph II/III): Active, not recruiting NCT04515147 (Ph II): Active, not recruiting NCT04449276 (Ph I): Active, not recruiting NCT04848467 (Ph III): Not yet recruiting |
|
CV7202 (CureVac) |
Lipid nanoparticle | mRNA encoding rabies virus glycoprotein | Rabies vaccine | NCT03713086 (Ph I): Active, not recruiting |
|
ARCT‐021/LUNAR‐COV19 (Arcturus) |
Lipid‐enabled and unlocked nucleomonomer agent mRNA (LUNAR®) | mRNA | COVID‐19 vaccine |
NCT04728347 (Ph II): Recruiting NCT04668339 (Ph II): Active, not recruiting NCT04480957 (Ph I/II): Recruiting |
|
ARCT‐810/LUNAR‐OTC (Arcturus) |
Lipid‐enabled and unlocked nucleomonomer agent mRNA (LUNAR®) | mRNA that enables synthesis of ornithine transcarbamylase enzyme | Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency | NCT04442347 (Ph I): Recruiting |
|
BP1002 (Bio‐Path Holdings) |
Liposome | Antisense designed to inhibit protein synthesis of Bcl‐2 | Advanced lymphoid malignancies | NCT04072458 (Ph I): Recruiting |
| SpFN_1B‐06‐PL + ALFQ (U.S. Army Medical Research and Development Command) | Army liposomal formulation (adjuvant) | Spike‐ferritin‐nanoparticle (vaccine) | COVID‐19 Vaccine | NCT04784767 (Ph I): Recruiting |
|
HDT‐301 (SENAI CIMATEC) |
Lipid‐Inorganic Nanoparticle (LION™); 15‐nm superparamagnetic iron oxide | repRNA | COVID‐19 Vaccine (repRNA) | NCT04844268: (Ph I): Not yet recruiting |
|
NTLA‐2001 (Intellia Therapeutics) |
Lipid nanoparticles | CRISPR/Cas9 for knockout edit to reduce transthyretin | Transthyretin amyloidosis | NCT04601051 (Ph I): Recruiting |
| Pure drug | ||||
|
NanoDoce® (NanOlogy) |
Large surface area microparticles (nanoparticulates) | Docetaxel | Urothelial carcinoma |
NCT03636256 (Ph I/II): Active, not yet recruiting NCT04060628: Available |
|
NanoPac® (NanOlogy) |
Large surface area microparticles (nanoparticulates) | Paclitaxel | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma, lung cancer |
NCT04314895 (Ph II): Recruiting NCT03077685 (Ph II): Recruiting NCT03756311: Available |
| Polymeric | ||||
|
PRECIOUS‐01 (Radboud University) |
Poly(lactic‐co‐glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticle | Threitolceramide‐6 and the New York Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma‐1 cancer‐testis antigen peptides | New York Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma‐1 positive cancers | NCT04751786 (Ph I): Recruiting |
| Protein‐based | ||||
|
GBP510 (SK Bioscience Co.) |
Self‐assembling protein nanoparticle immunogens | Various immunogens | COVID‐19 vaccine |
NCT04742738 (Ph I/II): Recruiting NCT04750343 (Ph I/II): Recruiting |
|
NanoFlu (Novavax) |
Recombinant hemagglutinin protein nanoparticle with saponin‐based Matrix‐M adjuvant | Recombinant hemagglutinin protein | Influenza vaccine | NCT04120194 (Ph III): Active, not recruiting |
|
NVX‐CoV2373 SARS‐CoV‐2 rS/Matrix‐M1 adjuvant (Novavax) |
Recombinant spike protein nanoparticle with saponin‐based Matrix‐M1 adjuvant | Recombinant spike protein | COVID‐19 vaccine |
NCT04611802 (Ph III): Recruiting NCT04368988 (Ph I/II): Active, not recruiting NCT04533399 (Ph II): Recruiting NCT04583995 (Ph III): Recruiting |
| Inorganic | ||||
|
SPIONS (Second Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University) |
Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) with spinning magnetic field | Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles | Osteosarcoma | NCT04316091 (Ph I): Not yet recruiting |
|
EO2002 (Emmecell) |
Magnetic nanoparticles with cultured human corneal endothelial cells | Cultured human corneal endothelial cells | Corneal edema | NCT04894110 (Ph I): Recruiting |
|
Carbon nanoparticles (YE Yingjiang) |
Carbon nanoparticles | Carbon nanoparticle | Lymph node tracer in rectal cancer | NCT03550001: Not yet recruiting |
|
Carbon nanoparticles (The First Affiliated Hospital with Nanjing Medical University) |
Carbon nanoparticles | Carbon nanoparticle | Lymph node tracer in breast cancer | NCT04482803: Recruiting |
|
Carbon nanoparticles (LI XIN‐XIANG) |
Carbon nanoparticles | Carbon nanoparticle | Lymph node tracer in colorectal cancer | NCT04759820 (Ph II/III): Recruiting |
Note: Trials are grouped by particle type.
5. CONCLUSION
The transformative role of lipid nanoparticles as mRNA delivery vehicles for combating COVID‐19 and their tremendous global impact during 2020 and 2021 has ushered in an unprecedented period for nanoparticle therapeutics. To date, >30 nanoparticles have been used in various clinical applications (Table 1) and >20 of these continue to be developed, with chronologically increasing activity in clinical trials (Figure 3 and Table S1). Of the 60 unapproved nanoparticle technologies currently being investigated in clinical trials, >100 active trials exist with >40 being added in this update alone (Table 2). Finally, since our previous update in 2019,3 there has been a massive surge in clinical introduction of new nanoparticle technologies, dominated by lipid nanoparticles for mRNA delivery; over 35 new nanoparticle technologies have entered clinical trials since 2019 (Table 3). Considering these recent updates and the global impact of nanoparticles in the clinic, especially as it relates to combating COVID‐19, the field of nanoparticle drug delivery is entering a new phase, wherein their development,19, 20 manufacturing,21, 22 and clinical utility23 is just beginning to scratch the surface.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Aaron Anselmo: Conceptualization; data curation; formal analysis; supervision; writing ‐ original draft; writing‐review & editing. Samir Mitragotri: Conceptualization; formal analysis; supervision; writing ‐ original draft; writing‐review & editing.
Supporting information
Appendix S1: Supporting information
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Samir Mitragotri acknowledges support from John A. Paulson School of Engineering & Applied Sciences and National Institutes of Health (1R01HL143806‐01).
Anselmo AC, Mitragotri S. Nanoparticles in the clinic: An update post COVID‐19 vaccines. Bioeng Transl Med. 2021;6(3):e10246. 10.1002/btm2.10246
Funding information National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Grant/Award Number: 1R01HL143806‐01; John A. Paulson School of Engineering & Applied Sciences
Contributor Information
Aaron C. Anselmo, aanselmo@email.unc.edu.
Samir Mitragotri, Email: mitragotri@seas.harvard.edu.
REFERENCES
- 1.Creech CB, Walker SC, Samuels RJ. SARS‐CoV‐2 vaccines. Jama. 2021;325(13):1318‐1320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Anselmo AC, Mitragotri S. Nanoparticles in the clinic. Bioeng Transl Med. 2016;1(1):10‐29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Anselmo AC, Mitragotri S. Nanoparticles in the clinic: an update. Bioeng Transl Med. 2019;4(3):e10143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Le TT et al. Evolution of the COVID‐19 vaccine development landscape. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020;19(10):667‐668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Liu C et al. Research and development on therapeutic agents and vaccines for COVID‐19 and related human coronavirus diseases. ACS Cent Sci. 2020;6(2):315‐331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Udugama B, Kadhiresan P, Kozlowski HN, et al. Diagnosing COVID‐19: the disease and tools for detection. ACS Nano. 2020;14(4):3822‐3835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lai CC, Shih TP, Ko WC, Tang HJ, Hsueh PR. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‐CoV‐2) and coronavirus disease‐2019 (COVID‐19): the epidemic and the challenges. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020;55(3):105924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Haynes BF. A new vaccine to battle Covid‐19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(5):470‐471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Verbeke R, Lentacker I, de Smedt SC, Dewitte H. The dawn of mRNA vaccines: the COVID‐19 case. J Control Release. 2021;333:511‐520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Milane L, Amiji M. Clinical approval of nanotechnology‐based SARS‐CoV‐2 mRNA vaccines: impact on translational nanomedicine. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2021;11(4):1309‐1315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jackson LA, Anderson EJ, Rouphael NG, et al. An mRNA vaccine against SARS‐CoV‐2—preliminary report. New Engl J Med. 2020;383:1920‐1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Baden LR, el Sahly HM, Essink B, et al. Efficacy and safety of the mRNA‐1273 SARS‐CoV‐2 vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(5):403‐416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Walsh EE, Frenck RW Jr, Falsey AR, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of two RNA‐based Covid‐19 vaccine candidates. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(25):2439‐2450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Polack FP, Thomas SJ, Kitchin N, et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid‐19 vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(27):2603‐2615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Corbett KS, Edwards DK, Leist SR, et al. SARS‐CoV‐2 mRNA vaccine design enabled by prototype pathogen preparedness. Nature. 2020;586(7830):567‐571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Let's talk about lipid nanoparticles. Nat Rev Mater. 2021;6(2):99‐99. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Reichmuth AM, Oberli MA, Jaklenec A, Langer R, Blankschtein D. mRNA vaccine delivery using lipid nanoparticles. Ther Deliv. 2016;7(5):319‐334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Baraniuk C. How to vaccinate the world against Covid‐19. BMJ. 2021;372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mitchell MJ, Billingsley MM, Haley RM, Wechsler ME, Peppas NA, Langer R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021;20(2):101‐124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zhang Y, Sun C, Wang C, Jankovic KE, Dong Y. Lipids and lipid derivatives for RNA delivery. Chem Rev. 2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Colombo S, Beck‐Broichsitter M, Bøtker JP, Malmsten M, Rantanen J, Bohr A. Transforming nanomedicine manufacturing toward quality by design and microfluidics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018;128:115‐131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Stavis SM, Fagan JA, Stopa M, Liddle JA. Nanoparticle manufacturing—heterogeneity through processes to products. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2018;1(9):4358‐4385. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gillmore JD, Gane E, Taubel J, et al. CRISPR‐Cas9 in vivo gene editing for transthyretin amyloidosis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:493‐502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Appendix S1: Supporting information


