Two crystallographically independent molecules are present in the asymmetric unit. O—H⋯O, N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds form rings and chains and π–π stacks further connect molecules in the crystal.
Keywords: crystal structure, 9H-carbazole, π–π stacks, N—H⋯O, O—H⋯O, C—H⋯O hydrogen bonding
Abstract
Two crystallographically independent molecules are present in the asymmetric unit of the title compound, C14H11NO2, with virtually identical geometries. The carbazole units are planar. The hydroxy group at position 1, carbaldehyde group at position 2, and methyl group at position 8 (with the exception of two H atoms) are coplanar with the attached benzene rings. The dihedral angle between the two benzene rings is 2.20 (9)° in molecule A and 2.01 (9)° in molecule B. The pyrrole ring makes dihedral angles of 0.82 (10) and 1.40 (10)° [0.84 (10) and 1.18 (10)° in molecule B] with the (–CH3)-substituted and (–OH and –CHO) substituted benzene rings, respectively. The molecular structure is stabilized by the intramolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, while the crystal structure features N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. A range of π–π contacts further stabilizes the crystal structure.
Chemical context
Nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds are key building blocks used to develop chemicals of biological and medicinal interest. Among nitrogen heterocycles, carbazole alkaloids represent an important class of natural products. The Indian medicinal plant Murraya koenigii spreng (Rutaceae) is a rich source of carbazole alkaloids (Knölker & Reddy, 2002 ▸), and a number of these natural products with novel structures and useful biological activities have been isolated from this plant over the past decades. The increase of isolable natural products as well as the pharmacological action of these carbazole derivatives has generated synthetic interest; consequently, the synthesis of carbazoles has been an active area of study.
Based on the structural, biological and pharmacological importance of carbazole derivatives, the present investigation was to devise a viable synthetic route to these compounds using different methodologies. For our synthetic strategy, 2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazol-1-ones prepared in our laboratory were used as precursors, opening new avenues for the synthesis of highly functionalized carbazole derivatives such as 1-hydroxyimino-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazoles, 1-hydroxycarbazoles, and 1-hydroxy-2-formylcarbazoles. The functionalized carbazoles thus prepared lead to mukonine isomers, oxazolocarbazoles, girinimbine isomers, pyranocarbazoles, indoloisoflavones, indolocoumarins, indoloxanthones, benzocarbazoles, carbazolyloxypropanolamines and pyrazolo-, isoxazolo-, furo-, oxazino-, pyrimido-, pyridazino-, pyrido-, pyrazino- and indolo-carbazoles in excellent yields (Shanmugasundaram & Rajendra Prasad, 1999 ▸; Sridharan & Rajendra Prasad, 2011 ▸; Sridharan, Beagle et al., 2008 ▸ and references cited therein). Herein, we report the synthesis and crystal structure of 1-hydroxy-8-methyl-9H-carbazole-2-carbaldehyde (Fig. 1 ▸), which is a potential precursor for the synthesis of many hetero-annulated carbazoles (Gunaseelan et al., 2007 ▸).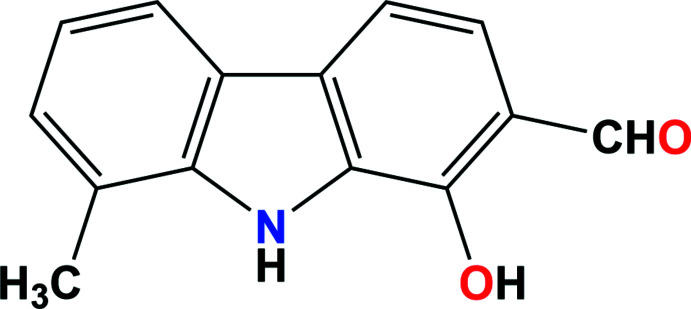
Figure 1.
The two crystallographically independent molecules with the atom-numbering scheme. Non-H atoms are shown at the 50% displacement ellipsoid probability level, H atoms are represented as small spheres.
Structural commentary
The title compound crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/c with two independent molecules (A and B, Fig. 1 ▸) in the asymmetric unit. They are superimposable and both are essentially planar. Placing inverted molecule B on molecule A gives the best fit, with the overlay of the two independent molecules shown in Fig. 2 ▸. The weighted r.m.s. fit of the 17 non-H fitted atoms is 0.034 Å, the r.m.s. bond fit is 0.003 Å and the r.m.s. angle fit is 0.383°. Both independent molecules, including the hydroxy group at position 1, carbaldehyde group at position 2, and methyl group at position 8 (with the exception of two H atoms) are near planar. The dihedral angle between the two benzene rings of the carbazole is 2.20 (9)° in molecule A and 2.01 (9)° in molecule B. The pyrrole ring makes dihedral angles of 0.82 (10) and 1.40 (10)° for molecule A and 0.84 (10) and 1.18 (10)° for molecule B with the methyl-substituted and hydroxide/carbaldehyde-substituted benzene rings, respectively. The compound exhibits intramolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bonding between the hydroxide and aldehyde groups (Table 1 ▸). Hydrogen bonds similar to the O1—H1D⋯O2 and O3—H3A⋯O4 bonds observed in this structure, forming S(6) ring motifs, have previously been observed (Bernstein et al., 1995 ▸).
Figure 2.
Least-squares overlay of the two independent molecules (inverted molecule B on molecule A). Fit rotation angle is −172.76°, r.m.s. fit = 0.087 Å.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C14—H14⋯O3i | 0.93 | 2.50 | 3.254 (2) | 138 |
| N1—H1⋯O4ii | 0.87 (2) | 2.00 (2) | 2.862 (2) | 174 (2) |
| O1—H1D⋯O2 | 0.94 (3) | 1.74 (3) | 2.602 (2) | 151 (3) |
| N2—H2⋯O2iii | 0.91 (2) | 1.97 (2) | 2.879 (2) | 173 (2) |
| O3—H3A⋯O4 | 0.90 (3) | 1.78 (3) | 2.595 (2) | 150 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y-1, z; (ii) x, -y+{\script{1\over 2}}, z+{\script{1\over 2}}; (iii) x, y+1, z.
Supramolecular features
In the crystal, molecules are connected into chains parallel to the c axis by intermolecular N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸, Fig. 3 ▸). Both crystallographically independent molecules are arranged in similar N1—H1⋯O4(x,  − y,
− y,  + z) and N2—H2⋯O2(x, 1 + y, z) hydrogen bonds. A C14—H14⋯O3(x, −1 + y, z) hydrogen bond is also present. A range of π–π contacts is also observed (Fig. 4 ▸). The distances between ring centroids are Cg1⋯Cg2(x, −1 + y, z) = 3.4604 (13) Å, Cg1⋯Cg3 (x, 1 + y, z) = 3.4896 (13) Å and Cg7⋯Cg9 (x, 1 + y, z) = 3.6279 (13) Å, where Cg1, Cg2, Cg3, Cg7 and Cg9 are the centroids of the N1/C7/C6/C10/C9, C2–C7, C8–C13, N2/C21/C20/C24/C23 and C22–C27 rings, respectively.
+ z) and N2—H2⋯O2(x, 1 + y, z) hydrogen bonds. A C14—H14⋯O3(x, −1 + y, z) hydrogen bond is also present. A range of π–π contacts is also observed (Fig. 4 ▸). The distances between ring centroids are Cg1⋯Cg2(x, −1 + y, z) = 3.4604 (13) Å, Cg1⋯Cg3 (x, 1 + y, z) = 3.4896 (13) Å and Cg7⋯Cg9 (x, 1 + y, z) = 3.6279 (13) Å, where Cg1, Cg2, Cg3, Cg7 and Cg9 are the centroids of the N1/C7/C6/C10/C9, C2–C7, C8–C13, N2/C21/C20/C24/C23 and C22–C27 rings, respectively.
Figure 3.
Perspective partial packing view of the title compound, viewed along the b axis, showing the hydrogen-bonding interactions. Black dashed lines indicate the N—H⋯O, O—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Figure 4.
Straw-style packing view of the title compound, viewed down the b axis, showing slipped π–π stacking interactions. Centroids are indicated by green spheres and contacts between centroids by black dotted lines.
Database survey
A search in the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, Version 5.42, update May 2021; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) for the structure 1-hydroxy-8-methyl-9H-carbazole-2-carbaldehyde gave two hits, viz. 2,2,10-trimethyl-2,3-dihydropyrano(2,3-a)carbazol-4(11H)-one (CSD refcode: BOGTOH; Sridharan, Prasad et al., 2008 ▸) and 1-(1-hydroxy-8-methyl-9H-carbazol-2-yl)ethanone (CSD refcode: WACYEG; Archana et al., 2010 ▸). A search for the structure of 9H-carbazole-1-ol gave 69 hits. 1-Hydroxy-3-methyl-9H-carbazole-2-carbaldehyde, C14H11NO2, (CSD refcode: NIFCUB; Gunaseelan et al., 2007 ▸) has the most similar structure to that of the title compound, with a 3-methyl rather than an 8-methyl group. The structure of NIFCUB is similarly stabilized by inter- and intramolecular N—H⋯O and O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Synthesis and crystallization
30% Sodium hydride in mineral oil (2.4 g) was washed with dry benzene and taken into a round-bottom flask containing dry benzene (100 ml). The flask was kept in an ice bath under stirring. Ethyl formate (8 ml) was added dropwise to the solution over a period of 10 minutes. Then 8-methyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazol-1-one (1.6 g, 0.008 mol) in dry benzene (25 ml) was added slowly and the reaction mixture was allowed to stir for another 36 h. The reaction was monitored by TLC. After completion of the reaction, benzene was removed in vacuo and the contents in the flask were transferred to a beaker containing water. It was neutralized with dilute HCl, filtered, washed with water and dried to get crude 1-hydroxy-8-methyl-9H-carbazole-2-carbaldehyde. It was purified by column chromatography over silica using petroleum ether:ethyl acetate (95:5) as eluant. The brown pure product obtained was recrystallized using glacial acetic acid (needle-shaped crystals, yield 0.965 g, 55%), m.p. 414 K (Fig. 5 ▸).
Figure 5.
Synthesis of the title compound.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. The indole NH hydrogen atoms, H1 and H2 and the hydroxyl OH hydrogen atoms H1D and H3A were located in a difference-Fourier map and freely refined. The remaining hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions with C—H bond distances of 0.93 Å (aromatic H), or 0.96 Å (methyl H) and were refined with anisotropic displacement parameters 1.2 and 1.5 times that of the parent carbon atoms.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C14H11NO2 |
| M r | 225.24 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 296 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 28.290 (5), 3.9052 (7), 20.264 (3) |
| β (°) | 105.817 (2) |
| V (Å3) | 2154.0 (6) |
| Z | 8 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.09 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.75 × 0.19 × 0.10 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker SMART APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005 ▸) |
| Tmin, Tmax | 0.830, 0.991 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 19760, 5344, 4453 |
| R int | 0.034 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.667 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.055, 0.146, 1.18 |
| No. of reflections | 5344 |
| No. of parameters | 325 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.31, −0.24 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021007210/yy2001sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021007210/yy2001Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021007210/yy2001Isup3.cdx
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021007210/yy2001Isup4.cml
CCDC reference: 1540679
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
AAT remembers the long time association and research collaboration with the late Professor Jerry P. Jasinski of the Department of Chemistry, Keene State College, USA. MS thanks the academic and administrative authorities of RV College of Engineering for their support and encouragement.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C14H11NO2 | F(000) = 944 |
| Mr = 225.24 | Dx = 1.389 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 28.290 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 7327 reflections |
| b = 3.9052 (7) Å | θ = 2.2–31.3° |
| c = 20.264 (3) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| β = 105.817 (2)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 2154.0 (6) Å3 | Needle, brown |
| Z = 8 | 0.75 × 0.19 × 0.10 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEXII CCD diffractometer | 5344 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 4453 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.034 |
| ω scans | θmax = 28.3°, θmin = 1.5° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005) | h = −37→37 |
| Tmin = 0.830, Tmax = 0.991 | k = −5→5 |
| 19760 measured reflections | l = −26→26 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.055 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| wR(F2) = 0.146 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.18 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0612P)2 + 1.1713P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 5344 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 325 parameters | Δρmax = 0.31 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.24 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.60695 (8) | 0.8782 (6) | 0.79934 (10) | 0.0305 (4) | |
| H1A | 0.586381 | 0.993978 | 0.822872 | 0.046* | |
| H1B | 0.636607 | 1.007032 | 0.804205 | 0.046* | |
| H1C | 0.614950 | 0.654265 | 0.818701 | 0.046* | |
| C2 | 0.58026 (7) | 0.8460 (5) | 0.72475 (10) | 0.0225 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.53306 (7) | 0.9707 (5) | 0.69748 (11) | 0.0269 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.517561 | 1.081062 | 0.726518 | 0.032* | |
| C4 | 0.50767 (7) | 0.9371 (5) | 0.62778 (11) | 0.0278 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.475869 | 1.021909 | 0.611961 | 0.033* | |
| C5 | 0.52935 (6) | 0.7800 (5) | 0.58267 (10) | 0.0239 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.512575 | 0.758554 | 0.536525 | 0.029* | |
| C6 | 0.57725 (6) | 0.6531 (5) | 0.60773 (9) | 0.0190 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.60179 (6) | 0.6862 (5) | 0.67805 (9) | 0.0187 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.69229 (6) | 0.2303 (5) | 0.61767 (9) | 0.0186 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.65285 (6) | 0.4087 (4) | 0.62986 (8) | 0.0171 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.61009 (6) | 0.4752 (5) | 0.57646 (8) | 0.0173 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.60642 (6) | 0.3678 (5) | 0.50886 (9) | 0.0213 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.578573 | 0.416290 | 0.473378 | 0.026* | |
| C12 | 0.64511 (7) | 0.1896 (5) | 0.49680 (9) | 0.0213 (4) | |
| H12 | 0.643093 | 0.114554 | 0.452561 | 0.026* | |
| C13 | 0.68800 (6) | 0.1176 (5) | 0.55022 (9) | 0.0199 (4) | |
| C14 | 0.72687 (7) | −0.0821 (5) | 0.53619 (10) | 0.0230 (4) | |
| H14 | 0.722444 | −0.163999 | 0.491820 | 0.028* | |
| C15 | 0.88208 (8) | 0.8160 (5) | 0.68439 (9) | 0.0265 (4) | |
| H15A | 0.902174 | 0.905029 | 0.726989 | 0.040* | |
| H15B | 0.860603 | 0.642822 | 0.693463 | 0.040* | |
| H15C | 0.862872 | 0.997972 | 0.658394 | 0.040* | |
| C16 | 0.91438 (7) | 0.6628 (5) | 0.64413 (9) | 0.0214 (4) | |
| C17 | 0.96492 (7) | 0.6431 (5) | 0.66858 (9) | 0.0256 (4) | |
| H17 | 0.979856 | 0.730010 | 0.711994 | 0.031* | |
| C18 | 0.99471 (7) | 0.4977 (5) | 0.63077 (10) | 0.0270 (4) | |
| H18 | 1.028583 | 0.491116 | 0.649516 | 0.032* | |
| C19 | 0.97440 (7) | 0.3645 (5) | 0.56619 (9) | 0.0232 (4) | |
| H19 | 0.994149 | 0.267196 | 0.541288 | 0.028* | |
| C20 | 0.92328 (6) | 0.3795 (5) | 0.53906 (9) | 0.0187 (3) | |
| C21 | 0.89409 (6) | 0.5292 (5) | 0.57814 (8) | 0.0179 (3) | |
| C22 | 0.80092 (6) | 0.2763 (5) | 0.42718 (9) | 0.0183 (3) | |
| C23 | 0.84263 (6) | 0.3534 (4) | 0.47993 (8) | 0.0176 (3) | |
| C24 | 0.89000 (6) | 0.2655 (5) | 0.47573 (8) | 0.0180 (3) | |
| C25 | 0.89635 (7) | 0.0985 (5) | 0.41705 (9) | 0.0218 (4) | |
| H25 | 0.927599 | 0.043979 | 0.413640 | 0.026* | |
| C26 | 0.85547 (7) | 0.0181 (5) | 0.36514 (9) | 0.0232 (4) | |
| H26 | 0.859196 | −0.093655 | 0.326343 | 0.028* | |
| C27 | 0.80755 (7) | 0.1021 (5) | 0.36941 (9) | 0.0206 (4) | |
| C28 | 0.76490 (7) | −0.0010 (5) | 0.31623 (9) | 0.0254 (4) | |
| H28 | 0.769894 | −0.116522 | 0.278565 | 0.030* | |
| N1 | 0.64768 (5) | 0.5391 (4) | 0.69071 (8) | 0.0191 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.84527 (5) | 0.5107 (4) | 0.54173 (7) | 0.0187 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.73268 (5) | 0.1687 (4) | 0.67024 (6) | 0.0238 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.76604 (5) | −0.1520 (4) | 0.57967 (7) | 0.0276 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.75629 (5) | 0.3697 (4) | 0.43310 (7) | 0.0230 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.72203 (5) | 0.0536 (4) | 0.31724 (7) | 0.0298 (3) | |
| H1 | 0.6700 (9) | 0.527 (7) | 0.7295 (13) | 0.033 (6)* | |
| H1D | 0.7530 (11) | 0.035 (9) | 0.6508 (16) | 0.065 (9)* | |
| H2 | 0.8187 (8) | 0.600 (6) | 0.5531 (12) | 0.031 (6)* | |
| H3A | 0.7344 (11) | 0.288 (9) | 0.3952 (16) | 0.063 (9)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0445 (12) | 0.0266 (10) | 0.0261 (10) | 0.0013 (9) | 0.0192 (9) | −0.0015 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0284 (9) | 0.0157 (9) | 0.0283 (9) | −0.0017 (7) | 0.0160 (8) | 0.0015 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0298 (10) | 0.0167 (9) | 0.0411 (11) | 0.0003 (7) | 0.0213 (9) | 0.0011 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0212 (9) | 0.0196 (9) | 0.0443 (12) | 0.0017 (7) | 0.0120 (8) | 0.0058 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0203 (8) | 0.0193 (9) | 0.0310 (10) | −0.0008 (7) | 0.0053 (7) | 0.0067 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0191 (8) | 0.0169 (8) | 0.0218 (8) | −0.0018 (6) | 0.0068 (6) | 0.0048 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0208 (8) | 0.0157 (8) | 0.0219 (8) | 0.0002 (6) | 0.0096 (7) | 0.0042 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0188 (8) | 0.0193 (9) | 0.0182 (8) | −0.0015 (7) | 0.0059 (6) | 0.0015 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0181 (7) | 0.0172 (8) | 0.0170 (8) | −0.0028 (6) | 0.0066 (6) | 0.0026 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0182 (7) | 0.0172 (8) | 0.0173 (8) | −0.0025 (6) | 0.0061 (6) | 0.0034 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0227 (8) | 0.0226 (9) | 0.0177 (8) | −0.0034 (7) | 0.0041 (6) | 0.0027 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0268 (9) | 0.0218 (9) | 0.0158 (8) | −0.0064 (7) | 0.0067 (7) | −0.0003 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0215 (8) | 0.0203 (9) | 0.0199 (8) | −0.0039 (7) | 0.0089 (6) | −0.0004 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0276 (9) | 0.0214 (9) | 0.0238 (9) | −0.0023 (7) | 0.0133 (7) | 0.0004 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0382 (10) | 0.0237 (10) | 0.0179 (8) | −0.0029 (8) | 0.0083 (7) | −0.0025 (7) |
| C16 | 0.0300 (9) | 0.0177 (9) | 0.0160 (8) | −0.0027 (7) | 0.0053 (7) | 0.0030 (7) |
| C17 | 0.0330 (10) | 0.0216 (9) | 0.0181 (8) | −0.0055 (8) | −0.0001 (7) | 0.0028 (7) |
| C18 | 0.0244 (9) | 0.0262 (10) | 0.0265 (9) | −0.0019 (7) | 0.0005 (7) | 0.0064 (8) |
| C19 | 0.0226 (8) | 0.0237 (10) | 0.0232 (9) | 0.0031 (7) | 0.0062 (7) | 0.0061 (7) |
| C20 | 0.0209 (8) | 0.0171 (8) | 0.0188 (8) | 0.0008 (7) | 0.0064 (6) | 0.0039 (6) |
| C21 | 0.0206 (8) | 0.0165 (8) | 0.0166 (8) | −0.0004 (6) | 0.0052 (6) | 0.0034 (6) |
| C22 | 0.0214 (8) | 0.0180 (8) | 0.0166 (8) | 0.0002 (7) | 0.0068 (6) | 0.0031 (6) |
| C23 | 0.0222 (8) | 0.0174 (8) | 0.0143 (8) | 0.0004 (7) | 0.0070 (6) | 0.0016 (6) |
| C24 | 0.0206 (8) | 0.0171 (8) | 0.0171 (8) | 0.0028 (6) | 0.0064 (6) | 0.0040 (6) |
| C25 | 0.0245 (9) | 0.0225 (9) | 0.0203 (8) | 0.0045 (7) | 0.0092 (7) | 0.0024 (7) |
| C26 | 0.0325 (10) | 0.0220 (9) | 0.0165 (8) | 0.0030 (8) | 0.0093 (7) | −0.0003 (7) |
| C27 | 0.0270 (9) | 0.0202 (9) | 0.0143 (8) | 0.0001 (7) | 0.0051 (6) | 0.0012 (7) |
| C28 | 0.0346 (10) | 0.0233 (10) | 0.0162 (8) | −0.0013 (8) | 0.0035 (7) | 0.0003 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0197 (7) | 0.0218 (8) | 0.0165 (7) | 0.0019 (6) | 0.0060 (6) | 0.0013 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0204 (7) | 0.0216 (8) | 0.0149 (7) | 0.0002 (6) | 0.0062 (5) | −0.0005 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0187 (6) | 0.0312 (8) | 0.0203 (6) | 0.0047 (5) | 0.0034 (5) | −0.0006 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0247 (7) | 0.0301 (8) | 0.0308 (7) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0123 (6) | −0.0014 (6) |
| O3 | 0.0186 (6) | 0.0318 (8) | 0.0187 (6) | −0.0013 (5) | 0.0051 (5) | −0.0013 (5) |
| O4 | 0.0278 (7) | 0.0397 (9) | 0.0193 (6) | −0.0043 (6) | 0.0019 (5) | −0.0011 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—C2 | 1.500 (3) | C15—H15B | 0.9600 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9600 | C15—H15C | 0.9600 |
| C1—H1B | 0.9600 | C16—C17 | 1.382 (3) |
| C1—H1C | 0.9600 | C16—C21 | 1.404 (2) |
| C2—C3 | 1.387 (3) | C17—C18 | 1.404 (3) |
| C2—C7 | 1.404 (2) | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.405 (3) | C18—C19 | 1.380 (3) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.376 (3) | C19—C20 | 1.401 (2) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C19—H19 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.402 (2) | C20—C21 | 1.417 (2) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C20—C24 | 1.440 (2) |
| C6—C7 | 1.411 (2) | C21—N2 | 1.379 (2) |
| C6—C10 | 1.438 (2) | C22—O3 | 1.350 (2) |
| C7—N1 | 1.378 (2) | C22—C23 | 1.392 (2) |
| C8—O1 | 1.354 (2) | C22—C27 | 1.410 (2) |
| C8—C9 | 1.393 (2) | C23—N2 | 1.379 (2) |
| C8—C13 | 1.409 (2) | C23—C24 | 1.408 (2) |
| C9—N1 | 1.378 (2) | C24—C25 | 1.410 (2) |
| C9—C10 | 1.410 (2) | C25—C26 | 1.371 (3) |
| C10—C11 | 1.409 (2) | C25—H25 | 0.9300 |
| C11—C12 | 1.374 (3) | C26—C27 | 1.420 (3) |
| C11—H11 | 0.9300 | C26—H26 | 0.9300 |
| C12—C13 | 1.417 (2) | C27—C28 | 1.439 (2) |
| C12—H12 | 0.9300 | C28—O4 | 1.237 (2) |
| C13—C14 | 1.438 (3) | C28—H28 | 0.9300 |
| C14—O2 | 1.244 (2) | N1—H1 | 0.87 (2) |
| C14—H14 | 0.9300 | N2—H2 | 0.91 (2) |
| C15—C16 | 1.505 (3) | O1—H1D | 0.94 (3) |
| C15—H15A | 0.9600 | O3—H3A | 0.90 (3) |
| C2—C1—H1A | 109.5 | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—H1B | 109.5 | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C17—C16—C21 | 115.81 (17) |
| C2—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C17—C16—C15 | 123.33 (17) |
| H1A—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C21—C16—C15 | 120.86 (16) |
| H1B—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C16—C17—C18 | 122.89 (17) |
| C3—C2—C7 | 115.79 (17) | C16—C17—H17 | 118.6 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 122.54 (17) | C18—C17—H17 | 118.6 |
| C7—C2—C1 | 121.68 (17) | C19—C18—C17 | 120.89 (18) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 122.71 (18) | C19—C18—H18 | 119.6 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 118.6 | C17—C18—H18 | 119.6 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 118.6 | C18—C19—C20 | 118.34 (18) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.74 (17) | C18—C19—H19 | 120.8 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.6 | C20—C19—H19 | 120.8 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.6 | C19—C20—C21 | 119.64 (16) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 118.62 (18) | C19—C20—C24 | 133.72 (17) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.7 | C21—C20—C24 | 106.64 (15) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.7 | N2—C21—C16 | 128.23 (16) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 119.64 (17) | N2—C21—C20 | 109.32 (15) |
| C5—C6—C10 | 133.48 (17) | C16—C21—C20 | 122.43 (16) |
| C7—C6—C10 | 106.86 (15) | O3—C22—C23 | 119.39 (15) |
| N1—C7—C2 | 128.29 (17) | O3—C22—C27 | 122.90 (16) |
| N1—C7—C6 | 109.21 (15) | C23—C22—C27 | 117.71 (16) |
| C2—C7—C6 | 122.50 (16) | N2—C23—C22 | 128.21 (16) |
| O1—C8—C9 | 119.60 (15) | N2—C23—C24 | 110.28 (15) |
| O1—C8—C13 | 122.58 (16) | C22—C23—C24 | 121.50 (16) |
| C9—C8—C13 | 117.81 (16) | C23—C24—C25 | 120.38 (16) |
| N1—C9—C8 | 128.95 (16) | C23—C24—C20 | 105.83 (15) |
| N1—C9—C10 | 109.92 (15) | C25—C24—C20 | 133.78 (16) |
| C8—C9—C10 | 121.13 (16) | C26—C25—C24 | 118.57 (16) |
| C11—C10—C9 | 120.79 (16) | C26—C25—H25 | 120.7 |
| C11—C10—C6 | 133.37 (16) | C24—C25—H25 | 120.7 |
| C9—C10—C6 | 105.84 (15) | C25—C26—C27 | 121.34 (17) |
| C12—C11—C10 | 118.20 (16) | C25—C26—H26 | 119.3 |
| C12—C11—H11 | 120.9 | C27—C26—H26 | 119.3 |
| C10—C11—H11 | 120.9 | C22—C27—C26 | 120.48 (16) |
| C11—C12—C13 | 121.50 (16) | C22—C27—C28 | 118.85 (17) |
| C11—C12—H12 | 119.3 | C26—C27—C28 | 120.62 (17) |
| C13—C12—H12 | 119.3 | O4—C28—C27 | 124.41 (18) |
| C8—C13—C12 | 120.56 (16) | O4—C28—H28 | 117.8 |
| C8—C13—C14 | 119.52 (16) | C27—C28—H28 | 117.8 |
| C12—C13—C14 | 119.89 (16) | C9—N1—C7 | 108.16 (14) |
| O2—C14—C13 | 124.09 (17) | C9—N1—H1 | 124.4 (16) |
| O2—C14—H14 | 118.0 | C7—N1—H1 | 127.5 (16) |
| C13—C14—H14 | 118.0 | C23—N2—C21 | 107.92 (15) |
| C16—C15—H15A | 109.5 | C23—N2—H2 | 123.7 (15) |
| C16—C15—H15B | 109.5 | C21—N2—H2 | 128.2 (15) |
| H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 | C8—O1—H1D | 104.5 (18) |
| C16—C15—H15C | 109.5 | C22—O3—H3A | 105.7 (19) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | 0.8 (3) | C18—C19—C20—C21 | 0.0 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −179.15 (19) | C18—C19—C20—C24 | −178.91 (19) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.9 (3) | C17—C16—C21—N2 | 179.02 (18) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.2 (3) | C15—C16—C21—N2 | −0.9 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 0.5 (3) | C17—C16—C21—C20 | 0.7 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C10 | 178.98 (19) | C15—C16—C21—C20 | −179.26 (17) |
| C3—C2—C7—N1 | −179.66 (18) | C19—C20—C21—N2 | −179.13 (16) |
| C1—C2—C7—N1 | 0.3 (3) | C24—C20—C21—N2 | 0.0 (2) |
| C3—C2—C7—C6 | 0.0 (3) | C19—C20—C21—C16 | −0.5 (3) |
| C1—C2—C7—C6 | 179.92 (17) | C24—C20—C21—C16 | 178.64 (16) |
| C5—C6—C7—N1 | 179.06 (16) | O3—C22—C23—N2 | 2.3 (3) |
| C10—C6—C7—N1 | 0.2 (2) | C27—C22—C23—N2 | −177.78 (17) |
| C5—C6—C7—C2 | −0.6 (3) | O3—C22—C23—C24 | −179.11 (16) |
| C10—C6—C7—C2 | −179.45 (16) | C27—C22—C23—C24 | 0.8 (3) |
| O1—C8—C9—N1 | −0.6 (3) | N2—C23—C24—C25 | 179.47 (16) |
| C13—C8—C9—N1 | 178.76 (17) | C22—C23—C24—C25 | 0.6 (3) |
| O1—C8—C9—C10 | −179.52 (16) | N2—C23—C24—C20 | −0.3 (2) |
| C13—C8—C9—C10 | −0.2 (3) | C22—C23—C24—C20 | −179.20 (16) |
| N1—C9—C10—C11 | 179.77 (16) | C19—C20—C24—C23 | 179.2 (2) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −1.1 (3) | C21—C20—C24—C23 | 0.18 (19) |
| N1—C9—C10—C6 | −0.63 (19) | C19—C20—C24—C25 | −0.6 (4) |
| C8—C9—C10—C6 | 178.49 (16) | C21—C20—C24—C25 | −179.59 (19) |
| C5—C6—C10—C11 | 1.2 (4) | C23—C24—C25—C26 | −1.3 (3) |
| C7—C6—C10—C11 | 179.77 (19) | C20—C24—C25—C26 | 178.46 (19) |
| C5—C6—C10—C9 | −178.36 (19) | C24—C25—C26—C27 | 0.5 (3) |
| C7—C6—C10—C9 | 0.24 (19) | O3—C22—C27—C26 | 178.33 (17) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | 1.6 (3) | C23—C22—C27—C26 | −1.6 (3) |
| C6—C10—C11—C12 | −177.90 (19) | O3—C22—C27—C28 | −4.1 (3) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | −0.8 (3) | C23—C22—C27—C28 | 175.89 (16) |
| O1—C8—C13—C12 | −179.70 (16) | C25—C26—C27—C22 | 1.0 (3) |
| C9—C8—C13—C12 | 1.0 (3) | C25—C26—C27—C28 | −176.49 (18) |
| O1—C8—C13—C14 | 2.4 (3) | C22—C27—C28—O4 | 0.3 (3) |
| C9—C8—C13—C14 | −176.92 (16) | C26—C27—C28—O4 | 177.80 (19) |
| C11—C12—C13—C8 | −0.5 (3) | C8—C9—N1—C7 | −178.24 (18) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | 177.38 (17) | C10—C9—N1—C7 | 0.8 (2) |
| C8—C13—C14—O2 | −3.4 (3) | C2—C7—N1—C9 | 179.03 (18) |
| C12—C13—C14—O2 | 178.69 (18) | C6—C7—N1—C9 | −0.6 (2) |
| C21—C16—C17—C18 | −0.4 (3) | C22—C23—N2—C21 | 179.13 (17) |
| C15—C16—C17—C18 | 179.59 (18) | C24—C23—N2—C21 | 0.4 (2) |
| C16—C17—C18—C19 | −0.1 (3) | C16—C21—N2—C23 | −178.75 (18) |
| C17—C18—C19—C20 | 0.3 (3) | C20—C21—N2—C23 | −0.3 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C14—H14···O3i | 0.93 | 2.50 | 3.254 (2) | 138 |
| N1—H1···O4ii | 0.87 (2) | 2.00 (2) | 2.862 (2) | 174 (2) |
| O1—H1D···O2 | 0.94 (3) | 1.74 (3) | 2.602 (2) | 151 (3) |
| N2—H2···O2iii | 0.91 (2) | 1.97 (2) | 2.879 (2) | 173 (2) |
| O3—H3A···O4 | 0.90 (3) | 1.78 (3) | 2.595 (2) | 150 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y−1, z; (ii) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (iii) x, y+1, z.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by Ohio Board of Regents grant 0087210; National Science Foundation grant 0087210 to YSU.
References
- Archana, R., Prabakaran, K., Rajendra Prasad, K. J., Thiruvalluvar, A. & Butcher, R. J. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o3146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2005). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Gunaseelan, A. T., Thiruvalluvar, A., Martin, A. E. & Prasad, K. J. R. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o2682–o2683.
- Knölker, H.-J. & Reddy, K. R. (2002). Chem. Rev. 102, 4303–4427. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shanmugasundaram, K. & Rajendra Prasad, K. J. (1999). Heterocycles, 51, 9, 2163–2169.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2020). Acta Cryst. E76, 1–11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sridharan, M., Beagle, L. K., Zeller, M. & Rajendra Prasad, K. J. (2008). J. Chem. Res. pp. 572–577.
- Sridharan, M. & Rajendra Prasad, K. J. (2011). J. Chem. Res. 53–59.
- Sridharan, M., Prasad, K. J. R., Ngendahimana, A. & Zeller, M. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021007210/yy2001sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021007210/yy2001Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021007210/yy2001Isup3.cdx
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021007210/yy2001Isup4.cml
CCDC reference: 1540679
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report







