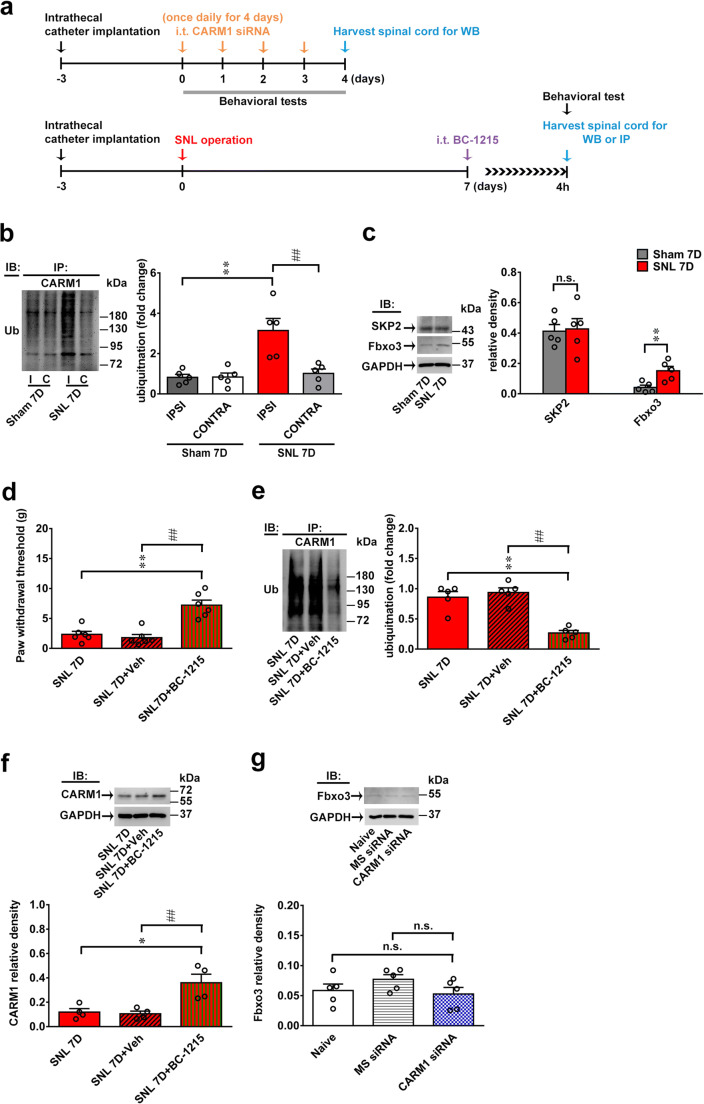
Fig. 3.
SNL induces spinal Fbxo3-dependent CARM1 ubiquitination to induce behavioral allodynia. (a) Diagram of the timeline of this experiment. (b) SNL increased CARM1 ubiquitination in the ipsilateral, not contralateral, dorsal horn at day 7 after the operation (SNL 7D). I, ipsilateral. C, contralateral. IB, immunoblotting. Sham 7D, sham operation at day 7. SNL 7D, SNL operation at day 7. **p < 0.01 versus Sham 7D IPSI. ##p < 0.01 versus SNL 7D CONTRA. Each group has 5 rats. Unpaired t tests. (c) Representative Western blot and statistical analyses (normalized to GAPDH) demonstrating SNL increased Fbxo3, not SKP2, expression in the ipsilateral dorsal horn on day 7 after operation. **p < 0.01 versus Sham 7D. Each group has 5 rats. Unpaired t tests. (d)–(f) Intrathecal BC-1215 (100 nM, 10 μL, at 4 h after injection) into SNL rats significantly increased the ipsilateral paw withdrawal threshold in accompanied with a decreased ubiquitination and increased expression of CARM1 protein in the ipsilateral dorsal horn. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, versus SNL 7D. ##p < 0.01 versus SNL 7D+Veh. Each group has 6 (d), 5 (e), or 4 (f) rats. (d) One-way ANOVA, F(2, 15) = 21.89, p < 0.0001. (e) One-way ANOVA, F(2, 12) = 24.68, p < 0.0001. (f) One-way ANOVA, F(2, 9) = 9.971, p = 0.0052. (g) Intrathecal injection of CARM1 siRNA (CARM1 siRNA; 100 ng; 10 μL; once daily for 4 days) into naïve rats did not affect the expression levels of Fbxo3 protein in the dorsal horn at day 4 after injection. Each group has 5 rats. One-way ANOVA, F(2, 12) = 1.601, p = 0.2419