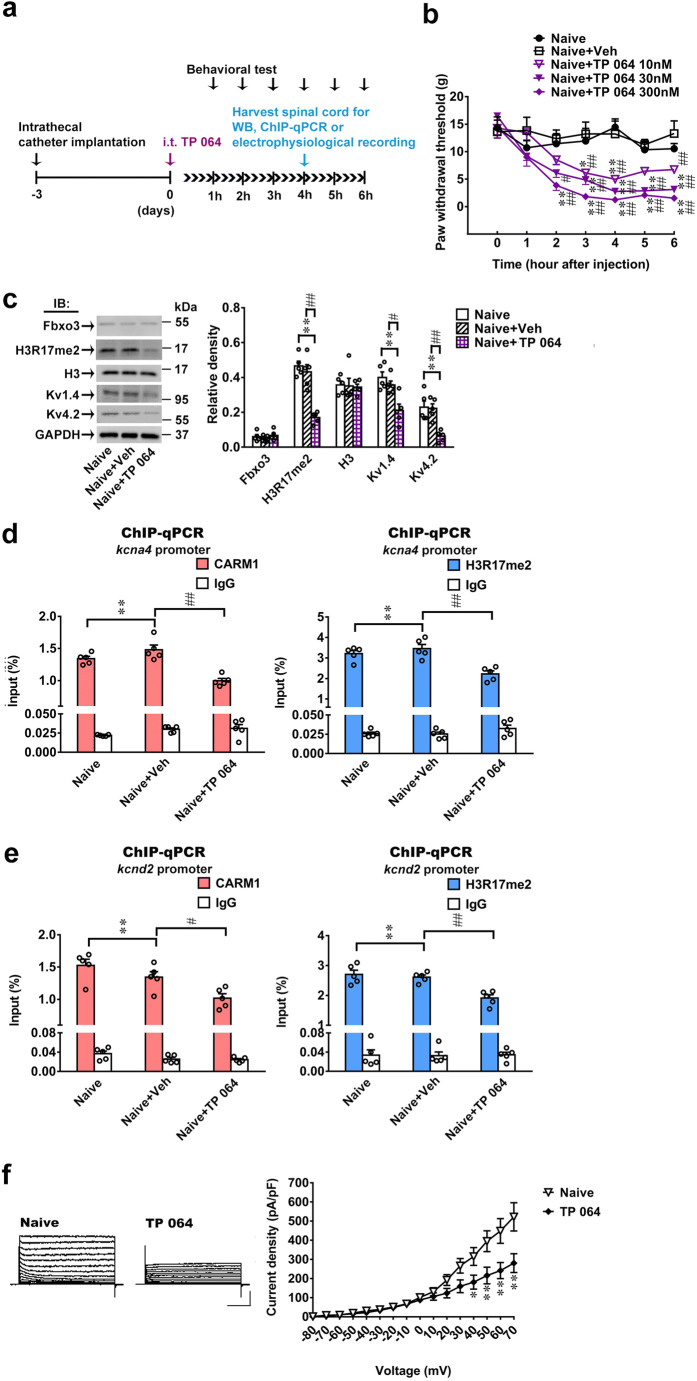
Fig. 8.
TP 064 induces allodynia by increasing spinal Fbxo3/CARM1/H3R17me2/ K+ channel signaling. (a) Diagram of the timeline of this experiment. (b) Intrathecal administration of TP 064 (10, 30, and 300 nM, 10 μL) decreased the paw withdrawal threshold of naïve rats. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus Naïve. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 versus Naïve+Veh. Each group has 6 rats. Two-way ANOVA, group, F(4, 25) = 86.28, p < 0.0001; time, F(6, 150) = 20.8, p < 0.0001; interaction, F(24, 150) = 3.014, p < 0.0001. (c) Intrathecal TP 064 (300 nM, 10 μL, at 4 h after injection) inhibited the expression levels of H3R17me2, Kv1.4 and Kv4.2, but not Fbxo3 and H3 in the dorsal horn. **p < 0.01 versus naïve. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 versus Naïve+Veh. Each group has 5 rats. Fbxo3, one-way ANOVA, F(2, 12) = 0.5578, p = 0.5866. H3R17me2, one-way ANOVA, F(2, 12) = 30.42, p < 0.0001. H3, one-way ANOVA, F(2, 12) = 0.04733, p = 0.9540. Kv1.4, one-way ANOVA, F(2, 12) = 9.952, p = 0.0028. Kv4.2, one-way ANOVA, F(2, 12) = 11.83, p = 0.0014. (d), (e) Intrathecal administration of TP 064 (300 nM, 10 μL, at 4 h after injection) significantly decreased the Kcna4 and Kcnd2 promoter fragments immunoprecipitated by CARM1 and H3R17me2-specific antibodies in the dorsal horn. **p < 0.01 versus naïve. Each group has 5 rats. (d) CARM1, one-way ANOVA, F(2, 12) = 22.47, p < 0.0001. (d) H3R17me2, one-way ANOVA, F(2, 12) = 14.52, p = 0.0006. (e) CARM1, one-way ANOVA, F(2, 12) = 9.195, p = 0.0038. (e) H3R17me2, one-way ANOVA, F(2, 12) = 15.78, p = 0.0006. (f) Representative traces of K+ currents recorded from dorsal horn neurons dissected from naïve (Naïve) and naïve with TP 064 (TP 064, 300 nM, 10 μL, at 4 h after injection) *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus Naïve. Each group has 8 rats. Two-way ANOVA, group, F(1, 14) = 5.371, p = 0.0376; time, F(15, 210) = 64.76, p < 0.0001; interaction, F(15, 210) = 6.525, p < 0.0001