Figure 2.
Polar metabolites in the post-infection lung reflect active efferocytosis and energetic depletion
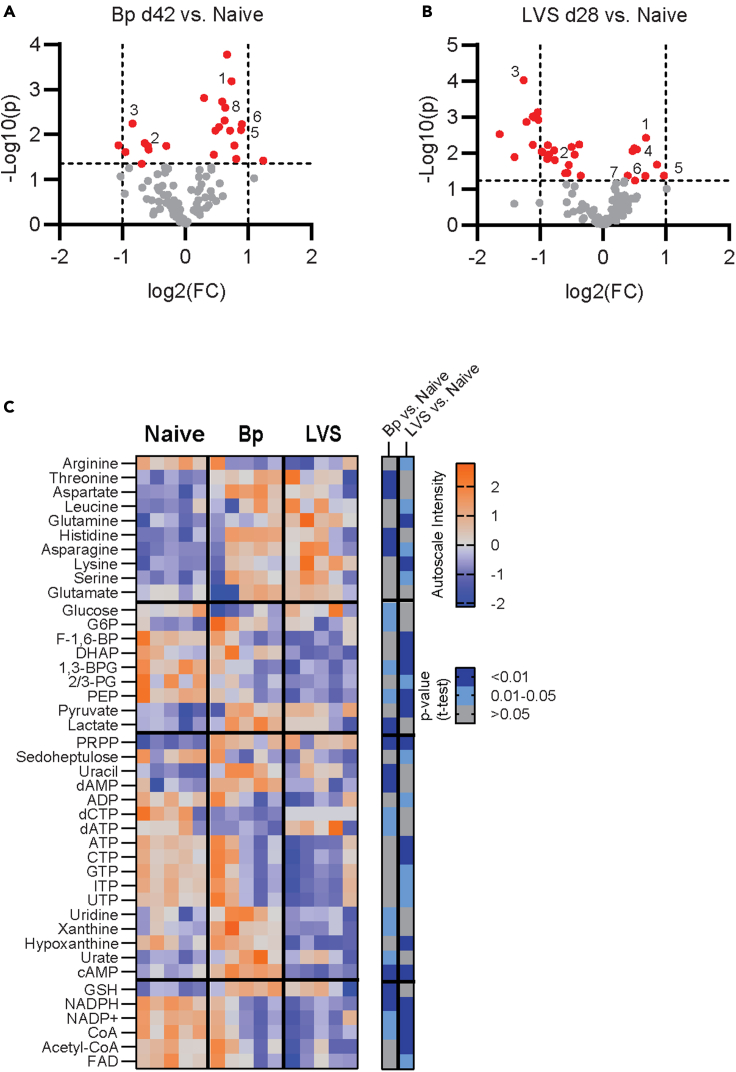
(A and B) Targeted metabolomics of experienced lungs are displayed post-infection with (A), Bordetella pertussis (Bp; day 42 post-infection) or (b), Francisella tularensis LVS (LVS; day 28 post-infection) as compared to naive animals. Features above a 10% FDR cutoff line, as calculated using Benjamini–Hochberg correction, are shown in red (Bp p = 0.044, LVS p = 0.058). Vertical lines reflect a fold change of 2 and –2. Common features of interest are number as (1) PRPP, (2) NADP+, (3) NADPH, (4) Glutamine, (5) Asparagine, (6) Uracil, (7) Glutamate, (8) Aspartate.
(C) Heatmap of the autoscaled value of metabolites of interest from each biological replicate are displayed with the accompanying p value from the binary comparison of each experienced group to naive. All heatmap features listed pass the 10% FDR cutoff for either Bp vs. naive or LVS vs. naive. G6P, glucose 6-phosphate; F-1,6-BP, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; 1,3-BPG, 1,3-bisphosphogylcerate; 2/3-PG, 2- and 3-phosphoglycerate pool; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; PRPP, phosphoribosyl diphosphate; cAMP, cyclic-AMP; GSH, reduced glutathione. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments with n = 5/group. See also Figure S2.