Abstract
PiggyBac(PB)-like elements (pble) are members of a eukaryotic DNA transposon family. This family is of interest to evolutionary genomics because pble transposases have been domesticated at least 9 times in vertebrates. The amino acid sequence of pble transposases can be split into three regions: an acidic N-terminal domain (~100 aa), a central domain (~400 aa) containing a DD[D/E] catalytic triad, and a cysteine-rich domain (CRD; ~90 aa). Two recent reports suggested that a functional CRD is required for pble transposase activity. Here we found that two CRD-deficient pble transposases, a PB variant and an isoform encoded by the domesticated PB-derived vertebrate transposase gene 5 (pgbd5) trigger transposition of the Ifp2 pble. When overexpressed in HeLa cells, these CRD-deficient transposases can insert Ifp2 elements with proper and improper transposon ends, associated with deleterious effects on cells. Finally, we found that mouse CRD-deficient transposase Pgbd5, as well as PB, do not insert pbles at random into chromosomes. Transposition events occurred more often in genic regions, in the neighbourhood of the transcription start sites and were often found in genes predominantly expressed in the human central nervous system.
Keywords: transposon, DNA cleavage, neuron, insertion preference, vertebrate
Introduction
Transposable elements (TEs) gather diverse discrete DNA sequences of prokaryotic and eukaryotic origins that use a wide range of mobility mechanisms to transpose within the genome of their hosts [1–4]. PiggyBac-like elements (pble) consist of a family of DNA transposons that have so far only been found in animal genomes and with copy numbers that vary widely between host species [5]. Pbles are able to jump from one chromosomal locus to another using cut-and-paste transposition which is enzymatically catalysed by the transposase they encode. The first pble to be identified was Ifp2 (a.k.a. piggyBac) from the cabbage looper moth Trichoplusia ni (Lepidoptera) [6]. It is the reference element in the piggyBac family for academic research purposes [7]. The Ifp2 DNA sequence is 2476 bp in length and contains an open reading frame (ORF) coding a 594 amino acid transposase named PB. The Ifp2 DNA sequence is flanked by 13 bp long terminal inverted repeats (TIR) and by 19 bp long subterminal inverted repeats (STIR) located internally at 3 and 31 nucleotides of distance of 5’ and 3’ TIR inner ends, respectively. PB excises the transposon from its donor chromosomal locus and reinserts it into a TTAA motif, which gets duplicated upon insertion.
Sequence analyses revealed that PB contains at least 3 domains. The first domain spans from residues 1 to 116, shows no overt structural features and displays an acidic pI of 4.41. The second domain is a macro domain that extends from residues 117 to 535 and has a basic pI (9.29); it contains several highly conserved residues, including the predicted catalytic residues (D268, D346 and D447) that are required for all transposition steps. On both sides of the catalytic domain (residues 263 to 457), recent structures obtained by cryo-electron-microscopy [8] revealed two DNA binding sub-domains (residues 117 to 263 and 457 to 535, respectively) that bind to Ifp2 TIRs. Finally, the third domain spans from residues 559 to 594, and contains a cysteine-rich domain (CRD, pI=9.07) for which the atomic structure was first solved by nuclear magnetic resonance [9]. This CRD was shown to bind to a 5’-TGCGT-3’/3’-ACGCA-5’ motif that is contained within the 19 bp subterminal inverted repeat between positions 178 and 199 of the Ifp2 sequence [9]. The CRD was also found to be vital for the dimerization of PB [10], the removal of the last seven residues being sufficient to yield a monomeric protein that still binds to Ifp2 ends in vitro. Finally, this CRD contains a nuclear localisation signal (NLS) that is required to mediate PB nuclear localisation [11].
Two studies [9,10] proposed non-exclusive roles for the CRD and the ability of PB to mediate transposition. In the first study, the authors concluded that the CRD was essential for Ifp2 transposition because the use of a CRD-deficient PB (PB.1–558) in an integration assay performed in mammalian cells did not lead to an increase in integration activity compared to controls done in the absence of the transposase [9]. The second study proposed that PB dimerisation might serve to prevent excessive transposition of Ifp2 since removal of the CRD led the monomeric PB to be more active in transposition excision [10]. It is also possible that the absence of the CRD may cause cytosolic retention since it contains a nuclear localization sequence (NLS).
Here we aimed to determine whether PB.1–558 fused to a simian virus 40 (SV40) NLS was able to mediate the transposition of Ifp2 into human cell chromosomes. First, we showed that both PB.1–558 and PB.NLS-1–558 had a negative effect on obtaining clones in integration assays. Second, we found that PB.NLS-1–558 was able to carry out the transposition of Ifp2 elements. Third, we compared the properties of PB.NLS-1–558 with those of another CRD-deficient piggyBac protein, the domesticated murine and human PGBD5 protein. Fourth, we evaluated the quality of Ifp2 ends neo-integrated into chromosomes by PB and the two CRD-deficient proteins, PB.NLS-1–558 and PGBD5. Finally, we determined whether the three proteins used similar or different pools of chromosomal insertion sites, whatever the state of Ifp2 transposon ends.
Results
PB.1–558 needs an NLS to locate into nuclei.
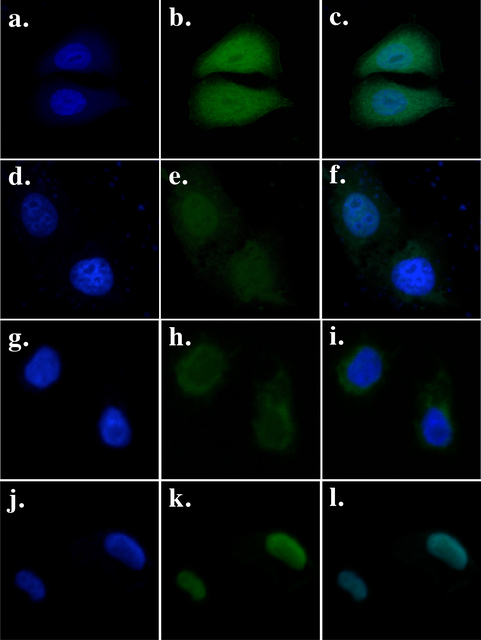
We made a CRD-deficient PB mutant (PB.1–558) and a construct in which its N-terminal end was fused with a SV40 NLS (PB.NLS-1–558). Such a position for the NLS does not modify the transposition activity of PB and preserves the activity of the added localization motif or protein domain [12,13]. To assess cellular localization of both proteins we made two more constructs in which the green fluorescent protein (GFP) was C-terminally fused to PB.1–558 and PB.NLS-1–558. An expression vector encoding GFP was used as a diffusion control within the cytoplasm and nucleus (Fig. 1a–c) and a vector encoding a PB-GFP fusion was used as a control for active import into the nuclei (Fig. 1d–f) [11]. Our data revealed that PB.1–558 is not enriched in the nucleus (Fig. 1g–i), which contrasts with its PB.NLS-1–558 counterpart that is almost completely nuclear (Fig. 1j–l).
Fig. 1. Cellular localization of GFP fusions in HeLa cells transiently transfected with a vector expressing GFP (a, b, c), PB-GFP (d, e, f), PB.1–558-GFP (g, h, i) and PB.NLS-1–558-GFP (j, k, l).
The left panels (a, d, g, j) show the nuclear genomic DNA staining by Hoechst 33342, the middle panels (b, e, h, k)) show GFP fluorescence, the right panels (c, f, I, l) correspond to merge pictures.
PB variants display cytotoxicity
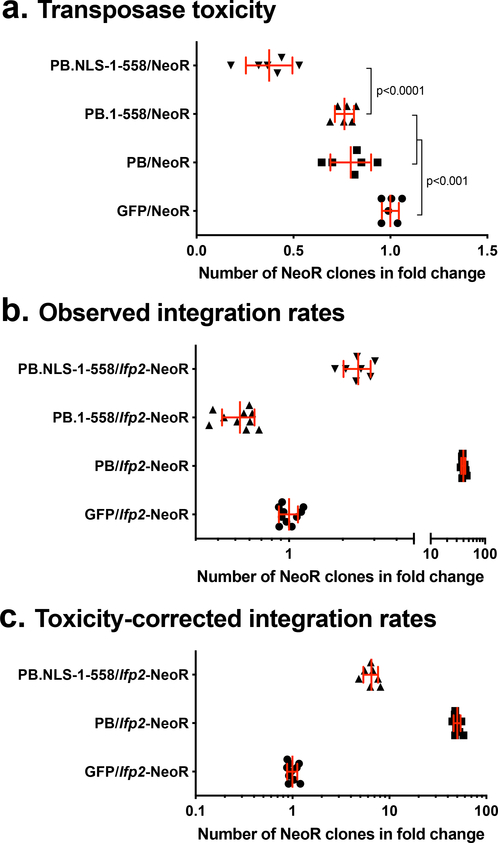
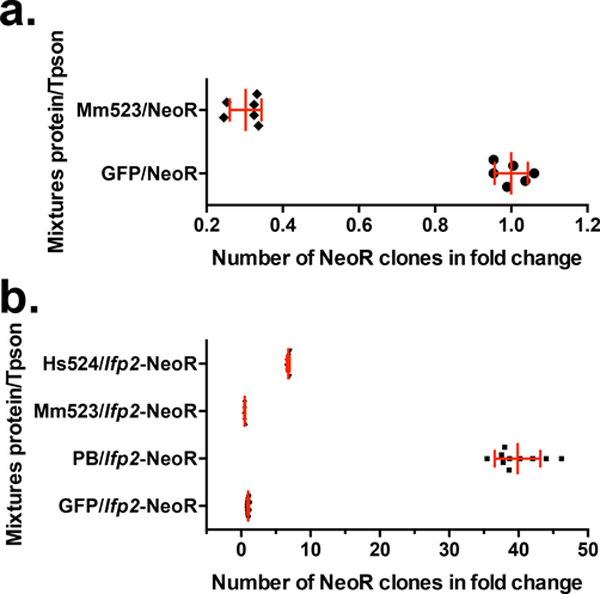
Prior to assaying the ability of the full-length PB, PB.1–558, and PB.NLS-1–558 to trigger transposition of an Ifp2 source, we checked whether these proteins impacted random integration rates into HeLa cell chromosomes. We used a DNA plasmid containing a gene cassette coding for a neomycin resistance (NeoR) without the Ifp2 sequence, the pBSK-NeoR plasmid. This was performed using a classic integration assay (see material and methods section). We observed that the integration rate of pBSK-NeoR into chromosomes was significantly lower in the presence of each of the three variants compared to a control GFP sequence (Fig. 2a; ~1.25, 1.31, 2.67 folds (1/fold change) for PB, PB.1–558, and PB.NLS-1–558, respectively). This indicated that PB and its variants have a deleterious effect on cells, including those that display random and stable integrations of NeoR into their chromosomes. The cytotoxicity of PB.NLS-1–558 is higher than that of PB and PB.1–558.
Fig. 2. Box plot representations of integration assay results.
(a) impact of the two PB variants (PB.1–558 and PB.NLS-1–558), PB and GFP on the rate of random integration of a NeoR cassette. (b) rates of NeoR clones resulting from the integration of Ifp2-NeoR when recombination was mediated by the two PB variants, PB and GFP. (c) rates of NeoR clones resulting from the integration of Ifp2-NeoR when recombination was mediated by PB.NLS-1–558, PB and GFP and corrected by the rate of toxicity of each protein calculated in (a). In (b) and (c), integration rates were expressed in rate NeoR clones that were normalized using controls done with GFP. In each plot, the red lines represented the median and the standard deviation, respectively.
The results of integration assays (Fig. 2b) performed with the Ifp2-NeoR transposon donor plasmid confirmed that PB.1–558 has a negative effect on obtaining NeoR clones. The number of clones was 1.5 times lower than that obtained with the GFP control and 60 times lower than that obtained with PB. This indicated that integration assays performed with PB.1–558 are affected by both: 1) the cytotoxicity of PB.1–558, and 2) the integration of the NeoR cassette into chromosomes.
The number of NeoR clones obtained with PB.NLS-1–558 was 2.5 times higher than that with the GFP control. Due to the cytotoxicity of PB.NLS-1–558, this number was likely underestimated. After correcting for PB.1–558 toxicity rate (Fig. 2c) we estimate the number of integration events to be ~7 times higher what is found with the GFP control. Overall, this means that PB.NLS-1–558 is roughly 8 times less efficient than PB for obtaining NeoR clones in an integration assay done in HeLa cells. Because cytotoxicity hampered our ability to directly evaluate integration rates and was likely dose-dependent as observed with PGBD5 [14], we focused our investigation on the ability of PB.NLS-1–558 to trigger Ifp2 transposition by characterizing integration events into chromosomes by NeoR clones.
Features of sites targeted by PB and PB.NLS-1–558 when integrating Ifp2 into chromosomes
To verify the presence of transposition events and to determine their sequence features, we produced fragment populations corresponding to Ifp2-chromosome junctions. These were made by LAM-PCR using genomic DNA (gDNA) of NeoR clone populations that were sequenced using Illumina Miseq technology. To prepare gDNA samples we used ~60000 clones from integration assays done with Ifp2-NeoR and PB, and ~1000 clones from integration assays done with Ifp2-NeoR and PB.NLS-1–558. Previous results of integration assays performed in HEK293 cells found that the rate of Ifp2 integration into chromosomes by proper transposition (i.e. with a perfect duplication of the “TTAA” TSD and conservation of the TIR sequence) was about 96–98% when PB was used as a transposase source [15,16].
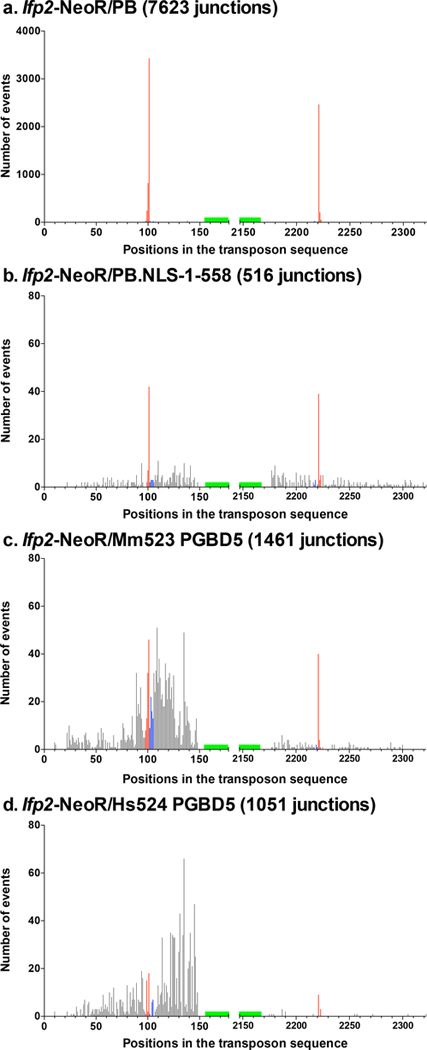
Using DNA sequence alignments, we characterized 7623 Ifp2/chromosome junctions resulting from integration events mediated by PB and 516 junctions mediated by PB.NLS-1–558, with Ifp2-NeoR as a transposon source (supplementary Table 1a and 2a). Sequenced junctions at the 5’ and the 3’ of Ifp2 ends were not equally represented in the sequence data, likely because of efficiency differences at certain steps of DNA fragment amplification during the LAM-PCR. Sequence junctions were further examined taking into account the conservation of TSD and TIR sequences, two features that were required to keep the capacity of neo-inserted elements to be efficiently remobilized during excision and insertion, i.e. to remain “active in transposition” [15,16]. Four kinds of junctions were observed: those displaying i) a full TIR sequence and a TTAA TSD (red bars from positions 101 to 104 and 2222 to 2225 in Fig. 3), ii) a region containing an intact TIR and a TTAA TSD juxtaposed to a little piece of plasmid backbone (black bars from positions 1 to 100 and 2226 to 2301 in Fig. 3a and b), iii) no TTAA TSD but a full TIR sequence (blue bars from positions 102 to 105 and 2218 to 2221 in Fig. 3), and iv) no TIR sequence lacking one or several nucleotides at its outer end (black bars from positions 107 to 178 and 2147 to 2217 in Fig. 3). The summary of results in Table 1 indicates that the rate of proper events when PB was used as a transposase was similar to that previously observed in other cell types, but 3.3% of junctions nevertheless displayed improper TSD, TIRs or both. Interestingly, 19.0% of junctions mediated by PB.NLS-1–558 were found to be proper, thus demonstrating that this variant is able to trigger canonical transposition events even though less efficiently than PB. Our results also indicated that PB.NLS-1–558 integrated Ifp2 into non-canonical TSDs approximately 25 times more often than PB. Furthermore, TIRs were damaged or accompanied by a piece of backbone sequence of variable length juxtaposing the transposon in the transposon donor plasmid in about 65% of Ifp2/chromosome junctions (while they represented only 2.25% of junctions among integration events triggered by PB). These observations suggested that the observed junctions resulted from both proper transposition events and improper integration events that could be mediated by both PB variants, but the rates of each kind of integration events were dramatically different between the two proteins.
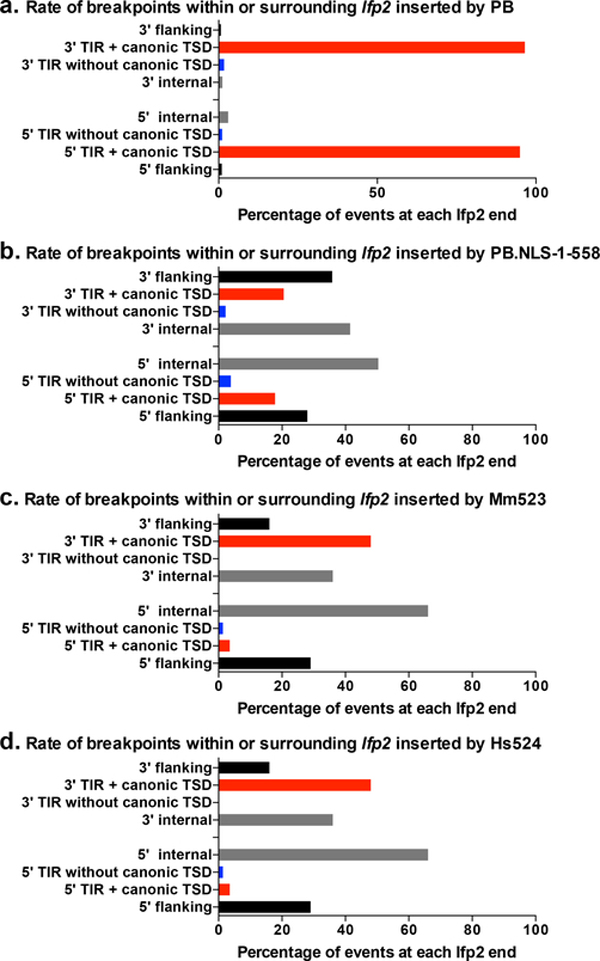
Fig. 3. Number and location of transposon breakpoints in pble sequences after transposition into chromosomes.
Histogram distributions of Ifp2-NeoR extremities transposed by PB (a), PB.NLS-1–558 (b), Mm523 (c) and Hs524 (d) (detailed in supplementary Tables 1 to 4). Red bars indicated insertion events with perfectly conserved TSD and TIR while blue bars located those in which TIR were perfectly conserved but the TSD did not correspond to a canonical TTAA at the outermost extremities of pbles. Black bars represented breakpoints within the transposon sequence and within plasmid backbone sequences juxtaposed to the transposon. Each bar corresponded to the number of junctions found at a single nucleotide position. Green boxes located the position of primers anchored within the transposon sequence and used at the last step of LAM-PCR. These graphics described the relative importance of wounds at transposon ends under our experimental conditions. However, they could not allow calculating wound rates at each of both ends due to the fact that the final LAM-PCR products in each dataset came from the gathering of several LAM-PCR reactions.
Table 1.
Presence of canonic TTAA TSD and-or TIR among transposon/chromosome junctions resulting from LAM-PCR products and originating from events mediated by PB variants.
| Transposase source | Transposon source | Proper TSD and TIR | Proper TSD improper TIR | Improper TSD/proper TIR | Improper TSD and TIR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PB | Ifp2-NeoR | 96.7 % (7370) | 1.05 % (78) | 1.05 % (80) | 1.2 % (95) |
| PB-NLS-1–558 | Ifp2-NeoR | 19.0 % (98) | 2.5 % (13) | 3.1 % (16) | 75.4 % (388) |
Next, we identified 5’ and 3’ junctions for events that occurred exactly at the same chromosomal insertion sites in both datasets. We observed that 7446 chromosomal sites were used and found 177 unambiguous insertion sites in our Lumpy raw file that were occupied several times. In these 177 sites, integration events occurred in both Ifp2 orientations when mobility was mediated by PB (supplementary Table 1b). A careful examination of the resulting bam file with IGV [17] revealed 11 cases of putative single integration events (supplementary Table 1b, case highlighted in cyan blue). Among them, three corresponded to Ifp2 transposons displaying at least one TIR damaged at its outer end, and one TIR was inserted into a duplicated TSD corresponding to a duplicated CATG motif. As previously described [18,19] we also found four sites in which both integration events occurred into non-canonical TSD (CATG, TATC, ACAT, TTCC; supplementary Table 1b) and 16 sites where two events occurred with the insertion of transposons with at least one improper end. These results suggest that virtually any type of non-canonical integration can be found at a very low frequency when Ifp2 was transposed by PB. In data resulting from the transposition of Ifp2 by PB.NLS-1–558, we found that 516 chromosomal sites were used and identified 32 unambiguous insertion sites for which integration events occurred in both orientations of the transposon. Four of these putatively corresponded to single integration events (supplementary Table 2b, case highlighted in cyan blue, two would correspond to canonical integrations by transposition and two with non-canonical TIR or TSD). The main difference with PB is that improper events were dramatically more frequent when transposition was mediated by PB.NLS-1–558.
PGBD5 a natural domesticated CRD-deficient pble transposase
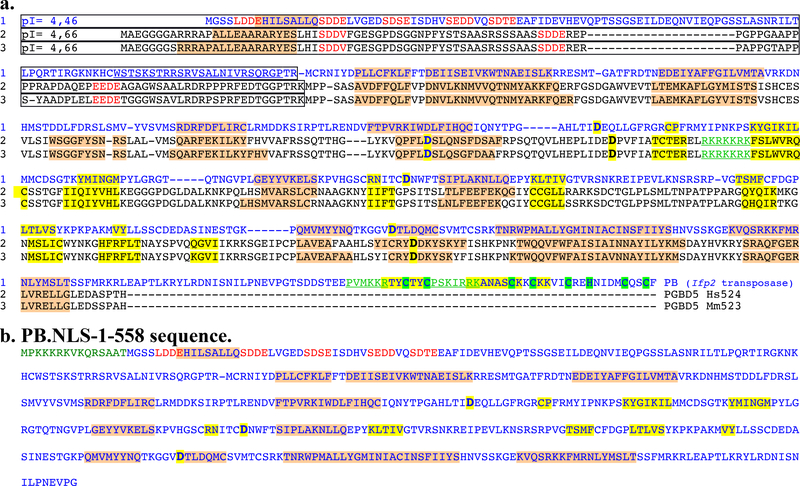
We compared the transposition features of the PB.NLS-1–558 variant to those of murine and human orthologues of the oldest domesticated piggyBac transposase since the origin of vertebrates, PGBD5 (Mm523 and Hs524) [20]. Alignment of three protein sequences (Fig. 4) revealed that both CRD-deficient proteins displayed an acidic N-terminal domain and a second domain with a basic pI (~9.2) containing an apparent catalytic triad composed of 3 acidic amino acid residues that were essential for transposition activity [20]. Another shared feature was their ability to trigger Ifp2 transposition [14,21]. This transposition ability was rather unexpected for PGBD5 compared to PB.NLS-1–558 because the PGDB5 catalytic triad was not located at the same positions as in pble transposases (Fig. 3, bold residues highlighted in yellow). PGBD5 acquired a new putative NLS that is centrally located in the sequences of Mm523 and Hs524 (Fig. 3, RKRKKRK motif typed in green and underlined). In agreement with the literature [14] we observed that the ectopic expression of murine PGBD5 isoform of 523 amino acids (Mm523) reduced the apparent efficiency of obtaining NeoR clones (Fig. 5a) that is close to that of PB.NLS-1–558 in HeLa cells (Fig. 2a). In integration assays done with the Ifp2-NeoR transposon donor plasmid under experimental conditions similar to those used above for PB.NLS-1–558, the rate of NeoR clones obtained with Mm523 (Fig. 5b) was similar to that obtained with the GFP control. In order to verify whether this was due to PGBD5 cytotoxicity, we used a second cellular system developed in human rhabdoid tumor G401 cells and in which the endogenous expression of PGBD5 (Hs524) was found to have little impact on cell viability [14]. Under these experimental conditions, we found that the rate of NeoR clones was sevenfold higher than that of the GFP control (Fig. 5b). Together, this indicates that the expression rate of CRD-deficient pble transposases strongly impact the outcome of integration assays.
Fig. 4. Sequence features of the Ifp2 transposase (PB) variants and two Mm523-like PGBD5 isoforms.
(a) Protein sequence alignment of Ifp2 transposase (PB) with two murine and human domesticated PGBD5 proteins corresponding to the orthologous Hs524 and Mm523 isoforms. (b) Sequence features of PB.NLS-1–558. Secondary structure predictions calculated with psipred (http://bioinf.cs.ucl.ac.uk/psipred/) and Jpred4 (http://www.compbio.dundee.ac.uk/jpred/) were highlighted in pink for α-helices and in orange for β-strands. The three proteins share two domains: a N-terminal domain that was few structured, with an acid pI (boxed regions) and repeated acid motifs (in red letters), a domain of ~400 amino acid residues that display a basic pI. PB contained a third C-terminal domain, the CRD, that contains cysteins (highlighted in green) able to assemble zinc finger folds. Aspartic residues inactivating the recombinase catalytic activity were bolded and highlighted in yellow [17,21]. The PB NLS and the putative NLS in PGBD5 isoforms were underlined and typed in green.
Fig. 5. Graphic representations of integration assay results.
(a) impact of Mm523 on the rate of random integration of a NeoR cassette. (b) rates of integration of an Ifp2-NeoR when recombination was mediated by PB and Mm523 in HeLa cells, and Hs524 in G401 cells. Integration rates were expressed in rate NeoR clones that were normalized using controls done with GFP (green). In each plot, the red lines represented the median and the standard deviation, respectively.
The sequence features of integration events were studied through Ifp2-chromosome junctions obtained with Mm523 and Hs524. We prepared gDNA samples from ~1800 and 1600 NeoR clones obtained from integration assays done with Ifp2-NeoR and, Mm523 or Hs524, respectively. Using the Mm523 gDNA sample, we obtained 1461 transposon/chromosome junctions that were analyzed as described above (supplementary Table 3a). The profiles of transposon/chromosome junctions were found to be similar between integration events mediated by PB.NLS-1–558 and Mm523 (Fig. 3c, and Table 2 versus last raw in Table 1). This was also verified by examining chromosomal sites where we found integration events in both orientations within the 1461 chromosomal sites used (supplementary Table 3a and b). When the junctions were categorized and analyzed in terms of percentages at each Ifp2 end for PB, PB.NLS-1–558 and Mm523 we observed that: i) proper junctions occurred more often at the 3’ end than at the 5’end (Fig. 6, red bars), and ii) among improper junctions, those without a canonical TSD and those located within TIR and juxtaposed with transposon sequences (Fig. 6, blue bars and internal black bars, i.e. wounds at transposition ends as exemplified in [22]) occurred more often than those located within the plasmid backbone sequences juxtaposed near the TSD and TIR of the donor plasmid (Fig. 3, flanking black bars). Using the Hs524 gDNA sample, we obtained 1051 transposon/chromosome junctions (supplementary Table 4a). The junction profile was overall similar to those of both CRD-deficient proteins (Fig. 3c and 6d), but it displayed a marked difference in that there were fourfold and twofold less proper insertion events by transposition than in those obtained with PB.NLS-1–558 and Mm523, respectively. Unexpectedly, this suggests that PGBD5 is more prone to trigger improper integration in rhabdoid tumor G401 cells, consistent with the proposal that PGBD5 exhibits aberrant activities in human rhabdoid tumors [14]. Since we observed that PB.NLS-1–558, Mm523 and Hs524 display similar junction profile, we wondered if their insertion site preferences might be similar.
Table 2.
Presence of canonic TTAA TSD and-or TIR among transposon/chromosome junctions resulting from LAM-PCR products and originating from events mediated by Mm523 and Hs524.
| Transposase source | Transposon source | Proper TSD and TIR | Proper TSD improper TIR | Improper TSD/proper TIR | Improper TSD and TIR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mm523 PGBD5 | Ifp2-NeoR | 10.0 % (147) | 5.4 % (80) | 4.3 % (64) | 80.3 % (1188) |
| Hs524 PGBD5 | Ifp2-NeoR | 4.6 % (48) | 2.1 % (22) | 1.3% (14) | 92.0 % (967) |
Fig. 6. Features of transposon breakpoints in Ifp2 transposed by PB (a), PB.NLS-1–558 (b), Mm523 (c) and Hs524 (d).
Black bars corresponded to percentages of breakpoints located within the plasmid backbone flanking the transposon or those located within inner transposon regions (from the position 2 in TIR to the primer used for the LAM-PCR). Red bars corresponded to those within transposons that displayed intact canonical TTAA TSD and TIRs. Blue bars corresponded to pbles displaying noncanonical TSD but intact TIRs.
Features of insertion sites targeted by PB variants and PGBD5 when integrating Ifp2 into chromosomes
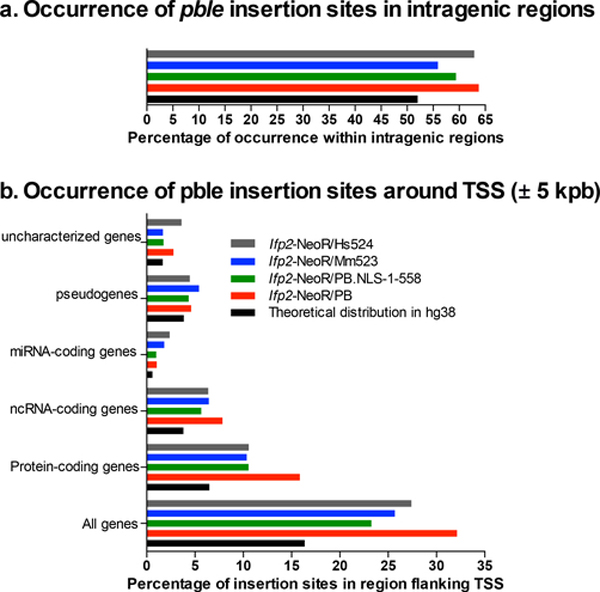
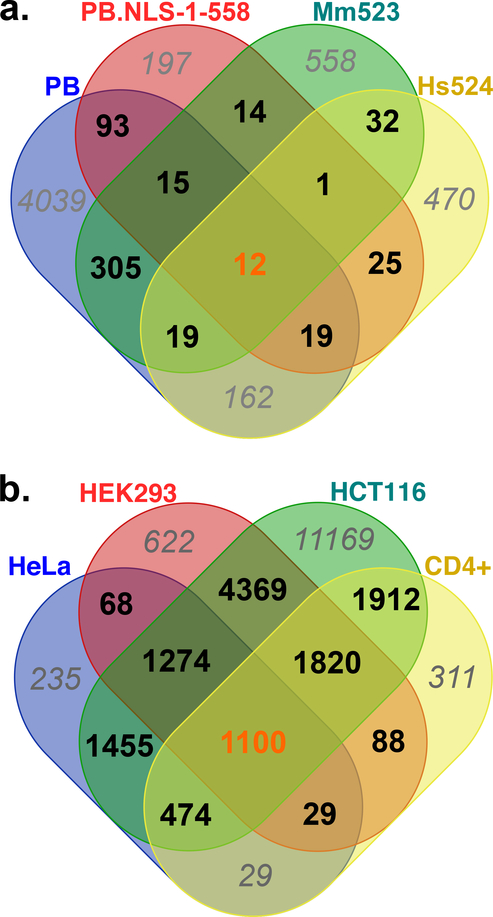
PB and PGBD5 have been shown to integrate Ifp2 into intragenic regions more frequently than expected by chance, specifically within transcription start site (TSS) regions flanking (± 5 kbp) protein-coding genes [23–26]. Using our junction data, we observed that PB, PB.NLS-1–558, Mm523, Hs524 did not distributed Ifp2 integrations at random into intergenic and intragenic regions (Fig. 7a; Chi2, p = 2.08×10−95, 2.21×10−10, 0.0026, and 3.72×10−81 respectively), but with a significant enrichment for intragenic regions (hypergeometric test, p ≪0.01 for the four proteins). Similar investigations were also done within regions flanking TSSs of five types of genes coding for: i) proteins, ii) non-coding RNA (ncRNA), iii) micro RNA (miRNA), or being annotated in hg38 as iv) pseudogenes or v) uncharacterized genes. We also found that Ifp2 was integrated more frequently than expected by chance within regions flanking TSSs in the 5 types of genes, except for the two CRD-deficient proteins into uncharacterized genes (Fig. 7b; Chi2, p = 2.58×10−9, 2.16×10−8, 8.27×10−12, and 3.43 ×10−9 respectively), and with a significant enrichment in each type of genes (hypergeometric test, p ≪0.01 for the four proteins), except for the miRNA and ncRNA genes in the PB.NLS-1–558 and Mm523 datasets, respectively (hypergeometric test, p = 0.043 and 0.051). In addition to these global distribution features, a striking feature was that our Lumpy raw files, after manual investigation using IGV, contained 166 (i. e. 177–11), 24 (44–20), 23 (26–3) and 11 (13–2) chromosomal sites, each displaying a fragment containing the Ifp2 element inserted in both orientations, i.e. inserted at least twice into these sites when integration events were mediated by PB, PB.NLS-1–558, Mm523 and Hs524, respectively. We also found common insertions sites among the PB, PB.NLS-1–558, Mm523 and Hs524 datasets (Table 3, lines 1, 3 and 5). These insertion events occurred at the same nucleotide position site but this was not due to sample contamination since they resulted from Ifp2 integration events in different orientations and in some cases from properly and improperly integrated Ifp2 transposons. The number of these observations was increased when using a 1000 bp window on both sides at each chromosomal insertion site (Table 3, lines 2, 4 and 6; regions called below insertion sites-containing regions (ISCR)).
Fig. 7. Proportions of Ifp2 insertions mediated by PB, PB.NLS-1–558, Mm523 and Hs524 in intragenic regions (a) and regions containing TSS (b).
taking into account the five gene categories: protein-coding genes, ncRNA-coding genes, miRNA-coding genes, pseudogenes and uncharacterized genes. Black bars indicated the expect percentage in a random distribution.
Table 3.
Number of chromosomal sites in common in each dataset pair and their statistical consitency in permutation tests.
| Feature of dataset 1 | Feature of dataset 2 | Random permutations features | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell line 1 | Transposon 1 | Transposase 1 | Cell line 2 | Transposon 2 | Transposase 2 | Window around insertion sites (±) in both datasets | Number of sites observed | Average number of sites expected per chance | Standard deviation | Z score | Probability = H0 was no differences between obs. and exp. |
| HeLa | Ifp2 | PB | HeLa | Ifp2 | PB.NLS-1–558 | 0 | 1 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | p<0.001 |
| HeLa | Ifp2 | PB | HeLa | Ifp2 | PB.NLS-1–558 | 1000 | 37 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | p<0.001 |
| HeLa | Ifp2 | PB | HeLa | Ifp2 | Mm523-PGBD5 | 0 | 83 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | p<0.001 |
| HeLa | Ifp2 | PB | HeLa | Ifp2 | Mm523-PGBD5 | 1000 | 175 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | p<0.001 |
| HeLa | Ifp2 | PB | G401 | Ifp2 | Hs524-PGBD5 | 0 | 24 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | p<0.001 |
| HeLa | Ifp2 | PB | G401 | Ifp2 | Hs524-PGBD5 | 1000 | 42 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | p<0.001 |
| HeLa | Ifp2 | PB | HEK293 | Ifp2 | PB | 0 | 21 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | p<0.001 |
| HeLa | Ifp2 | PB | HEK293 | Ifp2 | PB | 1000 | 471 | 260.162 | 17.0215 | 12.3865 | 0 |
| HeLa | Ifp2 | PB | HCT116 | Ifp2 | PB | 0 | 238 | 67.01 | 8.4329 | 20.2763 | 0 |
| HeLa | Ifp2 | PB | HCT116 | Ifp2 | PB | 1000 | 2387 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | p<0.006 |
| HeLa | Ifp2 | PB | CD4+ | Ifp2 | PB | 0 | 24 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | p<0.001 |
| HeLa | Ifp2 | PB | CD4- | Ifp2 | PB | 1000 | 213 | 97.684 | 10.2987 | 11,197 | 0 |
| HEK293 | Ifp2 | PB | HCT116 | Ifp2 | PB | 0 | 391 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | p<0.001 |
| HEK293 | Ifp2 | PB | HCT116 | Ifp2 | PB | 1000 | 6600 | 5419.484 | 93.3269 | 12.0060 | 0 |
| HEK293 | Ifp2 | PB | CD4+ | Ifp2 | PB | 0 | 362 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | p<0.001 |
| HEK293 | Ifp2 | PB | CD4+ | Ifp2 | PB | 1000 | 752 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | p<0.001 |
| HCT116 | Ifp2 | PB | CD4+ | Ifp2 | PB | 0 | 16 | 81.825 | 9.0919 | 17.5073 | 0 |
| HCT116 | Ifp2 | PB | CD4+ | Ifp2 | PB | 1000 | 5235 | 2213.501 | 50.9891 | 59.2576 | 0 |
| HEK293 | Sleeping Beauty | SB | CD4+ | Sleeping Beauty | SB | 0 | 3 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | p>0.083 |
| HEK293 | Sleeping Beauty | SB | CD4+ | Sleeping Beauty | SB | 1000 | 385 | 349.967 | 19.09 | 1.8350 | p=0.034 |
N.A., not appropriated to use a Z-test as the distribution of the 1000 permutations results did not fulfil normality in a Shapiro-Wilk test. In the most right column is typed in red probabilities supporting that there was no difference at a threshold of 0.01.
The choice of an insertion site by any pble transposase does not fully occur at random since a TTAA motif is used. In the human genome model hg38, there are 18,713,270 TTAA motifs. Public data about DNAse I hypersensitivity mapping revealed that 98% of them are located in open chromatin in HeLa cells (but also in HEK cells), i.e. accessible to DNA binding proteins such as transposases. This means that the probability of integrating an Ifp2 transposon twice into a single target site lies about 1.8 ×10−7 in hg38. Taking into account the size of datasets used herein, to find several insertions by chance into the same site is therefore unexpected under our experimental conditions.
Given the putative impact of some specific genomic features of HeLa cells such as their aneuploidy [27–30], we further investigated ISCR features in other cell lines taking advantage of public datasets. We used three of them that were produced from integration assays performed with Ifp2 and PB in HEK293 [23], in HCT116 [15] and in CD4+ [26] cells (21,967, 172,866 and 8954 chromosomal sites, respectively (Table S4a, b, c)).
First, we confirmed that the rate of insertions mediated by PB into intragenic regions in each of the four cell lines (HeLa, HEK293, HCT116 and CD4+; Table 4a, column 4) is 7 to 18% higher than expected by chance (51.6%; Table 4b, column 1). This preference could not be explained by the numbers of TTAA motifs in intragenic regions (53.1%; Table 3c, column 2), which is close to that expected by chance. In spite of variations of aneuploidy and chromatin profiles between the four cell lines, the insertion preference into intragenic regions does not appear to correlate to these features.
Table 4a.
Rate of regions containing insertion sites in genes and neuron genes in hg38
| 1, Dataset features: cells, transposon / transposase sources | 2, No of different ISCR* | 3, No & % of different ISCR overlapping a gene*** | 4, No of genes overlapped by ISCR** | 5, No & % of different ISCR overlapping a neuron gene*** | 6, No & % of neuron genes among genes overlapped by ISCR** | 7, p**** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HeLa, Ifp2 / PB | 7,623 | 5,060 (66.4%) | 4,663 | 2,231 (29.2%) | 1,587 (34.0%) | 2.1 × 10−82 |
| HeLa, Ifp2/PB.NLS-1–558 | 516 | 327 (63.2%) | 376 | 123 (23.8%) | 123 (37.6%) | 2.5 × 10−6 |
| HeLa, Ifp2 / Mm523 | 1,479 | 863 (58.4%) | 956 | 321 (21.7%) | 303 (31.7 %) | 3.1 × 10−11 |
| G401, Ifp2 / Hs524 | 1052 | 665 (63.2%) | 740 | 279 (26.5%) | 258 (38.8%) | 1.3 × 10−14 |
| HEK293, Ifp2/PB [22] | 21,967 | 15,226 (69.3%) | 9,370 | 7,173 (32.6%) | 3,032 (32.4%) | 1.9 × 10−150 |
| HCT116, Ifp2/PB [14] | 172,866 | 113,648 (67.7%) | 23,578 | 49,688 (28.8%) | 5,945 (25.3%) | 1.3 × 10−88 |
| CD4+, Ifp2 / PB [25] | 8,954 | 6,940 (77.5%) | 5,763 | 3,134 (35.0%) | 1,903 (33.0%) | 6.2 × 10−89 |
| HCT116, sleeping beauty/SB [14] | 28,490 | 17,534 (61.54%) | 10,460 | 7,776 (27.3%) | 3,229 (30.9%) | 2.5 × 10−128 |
| CD4+, sleeping beauty /SB [25] | 8,290 | 5,441 (64,63%) | 5,133 | 2,406 (29.0%) | 1,750 (34.1%) | 2.9 × 10−93 |
| HCT116, TcBuster/ TCBUSTER [14] | 17,227 | 11,841 (68.7%) | 8,522 | 5,517 (32.0%) | 2,820 (33.1%) | 4.9 × 10−151 |
Table 4b.
Numbers and sequence coverages (%) of genes and neuron genes in hg38
| 1, Genes | 2, Neuron genes |
|---|---|
| 30077 (51.6%) | 6854 (22.8%) |
In order to verify the statistical consistency of insertion sites shared between datasets, all pairs of datasets were compared taking into account the variation of TTAA motif distribution between intra and intergenic regions (Table 4c). P-values indicated that the number of commonly used chromosomal insertion sites was significantly more elevated than expected by chance (Table 3; raws 1 to 16) whatever the window used around the insertion sites (0 or 1000 bp). We also observed that 18 ISCR were shared by the four datasets obtained with Ifp2 and PB in the four cell lines.
Table 4c.
Numbers and rate of potential insertion sites for PB, SB and TcBuster in hg38
| 1, Number of potential insertion sites in hg38 | 2, Number & % of potential insertion sites in genes in hg38 | 3, Number & % of potential insertion sites in neuron genes in hg38 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ifp2 (TTAA) | 18,713,270 | 9,943,117 (53.1%) | 4,521,501 (24.2%) |
| sleeping beauty (TA) | 152,412,514 | 92,065,399 (60.4%) | 36,803,438 (24,1%) |
| TcBuster (NNNTANNN) | 130,938 | 74,733 (57.1%) | 33,940 (25.9%) |
, ISCR = insertion sites-containing regions, i.e. plus 1000 bp upstream and downstream each insertion site
, 2 genes can overlap an ISCR
, each genes and neurons genes = exons and introns of their transcriptional unit plus 5000 bp upstream and downstream
, hypergeometric test using H0 = no enrichment in neuron genes among genes overlapped by an ISCR.
We also examined insertion datasets obtained with the transposon sleeping beauty in HEK293 and CD4+ cells (28490 and 8290 insertion sites, respectively [15,26]). Taking into account the distribution of its TA targets in hg38 (Table 4c), results in Table 3 revealed that this transposon does not display a significant preference between available putative TA target sites. It displayed higher rates of insertion into intragenic regions (~62.5%, Table 4a) than predicted by chance (51.6%, Table 4b). In contrast to PB, this can however be correlated with TA density that is dramatically increased in these regions (60.4%, Table 4c) compared to intergenic ones.
In all, our data reveal that PB, PB.1–558, Mm523 and Hs524 insert Ifp2 preferentially into intragenic regions with some level of site preference between available TTAA target sites.
Features of genes targeted by Ifp2 insertions mediated by PB variants and PGBD5
We wondered whether insertion site preferences of pble transposases might also be seen at the level of some intragenic regions. We postulated that experimental conditions of transposition assays are conducive to forced integration of transposons into chromosomes. Therefore, we predicted that insertions should be enriched among ISCR shared by several datasets than among those unique to each dataset.
In the ontology analysis done with the 410 genes overlapped by ISCR and shared by at least two datasets among those obtained with PB, PB.NLS-1–558, Mm523 and Hs524 in HeLa cells (Figure 6a), we found that 35/50 significant terms were directly related to the nervous system (Table 5). This issue was therefore further investigated by verifying whether there was an enrichment of “neuron genes” among ISCR overlapping with genes. For this purpose, we used the 6854 “neuron genes” identified in hg19 based on the expression properties of 29165 genes (protein-, ncRNA- and miRNA-coding plus some uncharacterized genes and pseudogenes) in 216 distinct human brain structures [31]. We found that neuronally expressed genes were significantly enriched in each of the PB, PB.NLS-1–558, Mm523 and Hs524 datasets obtained in HeLa cells (Table 4a, columns 5,6,7). They were again enriched among the 697 genes overlapped by ISCR that were shared by at least two of four datasets. This enrichment in neuron genes was 31.7–38.8% in each of the four datasets and 37.2% (259/697) among the 697 shared genes. These results therefore support the notion that neuron genes are preferred regions for pble transposases to insert Ifp2.
Table 5.
Significant ontology terms resulting from the analysis of the 817 genes shared by PB, PB.NLS-1–558, Mm523 and Hs524.
| GO ID | GO Term | P Value* | Nr. Genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fused GO terms: synapse organization (6,51% genes) | |||
| G0:0034330 | cell junction organization | 0,001312 | 49 |
| G0:0034329 | cell junction assembly | 0,023703 | 32 |
| G0:0050808 | synapse organization | 0,000431 | 36 |
| G0:0099173 | postsynapse organization | 0,005316 | 19 |
| G0:0099084 | postsynaptic specialization organization | 0,013763 | 8 |
| Fused GO terms: regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction (14.61% genes) | |||
| G0:0044093 | positive regulation of molecular function | 0,018196 | 92 |
| G0:0007264 | small GTPase mediated signal transduction | 0,004348 | 40 |
| G0:0008047 | enzyme activator activity | 0,013464 | 37 |
| G0:0043087 | regulation of GTPase activity | 0,000939 | 37 |
| G0:0060589 | nucleoside-triphosphatase regulator activity | 0,000800 | 30 |
| G0:0030695 | GTPase regulator activity | 0,000726 | 28 |
| G0:0043547 | positive regulation of GTPase activity | 0,022595 | 30 |
| G0:0051056 | regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction | 0,000102 | 31 |
| G0:0005096 | GTPase activator activity | 0,000898 | 26 |
| Fused GO terms:nervous system development (37.32% genes) | |||
| G0:0007275 | multicellular organism development | 0,000027 | 238 |
| G0:0009653 | anatomical structure morphogenesis | 0,000016 | 139 |
| G0:0060322 | head development | 0,002424 | 53 |
| G0:0000902 | cell morphogenesis | 0,000148 | 67 |
| G0:0032989 | cellular component morphogenesis | 0,001750 | 52 |
| G0:0048468 | cell development | 0,006713 | 107 |
| G0:0048731 | system development | 0,000513 | 212 |
| G0:0051128 | regulation of cellular component organization | 0,020339 | 114 |
| G0:2000026 | regulation of multicellular organismal development | 0,048972 | 100 |
| G0:0048513 | animal organ development | 0,035004 | 158 |
| G0:0000904 | cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation | 0,004732 | 49 |
| G0:0007399 | nervous system development | 0,000000 | 142 |
| G0:0007417 | central nervous system development | 0,000026 | 69 |
| G0:0022008 | neurogenesis | 0,000002 | 99 |
| G0:0051960 | regulation of nervous system development | 0,001844 | 59 |
| G0:0120036 | plasma membrane bounded cell projection organization | 0,000084 | 88 |
| G0:0007420 | brain development | 0,005967 | 50 |
| G0:0120035 | regulation of plasma membrane bounded cell projection organization | 0,023390 | 44 |
| G0:0048699 | generation of neurons | 0,000001 | 96 |
| G0:0120039 | plasma membrane bounded cell projection morphogenesis | 0,000663 | 48 |
| G0:0030182 | neuron differentiation | 0,000000 | 90 |
| G0:0048666 | neuron development | 0,000141 | 71 |
| GO:0045664 | regulation of neuron differentiation | 0,047755 | 42 |
| GO:0031175 | neuron projection development | 0,000310 | 64 |
| GO:0048667 | cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation | 0,001687 | 43 |
| GO:0016358 | dendrite development | 0,043162 | 22 |
| GO:0061564 | axon development | 0,013767 | 37 |
| GO:0007409 | axonogenesis | 0,010504 | 35 |
Term PValue corrected with Bonferroni step down. GO terms related to neurogenesis and neuron
These observations were confirmed using datasets obtained in HEK293, HCT116 and CD4+ cells. First, we found that neuronally expressed genes were significantly enriched in each of the four datasets (Table 4a, columns 5,6,7). This did not appear to be related to the target density since the percentage of ISCR in those genes was found to be 3 to 8% more elevated than the rate of TTAA motifs in those genes (Table 4a, column 4 versus Table 4c, column 3). We found that genes overlapped by ISCR and shared by at least two of four datasets did not display a significant enrichment in neuron genes (3884/12618; 30.8%; Figure 6b). However, a very strong enrichment was found when only ISCR shared by the four datasets were kept for the analysis (705/1100, 64% neuron genes) and a strong depletion in neuron genes was found among genes occurring in only one dataset (2273/12186; 18.7%).
Finally, we evaluated whether the insertion preferences into neuronally expressed genes were specific to PB by analysing the same features in datasets obtained with two unrelated transposons [15,26]. Data obtained with sleeping beauty in HCT116 and CD4 cells and with a TcBuster in HCT116 cells indicated that both transposons also inserted more frequently into neuronally expressed genes than in other genes (Table 4a, column 4,5,6). Their insertion preferences were also about 6–8% above the density in their respective target motif (Table 4c, column 3). For sleeping beauty, we also found that there was an enrichment in neuronally expressed genes among genes that overlapped by ISCR and shared by both datasets (1143 neuron genes for 2813 genes; 40.63%) and a depletion in those which were only found in one dataset (2625/9791; 26.8%).
Altogether, these last results reveal that pble transposases insert Ifp2 more often than expected by chance into neuronally expressed genes. However, this apparent preference is also displayed by sleeping beauty and very likely by TcBuster, indicating that it is not specific of pble transposases. This is not related to the gene size and the number of TTAA and TA because the densities in target motifs are very close in neuron and non-neuron genes (TTAA: 5.318 ± 0.029 and 5.114 ± 0.015 motifs/kbp, respectively; TA: 44.68 ± 0.156 and 44.07 ± 0.083 motifs/kbp, respectively). Therefore, this might result from the enhanced accessibility of neuronally expressed genes or their association with DNA repair and chromatin remodeling factors that support DNA transposition, a property that would be shared by multiple cell lines as exemplified here.
Discussion
This study generated two sets of novel insights. First, the two CRD-deficient transposases PB.NLS-1–558 and PGBD5 (Mm523 and Hs524) mediate canonical Ifp2 transposition, but also non-canonical events that may result from events of improper transposition, transposase-dependent integration by recombination and random integration. We assume that these CRD-deficient transposases operate at a reduced efficiency than the “wild-type” or “full-length” piggyBac transposase but their cytotoxicity on host cells and the possibility that they do integration by transposase-dependent recombination indicated that they have nuclease activity, as previously suggested for PGBD5 isoforms [13]. Furthermore, cytotoxicity issues often arise from the balance between the level of expressed protein and the efficiency of mechanisms responsible for the maintenance of genome integrity, which varies widely from one cell line to another. Such effects could also be related to the cell cycle. This might explain why PB.NLS-1–558, which was always located in the nucleus, had a more negative effect than PB.1–558 (Fig. 2a), which was mainly cytoplasmic during most of the cell cycle and in contact with chromosomes only during the cell division phase.
The second insight from this work concerns the ability of PB and both CRD-deficient pble transposases to trigger integration events that did not seem to occur at random into chromosomes. However, we cannot assume strict insertion site specificity of pble transposases since only a small part of the observed insertions events in datasets are the same, down to the same nucleotide position. However, our data demonstrated that these transposases displayed real preferences for insertion into regions containing genes and frequently close to their TSS. In addition, our results supported that pble transposases frequently targeted their pble insertions into genes committed to the central nervous system function. This last point will need further experimental confirmation. Indeed, the lengths of genes involved in nervous system function were, on average, longer than those of other genes (for review see [32]). An alternative interpretation might be that the insertion sites we found were preferentially located in neuronally expressed genes due to their size. However, our results take into account the genome coverage and the density in TTAA motif and support that the observed insertion preferences are not related these factors.
Contribution to the understanding of piggyBac transposition.
Previous studies suggested two roles for the CRD of PB. The CRD might be an essential component of DNA-binding to the ends of Ifp2, mandatory for transposition [9]. This was confirmed in another study, which also indicated that the CRD was essential for the assembly of the transposase dimer, the active oligomer form for transposition [10]. Here we demonstrate that two CRD-deficient piggyBac transposases were able to trigger proper pble transposition. Therefore, the CRD is not essential for transposition but seems necessary for triggering proper transposition events, probably by driving precise DNA cleavages at pble ends and directing a strict choice of TSD.
Evolutionary reasons for domesticating a CRD-deficient pble transposase
These results, as well as previously published data [14,20,21], have highlighted two properties of PB, and perhaps of other pble transposases, that may have previously been underestimated in the context of transposase-coding gene domestication. First, while PB mostly mediates proper Ifp2 transposition, it is also sometimes responsible for improper transposition that leads to neo-inserted elements that are difficult or impossible to re-mobilise during new rounds of transposition. Second, pble transposases might display strong preferences for insertion and genome rearrangements. Indeed, we noted that PGBD5 is highly expressed in the mammalian nervous system [20] and that current publicly available data (https://www.gtexportal.org/home/gene/PGBD5; https://www.proteinatlas.org/search/PGBD5) widely support this conclusion. However, these data concern mRNA expression and data regarding mRNA translation and protein expression will be required. Nevertheless, if acquiring a mechanism for triggering irreversible DNA rearrangements in the early steps of vertebrate evolution in the nervous system can be considered advantageous, then PGBD5 seems to possess all the properties required to play such a role. The evolutionary history of the RAG1/RAG2 proteins [33] suggests that each time a domesticated transposase has emerged during evolution its domestication was concurrent with the domestication of its transposon targets. In the PGBD5 context, verifying that pbles are domesticated and are used as binding targets by PGBD5 for genome rearrangements will be challenging. Indeed, while PGBD5 is a highly conserved protein in vertebrates, the pble landscape in these genomes varies drastically from one host species to the next. In the human genome three pbles unrelated to PGBD5 are annotated: MER75, MER85 and Looper. In the mouse genome only one pble closely related to human Looper is annotated. In the zebrafish seven pbles that were not related to PGBD5 and to those present in human and mouse genomes, have been annotated. In the chicken genome no pble has been found so far [34,35]. It is possible that PGBD5 has been domesticated in order to mobilise multiple pbles for recombination. Its protein sequence conservation in chicken and the absence of pbles in this species suggests that it binds to other DNA binding targets, which may be related to the PGBD5-specific signal (PSS) sequences observed in human rhabdoid tumors [14].
Materials and methods
cDNA cloning of PGBD5 murine isoforms.
A single mouse brain (strain C57Bl6) was used for total RNA extraction using Tri-reagent (Sigma-Aldrich, St-Louis, MO, USA). cDNA synthesis was carried out using Omniscript RT kit and oligo dT primers (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA). PCR primers with appropriate flanking restriction sites were synthesized by Eurofins Genomics, Ebersberg, Germany. PCR was performed with Phusion High-Fidelity PCR Master Mix (ThermoScientific). Following agarose gel electrophoresis, PCR fragments were extracted (QIAquick gel extraction kit, Qiagen), submitted to enzyme restriction (EcoRI/XbaI for the long N-term isoform and EcoRI/XhoI for the short N-term isoform), purified (QIAquick PCR purification kit, Qiagen) and kept for cloning. Their sequence identity was verified by Sanger sequencing (Eurofins Genomics, Ebersberg, Germany). The primers used to amplify Mm523 (Accession N°: XM_006530804.1) isoforms are supplied in supplementary data 1a.
Integration assay.
Plasmid expression for transposases.
The plasmids pCS2-PB and pCS2-PB.NLS-1–558 encode the V5 tagged PB transposases. Each cDNA was inserted into the multi-cloning site of the pCS2+ vector (Life Technologies, Paisley, UK) as described [36]. The plasmid pCS2-Mm523 encodes a two myc tagged PGBD5 isoform 524 amino acid residues in size. Mm523 cDNA was inserted into the multi-cloning site of a modified pCS2 vector with an in-frame N-term 5XMyc tag [37]. The plasmid pCS2-GFP plasmid was built by cloning the gene coding for the green fluorescent protein gene into the multi-cloning site of the pCS2+ vector. pCS2-GFP was used as a negative control of transposition (i.e. absence of transposase expression).
Plasmids donor of transposon.
The plasmid pBSK-IFP2-TIR5’-NeoR-TIR3’ (supplementary data 1b) was built by introducing the IFP2 5’ and 3’ terminal regions (262 and 400 bp, respectively) into the pBluescript SK plasmid (pBSK). A cassette (NeoR) containing a SV40 promoter, the neomycin phosphotransferase ORF and a sv40 terminator was cloned between transposon ends as described [36]. NeoR was cloned in its middle using a BamHI site that was added to its sequence during DNA synthesis. The plasmid pBSK-NeoR was built by cloning the NeoR cassette into the multi-cloning site of a pBSK plasmid as described [38].
Integration assay in HeLa cells.
Assays were monitored as described [36]. Briefly, each sample of 100000 cells in a well of a 24-well plates of plaque assays was co-transfected with JetPEI (Polyplus- transfection, Illkirch-Graffenstaden) and 400 ng DNA plasmid and with equal amounts of donor of NeoR cassette included or not within a transposon and transposase sources (1:1 ratio). Two days post-transfection, each cell sample was transferred to a cell culture dish (100 mm diameter) and selected with a culture medium containing 800 μg/mL G418 sulfate (Eurobio Scientific, Les Ulis) for 15 days. After two washing with 1X saline phosphate buffer, cell clones were fixed and stained overnight with 70% EtOH-0.5% methylene blue and colonies > 0.5 mm in diameter were counted. Experiments were performed at least twice in triplicate.
Integration assay in G401 cells.
Assays were monitored as described [14]. Two clonal cell G401 lines were used. The first line was lentivirally transduced to constitutively express specific shRNA suppressing the expression of Hs524 PGBD5 [14]. The second line was modified as a control to constitutively express shRNA to target GFP which is not expressed, thereby preserving the endogenous expression of Hs524 PGBD5. Briefly, each sample of 100000 cells in a well of a 24-well plates of plaque assays was transfected with jetOptimus and 500 ng DNA plasmid pBSK-IFP2-TIR5’-NeoR-TIR3’ as recommended by the supplier (Polyplus- transfection, Illkirch-Graffenstaden). Two days post-transfection, each cell sample was transferred to a cell culture dish (100 mm diameter) and selected with a culture medium containing 2 mg/mL G418 sulfate (Eurobio Scientific, Les Ulis) for 15 days. After two washing with 1X saline phosphate buffer, cell clones were fixed and stained overnight with 70% EtOH-0.5% methylene blue and colonies > 0.5 mm in diameter were counted. Experiments were performed at least twice in triplicate.
Cellular localization of green fluorescent protein-fusion proteins
Plasmid expression for transposase-GFP fusions.
The plasmids pCS2-PB-GFP, pCS2-PB.1–558, pCS2-PB.NLS-1–558 and pCS2-Mm523-GFP were made as described [39].
Cell manipulation.
HeLa cells were plated at a density of 5 × 104 cells per well in 1 cm2 Lab-Tek™ chamber slides (Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and grown in DMEM (Gibco/Life Technologies, Paisley, UK) supplemented with 10 % heat inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS, Eurobio, France) at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2 for 48 h. Cells were transfected with 500 ng plasmid DNA and jetPEI™ (Polyplus Transfection, Illkirch, France) at an N/P ratio of 5 in DMEM 10% FBS following the Manufacturer’s instructions. Cells were then incubated with the complexes for 4 h. The transfection medium was then discarded and replaced by fresh DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS before being incubated for 48 hours at 37°C.
Imaging.
Cells on slides were fixed in 1X PBS/2% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min, and then permeabilised with PBS/1% (w/v) Triton-X100 for 10 min. The slides were washed three times for 5 min with 1x PBS. Nuclei were stained using Vectashield Vibrance “Antifade Mounting Medium (hardening) + DAPI” (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame CA, USA). All images of fluorescence were collected with an LSM 700 laser scanning microscope and the associated Zen software (Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany). All images shown correspond to one focal plane (0.5 μm). Images to be used for figures were pseudocolored by LSM Image browser software (Carl Zeiss, Thornwood, NY) and Photoshop (Adobe Systems, San Jose, CA) was on the resulting tiff files only to adjust for brightness and contrast.
Recovery of integration sites.
LAM-PCR and Illumina libraries.
Integration assays were done to produce cell populations containing integrated copies of the donor transposon. Fifteen days post-transfection, cell clones were harvested for genomic DNA preparation using the DNeasy kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). Linear amplification-mediated PCR (LAM-PCR) was performed to amplify the vector-genomic DNA junctions of Ifp2 vectors as described [40]. All PCR were done using the high fidelity Q5 DNA Polymerase (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA). For both approaches, 1 μg DNA was used for twice 50 rounds of linear amplification using a biotinylated primer anchored near one end of the NeoR cassette to enrich DNA species containing transposon-chromosomal DNA junctions (for sequences of (B)-NeoR 5’ and 3’ primers, see supplementary data 1c). One reaction was done per ends. The single-stranded products were immobilized on streptadivin-coated magnetic beads (Dynabeads M-280 Streptavidin, Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). All subsequent steps were performed on the magnetic bead-bound DNA. Two washes with water followed each step. Second strand synthesis was performed with random hexamer primers (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) using Klenow DNA polymerase (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA). The double-stranded DNA was split in two batches and subjected to restriction digests with DpnI for the first one and PciI, NcoI and BspHI for the second one using restriction enzymes. The DNA fragments with a CG-3’ or a CATG-3’ overhang ends were ligated to linkers displaying appropriate overhang ends and made from annealed oligonucleotides (supplementary data 1c).
To increase the specificity of the full process, an initial PCR was done using one biotinylated primer anchored within the 5’ or 3’ region of the transposon donor and one primer anchored within the linker (for sequences of (B)-TIR-UTR 5’ and 3’, and LC1 primers, see supplementary data 1c). PCR products were immobilized on streptadivin-coated magnetic beads and purified as described above. Next, the bead-bound DNA was subjected to a nested PCR using nested primers anchored within transposon ends and within linkers (supplementary data 1c). Final PCR products were purified, quantified and gathered in equimolar DNA amounts for each transposon vector (4 populations of LAM-PCR products) before being used to make Illumina libraries using NEBNext® Ultra™ II DNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina® and NEBNext Multiplex Oligos for Illumina (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA). Fragment size selection, library quality control and Illumina sequencing (MiSeq 250 nucleotides, TruSeq SBS Kit v3) were achieved at the Plateforme de Séquençage Haut Débit I2BC (Gif-sur-Yvette, France). DNA quantities were monitored at various steps in the procedure with the Qubit® dsDNA (Molecular Probes, Eugene, USA).
Computer analysis.
Trimmomatic [41] was used to filter Miseq reads using default parameters, except for SLIDINGWINDOW:5:20 and MINLEN:100. The purpose of the following steps was to recover chromosome-inserted DNA fragment junctions taking into account the plasmid backbone regions located 100-bp upstream and downstream the Ifp2-NeoR transposon. Filtered reads were first mapped to the sequence of plasmid backbone minus the 100-bp regions flanking on both sides the Ifp2-NeoR transposon with bwa-mem using default parameters [42]. Unmapped reads were then extracted reads using SAMtools view with parameters -b -f 4 [43] and bamToFastq from the BEDTools suite using default parameters [44]. Recovered unmapped reads were aligned using bwa-mem against a bwa bank gathering the sequences of hg38 chromosomes plus those of the Ifp2-NeoR transposon flanked by the 100-bp plasmid backbone regions on both sides (supplementary data 1d). Default parameters were used excepted for -w 1 and -r 1. The bam files resulting from each dataset alignment were analysed with Lumpy in order to identify split reads [45]. The parameters were -e -mw 2 -tt 0.0 and back_distance:20,weight:1,id:lumpy_v1,min_mapping_threshold:20. Structural variants (SV) characterized by “BND” for the broken end notations and displaying for each of them an SV with two positions, one genomic and one on the transposon, were extracted using a house python program (https://github.com/Leelouh/lumpy2site). Results were filtered taking into account a difference below 3 between the transposon breakpoint calculated by Lumpy and the maximal spread of read alignments in the transposon donor sequence for each integration event. Each TSD nucleotide motif at insertion site was obtained after extracting 10-bp sequences before and after the breakpoint in the chromosome sequences.
Gene ontology (GO) analyses were focused mostly on protein coding genes and those encoding long non-coding RNA (lncRNA). We used hg38 gene annotations from UCSC. Gene ontology was first investigated using DAVID (https://david.ncifcrf.gov/) and AmiGO2 (http://amigo.geneontology.org/amigo) to assess term enrichment. This was followed up by the Cytoscape plugin ClueGO [46,47].
Access of publicly available data
Sequences corresponding to Ifp2, Sleeping Beauty and TcBuster insertion sites in HEK 293 cells [23] were downloaded from public databases using accession numbers JS717545 to JS799249. Sequences corresponding to Ifp2 insertion sites in HCT116 cells [15] were recovered at https://www.genetics.org/content/suppl/2012/01/03/genetics.111.137315.DC1. Sequences corresponding to Ifp2 and Sleeping Beauty insertion sites in CD4+ cells [26] were recovered in the GSE58744 at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSM1419000 and https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSM1419001. For the last two sources, the positions of insertion sites were transformed in hg38 using liftover at https://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgLiftOver. All sites mapped in hg38 were supplied in supplementary Table 4.
PWMTrain [48] at https://ccg.epfl.ch/pwmtools/pwmtrain.php was used to calculate the position-specific weight matrix of TcBuster insertion sites using available data [23]. The numbers and the positions of putative insertion sites in hg38 for pbles (TTAA), sleeping beauty (TA) and TcBuster were calculated using PWMScan [48] at https://ccg.epfl.ch//pwmtools/pwmscan.php. The list of 6985 neuron genes in hg19 was recovered in supplemental data of [31] and was updated to hg38. 131 genes were removed. They corresponded to artefactual genes coding nc RNA that were withdrawn in hg 38. DNAse1 map for HeLa and HEK293 cells were recovered at http://hgdownload.soe.ucsc.edu/wgEncodeAwgDnaseUwdukeHelas3UniPk.narrowPeak.gzgoldenPath/hg19/encodeDCC/wgEncodeOpenChromDnase/, files and http://hgdownload.soe.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/hg19/encodeDCC/wgEncodeAwgDnaseUniform/wgEncodeAwgDnaseUwdukeHelas3UniPk.narrowPeak.gz. They were updated in hg38 using liftover. Values in graphs were medians, quartiles 1 and 3 and spread of experiments done at least twice in triplicate. Shapiro-Wilk tests were used to confirm the normality of each set of samples, t-test to analyse distribution differences between experimental samples, Chi2 test to analyse differences between an experimental distribution and a theoretical one, and logarithmic distribution test to analyse enrichments using free tools and tutorials available at http://www.anastat.fr/outils.php. Permutation tests (10,000 per test) were computed using in-house bash programs that accounted the distribution in TA and TTAA motifs in hg38. The normality of each distribution of permuted results was verified using a Shapiro-Wilk test using free tools and tutorials available at http://www.anastats.fr/outils.php. When the distributions were normal, probabilities were calculated from Z score at https://www.fourmilab.ch/rpkp/experiments/analysis/zCalc.html. When they were not normal, the distributions were used to determine the 1 and 0.1% thresholds at both tails and the observed values were positioned in regards to those values.
Data deposition.
All raw and processed data are available through the European Nucleotide Archive under accession number PRJEB36226, PRJEB36229, PRJEB41045 and PRJEB41053. Files describing the annotation of insertion sites copies in the hg38 release are supplied as supplementary Tables 1, 2 and 3.
Supplementary Material
Supplementary data 1. Transposon donor sequences and primers used in the study.
Supplementary Table 1. (a) Inventory of Ifp2-chromosome junctions resulting from integration events mediated by PB. Transposon breakpoints located at positions 102 and 2220, 103 and 2219, 104 and 2218, and 105 and 2217 had a TSD displaying a DTAA, DDAA, DDBA or DDBB nucleotide motif (IUPAC nucleotide code; blue bars in Fig. 3a). Those at positions 101 and 2221, 100 and 2222, 99 and 2223, and 98 and 2224 (red bars in Fig. 3a) displayed a TTAA TSD with upstream or downstream 0 nucleotide, one nucleotide, a dinucleotide or a trinucleotide that were identical in the plasmid backbone and the chromosome. As the origin of this specific trait could not be differentiated with a probability threshold below 1%, all junctions were considered in the analysis as originating from proper integration events. (b) Inventory of chromosomal site in which Ifp2 insertions were found several times. Insertions corresponding to a single putative integration event were highlighted in cyan blue and their duplicated TSD was highlighted in green. Integration events corresponding to proper transposon ends were typed in black while those with improper ends were typed in red.
Supplementary Table 2. (a) Inventory of Ifp2-chromosome junctions resulting from integration events mediated by PB.NLS-1–558. Transposon breakpoints located at positions 102 and 2220, 103 and 2219, 104 and 2218, and 105 and 2217 had a TSD displaying a DTAA, DDAA, DDBA or DDBB nucleotide motif (IUPAC nucleotide code; blue bars in Fig. 3b). Those at positions 101 and 2221, 100 and 2222, 99 and 2223, and 98 and 2224 (red bars in Fig. 3b) displayed a TTAA TSD with upstream or downstream 0 nucleotide, one nucleotide, a dinucleotide or a trinucleotide that were identical in the plasmid backbone and the chromosome. As the origin of this specific trait could not be differentiated with a probability threshold below 1%, all junctions were considered in the analysis as originating from proper integration events. (b) Inventory of chromosomal site in which Ifp2 insertions were found several times. Insertions corresponding to a single putative integration event were highlighted in cyan blue and their duplicated TSD was highlighted in green. Integration events corresponding to proper transposon ends were typed in black while those with improper ends were typed in red.
Supplementary Table 3. (a) Inventory of Ifp2-chromosome junctions resulting from integration events mediated by Mm523. Transposon breakpoints located at positions 102 and 2220, 103 and 2219, 104 and 2218, and 105 and 2217 had a TSD displaying a DTAA, DDAA, DDBA or DDBB nucleotide motif (IUPAC nucleotide code; blue bars in Fig. 3c) displayed a TTAA TSD with upstream or downstream 0 nucleotide, one nucleotide, a dinucleotide or a trinucleotide that were identical in the plasmid backbone and the chromosome. As the origin of this specific trait could not be differentiated with a probability threshold below 1%, all junctions were considered in the analysis as originating from proper integration events. (b) Inventory of chromosomal site in which Ifp2 insertions were found several times. Insertions corresponding to a single putative integration event were highlighted in cyan blue and their duplicated TSD was highlighted in green. Integration events corresponding to proper transposon ends were typed in black while those with improper ends were typed in red.
Supplementary Table 4. (a) Inventory of Ifp2-chromosome junctions resulting from integration events mediated by Hs524 in G401 cells. Transposon breakpoints located at positions 102 and 2220, 103 and 2219, 104 and 2218, and 105 and 2217 had a TSD displaying a DTAA, DDAA, DDBA or DDBB nucleotide motif (IUPAC nucleotide code; blue bars in Fig. 3c) displayed a TTAA TSD with upstream or downstream 0 nucleotide, one nucleotide, a dinucleotide or a trinucleotide that were identical in the plasmid backbone and the chromosome. As the origin of this specific trait could not be differentiated with a probability threshold below 1%, all junctions were considered in the analysis as originating from proper integration events. (b) Inventory of chromosomal site in which Ifp2 insertions were found several times. Insertions corresponding to a single putative integration event were highlighted in cyan blue and their duplicated TSD was highlighted in green. Integration events corresponding to proper transposon ends were typed in black while those with improper ends were typed in red.
Supplementary Table 5. Chromosomal positions mapped here in hg38 for Ifp2 insertion sites in HEK293 (a), HCT116 (b) and CD4+ (c) cells, sleeping beauty in HEK293 (d) and CD4+ (e), and TcBuster in HEK293 (f).
Fig. 8. Venn diagram representations of intragenic regions overlapped by insertion site-containing regions (± 1000 bp) between transposition assays done with PB, PB.NLS-1–558, Mm523 and Hs524 (a) and with PB in HeLa, HEK293, HCT116 and CD4+ cells (b).
The numbers of intragenic regions specific of datasets were italicized and typed in grey. Those shared by all datasets were typed in orange.
Highlights.
The C-terminal CRD in pble transposases is not essential for transposition
Two CRD-deficient pble transposases trigger transposition of Ifp2
Proper and improper insertions occur when CRD-deficient transposases mediate mobility
CRD-deficient and full-length pble transposases do not insert transposons at random
Features of the domesticated transposase PGBD5 originate from wild type transposase
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the C.N.R.S., the I.N.R.A., and the GDR CNRS 2157. It also received funds from a research program grants from the Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer, the Merck foundation, and the French National Society of Gastroenterology. Laura Helou holds a PhD fellowship from the Région Centre Val de Loire. We acknowledge the high-throughput sequencing facility of I2BC for its sequencing and bioinformatics expertise. Alex Kentsis is a consultant for Novartis and is supported by the National Cancer Institute grants R01 CA214812 and P30 CA008748. Yves Bigot, who was in charge of the achievement of this project does not have to thank the French National Research Agency for its financial support but he kindly thanks it for the excellent reviews embellished with arguments based on scientific and cultural novelties in the expertise of his yearly application file during the last decade.
Abbreviations:
- CRD
cysteine-rich domain
- gDNA
genomic DNA
- GFP
green fluorescent protein
- ISCR
insertion sites-containing regions
- NeoR
neomycin resistance
- NLS
nuclear localisation signal
- ORF
open reading frame
- PB
piggyBac transposase
- pble
piggyBac-like element
- PGBD or pgbd
“piggyBac derived transposase” protein or gene
- STIR
sub-terminal inverted repeats
- SV40
simian virus 40
- TE
transposable element
- TIR
terminal inverted repeats
- TSD
target site duplication
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Piégu B, Bire S, Arensburger P, Bigot Y (2016) A survey of transposable element classification systems--a call for a fundamental update to meet the challenge of their diversity and complexity. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 86, 90–109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Arensburger P, Piégu B, Bigot Y (2016) The future of transposable element annotation and their classification in the light of functional genomics - what we can learn from the fables of Jean de la Fontaine? Mob. Genet. Elements. 6, e1256852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Arkhipova IR (2017) Using bioinformatic and phylogenetic approaches to classify transposable elements and understand their complex evolutionary histories. Mob. DNA. 8, 19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Goerner-Potvin P, Bourque G (2018) Computational tools to unmask transposable elements. Nat. Rev. Genet 19, 688–704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bouallègue M, Rouault JD, Hua-Van A, Makni M, Capy P (2017) Molecular Evolution of piggyBac Superfamily: From Selfishness to Domestication. Gen. Biol. Evol 9, 323–339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cary LC, Goebel M, Corsaro BG, Wang HG, Rosen E, Fraser MJ (1989) Transposon mutagenesis of baculoviruses: analysis of Trichoplusia ni transposon IFP2 insertions within the FP-locus of nuclear polyhedrosis viruses. Virology. 172, 156–169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yusa K (2015) piggyBac Transposon. Microbiol. Spectr 3, MDNA3–0028–2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chen Q, Luo W, Veach RA, Hickman AB, Wilson MH, Dyda F (2020) Structural basis of seamless excision and specific targeting by piggyBac transposase. Nat Commun 11, 3446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Morellet N, Li X, Wieninger SA, Taylor JL, Bischerour J, Moriau S, Lescop E, Bardiaux B, Mathy N, Assrir N, Bétermier M, Nilges M, Hickman AB, Dyda F, Craig NL, Guittet E (2018) Sequence-specific DNA binding activity of the cross-brace zinc finger motif of the piggyBac transposase. Nucl. Acids. Res 46, 2660–2677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sharma R, Nirwal S, Narayanan N, Nair DT (2018) Dimerization through the RING-Finger domain attenuates excision activity of the piggyBac transposase. Biochemistry. 57, 2913–2922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Keith JH, Fraser TS, Fraser MJ Jr. (2008) Analysis of the piggyBac transposase reveals a functional nuclear targeting signal in the 94 c-terminal residues. BMC. Mol. Biol 9, 72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hong JB, Chou FJ, Ku AT, Fan HH, Lee TL, Huang YH, Yang TL, Su IC, Yu IS, Lin SW, Chien CL, Ho HN, Chen YT (2014) A nucleolus-predominant piggyBac transposase, NP-mPB, mediates elevated transposition efficiency in mammalian Cells. PLoS. One. 9, e89396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Luo W, Galvan DL, Woodard LE, Dorset D, Levy S, Wilson MH (2017) Comparative analysis of chimeric ZFP-, TALE- and Cas9-piggyBac transposases for integration into a single locus in human cells. Nucl. Acids. Res 45, 8411–8422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Henssen AG, Koche R, Zhuang J, Jiang E, Reed C, Eisenberg A, Still E, MacArthur IC, Rodríguez-Fos E, Gonzalez S, Puiggròs M, Blackford AN, Mason CE, de Stanchina E, Gönen M, Emde AK, Shah M, Arora K, Reeves C, Socci ND, Perlman E, Antonescu CR;, Roberts CWM, Steen H, Mullen E, Jackson SP, Torrents D, Weng Z, Armstrong SA, Kentsis A (2017) PGBD5 promotes site-specific oncogenic mutations in human tumors. Nat. Genet 49, 1005–1014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wang H, Mayhew D, Chen X, Johnston M, Mitra RD (2012) “Calling cards” for DNA-binding proteins in mammalian cells. Genetics. 190, 941–949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Li MA, Pettitt SJ, Eckert S, Ning Z, Rice S, Cadiñanos J, Yusa K, Conte N, Bradley A (2013) The piggyBac transposon displays local and distant reintegration preferences and can cause mutations at noncanonical integration sites. Mol. Cell. Biol 33, 1317–1330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Thorvaldsdóttir H, Robinson JT, Mesirov JP (2013) Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): high-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief. Bioinformatics. 14, 178–192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Elick TA, Lobo N, Fraser MJ Jr. (1997) Analysis of the cis-acting DNA elements required for piggyBac transposable element excision. Mol. Gen. Genet 255, 605–610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mitra R, Fain-Thornton J, Craig NL (2008) piggyBac can bypass DNA synthesis during cut and paste transposition. EMBO. J 27, 1097–1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pavelitz T, Gray LT, Padilla SL, Bailey AD, Weiner AM (2013) PGBD5: a neural-specific intron containing piggyBac transposase domesticated over 500 million years ago and conserved from cephalochordates to humans. Mob. DNA. 4, 23–39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Henssen AG, Henaff E, Jiang E, Eisenberg AR, Carson JR, Villasante CM, Ray M, Still E, Burns M, Gandara J, Feschotte C, Mason CE, Kentsis A (2015) Genomic DNA transposition induced by human PGBD5. Elife. 4, e10565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lohe AR, Timmons C, Beerman I, Lozovskaya ER, Hartl DL (2000) Self-inflicted wounds, template-directed gap repair and a recombination hotspot. Effects of the mariner transposase. Genetics. 154, 647–656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Woodard LE, Li X, Malani N, Kaja A, Hice RH, Atkinson PW, Bushman FD, Craig NL, Wilson MH (2012) Comparative analysis of the recently discovered hAT transposon TcBuster in human cells. PLoS. One. 7, e42666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wilson MH, Coates CJ, George AL Jr. (2007) PiggyBac transposon-mediated gene transfer in human cells. Mol. Ther 15, 139–145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Huang X, Guo H, Tammana S, Jung YC, Mellgren E, Bassi P, Cao Q, Tu ZJ, Kim YC, Ekker SC, Wu X, Wang SM, Zhou X (2010) Gene transfer efficiency and genome-wide integration profiling of Sleeping Beauty, Tol2, and piggyBac transposons in human primary T cells. Mol. Ther 18, 1803–1813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gogol-Döring A, Ammar I, Gupta S, Bunse M, Miskey C, Chen W, Uckert W, Schulz TF, Izsvák Z, Ivics Z (2016) Genome-wide profiling reveals remarkable parallels between insertion site selection properties of the MLV retrovirus and the piggyBac transposon in primary human CD4(+) T cells. Mol Ther 24, 592–606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Landry JJ, Pyl PT, Rausch T, Zichner T, Tekkedil MM, Stütz AM, Jauch A, Aiyar RS, Pau G, Delhomme N, Gagneur J, Korbel JO, Huber W, Steinmetz LM (2013) The genomic and transcriptomic landscape of a HeLa cell line. G3 (Bethesda). 3, 1213–1224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Adey A, Burton JN, Kitzman JO, Hiatt JB, Lewis AP, Martin BK, Qiu R, Lee C, Shendure J (2013) The haplotype-resolved genome and epigenome of the aneuploid HeLa cancer cell line. Nature. 500, 207–211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lin YC, Boone M, Meuris L, Lemmens I, Van Roy N, Soete A, Reumers J, Moisse M, Plaisance S, Drmanac R, Chen J, Speleman F, Lambrechts D, Van de Peer Y, Tavernier J, Callewaert N (2014) Genome dynamics of the human embryonic kidney 293 lineage in response to cell biology manipulations. Nat Commun 5, 4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Liu Y, Mi Y, Mueller T, Kreibich S, Williams EG, Van Drogen A, Borel C, Frank M, Germain PL, Bludau I, Mehnert M, Seifert M, Emmenlauer M, Sorg I, Bezrukov F, Bena FS, Zhou H, Dehio C, Testa G, Saez-Rodriguez J, Antonarakis SE, Hardt WD, Aebersold R (2019) Multi-omic measurements of heterogeneity in HeLa cells across laboratories. Nat Biotechnol 37, 314–322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Negi SK, Guda C (2017) Global gene expression profiling of healthy human brain and its application in studying neurological disorders. Sci. Rep 7, 897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zylka MJ, Simon JM, Philpot BD (2015) Gene length matters in neurons. Neuron 86, 353–355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhang Y, Cheng TC, Huang G, Lu Q, Surleac MD, Mandell JD, Pontarotti P, Petrescu AJ, Xu A, Xiong Y, Schatz DG (2019) Transposon molecular domestication and the evolution of the RAG recombinase. Nature. 569, 79–84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Guizard S, Piégu B, Arensburger P, Guillou F, Bigot Y (2016) Deep landscape update of dispersed and tandem repeats in the genome model of the red jungle fowl, Gallus gallus, using a series of de novo investigating tools. BMC Genomics. 17, 659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kapusta A, Suh A (2017) Evolution of bird genomes-a transposon’s-eye view. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci 1389, 164–185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bire S, Ley D, Casteret S, Mermod N, Bigot Y, Rouleux-Bonnin F (2013) Optimization of the piggyBac transposon using mRNA and insulators: toward a more reliable gene delivery system. PLoS. One. 8, e82559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Travnickova-Bendova Z, Cermakian N, Reppert SM, Sassone-Corsi P (2002) Bimodal regulation of mPeriod promoters by CREB-dependent signaling and CLOCK/BMAL1 activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 99, 7728–7733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bire S, Casteret S, Piégu B, Beauclair L, Moiré N, Arensbuger P, Bigot Y (2016) Mariner Transposons Contain a Silencer: Possible Role of the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2. PLoS. Genet 12, e1005902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Demattei MV, Hedhili S, Sinzelle L, Bressac C, Casteret S, Moiré N, Cambefort J, Thomas X, Pollet N, Gantet P, Bigot Y (2011) Nuclear importation of Mariner transposases among eukaryotes: motif requirements and homo-protein interactions. PLoS One. 6, e23693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Bartholomae CC, Glimm H, von Kalle C, Schmidt M (2012) Insertion site pattern: global approach by linear amplification-mediated PCR and mass sequencing. Meth. Mol. Biol 859, 255–265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics. 30, 2114–2120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Li H, Durbin R (2010) Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform, Bioinformatics. 26, 589–595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R, and 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. (2009) The Sequence alignment/map (SAM) format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 25, 2078–2079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Quinlan AR, Hall IM (2010) BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics. 26, 841–842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Layer RM, Chiang C, Quinlan AR, Hall IM (2014) LUMPY: a probabilistic framework for structural variant discovery. Gen. Biol 15, R84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Hackl H, Charoentong P, Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Fridman WF, Pagès F, Trajanoski Z, Galon J (2009) ClueGO: a Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics. 25, 1091–1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Mlecnik B, Galon J, Bindea G (2018) Comprehensive functional analysis of large lists of genes and proteins. J. Proteomics. 171, 2–10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Ambrosini G, Groux R, Bucher P (2018) PWMScan: A Fast Tool for Scanning Entire Genomes with a Position-Specific Weight Matrix. Bioinformatics. 34, 2483–2484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary data 1. Transposon donor sequences and primers used in the study.
Supplementary Table 1. (a) Inventory of Ifp2-chromosome junctions resulting from integration events mediated by PB. Transposon breakpoints located at positions 102 and 2220, 103 and 2219, 104 and 2218, and 105 and 2217 had a TSD displaying a DTAA, DDAA, DDBA or DDBB nucleotide motif (IUPAC nucleotide code; blue bars in Fig. 3a). Those at positions 101 and 2221, 100 and 2222, 99 and 2223, and 98 and 2224 (red bars in Fig. 3a) displayed a TTAA TSD with upstream or downstream 0 nucleotide, one nucleotide, a dinucleotide or a trinucleotide that were identical in the plasmid backbone and the chromosome. As the origin of this specific trait could not be differentiated with a probability threshold below 1%, all junctions were considered in the analysis as originating from proper integration events. (b) Inventory of chromosomal site in which Ifp2 insertions were found several times. Insertions corresponding to a single putative integration event were highlighted in cyan blue and their duplicated TSD was highlighted in green. Integration events corresponding to proper transposon ends were typed in black while those with improper ends were typed in red.
Supplementary Table 2. (a) Inventory of Ifp2-chromosome junctions resulting from integration events mediated by PB.NLS-1–558. Transposon breakpoints located at positions 102 and 2220, 103 and 2219, 104 and 2218, and 105 and 2217 had a TSD displaying a DTAA, DDAA, DDBA or DDBB nucleotide motif (IUPAC nucleotide code; blue bars in Fig. 3b). Those at positions 101 and 2221, 100 and 2222, 99 and 2223, and 98 and 2224 (red bars in Fig. 3b) displayed a TTAA TSD with upstream or downstream 0 nucleotide, one nucleotide, a dinucleotide or a trinucleotide that were identical in the plasmid backbone and the chromosome. As the origin of this specific trait could not be differentiated with a probability threshold below 1%, all junctions were considered in the analysis as originating from proper integration events. (b) Inventory of chromosomal site in which Ifp2 insertions were found several times. Insertions corresponding to a single putative integration event were highlighted in cyan blue and their duplicated TSD was highlighted in green. Integration events corresponding to proper transposon ends were typed in black while those with improper ends were typed in red.
Supplementary Table 3. (a) Inventory of Ifp2-chromosome junctions resulting from integration events mediated by Mm523. Transposon breakpoints located at positions 102 and 2220, 103 and 2219, 104 and 2218, and 105 and 2217 had a TSD displaying a DTAA, DDAA, DDBA or DDBB nucleotide motif (IUPAC nucleotide code; blue bars in Fig. 3c) displayed a TTAA TSD with upstream or downstream 0 nucleotide, one nucleotide, a dinucleotide or a trinucleotide that were identical in the plasmid backbone and the chromosome. As the origin of this specific trait could not be differentiated with a probability threshold below 1%, all junctions were considered in the analysis as originating from proper integration events. (b) Inventory of chromosomal site in which Ifp2 insertions were found several times. Insertions corresponding to a single putative integration event were highlighted in cyan blue and their duplicated TSD was highlighted in green. Integration events corresponding to proper transposon ends were typed in black while those with improper ends were typed in red.
Supplementary Table 4. (a) Inventory of Ifp2-chromosome junctions resulting from integration events mediated by Hs524 in G401 cells. Transposon breakpoints located at positions 102 and 2220, 103 and 2219, 104 and 2218, and 105 and 2217 had a TSD displaying a DTAA, DDAA, DDBA or DDBB nucleotide motif (IUPAC nucleotide code; blue bars in Fig. 3c) displayed a TTAA TSD with upstream or downstream 0 nucleotide, one nucleotide, a dinucleotide or a trinucleotide that were identical in the plasmid backbone and the chromosome. As the origin of this specific trait could not be differentiated with a probability threshold below 1%, all junctions were considered in the analysis as originating from proper integration events. (b) Inventory of chromosomal site in which Ifp2 insertions were found several times. Insertions corresponding to a single putative integration event were highlighted in cyan blue and their duplicated TSD was highlighted in green. Integration events corresponding to proper transposon ends were typed in black while those with improper ends were typed in red.
Supplementary Table 5. Chromosomal positions mapped here in hg38 for Ifp2 insertion sites in HEK293 (a), HCT116 (b) and CD4+ (c) cells, sleeping beauty in HEK293 (d) and CD4+ (e), and TcBuster in HEK293 (f).