To the editor:
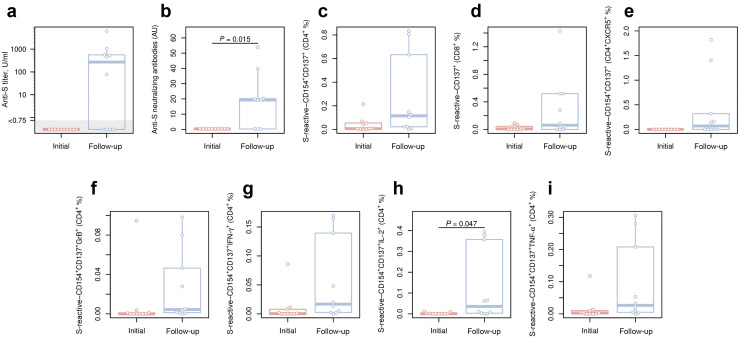
Renal transplant recipients (RTRs) are at a high risk for fatal coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).1 Vaccinations are indispensable to protect this vulnerable population. Unfortunately, >50% of solid organ recipients do not mount antibody responses after 2 doses of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) mRNA vaccines.2 , 3 We hypothesized that a third vaccine dose elicits protective humoral and cellular immune response in primary nonresponders. Ten RTRs under immunosuppression (Supplementary Table S1) without measurable SARS-CoV-2 spike antibodies 4 weeks after a second dose of BNT162b2 (Pfizer–BioNTech) received a third vaccine dose (mRNA-1273; Moderna), which was well-tolerated. For a description of the employed methods, see the Supplementary Methods. The third vaccination induced seroconversion in 6 subjects (60%) with a median antibody titer concentration of 542 (interquartile range, 478–923) U/ml and neutralizing capacity (Figure 1 a and b). Correspondingly, a strong increase in the magnitude of SARS-CoV-2 spike (S)-protein–reactive T-cell immunity (median, 0.08%) was observed in 9 subjects (90%; Figure 1c and d and Supplementary Table S1) with T-cell frequencies comparable to healthy individuals.2 Increased frequencies of cytokine-producing T cells and follicular T-helper cells indicated a gain of antiviral functionality (Figure 1e–i).
Figure 1.
Humoral and cellular response following the third vaccination in kidney transplant recipients in whom the primary vaccination failed. Renal transplant recipients with failed seroconversion after BNT162b2 (Pfizer–BioNTech) prime-boost vaccination were subjected to the third vaccination by mRNA-1273 (Moderna). Humoral and cellular immune responses before (red) and 2 weeks after (blue) the third vaccination are presented. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was performed for the assessment of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike (S)-protein–binding antibodies, and neutralizing antibody capacity was assessed by a pseudovirus system bearing the SARS-CoV-2 S-protein. S-protein–reactive T cells were analyzed by flow cytometry following an overnight stimulation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells with overlapping peptide pools (OPPs) spanning the S-protein of SARS-CoV-2. Activation markers CD154 and CD137 were used for the assessment and quantification of S-protein–reactive T cells within CD3+ T cells. Expression levels of cytokines, interferon gamma (IFNγ), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), and interleukin 2 (IL-2), as well as the effector molecule granzyme B (GrB), were analyzed among activated CD4+ T cells by intracellular staining and flow cytometry after stimulation with OPPs spanning the whole S-protein of SARS-CoV-2. Differences between the subcohorts were analyzed using the paired, 2-sided t test. The significance threshold was set at 0.05. Box plots depict the median and first and third quartiles of a variable; the maximum length of the whiskers corresponds to 1.5× the interquartile range. (a) Titers of anti–SARS-CoV-2 S-protein–binding antibodies assessed by ELISA. (b) Neutralizing antibody titers for the SARS-CoV-2 S-protein. (c) Frequencies of S-reactive CD4+ T cells, as defined by CD154+CD137+ expression. (d) Frequencies of S-reactive CD8+ T cells, as defined by CD137 expression and cytokine production. (e) Frequencies of S-reactive follicular CD4+ T-helper cells, as defined by the expression of CXC chemokine receptor 5 (CXCR5). (f–i) Frequencies of S-reactive CD4+ T cells producing (f) GrB, (g) IFNγ, (h) IL2, and (i) TNFα. AU, arbitrary unit.
Compared with recent data showing increased SARS-CoV-2 S-protein antibody levels in transplant patients after 3-dose SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination,4 , 5 our study provides a deeper immunologic characterization of vaccination-specific immunity, as demonstrated by antibody neutralizing capacity and spike-reactive T-cell immunity.
In summary, a third dose of an mRNA vaccine elicits a humoral and cellular response in 60% and 90% of RTR patients, respectively, who failed the primary vaccination. Although larger cohort studies with longer observation time are needed to confirm our results, the exceptionally high risk of fatal COVID-19 in RTRs supports consideration of a third vaccination in clinical practice.
Data Statement
Data will be available on request.
Acknowledgments
We feel deep gratitude to the patients who donated their blood samples and clinical data for this project. We would like to acknowledge the excellent technical assistance as well as the expertise of immune diagnostic laboratory (Sarah Skrzypczyk, Eva Kohut, Julia Kurek, and Jan Zapka) of the Center for Translational Medicine at Marien Hospital Herne. This work was supported by grants of the Mercator Foundation, German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) NoChro (No. 13GW0338B), and AiF/ZIM project EpiCov.
Footnotes
Table S1. Study population. Description of the demographic and clinical characteristics of the cohort, including information on the anti–severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) humoral immune response after the first, second, and third doses and corresponding cellular immune response.
Supplementary Methods. Concise description of the employed methods.
Supplementary Material
References
- 1.ERA-EDTA Council; ERACODA Working Group Chronic kidney disease is a key risk factor for severe COVID-19: a call to action by the ERA-EDTA. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2021;36:87–94. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfaa314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sattler A., Schrezenmeier E., Weber U.A. Impaired humoral and cellular immunity after SARS-CoV2 BNT162b2 (Tozinameran) prime-boost vaccination in kidney transplant recipients. J Clin Invest. 2021;131 doi: 10.1172/JCI150175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Miele M., Busà R., Russelli G. Impaired anti-SARS-CoV-2 humoral and cellular immune response induced by Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in solid organ transplanted patients. Am J Transplant. 2021;21:2919–2921. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kamar N., Abravanel F., Marion O. Three doses of an mRNA Covid-19 vaccine in solid-organ transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:661–662. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2108861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Werbel W.A., Boyarsky B.J., Ou M.T. Safety and immunogenicity of a third dose of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in solid organ transplant recipients: a case series. Ann Intern Med. 2021;174:1330–1332. doi: 10.7326/L21-0282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.