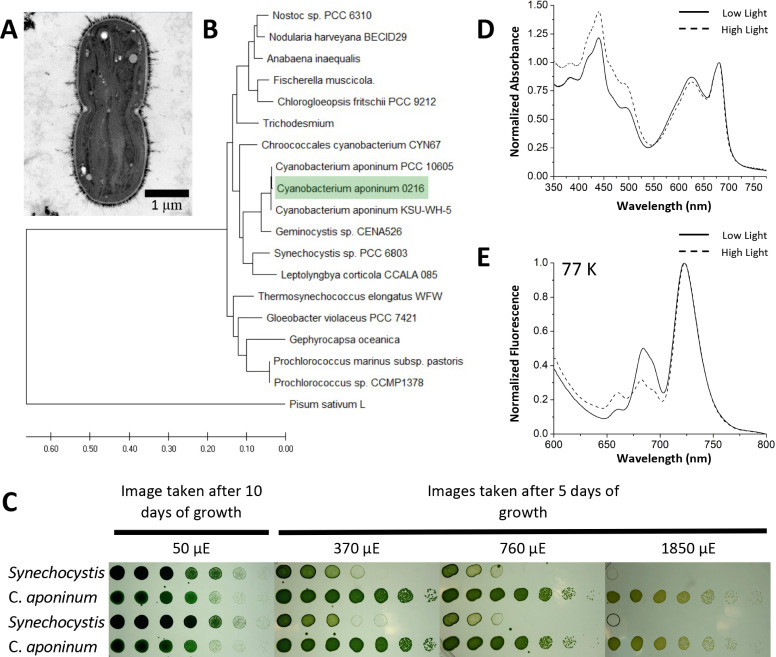
Figure 1. Isolation of a high-light-tolerant cyanobacteria.
(A) Cross-sectional negative stained image of C. aponinum fixed in acrylic medium. (B) Phylogenetic analysis based on C. aponinum 16 S rRNA. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA7. (C) Serial dilutions of Synechocystis and C. aponinum on BG11 plates. Cells were serially diluted in ¼ steps and incubated at 30°C for 5 days (light intensities > 370 µmol photons m–2s–1) and 10 days (light intensity = 50 µmol photons m–2s–1) (D) in vivo absorption spectra (normalized to the max wavelength of the Qy transition) of C. aponinum cells grown in low light (45 µmol photons m–2s–1) and high light (450 µmol photons m–2s–1). (E) 77 K fluorescence spectra (normalized to the max emission wavelength) of whole cells excited at 440 nm.