Abstract
The study results serve as a reminder for parents, children, and drivers to be alert to the danger of traffic crashes on Halloween. The aim of this study was to examine whether Halloween is associated with a higher incidence of traffic injuries and whether traffic injuries sustained on Halloween are more severe than those sustained on other days. The U.K. STATS19 database, including the data of all road traffic crashes occurring from 1990 to 2017, was employed. A total of 73,587 pediatric traffic casualties (involving pedestrians, cyclists, and moped riders) were included. Between 17:00 and 19:00 (17:00~18:59) on Halloween, the number of casualties was higher than that on other public holidays and usual days. The logistic regression model revealed that, between 17:00 and 18:00 (17:00~17:59), the risk of being killed or seriously injured on Halloween was 34.2% higher (odds ratio = 1.342; 95% CI = 1.065–1.692) than that on other days. Pediatric crashes occurring on Halloween are associated with a higher number of injuries and increased injury severity.
Keywords: Halloween, pediatric traffic injury, injury severity
1. Introduction
Injury is a leading cause of death in children [1]. Pedestrian injury is the second leading cause of injury-related death in the United States for children aged 5 to 14 years [2]. Almost one-fifth (19%) of children aged 14 years and younger who were killed in traffic crashes were found to be pedestrians [3]. Children living in an urban or high-density area are at higher risk of being injured or killed as a pedestrian. Incidents resulting in child pedestrian fatalities are the most frequent during spring and fall, with the highest number of child pedestrian deaths caused by motor vehicle crashes occurring during May and October [4].
On holidays, many activities are held in which people participate in a creative environment where injuries commonly occur. The holidays with the highest number of injuries per year were discovered to be Labor Day, Memorial Day, the Fourth of July, and Halloween [5]. Researchers have evaluated the injury risk associated with specific holidays. Some studies have investigated the occurrence of firework-related injuries on the Fourth of July [6,7], whereas other studies have determined the risk of hand lacerations during the carving of Halloween pumpkins [8]. Research focusing on Christmas has investigated eye injuries caused by Christmas trees [9], inhalation of Christmas ornaments, ingestion of decorations, and effects of toxic plants such as mistletoe [10].
On average, 41 million children trick-or-treat every Halloween. In the day and in the evening on this specific holiday, children are outdoors trick-or-treating, walking along sidewalks and roadways, and crossing streets. Children are particularly vulnerable to injuries as a pedestrian. Because their cognitive, developmental, behavioral, physical, and sensory abilities are not as efficient as those of adults, they tend to have difficulty making appropriate judgment when faced with a traffic threat. Parents often misestimate their child’s ability to judge pedestrian danger, which makes this phenomenon even more concerning [11]. Children are impulsive and have not yet developed the skills to judge how far away a car is and how quickly it is approaching [12].
Both children and parents must understand the potential dangers that children face on Halloween and the steps they can take to remain safe. In this study, we proposed two research hypotheses: first, more traffic injuries occur on Halloween than on other days of the year; and second, traffic injuries sustained on Halloween are generally more severe than those sustained on other days of the year.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
The current research used the U.K. STATS19 database, which contains the data of all road traffic accidents. Crashes that result in personal injury must be reported to the police within 30 days. The variables collected in this study were crash, vehicle, and casualty characteristics. This study was approved by the Taipei Medical University Joint Institutional Review Board (N202011030. MOST 110-2410-H-038-016-MY2).
2.2. Casualties
This study focused on child casualties who were pedestrians and bicyclists involved in crashes with a bicycle, motorcycle, or motor vehicle. On Halloween, celebrations such as trick-or-treating generally begin at dusk (i.e., after 16:00); thus, data were collected for the period of 16:00 to 00:00 (16:00~23:59). Pediatric casualties aged 4 to 17 years were included in the analysis. We excluded casualties with missing data for sex, age, speed limit, crash time, or vehicle type. A total of 73,587 casualties over the period from 1990 to 2017 were included in the final dataset.
2.3. Outcome and Variable Definitions
In the STATS19 database, the injury severity levels are fatal, serious, and slight injuries. The definition of serious injury is as follows: injury that results in hospitalization or any of the following injuries: fracture, concussion, internal injuries, crushing, and severe general shock requiring medical treatment. Slight injuries include mild injuries such as sprains (including whiplash), bruises, and cuts requiring roadside attention. Injuries not requiring medical treatment are also classified as slight injuries. Fatal injury is defined as injuries that cause death fewer than 30 days after the accident. Fatal and serious injuries are combined together as killed or seriously injured (KSIs).
Types of vehicles involved in pediatric crashes include bicycles, motorcycles, automobiles, and large vehicles. Weather was categorized as either fine or adverse, which included rain and snow. Road surface condition was categorized as dry and not dry. U.K. car speed limits are generally 30 mph in urban areas, 60 mph on main single-carriageway roads, and 70 mph on dual carriageways and motorways. Thus, we used 30 mph as a threshold for urban and rural road type. Roads with speed limits of 30 miles per hour and higher were defined as rural, whereas those with speed limits lower than 30 miles per hour were defined as urban.
Days on which crashes occurred were classified into four categories: Halloween (31 October), public holidays, weekdays, and weekend days. The public holidays considered were New Year’s Day, Good Friday, Easter Monday, summer bank holidays, spring bank holidays, Christmas Day, Boxing Day, the Queen’s 2002 Golden Jubilee, and the Queen’s 2012 Diamond Jubilee.
Because the activities on Halloween start in the evening and last until midnight, during this period, the children may be particularly vulnerable to traffic injuries during their activities. Hourly variation in injury risk was examined, with a focus on crashes that occurred between 16:00 and 00:00 (16:00~23:59). Injury prevalence (for both all injuries and KSIs) and injury severity (the proportion of KSIs) were evaluated.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The primary analysis compared the mean hourly numbers of casualties and KSIs across the four categories of days. In addition, to investigate the effect of Halloween on injury severity, we compared the proportion of KSIs among casualties across sex, weather condition, road type, vehicle type, and day type subgroups in each period using the chi-square test. A multiple logistic regression model was used to explore the associations between potential risk factors and KSIs and to calculate adjusted odds ratios (AORs). An alpha value of 0.05 was used, yielding a confidence level of 95%. Complete case analysis was performed in this study. Missing data were considered to be at least missing at random, and cases with missing data were thus excluded from the analysis.
3. Results
Table 1 shows the characteristics of casualties that occurred from 1990 to 2017. A total of 73,587 casualties were included in this study; more casualties occurred among girls than among boys (59.28% vs. 40.72%). As high as 91% of crashes occurred in an urban setting. More than 90% of casualties resulted from a crash with an automobile. Among these casualties, almost 24.77% were classified as KSI. The number of casualties was higher on weekdays, which accounted for 71.16% of the total, followed by public holidays (approximately 20.80%), Halloweens (1.91%), and weekend days (1.13%).
Table 1.
Characteristics of casualties from 1990 to 2017.
| Characteristic | Number of Casualties | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Female | 43,625 | 59.28 |
| Male | 29,962 | 40.72 |
| Road type | ||
| Rural | 6504 | 8.84 |
| Urban | 67,083 | 91.16 |
| Weather | ||
| Fine | 59,076 | 80.28 |
| Adverse | 14,511 | 19.72 |
| Road condition | ||
| Dry | 46,753 | 63.53 |
| Not dry | 26,834 | 36.47 |
| Period of 16:00 to 00:00 | ||
| Weekday | 56,041 | 71.16 |
| Weekend day | 831 | 1.13 |
| Public holiday | 15,308 | 20.80 |
| Halloween | 1407 | 1.91 |
| Period of 16:00 to 17:00 | ||
| Weekday | 8508 | 85.27 |
| Weekend day | 59 | 0.59 |
| Public holiday | 1283 | 12.86 |
| Halloween | 128 | 1.28 |
| Period of 17:00 to 18:00 | ||
| Weekday | 9645 | 79.56 |
| Weekend day | 43 | 0.35 |
| Public holiday | 2062 | 17.01 |
| Halloween | 373 | 3.08 |
| Period of 18:00 to 19:00 | ||
| Weekday | 10,284 | 77.90 |
| Weekend day | 49 | 0.37 |
| Public holiday | 2500 | 18.94 |
| Halloween | 368 | 2.79 |
| Period of 19:00 to 20:00 | ||
| Weekday | 9679 | 75.81 |
| Weekend day | 160 | 1.25 |
| Public holiday | 2670 | 20.91 |
| Halloween | 259 | 2.03 |
| Period of 20:00 to 21:00 | ||
| Weekday | 7269 | 71.58 |
| Weekend day | 233 | 2.29 |
| Public holiday | 2509 | 24.71 |
| Halloween | 144 | 1.42 |
| Period of 21:00 to 22:00 | ||
| Weekday | 5828 | 72.45 |
| Weekend day | 153 | 1.90 |
| Public holiday | 1995 | 24.80 |
| Halloween | 68 | 0.85 |
| Period of 22:00 to 23:00 | ||
| Weekday | 3073 | 68.36 |
| Weekend day | 78 | 1.74 |
| Public holiday | 1298 | 28.88 |
| Halloween | 46 | 1.02 |
| Period of 23:00 to 00:00 | ||
| Weekday | 1755 | 62.17 |
| Weekend day | 56 | 1.98 |
| Public holiday | 991 | 35.10 |
| Halloween | 21 | 0.74 |
| Type of vehicle involved | ||
| Automobile | 66,926 | 90.95 |
| Large vehicle | 4215 | 5.73 |
| Motorcycle | 2105 | 2.86 |
| Bicycle | 341 | 0.46 |
| Injury severity | ||
| Slight injury | 55,358 | 75.23 |
| KSI | 18,229 | 24.77 |
| Total | 73,587 | 100.00 |
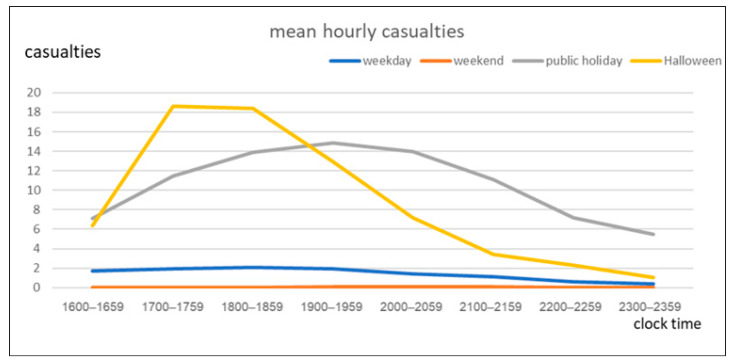
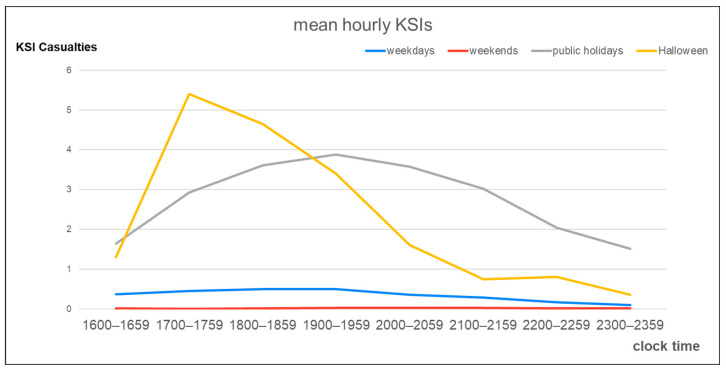
Figure 1 presents the mean number of hourly casualties over the period from 16:00 to 00:00 (16:00~23:59). From 17:00 to 19:00 (17:00~18:59), the number of casualties was higher on Halloweens (18.6 and 18.4 cases/h, respectively) than on the other day types. Figure 2 illustrates the mean number of hourly KSIs for the different day types. During the hours from 17:00 to 19:00 (17:00~18:59), the number of KSIs per hour was the highest on Halloweens (5.4 and 4.6 cases/h, respectively).
Figure 1.
Mean hourly casualties by type of day.
Figure 2.
Mean number of hourly KSIs by type of day.
Table 2 presents the distribution of KSIs by each independent variable. Boys were more likely to sustain KSIs than girls (25.87% vs. 23.17%). The KSI risk was higher on rural roads (40.73%) than on urban roads (23.22%). The KSI percentage was the highest for children involved in a crash with a large vehicle (30.65%) compared with crashes with the other vehicle types. In the period from 17:00 to 18:00 (17:00~17:59), the proportion of KSIs showed a significant difference, which was the highest for crashes on Halloweens (28.95%) compared with crashes on other day types.
Table 2.
Distribution of injury severity by risk factor during 1990 to 2017.
| Characteristics | KSI n (%) | Slight Injury n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | <0.001 | ||
| Female | 6943 (23.17%) | 23,019 (76.83%) | |
| Male | 11,286 (25.87%) | 32,339 (74.13%) | |
| Road type | <0.001 | ||
| Rural | 2649 (40.73%) | 3855 (59.27%) | |
| Urban | 15,580 (23.22%) | 51,503 (76.78%) | |
| Weather | <0.001 | ||
| Fine | 14,912 (25.24%) | 44,164 (74.76%) | |
| Adverse | 3317 (22.86%) | 11,194 (77.14%) | |
| Road condition | 0.662 | ||
| Dry | 11,557 (24.72%) | 35,196 (75.28%) | |
| Not dry | 6672 (24.86%) | 20,162 (75.14%) | |
| Period of 16:00 to 17:00 | 0.450 | ||
| Weekday | 1865 (21.92%) | 6643 (78.08%) | |
| Weekend day | 17 (28.81%) | 42 (71.19%) | |
| Public holiday | 296 (23.07%) | 987 (76.93%) | |
| Halloween | 26 (20.31%) | 102 (79.69%) | |
| Period of 17:00 to 18:00 | 0.021 | ||
| Weekday | 2267 (23.50%) | 7378 (76.50%) | |
| Weekend day | 8 (18.60%) | 35 (81.40%) | |
| Public holiday | 527 (25.56%) | 1535 (74.44%) | |
| Halloween | 108 (28.95%) | 265 (71.05%) | |
| Period of 18:00 to 19:00 | 0.304 | ||
| Weekday | 2487 (24.18%) | 7797 (75.82%) | |
| Weekend day | 13 (26.53%) | 36 (73.47%) | |
| Public holiday | 649 (25.96%) | 1851 (74.04%) | |
| Halloween | 93 (25.27%) | 275 (74.73%) | |
| Period of 19:00 to 20:00 | 0.576 | ||
| Weekday | 2490 (25.73%) | 7189 (74.27%) | |
| Weekend day | 34 (21.25%) | 126 (78.75%) | |
| Public holiday | 699 (26.18%) | 1971 (73.82%) | |
| Halloween | 68 (26.25%) | 191 (73.75%) | |
| Period of 20:00 to 21:00 | 0.705 | ||
| Weekday | 1825 (25.11%) | 5444 (74.89%) | |
| Weekend day | 54 (23.18%) | 179 (76.82%) | |
| Public holiday | 642 (25.59%) | 1867 (74.41%) | |
| Halloween | 32 (22.22%) | 112 (77.78%) | |
| Period of 21:00 to 22:00 | 0.040 | ||
| Weekday | 1404 (24.09%) | 4424 (75.91%) | |
| Weekend day | 38 (24.84%) | 115 (75.16%) | |
| Public holiday | 544 (27.27%) | 1451 (72.73%) | |
| Halloween | 15 (22.06%) | 53 (77.94%) | |
| Period of 22:00 to 23:00 | 0.342 | ||
| Weekday | 851 (27.69%) | 2222 (72.31%) | |
| Weekend day | 16 (20.51%) | 62 (79.49%) | |
| Public holiday | 367 (28.27%) | 931 (71.73%) | |
| Halloween | 16 (34.78%) | 30 (65.22%) | |
| Period of 23:00 to 00:00 | 0.903 | ||
| Weekday | 486 (27.69%) | 1269 (72.31) | |
| Weekend day | 14 (25.00%) | 42 (75.00%) | |
| Public holiday | 271 (27.35%) | 720 (72.65%) | |
| Halloween | 7 (33.33%) | 14 (66.67%) | |
| Type of vehicle involved | <0.001 | ||
| Automobile | 16,383 (24.48%) | 50,543 (75.52%) | |
| Large vehicle | 1292 (30.65%) | 2933 (69.35%) | |
| Motorcycle | 477 (22.66%) | 1628 (77.34%) | |
| Bicycle | 77 (22.58%) | 264 (77.42%) |
Table 3 presents the results of logistic regression analysis of KSI risk factors. From 17:00 to 16:00 (17:00~17:59), pediatric casualties involved in a crash on Halloween were 34.2% more likely to sustain KSIs than were those involved in a crash on a different day type (AOR = 1.342; 95% CI = 1.065–1.692). Other KSI risk factors included a crash involving an automobile (AOR = 1.443; 95% CI = 1.108–1.879), when the casualties were boys (AOR = 1.156; 95% CI = 1.117–1.197), a crash occurring in a rural area (AOR = 2.261; 95% CI = 2.144–2.385), fine weather (AOR = 1.209; 95% CI = 1.151–1.274), and a wet road surface (AOR = 1.1; 95% CI = 1.051–1.143).
Table 3.
Logistic regression results of factors associated with KSI casualties.
| Variables | β | Standard Error | AOR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 0.145 | 0.018 | 1.156 (1.117–1.197) | <0.001 |
| Female (ref) | - | |||
| Road type | ||||
| Rural | 0.816 | 0.027 | 2.261 (2.144–2.385) | <0.001 |
| Urban (ref) | - | |||
| Weather | ||||
| Fine | 0.190 | 0.027 | 1.209 (1.148–1.274) | <0.001 |
| Adverse (ref) | - | |||
| Road condition | ||||
| Not dry | 0.092 | 0.022 | 1.100 (1.051–1.143) | <0.001 |
| Dry (ref) | - | |||
| Type of vehicle involved | ||||
| Motorcycle | −0.027 | 0.141 | 0.974 (0.739–1.283) | 0.850 |
| Automobile | 0.367 | 0.135 | 1.443 (1.108–1.879) | 0.006 |
| Large vehicle | 0.065 | 0.131 | 1.067 (0.826–1.378) | 0.621 |
| Bicycle (ref) | - | |||
| Period of 16:00 to 17:00 | ||||
| Halloween | −0.032 | 0.222 | 0.969 (0.626–1.498) | 0.886 |
| Public holiday | 0.092 | 0.072 | 1.096 (0.952–1.262) | 0.203 |
| Weekend day | 0.406 | 0.291 | 1.501 (0.849–2.652) | 0.162 |
| Weekday (ref) | - | - | ||
| Period of 17:00 to 18:00 | ||||
| Halloween | 0.294 | 0.118 | 1.342 (1.065–1.692) | 0.013 |
| Public holiday | −0.108 | 0.056 | 1.114 (0.997–1.244) | 0.057 |
| Weekend day | −0.356 | 0.396 | 0.701 (0.322–1.524) | 0.369 |
| Weekday (ref) | - | - | ||
| Period of 18:00 to 19:00 | ||||
| Halloween | 0.078 | 0.123 | 1.081 (0.849–1.376) | 0.527 |
| Public holiday | 0.095 | 0.052 | 1.100 (0.994–1.216) | 0.066 |
| Weekend day | 0.119 | 0.327 | 1.127 (0.593–2.140) | 0.716 |
| Weekday (ref) | - | - | ||
| Period of 19:00 to 20:00 | ||||
| Halloween | 0.053 | 0.144 | 1.054 (0.795–1.398) | 0.714 |
| Public holiday | 0.026 | 0.050 | 1.027 (0.931–1.133) | 0.599 |
| Weekend day | −0.199 | 0.195 | 0.820 (0.559–1.202) | 0.309 |
| Weekday (ref) | - | - | ||
| Period of 20:00 to 21:00 | ||||
| Halloween | −0.159 | 0.204 | 0.853 (0.572–1.271) | 0.434 |
| Public holiday | 0.009 | 0.054 | 1.010 (0.908–1.121) | 0.867 |
| Weekend day | −0.125 | 0.159 | 0.883 (0.647–1.206) | 0.433 |
| Weekday (ref) | - | - | ||
| Period of 21:00 to 22:00 | ||||
| Halloween | −0.125 | 0.296 | 0.882 (0.493–1.577) | 0.672 |
| Public holiday | 0.156 | 0.060 | 1.170 (1.040–1.314) | 0.009 |
| Weekend day | 0.071 | 0.191 | 1.073 (0.738–1.560) | 0.712 |
| Weekday (ref) | - | - | ||
| Period of 22:00 to 23:00 | ||||
| Halloween | 0.212 | 0.319 | 1.237 (0.662–2.311) | 0.506 |
| Public holiday | 0.013 | 0.075 | 1.013 (0.875–1.173) | 0.862 |
| Weekend day | −0.389 | 0.286 | 0.678 (0.387–1.188) | 0.174 |
| Weekday (ref) | - | - | ||
| Period of 23:00 to 00:00 | ||||
| Halloween | 0.257 | 0.474 | 1.293 (0.511–3.272) | 0.588 |
| Public holiday | −0.023 | 0.091 | 0.977 (0.818–1.168) | 0.799 |
| Weekend day | −0.054 | 0.320 | 0.947 (0.506–1.773) | 0.865 |
| Weekday (ref) | - | - |
4. Discussion
Our research indicates that, between 17:00 and 19:00 (17:00~18:59) on Halloween, the numbers of all injuries and specifically KSIs among children injured in a traffic crashes were higher than those on all the other days and holidays. In the event that crashes occurred between 17:00 and 18:00 (17:00~17:59) on Halloween, pediatric casualties were 34% more likely to sustain KSIs than those that occurred on a different day and in different periods. Two points relating to our results are worthy of note: (a) both all injuries and KSIs are more prevalent between 17:00 and 19:00 (17:00~18:59) on Halloween; and (b) injuries that occur between 17:00 and 18:00 (17:00~17:59) on Halloween are more severe than those occurring at any other time and day.
A few studies have revealed no significant difference in relative risks during the Halloween season in most situations, including vehicle accidents, accidental poisoning and drowning, and adverse drug effects [13]. Our results derived from the U.K. STATS19 dataset are similar to studies reporting a 49% increase in the risks of pediatric fatal pedestrian crashes on Halloweens in the United States [14,15]. In addition to the results showing a higher number of fatalities on this holiday, our study contributes to the pediatric injury literature by concluding that injury severity is the highest between 17:00 and 18:00 (17:00~17:59) on Halloween. The general rule appears to be trick-or-treating starts around 16:00 or 17:00 and should end around 20:00 [16]. The rush hour is a time when commuters and students are on their way to work/school and, in the United Kingdom, this is generally considered to be between 16:00 and 19:00 in the evening [17]. The activities on the Halloween start during the rush hour, which may lead to more traffic casualties and more severe injuries. Our result indicates that parents, children, and drivers should stay alert to the potential danger of crashes during this time.
Recently, scholars have reported that insufficient awareness of road safety, high degree of urbanization, high population density, and high traffic volume are risk factors for pediatrics casualties. The dusk hours—late afternoon and early evening—are also a high-risk period [15,18]. Some studies have demonstrated that distraction may have an adverse effect on pediatric pedestrian safety [12,19,20,21]. Trick-or-treating is one of main activities conducted on Halloween. Children dress up in various costumes such as a ghost, ring each neighbor’s doorbell, and shout “trick or treat!” Wearing a costume at night and knocking on doors increase the risk of a crash.
According to the report from the European, in the pedestrian casualties, some factors such as male, crash with the car, and area speed limit of about 30 mph are associated with severe injuries [22]. Our study also has similar results.
The World Health Organization has proposed the 3E strategies—education, engineering, and enforcement—for reducing the risks to pedestrian children [23]. A comprehensive model should be developed and should combine education with community and environmental interventions. The public and parents must recognize that children participating in various activities on Halloween have a high risk of being involved in an accident and being severely injured. Strengthening safety education for both parents and children—adding reflective panels to costumes, increasing numbers of community road caretakers, and reminding drivers to slow down on this holiday—may be effective countermeasures.
5. Limitations
This study has some limitations. First, limited data were available for some independent variables, such as the education level of parents, community economy, traffic volume, and geographic distribution of communities and road types, and these variables may crucially affect the number and type of crashes involving children. Moreover, this study used a national database in which information on injury sites was unavailable. Analysis with consideration of different injury sites is necessary for developing effective preventive policies. Further studies should include these factors and a dataset combined with hospital-based data in analysis. In addition, many factors are insignificant, which may be affected by the heterogeneity of individuals; a mixed logit model such as random parameters Bayesian LASSO modeling may be used in the future study to resolve the problem [24].
6. Conclusions
Children are more likely to sustain road traffic injuries on this holiday. Our research indicates that, between 17:00 and 19:00 (17:00~18:59) on Halloween days, the numbers of all injuries and specifically KSIs among pediatrics traffic casualties were higher than those on all the other day types. Moreover, for a crash that occurred between 17:00 and 18:00 (17:00~17:59) on Halloween, KSIs were 34.2% more likely in pediatrics casualties than on other days and at other times. Our results indicate that parents, children, and drivers should stay alert to the potential dangers faced by children during this time.
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to the Taipei Medical University, which has supported this research.
Author Contributions
L.-M.H.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing—original draft. B.S.W.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing—original draft. P.-L.C.: Conceptualization. W.S.: Conceptualization. H.-A.L.: Conceptualization. C.-W.P.: Conceptualization, Writing—review & editing, Supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
One author (C.-W.P) received funding from MOST, Taiwan (Grant numbers: MOST 109-2314-B-038-066 and MOST 110-2410-H-038-016-MY2). The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by Taipei Medical University Joint Institutional Review Board (N202011030).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The current research used the U.K. STATS19 database, which contains the data of all road traffic accidents.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Hughes K., McHale P., Wyke S., Lowey H., Bellis M.A. Child injury: Using national emergency department monitoring systems to identify temporal and demographic risk factors. Inj. Prev. J. Int. Soc. Child Adolesc. Inj. Prev. 2014;20:74–80. doi: 10.1136/injuryprev-2013-040816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chakravarthy B., Vaca F.E., Lotfipour S., Bradley D. Pediatric pedestrian injuries: Emergency care considerations. Pediatric Emerg. Care. 2007;23:738–744. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0b013e318156acea. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kahn C.A. Commentary: It’s the little things that matter. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2014;63:243–246. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2013.12.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Donahue M., Dukehart J. Latest Trends in Child Pedestrian Safety: A Five Year Review. Safe Kids Worldwide; Washington, DC, USA: 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 5.D’Ippolito A., Collins C.L., Comstock R.D. Epidemiology of pediatric holiday-related injuries presenting to US emergency departments. Pediatrics. 2010;125:931–937. doi: 10.1542/peds.2009-0307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kratz A., Petrov A., Polyakov P., Levy J., Lifshitz T. Ocular injuries related to Independence Day celebrations. Harefuah. 2006;145:254–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Witsaman R.J., Comstock R.D., Smith G.A. Pediatric fireworks-related injuries in the United States: 1990–2003. Pediatrics. 2006;118:296–303. doi: 10.1542/peds.2006-0790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hankin F.M., Noellert R.C., Wilson M.R. Hazards of pumpkin carving. Am. Fam. Phys. 1988;38:221–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Brazier D.J. Eye damage from Christmas trees. Lancet. 1984;2:1335. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(84)90838-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Philip J., Bresnihan M., Chambers N. A Christmas tree in the larynx. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2004;14:1016–1020. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9592.2004.01510.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Schieber R.A., Thompson N.J. Developmental risk factors for childhood pedestrian injuries. Inj. Prev. J. Int. Soc. Child Adolesc. Inj. Prev. 1996;2:228–236. doi: 10.1136/ip.2.3.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Schwebel D.C., Davis A.L., O’Neal E.E. Child Pedestrian Injury: A Review of Behavioral Risks and Preventive Strategies. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2012;6:292–302. doi: 10.1177/0885066611404876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zhang H., Khan A. Risk of preventable injuries associated with Halloween. Public Health. 2020;189:94–96. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2020.10.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Atlanta, GA, USA: 1997. Childhood pedestrian deaths during Halloween--United States, 1975-1996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Staples J.A., Yip C., Redelmeier D.A. Pedestrian Fatalities Associated With Halloween in the United States. JAMA Pediatrics. 2019;173:101–103. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2018.4052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wynne K. Trick or Treat Times 2020: When Does Halloween Night Start and End for Kids? [(accessed on 24 August 2021)]; Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwimzuqi8NLyAhVXc3AKHYLNDHcQtwJ6BAgEEAM&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.newsweek.com%2Ftrick-treat-times-2020-when-does-halloween-night-start-end-kids-1543369&usg=AOvVaw2iVTjaivcD9Zag3ZzVLpvy.
- 17.BV T.I. London Traffic 2020. [(accessed on 24 August 2021)]; Available online: https://www.tomtom.com/en_gb/traffic-index/london-traffic/
- 18.Wazana A., Krueger P., Raina P., Chambers L. A review of risk factors for child pedestrian injuries: Are they modifiable? Inj. Prev. J. Int. Soc. Child Adolesc. Inj. Prev. 1997;3:295–304. doi: 10.1136/ip.3.4.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hatfield J., Murphy S. The effects of mobile phone use on pedestrian crossing behaviour at signalized and unsignalized intersections. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2007;39:197–205. doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2006.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nasar J., Hecht P., Wener R. Mobile telephones, distracted attention, and pedestrian safety. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2008;40:69–75. doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2007.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bungum T.J., Day C., Henry L.J. The association of distraction and caution displayed by pedestrians at a lighted crosswalk. J. Community Health. 2005;30:269–279. doi: 10.1007/s10900-005-3705-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Aarts L.T., Commandeur J.J.F., Welsh R., Niesen S., Lerner M., Thomas P., Bos N., Davidse R.J. Study on Serious Road Traffic Injuries in the EU. European Commission; Brussels, Belgium: 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 23.World Health Organization Manifesto for Safe Communities. Safety—A Universal Concern and Responsibility for All; Proceedings of the First World Conference on Accident and Injury Prevention; Stockholm, Sweden. 17–20 September 1989. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zhou Y., Jiang X., Fu C., Liu H. Operational factor analysis of the aggressive taxi speeders using random parameters Bayesian LASSO modeling approach. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2021;157:106183. doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2021.106183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The current research used the U.K. STATS19 database, which contains the data of all road traffic accidents.