Video
Video showing endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty performed after failed modified primary obesity surgery endoluminal procedure.
Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; ESG, endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty; POSE-2, modified primary obesity surgery endoluminal
Introduction
Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) or gastric plication is a recent, minimally invasive treatment in bariatric endoscopy. The basic mechanisms of action are gastric volume reduction and alteration of gastric peristalsis.1 Currently, 3 devices are used in daily clinical practice: Apollo Overstitch (Apollo Endosurgery, Austin, Tex, USA), Endomina (Endo Tools Therapeutics, SA-ETT, Gosselies, Belgium), and an incisionless operating platform (USGI Medical, San Clemente, Calif, USA). They are used to perform the modified primary obesity surgery endoluminal (POSE-2) procedure. Of these, Endomina is used only in Europe.
ESG seems to be safe and effective in selected patients, and effectiveness is similar for all of the mentioned devices.2, 3, 4, 5, 6 Between these devices, ESG with Apollo Overstitch is the most explored. In case of failure of weight loss, redo ESG after primary ESG (both with Apollo Overstitch) has been proved to be safe and effective, with 100% of technical success and about 19% of total body weight loss within 1 year.7,8 To our knowledge, ESG with Apollo Overstitch after failed POSE-2 procedure has not yet been described. Here, we describe the clinical results and technical aspects of the first case of ESG with Apollo Overstitch after a previous POSE-2 procedure.5
Case report
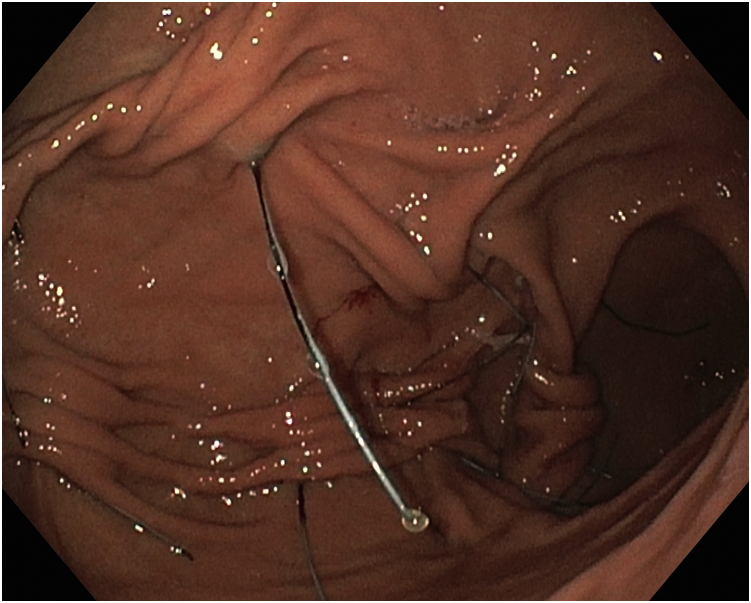
A 40-year-old female patient with obesity (body mass index [BMI] 36 kg/m2) with hypertension and dyslipidemia who had refused bariatric surgery underwent the POSE-2 procedure after multidisciplinary team evaluation. The POSE-2 procedure was done in June 2019. The patient lost 19 kg (21% of total body weight loss) in 1 year, with a BMI of 28.8 kg/m2. In November 2020, the patient lost her sense of satiety, and her BMI progressively increased to BMI 31.6 kg/m2. On gastroscopy, all of the stitches of the POSE-2 procedure were almost completely opened (Fig. 1). The patient underwent a new multidisciplinary team evaluation, and a redo procedure with Apollo Overstitch was indicated.
Figure 1.
EGD showed modified primary obesity surgery endoluminal stitches to be almost completely opened.
Description of the technique and technical aspects
The procedure (Video 1 available online at www.giejournal.org) was done with the standard Apollo Overstitch suturing device and a double-channel gastroscope (2TGIF-180, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan), with CO2 inflation and endotracheal intubation and the patient in a supine position. The remnant stitches of the POSE-2 were left in place.
Suturing started from the gastric incisura toward the fundus, leaving the fundus untouched. Sutures were placed on intact gastric mucosa; we took care not to suture over the previous stitches of the POSE-2 procedure. It is crucial to avoid the POSE-2 sutures to avoid needle engagement in those of the Overstitch device. The suture lines were straight whenever possible, starting from the anterior gastric wall, passing through the greater curvature, and ending at the posterior gastric wall (Fig. 2).
Figure 2.
During the suturing, avoid overlapping the different suture lines (blue dots).
A maximum of 4 bites was used7 to avoid too much stirring of the stomach, which could lead to too much pressure on the gastric wall and eventually to gastric perforation. Adding too much pressure between the sutures should also be avoided to reduce the pressure on the stomach. In addition, it should be kept in mind that every bite induces an inflammatory reaction of the gastric serosa and generates adherences on the external gastric wall. Essentially, the difference in the redo ESG over POSE-2 is in the suture pattern. In the present case, up to 4 bites in a straight line were done per suture, whereas normally in an ESG up to 6 bites with a U pattern are performed.
A total of 5 sutures were placed with 4 bites each. The last suture line was placed about 4 cm distal to the cardia. Mean operation time was 32 minutes. Using CO2 and avoiding overinsufflation is essential. Gentle and slow pulling of the sutures is recommended because this improves the surgeon's ability to assess of the generated tension. Finally, all liquid content in the stomach should be aspirated, especially if it contains blood; this will reduce postoperative nausea and vomiting.
The final aspect of the gastric sleeve was similar to a primary ESG (Fig. 3A and B). No adverse events occurred, and the patient was discharged the next day.
Figure 3.
The final result after endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty. (A) View from the gastric fundus and (B) the antrum in retrovision.
Clinical outcomes
After 1 month, the patient lost 7.5 kg, for a BMI of 28.8 kg/m2, with no delayed adverse events and excellent sense of satiety. At 6 months, her BMI was 26.4 kg/m2, with excellent feeling of satiety. The patient started aerobic physical activity and maintained a good sense of satiety.
Conclusions
ESG is a safe, feasible, and effective procedure after modified primary obesity surgery endoluminal procedure.
Disclosure
Dr Costanagna is a consultant for Cook Medical, Boston Scientific, and Olympus. Dr Boškoski is a consultant for Apollo Endosurgery, Cook Medical, Boston Scientific, and Endo Tools and is a research grant holder for Apollo Endosurgery. All other authors disclosed no financial relationships.
Footnotes
If you would like to chat with an author of this article, you may contact Dr Bove at vincenzo.bove@policlinicogemelli.it.
Supplementary data
Video showing endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty performed after failed modified primary obesity surgery endoluminal procedure.
References
- 1.Abu Dayyeh B.K., Rajan E., Gostout C.J. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty: a potential endoscopic alternative to surgical sleeve gastrectomy for treatment of obesity. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013;78:530–535. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2013.04.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Marincola G., Gallo C., Hassan C. Erratum: Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy versus endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endosc Int Open. 2021;9:C1. doi: 10.1055/a-1300-1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Huberty V, Boskoski I, Bove V, et al. Endoscopic sutured gastroplasty in addition to lifestyle modification: short-term efficacy in a controlled randomized trial. Gut. Epub 2020 Oct 28. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 4.Espinós J.C., Turró R., Moragas G. Gastrointestinal physiological changes and their relationship to weight loss following the POSE procedure. Obes Surg. 2016;26:1081–1089. doi: 10.1007/s11695-015-1863-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lopez-Nava G., Asokkumar R., Turró Arau R. Modified primary obesity surgery endoluminal (POSE-2) procedure for the treatment of obesity. VideoGIE. 2020;5:91–93. doi: 10.1016/j.vgie.2019.11.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Storm A.C., Abu Dayyeh B.K. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty for obesity: defining the risk and reward after more than 1600 procedures. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019;89:1139–1140. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2019.02.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Boškoski I, Pontecorvi V, Gallo C, et al. Redo endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty: technical aspects and short-term outcomes. Ther Adv Gastroenterol. Epub 2020 Jan 20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 8.de Moura D.T.H., Barrichello S., Jr., de Moura E.G.H. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty in the management of weight regain after sleeve gastrectomy. Endoscopy. 2020;52:202–210. doi: 10.1055/a-1086-0627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Video showing endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty performed after failed modified primary obesity surgery endoluminal procedure.
Video showing endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty performed after failed modified primary obesity surgery endoluminal procedure.