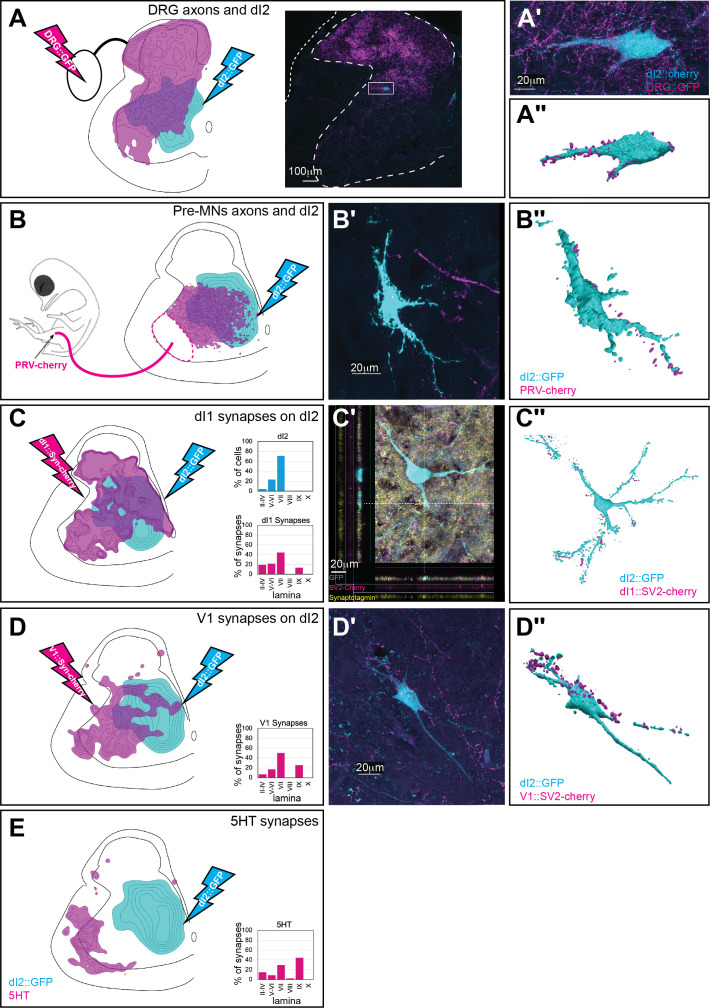
Figure 4. Synaptic inputs to dI2 neurons.
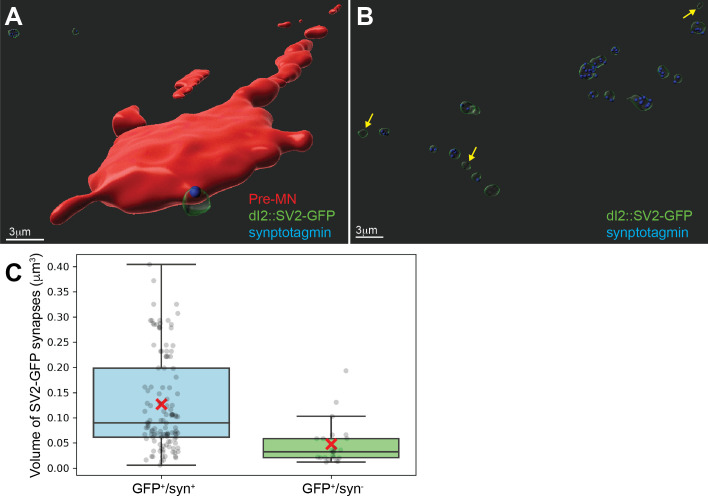
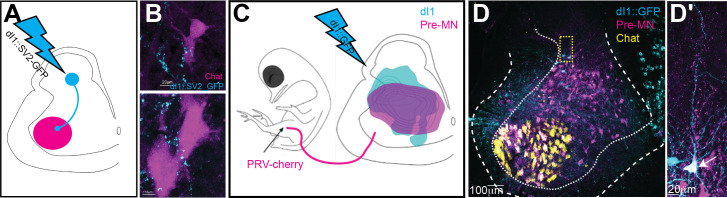
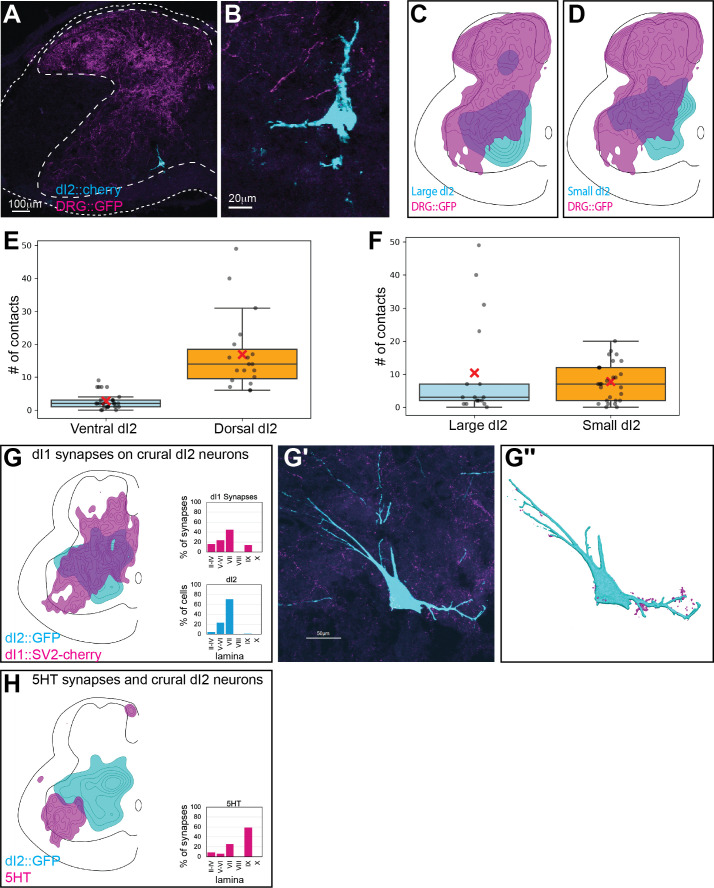
Schematic representations of the experimental design for labeling dI2::GFP or dI2::Cherry interneurons (INs; cyan) and potential sources of synaptic inputs (magenta). The soma densities of dI2 INs and the synaptic densities are illustrated in (A–E). The density values presented are 10–80%, 20–80%, 25–80%, 30–50%, and 20–80%, respectively. The laminar distributions are illustrated on the right side of (A–E). Examples of dI2 neurons contacted by axons or synaptic boutons are shown in (A′–D′), and their 3D reconstruction is shown in (A″–D″). Genetic labeling was achieved using specific enhancers (Figure 1—figure supplement 1A) introduced by electroporation at HH18. (A) Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons form contacts on dI2 neurons. Inset in (A): cross-section of embryonic day (E) 17 embryos at the crural plexus level of the lumbar cord. A dorsally located dI2 neuron contacted by numerous sensory afferents, magnified in (A′) and 3D-reconstructed in (A″) (N = 18 sections, the scheme was constructed based on one representative embryo). (B) Premotor neurons (pre-MNs) form contacts on dI2 neurons. dI2 neurons were labeled at HH18. At E13, PRV virus was injected into the leg musculature, and the embryo was incubated until the infection of the pre-MNs (39 hr) (N = 34 sections, the scheme was constructed based on two representative embryos). (C) dI1 neurons form synapses on dI2 neurons. (N = 8568 synapses, 2 embryos). (C′) A representative SV2::Cherry synapse on dI2 dendrites positive for synaptotagmin. Demonstrated by horizontal and vertical optical sections in the Z-axis (see cursors and color channels). (D) V1 neurons form synapses on dI2 neurons (N = 1923 synapses, 2 embryos). (E) dI2 neurons are not contacted by 5-HT synaptic terminals (N = 1718 synapses, 1 embryo). E17 cross-sections of dI2::GFP-labeled embryos were stained for 5-HT. See Figure 4—source data 1.