Figure 1.
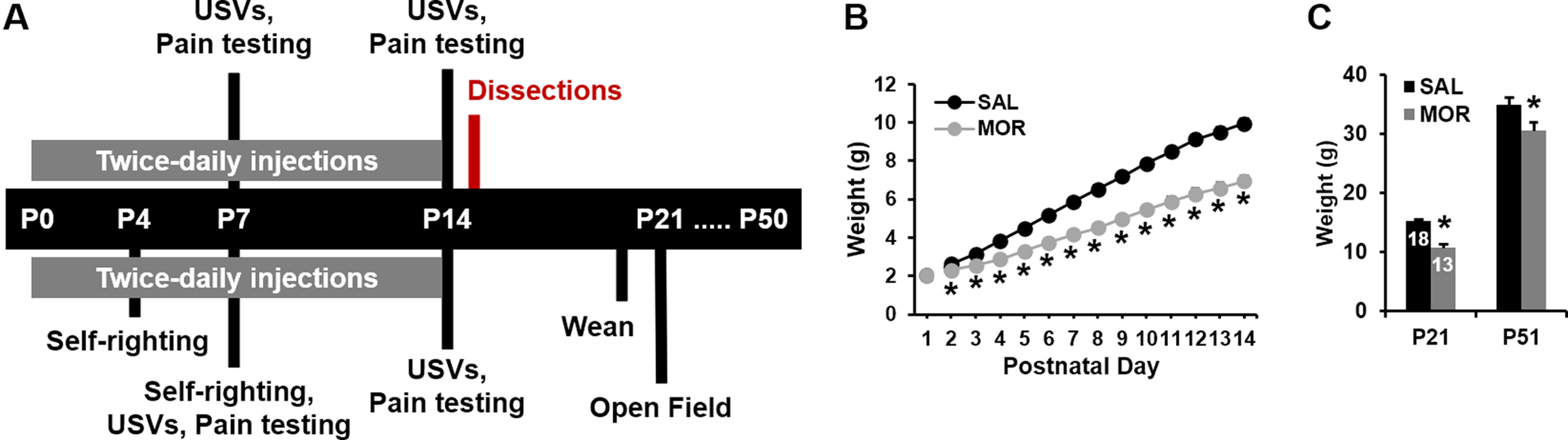
Experimental timeline for repeated neonatal opioid exposure and reduced weight gain. A, Mice underwent assessment for USVs and thermal nociception. A subset of mice also underwent self-righting assessment at P4 and P7 and testing for locomotor activity and center time in the open field on P21. B, In examining changes in body weight, a two-way ANOVA (treatment, sex) revealed no main effect of treatment on P1 (saline, n = 29; morphine, n = 25; F(1,50) = 0.61, p = 0.44). Thus, body weight was not significantly different between treatment groups before the first injections. There was the expected main effect of sex (F(1,50) = 11.10, p = 0.002) but no treatment × sex interaction (F(1,50) = 0.78; p = 0.31). Body weight was subsequently analyzed from P2 to P14 via RM ANOVA, with treatment and sex as factors and postnatal day as the RM. Mauchly’s test indicated the assumption of sphericity had been violated (χ2(77) = 1711.02, p < 0.001), so the Greenhouse–Geisser correction was applied (ε = 0.11). There was a main effect of treatment (saline, n = 41; morphine, n = 35; F(1,72) = 98.04, p <0.001), postnatal day (F(1.36,97.97) = 1526.99, p < 0.001), and treatment × postnatal day interaction (F(1.36,97.97) = 72.61, p < 0.001), but no treatment × sex × postnatal day interaction (F(1.36,97.97) = 0.07; p = 0.86); thus, the sex-combined data are presented. Post hoc pairwise t tests revealed significantly lower body weight in the morphine group (*Bonferroni-adjusted t tests; all p < 3 × 10−4; αadjusted = 0.004). C, In examining body weight in the subset of mice that was assessed at P21 and P51, RM ANOVA indicated a main effect of treatment (F(1,27) = 29.09, p < 0.001), sex (F(1,27) = 25.119, p < 0.001), postnatal day (F(1,27) = 1174.26, p < 0.001), and postnatal day × sex interaction (F(1,27) = 31.17, p < 0.001). In support of the treatment effect, morphine mice had significantly lower body weight compared with saline mice at both P21 (*t(1,29) = −7.33; p < 0.001) and P50 (*t(1,29) = −2.27; p = 0.03).
