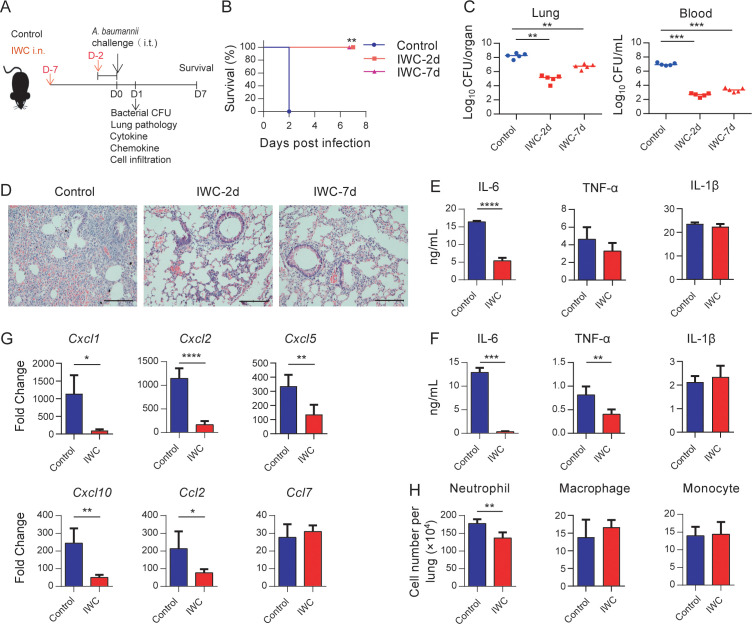
Figure 1. Rapid protection against A. baumannii pneumonia by a single intranasal vaccination.
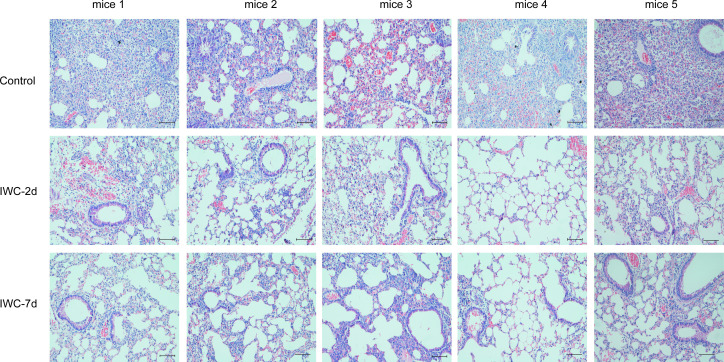
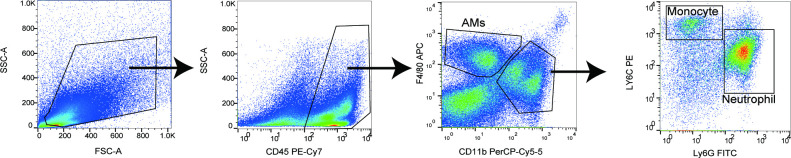
(A) Schematic diagram of the experimental procedure. C57BL/6 mice were immunized intranasally (i.n.) with inactivated whole cell (IWC) of A. baumannii strain LAC-4 and challenged intratracheally (i.t.) with LAC-4 at day 2 (IWC-2d) or day 7 (IWC-7d) after immunization (n = 5/group). (B) Survival of mice was recorded for 7 days. **p<0.01 determined by log-rank test. (C) Bacterial burdens in lungs and blood at 24 hr post infection (hpi) were determined. Each plot represents one mouse. The line indicates the median of the data. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 evaluated by ordinary one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey`s multiple comparisons test. (D) Representative histopathological images of lungs at 24 hpi. Scale bars: 100 μm. (E–G) IWC-immunized mice were challenged at day 7 and were sacrificed at 24 hpi. Levels of inflammatory cytokines in the lungs (E) and serum (F) were detected by ELISA. (G) Transcriptional levels of chemokines in the lungs were detected by real-time PCR. (H) Numbers of neutrophils in the lungs were detected by flow cytometry. Data are mean ± SD. n = 4–5 mice/group. For (E–H), *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, and ****p<0.0001, determined by two-tailed unpaired t test. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments.