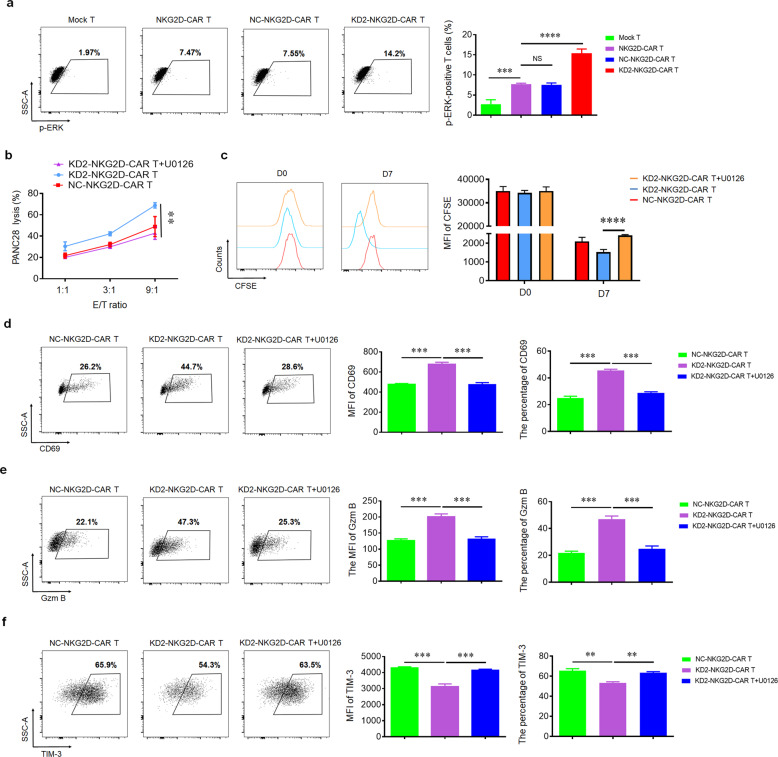
Fig. 4. 4.1R deficiency regulated the function of CAR T cells via ERK signaling pathway.
a Mock T, NKG2D-CAR T, NC-NKG2D-CAR T, and KD2-NKG2D-CAR T were co-incubated with PANC28 at a 9:1 ratio for 16 h. The expression of p-ERK was detected by flow cytometry (left), and the percentage of p-ERK-positive T cells was statistically analyzed (right) (n = 3). b Line plots displayed the cytotoxicity of NC-NKG2D-CAR T and KD2-NKG2D-CAR T against PANC28 at a different effector to target (E:T) ratios for 16 h in the absence and presence of 10 μM U0126. c NC-NKG2D-CAR T and KD2-NKG2D-CAR T were co-incubated with PANC28 at a different effector to target (E:T) ratios for 7 days in the absence and presence of 10 μM U0126. CFSE dilution was used as a measure of cell proliferation (left), and MFI was calculated (right) (n = 3). NC-NKG2D-CAR T and KD2-NKG2D-CAR T were co-incubated with PANC28 at a different effector to target (E:T) ratios for 16 h in the absence and presence of 10 μM U0126. The expression of CD69 (d), Gzm B (e), and TIM-3 (f) was detected by flow cytometry (left). MFI and percentage were statistically analyzed and shown in column chart (middle and right) (n = 3). Data were representative of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, NS not significant.