Abstract
This study examines the antibody responses to a third dose (100 μg) of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine among kidney transplant recipients in France who had not responded to 2 doses of the vaccine.
Studies have reported low seroconversion rates (58% after the second dose) in solid organ transplant recipients who received a messenger RNA (mRNA) SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.1,2 Based on this evidence, the French National Authority for Health issued a recommendation in April 2021 to administer a third vaccine dose in immunosuppressed patients who did not respond after 2 doses. We examined the antibody responses of kidney transplant recipients who did not respond to 2 doses and received a third dose (100 μg) of the mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccine.
Methods
All kidney transplant recipients followed up in the outpatient Kidney Transplantation Department of Strasbourg University Hospital between January 20, 2021, and June 3, 2021, with a negative history for COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2 antispike IgG levels less than 50 arbitrary units (AU) per milliliter on the day of the first vaccine injection and 1 month after the second dose were included. All patients received a third vaccine dose between April 9, 2021, and May 12, 2021. The study protocol was approved by the local ethics committee and written informed consent was obtained.
Anti–receptor-binding domain IgG response after the third vaccine dose was assessed using the ARCHITECT IgG II Quant test (Abbott). According to the manufacturer, titers greater than 50 AU/mL were considered positive (detection range, 6.8–80 000 AU/mL; positive agreement, 99.4%; negative agreement, 99.6%). The results of this assay have been shown to correlate with in vitro neutralization of SARS-CoV-2.3 Mean differences adjusted for the factors in the Table were calculated using general linear models. All calculations were performed using GraphPad Prism version 8.0 (GraphPad) and SPSS version 2020.0.0 (IBM). P < .05 (2-sided) was considered statistically significant.
Table. Association Between Patient Characteristics, Immunosuppression, and Antibody Titers After the Third Dose of a SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccine in 159 Kidney Transplant Recipients.
| Variables | Sample, No. (%) | Antibody titers, mean (SD) | Adjusted mean difference (95% CI)a | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, y | ||||
| ≤60 | 93 (58.5) | 720.64 (1436.17) | −94.10 (−214 to 26) | .73 |
| >60 | 66 (41.5) | 777.77 (1974.04) | ||
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 98 (61.6) | 1009.70 (1967.29) | 280.22 (−240.59 to 801.03) | .29 |
| Female | 61 (38.4) | 318.06 (910.83) | ||
| BMIb | ||||
| <25 | 72 (45.3) | 790.28 (1532.48) | 98.57 (−394.18 to 591.32) | .69 |
| ≥25 | 87 (54.7) | 706.34 (1791.95) | ||
| Time from transplantation, y | ||||
| >3 | 102 (64.2) | 882.33 (1847.79) | 166.69 (−346.26 to 679.64) | .52 |
| ≤3 | 57 (35.8) | 497.45 (1288.08) | ||
| Donor type | ||||
| Living donor | 36 (22.6) | 596.54 (1273.02) | 7.69 (−586.47 to 601.86) | .98 |
| Deceased donor | 123 (77.4) | 787.61 (1777.45) | ||
| Immunosuppression maintenance therapy | ||||
| Tacrolimus + MMF/MPA + steroids | 84 (52.8) | 316.72 (797.73) | −697.28 (−1193.00 to −201.56) | .006 |
| All other regimens | 75 (47.2) | 1223.31 (2198.86) | ||
| Serum creatinine, mg/dL | ||||
| <1.47 | 81 (50.9) | 766.84 (1305.64) | 153.26 (−350.37 to 656.89) | .55 |
| ≥1.47 | 78 (49.1) | 721.00 (1995.83) | ||
| Antibody titers after the second vaccine dose, AU/mL | ||||
| >6.8 and <50 | 64 (40.3) | 1426.88 (1947.30) | 894.89 (377.41 to 1410.37) | .001 |
| ≤6.8 | 95 (59.7) | 284.55 (1281.55) |
Abbreviations: AU, arbitrary units; BMI, body mass index; MMF, mycophenolate mofetil; MPA, mycophenolic acid; mRNA, messenger RNA.
SI conversion factor: To convert creatinine values to mmol/L, multiply by 88.4.
Model adjusted for sex, BMI, donor type, time from kidney transplantation, serum creatinine level, triple immunosuppression (tacrolimus + MMF/MPA + steroids), and antibody titers after the second dose.
Calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared.
Results
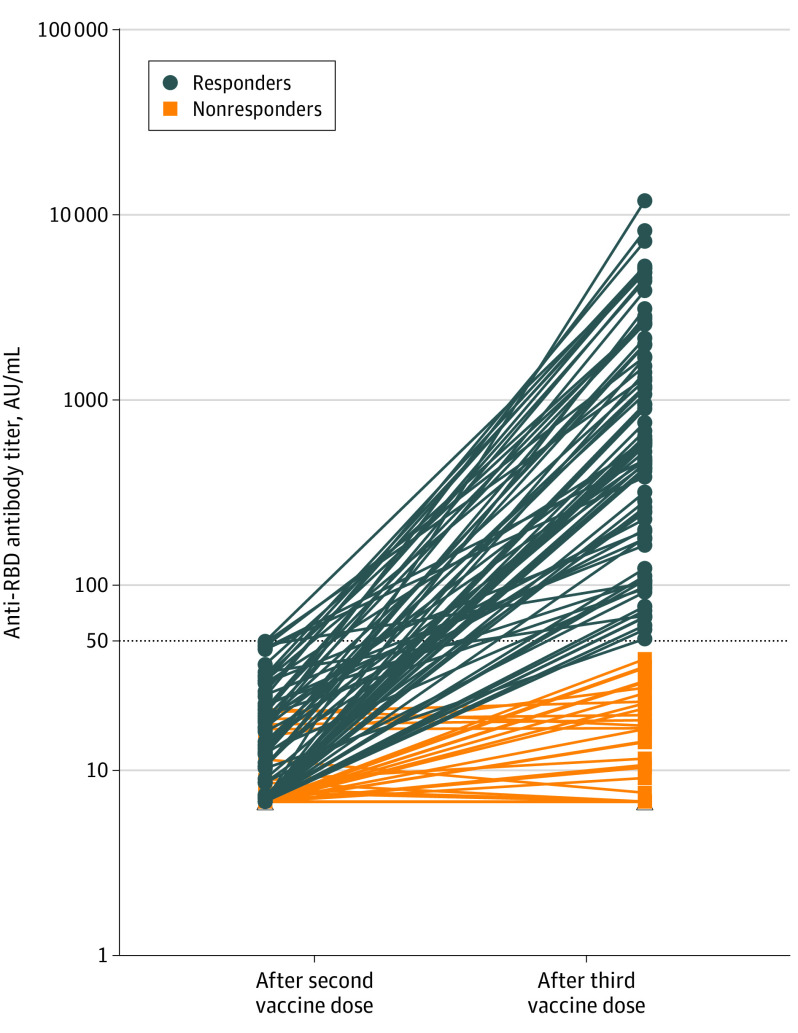
One month after the second dose, 159 kidney transplant recipients had IgG levels less than 50 AU/mL. The median age was 57.6 years (interquartile range [IQR], 49.6-66.1 years), 61.6% were men, and the median time from transplantation was 5.3 years (IQR, 1.9-11.1 years) (Table). Ninety-five patients (59.7%) had no antibody response after 2 doses (titers <6.8 AU/mL), and 64 patients (40.3%) showed a response below the positivity limit (titers, 6.8-49.9 AU/mL). The third dose was injected a median of 51 days (IQR, 48-59 days) after the second dose. The antibody response was measured a median of 28 days (IQR, 27-33 days) after the third vaccine injection, and 78 patients (49%) had antibody levels greater than 50 AU/mL (median antibody titers of responders, 586 AU/mL; IQR, 197.2-1920.1 AU/mL) (Figure). Patients who had a weak response after the second dose were more likely to develop an antibody response after the third dose compared with those without an antibody response (81.3% vs 27.4%, respectively; mean adjusted difference of antibody titers, 894.89 AU/mL [95% CI, 377.41-1410.37 AU/mL]; P = .001). Patients taking tacrolimus, mycophenolate, and steroids were less likely to develop anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies than those treated with other regimens (35% vs 63%, respectively; mean adjusted difference of antibody titers, −697.28 AU/mL [95% CI, −1193.00 to −201.56 AU/mL]; P = .006). Other variables associated with the titers of antibodies are shown in the Table. No severe adverse events were observed after the third dose.
Figure. Anti–Receptor-Binding Domain (RBG) IgG Antibody Titers Measured 28 Days After the Third Dose of mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in 159 Kidney Transplant Recipients.
Horizontal dotted line indicates the cutoff for positivity (50 arbitrary units [AU]/mL). Blue lines indicate the antibody titers of kidney transplant recipients who seroconverted after the third dose (titers ≥50 AU/mL); orange lines, the evolution of antibody titers among nonresponders (titers <50 AU/mL). mRNA indicates messenger RNA.
Discussion
This study found that a third dose of mRNA-1273 vaccine induced a serologic response in 49% of kidney transplant recipients who did not respond after 2 doses. The findings in this large group of kidney transplant recipients are in accordance with other studies of solid organ transplant recipients.4,5 However, 51% of the patients did not develop anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies after the third dose, especially those receiving triple immunosuppression. The possibility that patients developed cellular immunity capable of conferring protection against severe disease was not assessed. However, the occurrence of severe COVID-19 in some vaccinated transplant recipients may suggest a lack of immunity.6
Limitations of this study include that detailed B-cell and T-cell studies were not performed and that the antibody level that correlates with protection is unknown.
In conclusion, the use of a third dose of vaccine may be considered in organ transplant recipients.
Section Editors: Jody W. Zylke, MD, Deputy Editor; Kristin Walter, MD, Associate Editor.
References
- 1.Boyarsky BJ, Werbel WA, Avery RK, et al. Immunogenicity of a single dose of SARS-CoV-2 messenger RNA vaccine in solid organ transplant recipients. JAMA. 2021;325(17):1784-1786. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.4385 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Boyarsky BJ, Werbel WA, Avery RK, et al. Antibody response to 2-dose SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine series in solid organ transplant recipients. JAMA. 2021;325(21):2204-2206. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.7489 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Prendecki M, Clarke C, Brown J, et al. Effect of previous SARS-CoV-2 infection on humoral and T-cell responses to single-dose BNT162b2 vaccine. Lancet. 2021;397(10280):1178-1181. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00502-X [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Werbel WA, Boyarsky BJ, Ou MT, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a third dose of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in solid organ transplant recipients: a case series. Ann Intern Med. Published online June 15, 2021. doi: 10.7326/L21-0282 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kamar N, Abravanel F, Marion O, Couat C, Izopet J, Del Bello A. Three doses of an mRNA Covid-19 vaccine in solid-organ transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. Published online June 23, 2021. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2108861 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Caillard S, Chavarot N, Bertrand D, et al. ; French Society of Transplantation . Occurrence of severe COVID-19 in vaccinated transplant patients. Kidney Int. Published online May 23, 2021. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2021.05.011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]