Abstract
Origanumvulgare L. (O. vulgare) is an important medicinal herb of the family Lamiaceae. In the current study, we explained the critical evaluation of traditional uses, the phytochemistry and the antimicrobial properties of O. vulgare and its subspecies, with a focus on the mechanisms of actions of the most important phytochemicals from O. vulgare subspecies. The most important phytochemicals of O. vulgare are volatile (essential oil) and non-volatile phenolic compounds (phenolic acids & flavonoids). The constituents of the O. vulgare essential oil (EO) include high percentages of thymol and carvacrol with excellent antimicrobial activity alone or in combination with other antibiotics. Interesting results have been reported the remarkable antimicrobial activities of infusion or tea products of O. vulgare with a high amount of EO against multidrug-resistant bacterial and fungal microorganism (such as Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Candida albicans and Pseudomonas aeruginosa). The most important antibacterial mechanisms of O. vulgare are enzyme inhibition, efflux pump inhibition, ATP depletion, biofilm formation inhibition and cytoplasmic membrane damage. The antimicrobial activity of the hirtum subspecies has been confirmed in different in-vitro and in-vivo studies. The present review confirms the clinical and preclinical research showing the O. vulgare and its subspecies antimicrobial effects.
Key Words: Origanum vulgare L., Phytochemistry, Traditional uses, Antimicrobial activities
Introduction
Members of the genus Origanum comprise the most important herbaceous and aromatic medicinal plants from the family Lamiaceae that distributes in warm and mountainous areas. O. vulgare L. (known as “oregano”) as the most diverse species in the genus are spread in the Mediterranean region and Western and Southwestern Eurasia region (1). Ietswaart identified morphologically six subspecies of O. vulgare (1): glandulosum (Desf.) Ietsw., gracile (K.Koch) Ietsw., hirtum (Link) Ietsw., virens (Hoffmanns. & Link) Ietsw., viridulum (Martrin-Donos) Nyman., and vulgare. These subspecies are well accepted in 2013 with “The Plant List” (www.theplantlist.org). In Iran O. vulgare includes three subspecies (subsp. viride, subsp. vulgare and subsp. gracile) that grow mainly in northern parts of the country (2) and their morphological diversity of wild varieties reviewed by Andy et al. (3). The term “oregano” can be confusing because it is known to be a vernacular term for many other species, for example, Mexican oregano (Lippia graveolens Kunth). Therefore, for more clarity we stick to the term Origanum vulgare L. To date, over 100 volatile and non-volatile ingredients have been recognized in the oil and various extracts of O. vulgare. Based on hydrophilic and hydrophobic features, there are exist two main groups of phytochemicals in O. vulgare, include essential oils (EOs) and phenolic compounds (flavonoids and phenolic acids). Others biological active compounds consist of terpenoids, tannins and sterols (4). Different subspecies of O. vulgare are found in wild varieties on various soils with different fertility and rather low temperatures, but many other ones can be cultivated as medicinal, culinary and garden plants and play a very important role in the economy and constitutes one of the most cultivated aromatic plants worldwide. One of the largest global markets is related to O. vulgare ssp. hirtum (known as Greek oregano) due to its perfect quality and high EO concentration which is predominantly expanding in Turkey, Greek, Cyprus and Italy (5, 6). Some of the uses for O. vulgare in traditional medicine are respiratory disorders, stomachache, painful menstruation, rheumatoid arthritis, analgesics, nutritive disturbance and urinary problems as a diuretic and antiurolithic (7, 8). From the last two decades, following the increasing of antibacterial resistance as a menace to global health, the interest of scientists has been devoted to antimicrobial studies (9). According to the literature, about two-thirds of clinically antibacterial therapies are designed on the basis of natural products (10). Different studies show that essential oils are safe antibacterial compounds in combating infections (11). Eos constituents that can inhibit the growth of bacteria, yeasts and moulds and resistance to them could be more difficult than to single antibiotic molecule (12). Various species of O. vulgare are among the most studied plants due to the potential antibacterial effects that are different based on the species of microorganisms (wild, reference, drug-sensitive, or resistant) and the type of plant extraction (EOs or various extracts), and it should be taken in this regard whenever exploring the plants’ potential for developing new antimicrobial drugs. Regarding the importance of this species, the biological effects of EOs, extracts or the main constituents have been previously reviewed (13). However, this review article concentrated on the variation of the non-volatile and volatile ingredients of O. vulgare, their traditional therapeutic effects and focusing on antimicrobial activities.
Search method
The current review consists of scientific studies regarding the O. vulgare subspecies published between 2000 and 2020. At the first of this study, 307 papers were evaluated and among these studies, 111 references focusing on ethnopharmacology data, phytochemistry and pharmacology studies of the O. vulgare and its subspecies were selected. Another 56 papers were used to complete the current review article. Six subspecies were indicated according to the plant list website classification (www.theplantlist.org). Furthermore, an older text from 1990 about the traditional uses of O. vulgare has also been mentioned and studied. Information was gathered by searching the internet (PubMed, Francis & Taylor, Wiley, Scopus, Web of Science, ACS, ScienceDirect, Springer, Google Scholar and The Plant List Database). The authors have also checked the libraries, Iranian traditional books and some thesis works that were considered firstly. The data from patents, congress abstracts and symposiums were omitted because of the uncompleted source in comparison to data from full papers and books. All related databases were searched for the terms “Origanum vulgare” and its subspecies, ” antimicrobial”/”phytochemistry”/”traditional”.
Traditional uses
For centuries, O. vulgare has traditionally been used to flavor foods and treatment of various diseases due to the high percentage of their EO (14). In the 7th century B.C, O. vulgare was used to flavor fish, meat, vegetables and wine (15). The useful subspecies of O. vulgare in culinary include ssp. gracile, ssp. glandulosum, ssp. hirtum (16). Some of the uses for O. vulgare in traditional medicine are respiratory disorders, stomachache, painful menstruation, rheumatoid arthritis, nutritive disturbance and urinary problems as a diuretic and antiurolithic. Aerial parts of the plant were mostly used. In 2018, Bahmani et al. reviewed the therapeutic effects of O. vulgare based on Iran’s ethnopharmacological documents (17). All of them reported that in Iran, O. vulgare is used for flavoring in cooking and in traditional medicine as a tonic, expectorant, carminative, stimulant and antibacterial agent (18, 19).
The forms of consumption are very diverse according to the symptoms, including tea or tincture that is used against cold and digestive or respiratory disorders and improve the general health of the body (7). Decoction or infusion preparation of O. vulgare has been used for expectorant, antiseptic, digestive aid and antispasmodic properties (20). Pieroni et al. reported on smoke inhalation to relieve toothache (21). The routinely used O. vulgare subspecies, their consumed part, methods of preparations and important traditional features are summarized in Table S1 (in supplementary file).
Phytochemistry
Volatile compounds
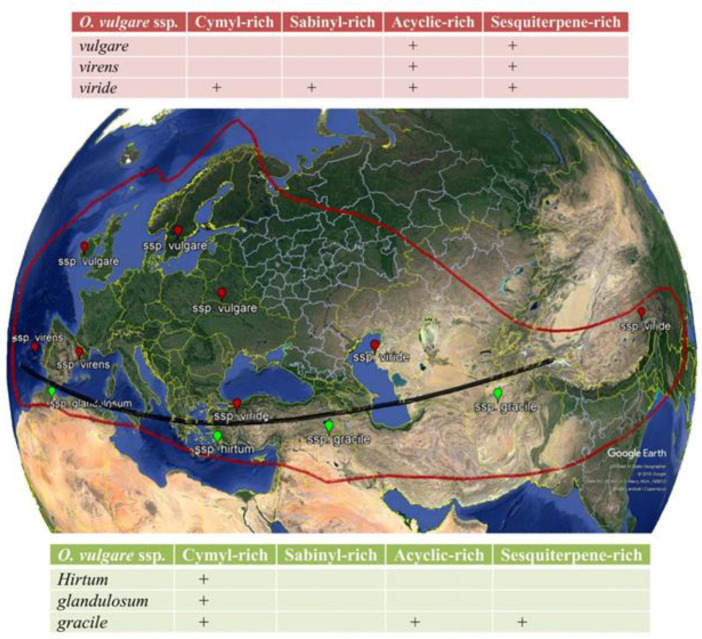
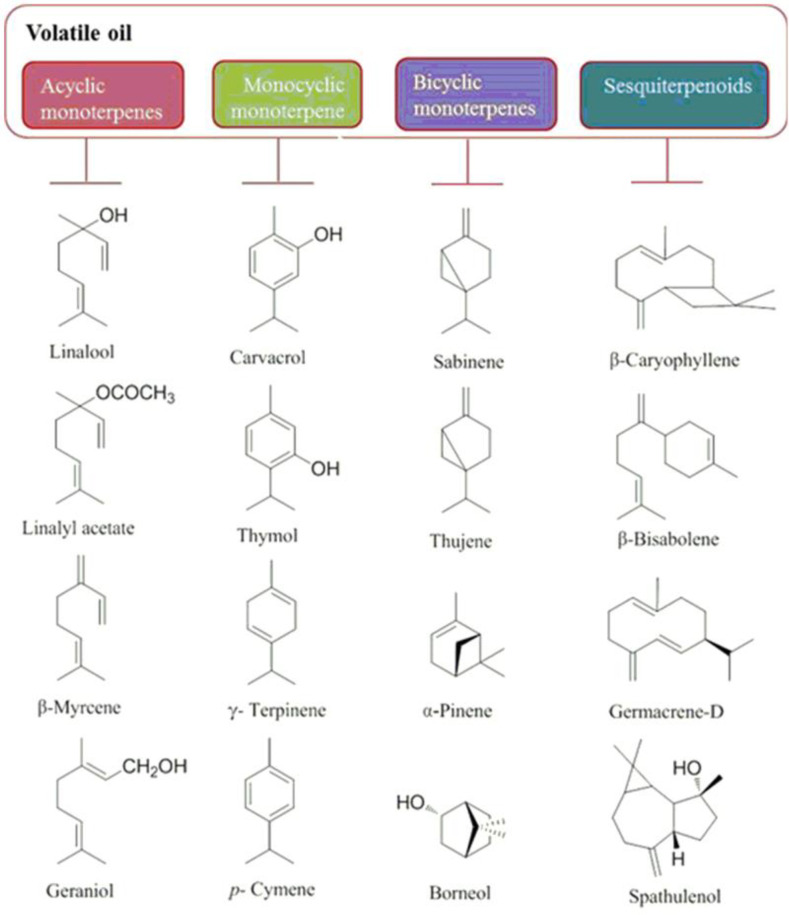
Essential oils are the main group among many compounds obtained from O. vulgare. As demonstrated in Table S2 (in supplementary file) and Figure 1, regarding the geographic origin, extraction method, plant’s developmental stage, growing conditions and harvest time, oil yield and volatile compositions is diverse. Therefore, a detailed comparison between various reports is very difficult. In general, O. vulgare EO is a great source of monocyclic monoterpenes (thymol, γ-terpinene, carvacrol, and p-cymene), acyclic monoterpenes (geraniol, linalyl acetate, linalool and β-myrcene) and bicyclic monoterpenes (sabinyl compounds) and sesquiterpenoids (β-bisabolene, β-caryophyllene, spathulenol and germacrene-D) have also been reported depending on the chemotype (Figure 2). Several studies have reported that subspecies grown in northern Mediterranean areas are poor sources of volatiles (with complex compositions of phenolic monoterpenoids, acyclic compounds, camphane type compounds, sabinyl-compounds and larger numbers of sesquiterpenes); whereas, those grown in southern regions are enrichment in EO with phenolic monoterpenoids (cymyl compounds), mainly carvacrol or thymol that can constitute up to 70% of the total oil (Figure 1) (22-26). Furthermore, γ-terpinene and p-cymene have been reported in considerable amounts with different concentrations, attributed to the reverse relationship with carvacrol (γ-terpinene converts to p-cymene autoxidation and subsequently converts to carvacrol by hydroxylation) (27). The main ingredients of ssp. glandulosum EO is thymol, carvacrol and their methyl ethers (28). The EO of the same subspecies from Tunisia (29) the percentage of carvacrol was high, while from another region of the same country (30) and also in Algeria (31), the percentage of thymol and p-cymene was higher than other EO ingredients. The main components of the ssp. gracile EO collected from Iran were carvacrol (60.6%), γ-terpinene (16.64%) and p-cymene (13.54%) (4, 32); and EO of this subspecies from Turkey consists of β-caryophyllene (17.54%) and germacrene D (12.75%) (33), whereas EO of ssp. gracile from France identified by high percentage of the sabinene (26.0%), germacrene D (13.7%) and β-caryophyllene (6.6%) (34). According to the literature, the ssp. hirtum has a higher EO yield than other O. vulgare ssp. In 2014, the carvacrol and thymol chemotypes were characterized (35). In these chemotypes, usually, the percentage of carvacrol is high and the percentage of thymol was low (36), while another study showed the main components of EO from Turkey is linalool (96.31%) (37). As shown in Table S2, ssp. virens has a high diversity in EO and the main ingredients of EO from different regions are carvacrol, linalool, thymol, α-bisabolene, germacrene D and γ-terpinene. The thymol (58%) (38) and carvacrol chemotype (68%) have been reported from Portugal (39, 40), whereas linalool chemotype (76.8%) (41, 42) have collected in Mediterranean regions and Spain. Moreover, Germacrene D chemotype (34) has been reported in France. The Iranian species of O. vulgare were characterized by the amount of α-bisabolene and sabinene (4) in oils. γ-Terpinene chemotypes were collected from Corsica (20.1%) and Central Portugal (34.2%) (40, 43). EO of ssp viridulum from Turkey has a high percentage of caryophyllene oxide (25.01%) and linalool (8.32%) (44). Other researches in Iran and Balkan demonstrated that thymol is the major constituents in both oils, followed by 4-terpineol and γ-terpinene (45, 46). In 1998, Chalchat showed that ssp. vulgare, incorporate at least nine chemotypes of EO, including: thymol, sabinene, O-cymene, β-caryophyllene, germacrene D, β-ocimene, terpinen-4-ol, spathulenol and cis-sabinene hydrate as shown in Table S2 (47).
Figure 1.
Simplified presentation of the distribution of the six Origanum vulgare ssp. Above the black line, the taxa are poor in essential oil, whereas the essential oil rich subspecies of O. vulgare occur below the line (reflecting data collected from Kokkini, 1996 and Ietswaart, 1980)
Figure 2.
Chemical structures of main volatile compounds of O. vulgare
Non-volatile phenolic compounds
A comprehensive overview of phenolic ingredients of O. vulgare with different origins is summarized in Table S3 and Figures S1 and S2 (in supplementary file). The major phenolic acid (1-12) that has been identified in O. vulgare species is rosmarinic acid (12) (44, 48-53). Both free flavonoids (flavones, flavonols, flavanones and dihydroflavonols) and flavonoid glycosides are present in Origanum species (54). The most abundant flavonoids of O. vulgare are flavons. In addition, 6-substituted and 6, 8-disubstituted flavonoids are uncommon elsewhere, present in the genus (48, 55 and 56). A number of O-glycosides and C-glycosides have been found in O. vulgare. Luteolin (36) is the most common aglycone, followed by apigenin (35); most sugar moieties are glucosides and glucuronides (54). The cultivar, geographical, environmental factors and different experimental protocols can affect the concentration and distribution of compounds in O. vulgare. Therefore, a detailed comparison between various reports is very difficult. For example, rosmarinic acid exhibited different contents between various chemotypes within the species of ssp. hirtum and European O. vulgare were ranging from 13.73 to 63.69 mg/g on a dry weight basis (57); these results showed a broader range of rosmarinic acid in comparison with Austrian O. vulgare ssp. vulgare chosen plants of 19 populations (9.4 to 37.2 mg/g dry mass) (24). Liang et al. (2010) identified a new phenolic glucoside, origanoside (15), from the ethyl acetate soluble part of the methanol extract of O. vulgare (58). Zhang et al. (2014) also isolated six new phenolic compounds (18, 19, 57-60) along with known ones (3, 4, 12 and 15) from the ethanol extract (59). Rosmarinic acid methyl ester (13) was isolated from O. vulgare, which exhibited depigmentation activity (60). Two protocatechuic acid ester derivatives, origanol A (16) and origanol B (17) had been reported from the methanolic extract of O. vulgare collected from India (61). Liu and coworkers identified three new polyphenolic compounds, origanine A−C (20-22) (62). In 2003, a novel dihydrobenzodioxane derivative, origalignanol (23) and known polyphenolic compounds include salvianolic acid A (24), salvianolic acid C (25), lithospermic acid (26), apigenin7-O-D-glucuronide (51), luteolin (36), luteolin 7-O-D-glucopyranoside (45), luteolin7-O-D-glucuronide (50) were isolated from the aqueous ethanolic extract of O. vulgare (63).
Triterpenoids
The major triterpenoids that have been reported from O. vulgare are pentacyclic triterpenoids such as ursolic and oleanolic acids that are common to most Labiatae, whereas diterpenoids have not been found in O. vulgare (54). Rao et al. (2011) reported the presence of ursolic acid, oleanolic acid, β-sitosterol and triacontanol in an ethanolic extract of O. vulgare from India (61). Moreover, Baranauskaite et al. (2016) reported the presence of ursolic acid and oleanolic acid from ssp. hirtum by maceration in ethanol/non-aqueous solvent (glycerol or propylene glycol) (64). Assiri et al. (2016) analyzed the cold-pressed oil to determine lipid profile, fatty acid, tocols and phenolic contents. The neutral lipids exhibited the maximum content, then glycolipids and phospholipids. The main fatty acids included linoleic, oleic, stearic and palmitic acids. Tocols include γ-tocopherol, α-tocotrienol and γ-tocotrienol with 32.1%, 25.8% and 21.3% of total measured tocols, respectively (65). The FTIR analysis of O. vulgare seeds demonstrates the existence of alkenes, aliphatic fluoro compounds, alcohols, ethers, carboxylic acids, esters, hydrogenated alcohols and phenols (66). Koukoulitsa et al. (2006) have also isolated two polar compounds (12-hydroxyjasmonic acid 12-O-β-glucopyranoside and p-menth-3-ene1, 2-diol 1-O-β-glucopyranoside) from the aerial parts of ssp. hirtum growing uncultivated in Greece (67). It was reported that hexane extract of ssp. viridulum contained fatty acids and hydrocarbons such as hexadecanoic acid methyl ester, 9,12-octadecadienoic acid methyl ester, 9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid methyl ester, cyclotetracosane and 1-eicosanol (44).
Antimicrobial activity
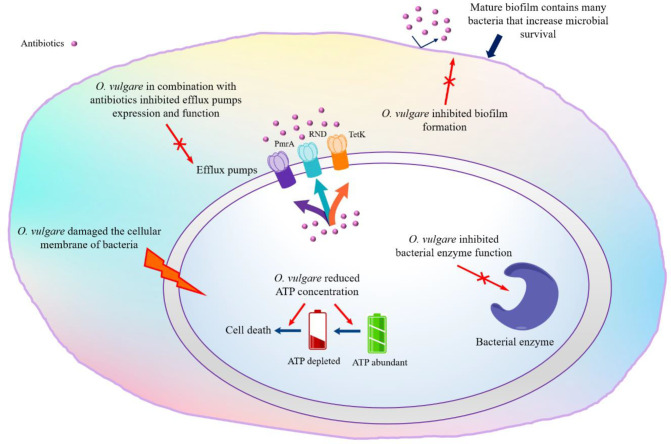
Various studies evaluated the inhibitory effects of EOs, extracts or the main constituents from O. vulgare against different pathogenic bacteria. Diverse mechanisms of an EO activity on bacterial cells have been proposed to explain the antibacterial activities (68). Schematic Figure 3 illustrates different mechanisms of O. vulgare antibacterial activity.
Figure 3.
Different mechanisms of O. vulgare antibacterial activity
Mechanisms of action
Bacterial enzyme inhibition: One of the proposed mechanisms is inhibition the production or activity of bacterial enzymes (such as lipase and coagulase) that was mediated by EO of O. vulgare (at 0.03 and 0.015 μL/mL) against S. aureus (69).
Efflux pumps inhibition: Potential antibacterial synergy of EOs in combination with antibiotics to inhibition of efflux pumps that is another possible mechanism of action (70), is measured by fractional inhibitory concentration index (FICI). O. vulgare EOs in combination with ciprofloxacin and ethidium bromide, exerted synergistic (FICI from 0.22 to 0.75) activity against fluoroquinolone resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae clinical isolates by inhibition of the PmrA efflux pump gene expression (71). In contrast, results by Perrin et al. did not show any additive or synergistic effect between EO and antibiotics against the model strain Burkholderia cenocepacia J2315. The obtained data showed an intracellular mechanism of action and the addition of the efflux pumps inhibitor (Phe-Arg -naphthylamide dihydrochloride, which acting on RND efflux pumps) significantly increased EO activity depend on the inactivation of different cellular, molecular targets (72). Furthermore, co-administration of tetracycline with O. vulgare EO (fourfold), carvacrol and thymol (twofold) exerted synergistic activity against S. aureus by inhibition of the TetK efflux protein (73). In addition, a significant synergistic effect between ciprofloxacin and phenolic (FICl < 0.5), nonphenolic (FICI > 4.0, antagonistic activity) fractions and volatile oil (FICl < 0.5) against S. typhi was reported (74).
Antibiofilm agents: Another antibacterial mechanism of EO is biofilm eradication; for example, O. vulgare EO (MIC: 0.25-0.5 mg/mL) acts as a potent antibiofilm agent of S. pyogenes (at concertation of 0.5 mg/mL) with dual actions, preventing and eradicating. This biofilm inhibition is attributable to the killing of its planktonic cells (time to kill 99.9%, 5 min) (75). When screening 79 essential oil for antibiofilm ability against UPEC (uropathogenic Escherichia coli), Lee et al. (2017) found that O. vulgare EO, carvacrol and thymol noticeably decreased fimbriae production and swarming motility of UPEC at sub-inhibitory concentrations (<0.01%) and their results showed that the hemagglutinating ability of UPEC in the presence of carvacrol and thymol decreased and UPEC easily killed by human whole blood (76).
Effect on the cytoplasmic membrane: Some studies considered the correlation between antimicrobial properties of EO and its phenolic compounds (carvacrol and thymol). For investigation of the antibacterial mechanism of carvacrol and thymol (with the same system of delocalized electrons) against Bacillus cereus, liposomal models were used. Carvacrol damaged the cellular membrane and reduced the pH gradient in the cellular membrane that leads to the proton motive force, reduction in the ATP pool and cell death (77). Khan et al. (2017) showed that carvacrol and thymol exhibited potent bactericidal (IC50: 65 and 54 µg/ml, respectively) and antibiofilm activity (at concertation of 100 μg/ml) against Streptococcus mutans (78). The same research also demonstrated the growth inhibition of E. coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Micrococcus luteus, and S. aureus at IC50 values from 107-286 μg/mL for aqueous distillates (carvacrol 92.5%) and at IC50 values from 214-383 μg/mL for volatile oil from the aerial parts (carvacrol 70.2%), the IC50 value of carvacrol was in the range of 53–151 µg/mL (25).
Effect on ATP concentration: One of the antibacterial mechanisms is that O. vulgare EOs in combination with gamma radiation has an effect on periplasmic peptidoglycan composition and ATP concentration of Listeria monocytogenes, Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, which leads to cell wall damage (79-81).
Effective preparation
Decoction: Decoction is a method of extraction by boiling hard plant material such as roots, bark, seeds, and wood to primarily extract the mineral salts and bitter principles of plants. It was found that decoction did not possess any antibacterial effect against all isolates (82); because decoction consists of maximal levels of flavonoids and total phenolic compounds (rosmarinic acid) that gave higher antioxidant activity (20).
Infusion: Infusion is the process of extracting chemical compounds from soft ingredients like leaves, flowers and citrus. Plant materials are suspended in hot water and closed the head of the extraction dish; the short brewing time helps to retain the vitamins and volatile ingredients while drinking. Some studies showed that the infusion was more effective against Brevibacillus laterosporus and Bacillus polymyxa (17.5-17.0 mm respectively) than the EO of O.vulgare against Staphylococcus saprophyticus and Bacillus circulans (16.8-14.5 mm respectively), while decoction has no antibacterial activity (83). Chaudhry et al. (2007) found that the antibacterial activity of O.vulgare infusion was similar to the EO (Citrobacter spp. 24 mm) and exhibited significant inhibitory activity against Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella ozaenae and Enterobacter aerogenes (20.1, 19.5and 18 mm) (82).
Extraction: O.vulgare extracts (cyclohexane, dichloromethane and methanol extracts) have a moderate antimicrobial activity (MIC 62.5-125 µg/mL) against S. aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, M. luteus, Bacillus subtilis, Enterococcus feacalis, K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa and Salmonella abony. A. Cyclohexane extract has no activity against Helicobacter pylori, while dichloromethane and methanol extracts were active (MIC 250-500 µg/mL) (84). Methanol extract consists of the bioactive alkaloid (1.5%) and flavonoid (2.5%), was significantly active against multidrug-resistance (MDR) strains (S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, E. coli) isolated from the sore throat of patients (MIC 3.91 to 15.63 µg/mL) (85). In another study, significant antimicrobial activity against ulcer-associated H. pylori (ZI 10-15 mm) was found dependent on the high percentage of phenolic compounds and rosmarinic acid (100 μg per disk) in ethanol extract of O. vulgare (86). Licˇina et al. (2013) found that the potential inhibitory effect was showed by water extract against 19 strains bacteria (MIC <0.16–5 mg/mL). S. aureus and Bacillus spp. strains were sensitive to all extracts (water, acetone, ethanol, diethyl ether and ethyl acetate) with MIC values of 0.16–0.6 mg/mL (7). Akrayi et al. reported the low antibacterial activity of water extract (MIC < 12% v/v) against P. aeruginosa, K. pneumonia, E. coli, and Proteus mirabilis (87). In another study, inhibitory effects of methanolic extract of O. vulgare were evaluated toward ten bacterial and one C. albicans strains. Results showed that extract was active against Porphyromonas gingivalis, Parvimonas micra (MIC 0.3 mg/mL) and had almost no effect on E. coli and C. albicans (MIC 10 mg/mL) and reduced biofilm generation of S. mutans at 5.00 mg/mL (88).
Martins et al. using hydroalcoholic extract, decoction and infusion of O. vulgare, reported similar inhibitory effects against almost all the tested bacteria, while the hydroalcoholic extract showed relatively higher antibacterial activity against E. coli and Proteus vulgaris (20). The concentration used by Martins et al. (20 mg/mL) was noticeably less than the tested by those authors (200 and 100 mg/mL). It should be highlighted that EO contains antimicrobial substances (carvacrol and thymol) more than its methanol, ethanol, water and hexane extracts (89).
In-vivo antibacterial studies
In an animal mouse model (n = 5 BALB/c mice, 2 MIC against P. acnes for 3 days, 2% erythromycin as positive control), a nanoemulsion with O. vulgare EO demonstrated to be effective on acne compared to the reference antibiotic (90). Antibacterial activity against H. pylori potential of a mixture of Satureja hortensis and O. vulgare ssp.hirtum EOs (2:1) was investigated in-vivo (n = 12 Balb/c mice, 2 Mix, for 5 days). By oral administration of this mixture, 70% of the animal group had been treated without any adverse effect or immune response that make this combination a safe and effective antibacterial treatment against H. pylori (91).
Antibacterial clinical trial
The clinical trial (92) evaluated wound healing properties of O. vulgare extract ointment (3%, 40 patients undergone surgical excision) in comparison to the control group. The study proved that the ointment reduced bacterial contamination (S. aureus, 22%) and infection on post-surgical wounds.
Antifungal effects
Mechanisms of action
Effect on fungal cell wall: One of the mechanisms of antifungal activity is related to an attack on the cell wall and retraction of the mycelium cytoplasm and finally resulting in the death of hyphae. The EO of O. vulgare ssp. virens showed antifungal activity against human fungal pathogens (Candida, Cryptococcus, Dermatophyte and Aspergillus strains) with MIC values from 0.16 to 2.5 μL/mL. The result indicated that EOs lead to cell membrane disturbance, resulting in cell death. Antifungal potencies appeared to be enhanced in high carvacrol percentage, and the inhibition of filamentation correlated more with γ-terpinene content (40).
Fungal enzyme inhibition: Brondani et al. (93) demonstrated that O. vulgare EO at 1%, 5% and 10% (in DMSO) demonstrated significant reductions in phospholipase enzyme generation by Candida albicans (15 strains isolated from prosthetic stomatitis patients). Moreover, the mode of antifungal activity could be related to the EO components intervention in enzymatic reactions of cell wall synthesis affecting the morphogenesis and growth of fungal (94).
Anti-Candida activity
The efficacy of O. vulgare on Candida species was proved by Stiles et al. (95) for O. vulgare and nystatin against Candida isolates obtained from human stools (40–45 and 22–25 mm, respectively). Cleff et al. (96) studied the effect of O. vulgare against reference strains of Candida and found that all were susceptible to the EO (MIC 1.2-5 μL/mL). Rosato et al. (97) (11.9 mm for O. vulgare and 17.8 mm for Origanum vulgare+Nystatin) and Souza et al. (94) (MIC 80 μL/mL for EO, 50 μL/mL for ketoconazole) observed that the O. vulgare EO inhibited all the Candida species in their study. In Bhat et al. study, hydrodistillation was a suitable extraction method and MIC was 0.024% which was much lesser than for fluconazole (0.25%) and the active functional group was carvacrol usually found in antifungal herbs (98). Another study showed that the antifungal effect of nystatin on Candida albicans was more than that of aqueous and alcoholic extracts of O. vulgare (99). In-vitro investigation showed strong antifungal (C. albicans strains MIC 36-57 µg/mL) activity than antibacterial activity (MIC 64-120 µg/mL), of O. vulgare spp. glandulosum EO (100).
Effect against other fungi
In-vitro study of O. vulgare EO and its major constituents revealed the highest antifungal activity for γ-terpinene with MIC ranging from 62 to 500 µg/ mL against Sporothrix schenckii, and 125 to 250 µg/mL against Sporothrix brasiliensis (101). In contrast, the results of another study showed significant bacterial activity but a weak antifungal effect of the O. vulgare EO (7).
Antiviral activity
The O. vulgare EO evaluated in the Meneses et al. study showed antiviral activities (CC50 < 100 µg/mL and MIC 3.7 µg/mL) against yellow fever virus via direct virus inactivation (102). Other reports include O. vulgare EO, toward murine norovirus and feline calicivirus with inactivation rates of 1.62 and 3.75 log, respectively (103). Treatment of equine arteritis virus resulted in a significant reduction in viral particle production (6.08 to 1.75 log in the presence of 100 µL ethanolic extract of O. vulgare). Among the main compounds evaluated, quercetin was the most prominent as incubation reduces virus titer (100.6 TCID50/100 µL) (104). Other reports of the antimicrobial activity of O. vulgare have been summarized in Table S4 (in supplementary file).
Safety and side effects
The O. vulgare EO and its main constituents, carvacrol and thymol, have been classified Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for human usage by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Parliament has approved culinary consumption (EP) and Council (105, 106). However, must keep in mind that EO of O. vulgare can be considered safe when used correctly and with precaution because of the toxic effects of carvacrol and thymol concentrated in the essential oil (20). There are a few reports on the adverse effects of O. vulgare essential oil (107).
Conclusion
The result of this survey will be helpful in the utilization of O. vulgare as a source of useful bioactive compounds. Large numbers of O. vulgare species are phytochemically investigated and results showed that their essential oil and extracts possess variable constituents and concentration that can be dependent on diverse factors such as species, soil conditions, climatic, harvest season, geographical location, growth conditions and extraction technique which emphasize the need to standardize quality control studies in the production of O. vulgare preparations. The EO of O. vulgare is the most investigated, and fascinating results have been reported, especially concerning its antimicrobial activity attributed to two main categories of phytochemicals: 1) Volatile compounds: EO comprises a large number of phytochemicals specially carvacrol and thymol. 2) Non-volatile phenolic compounds: Rosmarinic acid as phenolic acids is abundant in O. vulgare extracts. In addition, Flavones are the main flavonoids and luteolin is the most common one followed by apigenin.
Different studies demonstrated the remarkable antimicrobial effect of O. vulgare against a range of bacteria and fungi, especially MRSA, E. coli and C.albicans. Carvacrol and thymol showed a strong antimicrobial effect, especially against resistant microorganisms. For as much as thymol and carvacrol are volatile compounds, so infusion or tea products of O.vulgare have more amounts of these volatile ingredients and more effective than decoction and different extracts of O.vulgare. Furthermore, essential oil and different extracts are typically more effective than pure compounds because of the synergistic effect and mechanism of action involving different targets rather than a single mechanism. Consequently, further studies are required to identify various mechanisms of action and the effective dosage of EOs for clinical trials.
Finally, we can summarize our results as follows: O. vulgare appears as a particularly interesting platform for development into possible consumption in modern antibacterial products from ethnomedical traditions. The most investigated subspecies of O. vulgare is Hirtum and traditional uses reported for all subspecies have been confirmed by in-vitro and in-vivo antimicrobial studies, even if further studies are required for clinical trials. The major limitation in this research is the lack of well-designed, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trials that can improve our current knowledge on the efficacy of O. vulgare ssp. in humans. The O. vulgare EO and its main constituents have been classified Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for human usage by the FDA and traditional preparations and uses that do not show relevant toxicological properties.
To expand and promote research on O. vulgare and its subspecies, the following approaches could be considered of value: standardize quality control studies in the production of various O. vulgare preparations; identify different mechanisms of action and the effective dosage of EOs for clinical trials; explain the biosynthetic pathways, the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics properties (absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion) and the toxicities (chronic and acute toxicity studies) of compounds present in O. vulgare and its subspecies; further studies for the use of O. vulgare various extracts, fractions or pure compounds as effective antimicrobial agents; design new studies concerning the traditional uses and scientific researches for the development of new perspectives for design a of new drugs.
Conflict of interest
All authors involved have no commercial association or other arrangements that might pose or imply a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
This study was partially supported by the Mashhad University of Medical Sciences.
References
- 1.Ietswaart JH. A taxonomic revision of the genus Origanum (Labiatae) Leiden University Press The Hague; 1980. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mozaffarian V. A dictionary of Iranian plant names. Tehran: Farhang Moaser; 1996. p. 396. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Andi SA, Nazeri V, Zamani Z, Hadian J. Morphological diversity of wild Origanum vulgare (Lamiaceae) in Iran. 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Morshedloo MR, Craker LE, Salami A, Nazeri V, Sang H, Maggi F. Effect of prolonged water stress on essential oil content, compositions and gene expression patterns of mono-and sesquiterpene synthesis in two oregano (Origanum vulgare L ) subspecies. Plant Physiol. Biochem. . 2017;111:119–28. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.11.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Aboukhalid K, Al Faiz C, Douaik A, Bakha M, Kursa K, Agacka-Mołdoch M, Machon N, Tomi F, Lamiri A. Influence of environmental factors on essential oil variability in Origanum compactum Benth. growing wild in Morocco. Chem. Biodivers. . 2017;14:e1700158. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201700158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Skoufogianni E, Solomou AD, Danalatos NG. Ecology, Cultivation and Utilization of the Aromatic Greek Oregano (Origanum vulgare L ): A Review. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj Napoca. . 2019;47:545–52. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ličina BZ, Stefanović OD, Vasić SM, Radojević ID, Dekić MS, Čomić LR. Biological activities of the extracts from wild growing Origanum vulgare L. Food control. . 2013;33:498–504. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Khaki MRA, Pahlavan Y, Sepehri G, Sheibani V, Pahlavan B. Antinociceptive effect of aqueous extract of Origanum vulgare L in male rats: possible involvement of the GABAergic system. Iran. J. Pharm. Sci. . 2013;12:407. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Qamar MU, Rasool MH, Jahan S, Shafique M, Aslam B. Antimicrobial resistance antimicrobials, antibiotic resistance, antibiofilm strategies and activity methods. BoD–Books on Demand. . 2019 [Google Scholar]
- 10.Farha MA, Brown ED. Strategies for target identification of antimicrobial natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. . 2016;33:668–680. doi: 10.1039/c5np00127g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Oulia P, Saderi H, Rasouli I, Sefidkon F. Antimicrobial characteristics of some herbal Oils on Pseudomonas aeruginosa with special reference to their chemical compositions. 2009:107–14. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Burt S. Essential oils: their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods—a review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. . 2004;94:223–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.03.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pezzani R, Vitalini S, Iriti M. Bioactivities of Origanum vulgare L : an update. Phytochem. Rev. . 2017;16:1253–68. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lukas B, Schmiderer C, Mitteregger U, Novak J. Arbutin in marjoram and oregano. Food Chem. . 2010;121:185–90. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Padulosi S. Proceedings of the IPGRI International Workshop on Oregano. 8-12 May 1996, CIHEAM, Valenzano (Bari), Italy: Bioversity International. 1997. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yan F, Azizi A, Janke S, Schwarz M, Zeller S, Honermeier B. Antioxidant capacity variation in the oregano (Origanum vulgare L) collection of the German National Genebank. Ind. Crops Prod. . 2016;92:19–25. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bahmani M, Khaksarian M, Rafieian-Kopaei M, Abbasi N. Overview of the therapeutic effects of Origanum vulgare and Hypericum perforatum based on Iran’s ethnopharmacological documents. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. . 2018:12. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mozaffarian V. Identification of medicinal and aromatic plants of Iran. Tehran. Iran: Farhang Moaser Publishers; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zargari A. Medicinal plants. Vol 2. University of Tehran Pub, Tehran, Iran; 1990. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Martins N, Barros L, Santos-Buelga C, Henriques M, Silva S, Ferreira IC. Decoction, infusion and hydroalcoholic extract of Origanum vulgare L : different performances regarding bioactivity and phenolic compounds. Food Chem. . 2014;158:73–80. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.02.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pieroni A, Quave CL, Santoro RF. Folk pharmaceutical knowledge in the territory of the Dolomiti Lucane, inland southern Italy. J. Ethnopharmacol. . 2004;95:373–84. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2004.08.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kokkini S. Taxonomy, diversity and distribution of Origanum. Oregano: proceedings of the IPGRI international workshop on oregano. . 1996 [Google Scholar]
- 23.Skoula M, Harborne JB. The taxonomy and chemistry of Origanum. In: Kintzios S, editor. The taxonomy and chemistry of Origanum. Kintzios S., medicinal and aromatic plants–industrial profiles–oregan, The genera Origanum and Lipia. Taylor & Francis: London: 108 pp. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lukas B, Schmiderer C, Novak J. Phytochemical diversity of Origanum vulgare L subsp vulgare (Lamiaceae) from Austria. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. . 2013;50:106–13. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Khan M, Khan ST, Khan NA, Mahmood A, Al-Kedhairy AA, Alkhathlan HZ. The composition of the essential oil and aqueous distillate of Origanum vulgare L growing in Saudi Arabia and evaluation of their antibacterial activity. Arab. J. Chem. . 2018;11:1189–200. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lukas B, Schmiderer C, Novak J. Essential oil diversity of European Origanum vulgare L(Lamiaceae) Phytochemistry . 2015;119:32–40. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2015.09.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.De Mastro G, Tarraf W, Verdini L, Brunetti G, Ruta C. Essential oil diversity of Origanum vulgare populations from Southern Italy. Food Chem. . 2017;235:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.05.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Houmani Z, Azzoudj S, Naxakis G, Skoula M. The essential oil composition of Algerian Zaâtar: Origanum spp and Thymus spp. J. Herbs Spices Med. Plants . 2002;9:275–80. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Béjaoui A, Chaabane H, Jemli M, Boulila A, Boussaid M. Essential oil composition and antibacterial activity of Origanum vulgare subsp glandulosum Des at different phenological stages. J. Med. Food . 2013;16:1115–20. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2013.0079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mechergui K, Jaouadi W, Coelho JP, Khouja ML. Effect of harvest year on production, chemical composition and antioxidant activities of essential oil of oregano (Origanum vulgare subsp glandulosum (Desf ) Ietswaart) growing in North Africa. Ind. Crops Prod. . 2016;90:32–7. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Semra I, Benmerache A, Chibani S, Kabouche A, Abuhamdah S, Kabouche Z. Composition and antioxidant activity of the essential oil of Origanum glandulosum Desf. from Algeria. Der Pharm. Lett. . 2013;5:381–5. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Moradi M, Hassani A, Ehsani A, Hashemi M, Raeisi M, Naghibi SS. Phytochemical and Antibacterial Properties of Origanum vulgare ssp gracile Growing Wild in Kurdistan Province of Iran. J. Food Qual. Hazards Control . 2014;1:120–4. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sezik E, Tümen G, Kirimer N, Özek T, Baser K. Essential oil composition of four Origanum vulgare subspecies of Anatolian origin. J. Essent. Oil Res. . 1993;5:425–31. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Chalchat J, Pasquier B. Chemical Studies of Origanum vulgare L ssp gracile (Koch) letswaart and Origanum vulgare L ssp virens (Hoffm et Link) letswaart. J. Essent. Oil Res. . 1999;11:143–4. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Shafiee-Hajiabad M, Hardt M, Honermeier B. Comparative investigation about the trichome morphology of Common oregano (Origanum vulgare L subsp vulgare) and Greek oregano (Origanum vulgare L subsp hirtum) J. Appl. Res. Med. Aroma. . 2014;1:50–8. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Skoula M, Gotsiou P, Naxakis G, Johnson CB. A chemosystematic investigation on the mono-and sesquiterpenoids in the genus Origanum (Labiatae) Phytochemistry . 1999;52:649–57. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sarikurkcu C, Zengin G, Oskay M, Uysal S, Ceylan R, Aktumsek A. Composition, antioxidant, antimicrobial and enzyme inhibition activities of two Origanum vulgare subspecies (subsp vulgare and subsp hirtum) essential oils. Ind. Crops Prod. . 2015;70:178–84. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Castilho PC, Savluchinske-Feio S, Weinhold TS, Gouveia SC. Evaluation of the antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of essential oils, extracts and their main components from oregano from Madeira Island, Portugal. Food control . 2012;23:552–8. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Camiletti BX, Asensio CM, Gadban LC, Pecci MdlPG, Conles MY, Lucini EI. Essential oils and their combinations with iprodione fungicide as potential antifungal agents against withe rot (Sclerotium cepivorum Berk) in garlic (Allium sativum L ) crops. Ind. Crops Prod. . 2016;85:117–24. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Vale-Silva L, Silva MJ, Oliveira D, Gonçalves MJ, Cavaleiro C, Salgueiro L, Pinto E. Correlation of the chemical composition of essential oils from Origanum vulgare subsp virens with their in-vitro activity against pathogenic yeasts and filamentous fungi. J. Med. Microbiol. . 2012;61:252–60. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.036988-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Figuérédo G, Cabassu P, Chalchat JC, Pasquier B. Studies of Mediterranean oregano populations VIII—Chemical composition of essential oils of oreganos of various origins. Flavour Frag. J. . 2006;21:134–9. [Google Scholar]
- 42.García-Beltrán J, Esteban M. Properties and Applications of Plants of Origanum Sp. Genus. SM J. Biol. . 2016;2:1006–15. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lukas B, Schmiderer C, Mitteregger U, Franz C, Novak J. Essential oil compounds of Origanum vulgare (Lamiaceae) from Corsica. Nat. Prod. Commun. . 2008;3:1934578X0800300717. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Koldaş S, Demirtas I, Ozen T, Demirci MA, Behçet L. Phytochemical screening, anticancer and antioxidant activities of Origanum vulgare L ssp viride (Boiss ) Hayek a plant of traditional usage. J. Sci. Food Agr. . 2015;95:786–98. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.6903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hashemi SMB, Nikmaram N, Esteghlal S, Khaneghah AM, Niakousari M, Barba FJ, Roohinejad S, Koubaa M. Efficiency of ohmic assisted hydrodistillation for the extraction of essential oil from oregano (Origanum vulgare subsp viride) spices. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. . 2017;41:172–8. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Andi SA, Nazeri V, Hadian J, Zamani Z. Chemical Composition of Essential Oil of Origanum vulgare ssp. viride from Iran. J. Essent. Oil-Bear. Plants . 2011;14:805–9. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Chalchat J, Pasquier B. Morphological and chemical studies of Origanum clones: Origanum vulgare L ssp vulgare. J. Essent. Oil Res. . 1998;10:119–25. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Gutiérrez-Grijalva EP, Picos-Salas MA, Leyva-López N, Criollo-Mendoza MS, Vazquez-Olivo G, Heredia JB. Flavonoids and phenolic acids from oregano: Occurrence, biological activity and health benefits. Plants . 2017;7:2. doi: 10.3390/plants7010002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.W’glarz Z, Osidska E, Geszprych A, Przybyb J. Intraspecific variability of wild marjoram (Origanum vulgare L ) naturally occurring in Poland. Rev. bras. plantas med. . 2006;8:23–6. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Radušienė J, Ivanauskas L, Janulis V, Jakštas V. Composition and variability of phenolic compounds in Origanum vulgare from Lithuania. Biologija . 2008;54:45–9. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Miron T, Plaza M, Bahrim G, Ibáñez E, Herrero M. Chemical composition of bioactive pressurized extracts of Romanian aromatic plants. J. Chromatogr. A . 2011;1218:4918–27. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2010.11.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Vallverdú-Queralt A, Regueiro J, Martínez-Huélamo M, Alvarenga JFR, Leal LN, Lamuela-Raventos RM. A comprehensive study on the phenolic profile of widely used culinary herbs and spices: Rosemary, thyme, oregano, cinnamon, cumin and bay. Food Chem. . 2014;154:299–307. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.12.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kikuzaki H, Nakatani N. Structure of a new antioxidative phenolic acid from oregano (Origanum vulgare L ) Agric. Biol. Chem. . 1989;53:519–24. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kintzios SE. Oregano: the genera Origanum and Lippia. CRC press ; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Skoula M, Grayer RJ, Kite GC, Veitch NC. Exudate flavones and flavanones in Origanum species and their interspecific variation. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. . 2008;36:646–54. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Tomás-Barberán FA, Grayer-Barkmeijer RJ, Gil MI, Harborne JB. Distribution of 6-hydroxy-, 6-methoxy-and 8-hydroxyflavone glycosides in the Labiatae, the Scrophulariaceae and related families. Phytochemistry . 1988;27:2631–45. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Shen D, Pan MH, Wu QL, Park CH, Juliani HR, Ho CT, Simon JE. LC-MS method for the simultaneous quantitation of the anti-inflammatory constituents in oregano (Origanum species) J. Agric. Food Chem. . 2010;58:7119–25. doi: 10.1021/jf100636h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Liang CH, Chou TH, Ding HY. Inhibition of melanogensis by a novel origanoside from Origanum vulgare. J. Dermatol. Sci. . 2010;57:170–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2009.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Zhang XL, Guo YS, Wang CH, Li GQ, Xu JJ, Chung HY, Ye WC, Li YL, Wang GC. Phenolic compounds from Origanum vulgare and their antioxidant and antiviral activities. Food Chem. . 2014;152:300–6. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.11.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Ding HY, Chou TH, Liang CH. Antioxidant and antimelanogenic properties of rosmarinic acid methyl ester from Origanum vulgare. Food Chem. . 2010;123:254–62. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Rao GV, Mukhopadhyay T, Annamalai T, Radhakrishnan N, Sahoo M. Chemical constituents and biological studies of Origanum vulgare Linn. Pharmacogn. Res. . 2011;3:143. doi: 10.4103/0974-8490.81964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Liu H, Zheng A, Liu H, Yu H, Wu X, Xiao C, Dai H, Hao F, Zhang L, Wang Y, Tang H. Identification of three novel polyphenolic compounds, origanine A–C, with unique skeleton from Origanum vulgare L using the hyphenated LC-DAD-SPE-NMR/MS methods. J. Agric. Food Chem. . 2011;60:129–35. doi: 10.1021/jf204406u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Lin YL, Wang CN, Shiao YJ, Liu TY, Wang WY. Benzolignanoid and polyphenols from Origanum vulgare. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. . 2003;50:1079–83. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Baranauskaitė J, Jakštas V, Ivanauskas L, Kopustinskienė DM, Drakšienė G, Masteikova R, Bernatonienė J. Optimization of carvacrol, rosmarinic, oleanolic and ursolic acid extraction from oregano herbs (Origanum onites L Origanum vulgare spp hirtum and Origanum vulgare L) Nat. Prod. Res. . 2016;30:672–4. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2015.1038998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Assiri AM, Elbanna K, Al-Thubiani A, Ramadan MF. Cold-pressed oregano (Origanum vulgare) oil: a rich source of bioactive lipids with novel antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. Eur. Food Res. Technol. . 2016;242:1013–23. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Al-Tameme HJ, Hameed IH, Idan SA, Hadi MY. Biochemical analysis of Origanum vulgare seeds by fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) J. Pharmacognosy Phytother. . 2015;7:221–37. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Koukoulitsa C, Zika C, Geromichalos GD, Demopoulos VJ, Skaltsa H. Evaluation of aldose reductase inhibition and docking studies of some secondary metabolites, isolated from Origanum vulgare L ssp hirtum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. . 2006;14:1653–59. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2005.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Nazzaro F, Fratianni F, De Martino L, Coppola R, De Feo V. Effect of essential oils on pathogenic bacteria. Pharmaceuticals . 2013;6:1451–74. doi: 10.3390/ph6121451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.de Barros JC, da Conceição ML, Neto NJ, da Costa AC, Júnior JP, Junior ID, de Souza EL. Interference of Origanum vulgare L essential oil on the growth and some physiological characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from foods. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. . 2009;42:1139–43. [Google Scholar]
- 70.Langeveld WT, Veldhuizen EJ, Burt SA. Synergy between essential oil components and antibiotics: a review. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. . 2014;40:76–94. doi: 10.3109/1040841X.2013.763219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Ghafari O, Sharifi A, Ahmadi A, Nayeri Fasaei B. Antibacterial and anti-PmrA activity of plant essential oils against fluoroquinolone-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae clinical isolates. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. . 2018;67:564–9. doi: 10.1111/lam.13050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Perrin E, Maggini V, Maida I, Gallo E, Lombardo K, Madarena MP, Buroni S, Scoffone VC, Firenzuoli F, Mengoni A, Fani R. Antimicrobial activity of six essential oils against Burkholderia cepacia complex: insights into mechanism (s) of action. Future Microbiol. . 2018;13:59–67. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2017-0121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Cirino ICS, Menezes-Silva SMP, Silva HTD, de Souza EL, Siqueira-Júnior JP. The essential oil from Origanum vulgare and its individual constituents carvacrol and thymol enhance the effect of tetracycline against Staphylococcus aureus. Chemotherapy . 2014;60:290–3. doi: 10.1159/000381175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Bharti V, Vasudeva N, Sharma S, Duhan JS. Antibacterial activities of Origanum vulgare alone and in combination with different antimicrobials against clinical isolates of Salmonella typhi. Anc. Sci. Life . 2013;32:212–6. doi: 10.4103/0257-7941.131974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Wijesundara NM, Rupasinghe HV. Essential oils from Origanum vulgare and Salvia officinalis exhibit antibacterial and anti-biofilm activities against Streptococcus pyogenes. Microb. Pathog. . 2018;117:118–27. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.02.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Lee JH, Kim YG, Lee J. Carvacrol-rich oregano oil and thymol-rich thyme red oil inhibit biofilm formation and the virulence of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. J. Appl. Microbiol. . 2017;123:1420–8. doi: 10.1111/jam.13602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Ultee A, Bennik M, Moezelaar R. The phenolic hydroxyl group of carvacrol is essential for action against the food-borne pathogen Bacillus cereus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. . 2002;68:1561–8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.4.1561-1568.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Khan ST, Khan M, Ahmad J, Wahab R, Abd-Elkader OH, Musarrat J, Alkhathlan HZ, Al-Kedhairy AA. Thymol and carvacrol induce autolysis, stress, growth inhibition and reduce the biofilm formation by Streptococcus mutans. Amb Express . 2017;7:49. doi: 10.1186/s13568-017-0344-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Caillet S, Lacroix M. Effect of gamma radiation and oregano essential oil on murein and ATP concentration of Listeria monocytogenes. J. Food Prot. . 2006;69:2961–9. doi: 10.4315/0362-028x-69.12.2961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Caillet S, Shareck F, Lacroix M. Effect of gamma radiation and oregano essential oil on murein and ATP concentration of Escherichia coli O157: H7. J. Food Prot. . 2005;68:2571–9. doi: 10.4315/0362-028x-68.12.2571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Caillet S, Ursachi L, Shareck F, Lacroix M. Effect of gamma radiation and oregano essential oil on murein and ATP concentration of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Food Sci. . 2009;74:M499–M508. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2009.01368.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Chaudhry NMA, Saeed S, Tariq P. Antibacterial effects of oregano (Origanum vulgare) against gram negative bacilli. Pak. J. Bot. . 2007;39:609. [Google Scholar]
- 83.Saeed S, Tariq P. Antibacterial activity of oregano (Origanum vulgare Linn against gram positive bacteria. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. . 2009;22:421–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Brđanin S, Bogdanović N, Kolundžić M, Milenković M, Golić N, Kojić M, Kundaković T. Antimicrobial activity of oregano (Origanum vulgare L ): And basil (Ocimum basilicum L ): Extracts. Adv. Technol. . 2015;4:5–10. [Google Scholar]
- 85.Mehreen A, Waheed M, Liaqat I, Arshad N. Phytochemical, Antimicrobial, and Toxicological Evaluation of Traditional Herbs Used to Treat Sore Throat. Biomed. Res. Int. . 2016;2016:8503426. doi: 10.1155/2016/8503426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Chun SS, Vattem DA, Lin YT, Shetty K. Phenolic antioxidants from clonal oregano (Origanum vulgare) with antimicrobial activity against Helicobacter pylori. Process Biochem. . 2005;40:809–16. [Google Scholar]
- 87.Akrayi HF, Salih RM, Hamad PA. In-vitro screening of antibacterial properties of rhus coriaria and Origanum vulgare against some pathogenic bacteria. Aro Sci. J. . 2016;3:35–41. [Google Scholar]
- 88.Hickl J, Argyropoulou A, Sakavitsi ME, Halabalaki M, Al-Ahmad A, Hellwig E, Aligiannis N, Skaltsounis AL, Wittmer A, Vach K, Karygianni L. Mediterranean herb extracts inhibit microbial growth of representative oral microorganisms and biofilm formation of Streptococcus mutans. PLoS One . 2018;13 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Şahin F, Güllüce M, Daferera D, Sökmen A, Sökmen M, Polissiou M, Agar G, Özer H. Biological activities of the essential oils and methanol extract of Origanum vulgare ssp vulgare in the Eastern Anatolia region of Turkey. Food control . 2004;15:549–57. [Google Scholar]
- 90.Taleb MH, Abdeltawab NF, Shamma RN, Abdelgayed SS, Mohamed SS, Farag MA, Ramadan MA. Origanum vulgare L essential oil as a potential anti-acne topical nanoemulsion—in-vitro and in-vivo study. Molecules . 2018;23:2164. doi: 10.3390/molecules23092164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Harmati M, Gyukity-Sebestyen E, Dobra G, Terhes G, Urban E, Decsi G, Mimica‐Dukić N, Lesjak M, Simin N, Pap B, Nemeth IB. Binary mixture of Satureja hortensis and Origanum vulgare subsp hirtum essential oils: in-vivo therapeutic efficiency against Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter . 2017;22 doi: 10.1111/hel.12350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Ragi J, Pappert A, Rao B, Havkin-Frenkel D, Milgraum S. Oregano extract ointment for wound healing: a randomized, double-blind, petrolatum-controlled study evaluating efficacy. J. Drugs Dermatol. . 2011;10:1168–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Brondani LP, da Silva Neto TA, Freitag RA, Lund RG. Evaluation of anti-enzyme properties of Origanum vulgare essential oil against oral Candida albicans. J. Mycol. Med. . 2018;28:94–100. doi: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2017.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Souza NAB, Lima EdO, Guedes DN, Pereira FdO, Souza ELd, Sousa FBd. Efficacy of Origanum essential oils for inhibition of potentially pathogenic fungi. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. . 2010;46:499–508. [Google Scholar]
- 95.Stiles JC, Sparks W, Ronzio RA. The inhibition of Candida albicans by oregano. J Appl Nutr . 1995;47:96–102. [Google Scholar]
- 96.Cleff MB, Meinerz AR, Xavier M, Schuch LF, Meireles MCA, Rodrigues MR, Mello JR. In-vitro activity of Origanum vulgare essential oil against Candida species. Braz. J. Microbiol. . 2010;41:116–23. doi: 10.1590/S1517-838220100001000018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Rosato A, Vitali C, Piarulli M, Mazzotta M, Argentieri MP, Mallamaci R. In-vitro synergic efficacy of the combination of Nystatin with the essential oils of Origanum vulgare and Pelargonium graveolens against some Candida species. Phytomedicine . 2009;16:972–5. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2009.02.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Bhat V, Sharma S, Shetty V, Shastry C, Rao CV, Shenoy S, Saha S, Balaji S. Characterization of herbal antifungal agent, Origanum vulgare against oral Candida spp isolated from patients with Candida-Associated denture stomatitis: An in-vitro study. Contemp. Clin. Dent. . 2018;9:S3. doi: 10.4103/ccd.ccd_537_17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Movaghari Pour A, Sheikh Fathollahi M, Poor Zamani M, Abedini S, Jamali Z. Comparison of Anti-Fungal Effect of Origanum Vulgare Extract Versus Nystatin On Candida Albicans; an In-vitro Study. J. Mashhad Dent. Sch. . 2018;42:271–7. [Google Scholar]
- 100.Bendahou M, Muselli A, Grignon-Dubois M, Benyoucef M, Desjobert JM, Bernardini AF, Costa J. Antimicrobial activity and chemical composition of Origanum glandulosum Des essential oil and extract obtained by microwave extraction: Comparison with hydrodistillation. Food Chem. . 2008;106:132–9. [Google Scholar]
- 101.Couto CS, Raposo NR, Rozental S, Borba-Santos LP, Bezerra LM, de Almeida PA, Brandão MA. Chemical composition and antifungal properties of essential oil of Origanum vulgare Linnaeus (Lamiaceae) against Sporothrix schenckii and Sporothrix brasiliensis. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. . 2015;14:1207–12. [Google Scholar]
- 102.Meneses R, Ocazionez RE, Martinez JR, Stashenko EE. Inhibitory effect of essential oils obtained from plants grown in Colombia on yellow fever virus replication in-vitro. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. . 2009;8:8. doi: 10.1186/1476-0711-8-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Elizaquível P, Azizkhani M, Aznar R, Sánchez G. The effect of essential oils on norovirus surrogates. Food Control. . 2013;32:275–8. [Google Scholar]
- 104.Einhardt Blank D, Almeida Corrêa R, Freitag RA, Brum Cleff M, de Oliveira Hübner S. Anti-equine arteritis virus activity of ethanolic extract and compounds from Origanum vulgare. Semina:Cienc. Agrar. . 2017:38. [Google Scholar]
- 105.Burdock GA, Carabin IG. Generally recognized as safe (GRAS): history and description. Toxicol. Lett. . 2004;150:3–18. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2003.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Hyldgaard M, Mygind T, Meyer RL. Essential oils in food preservation: mode of action, synergies, and interactions with food matrix components. Front. Microbiol. . 2012;3:12. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Cleff MB, Meinerz AR, Sallis ES, Antunes TA, Mattei A, Rodrigues MR, Meireles MC, Mello JR. Pre-clinic toxicity of the repeate-dose of Origanum vulgare L (Origanum) essential oil in Wistar rats. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. . 2008;27:704–9. [Google Scholar]
- 108.Šavikin K, Zdunić G, Menković N, Živković J, Ćujić N, Tereščenko M, Bigović D. Ethnobotanical study on traditional use of medicinal plants in South-Western Serbia, Zlatibor district. J. Ethnopharmacol. . 2013;146:803–10. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Jarić S, Mačukanović-Jocić M, Djurdjević L, Mitrović M, Kostić O, Karadžić B, Pavlović P. An ethnobotanical survey of traditionally used plants on Suva planina mountain (south-eastern Serbia) J. Ethnopharmacol. . 2015;175:93–108. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Zlatković BK, Bogosavljević SS, Radivojević AR, Pavlović MA. Traditional use of the native medicinal plant resource of Mt Rtanj (Eastern Serbia): Ethnobotanical evaluation and comparison. J. Ethnopharmacol. . 2014;151:704–13. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.11.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Pieroni A, Giusti ME, Quave CL. Cross-cultural ethnobiology in the Western Balkans: medical ethnobotany and ethnozoology among Albanians and Serbs in the Pešter Plateau, Sandžak, South-Western Serbia. Hum. Ecol. . 2011;39:333. [Google Scholar]
- 112.Tahraoui A, El-Hilaly J, Israili Z, Lyoussi B. Ethnopharmacological survey of plants used in the traditional treatment of hypertension and diabetes in south-eastern Morocco (Errachidia province) J. Ethnopharmacol. . 2007;110:105–17. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2006.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Ennabili A, Gharnit N, El Hamdouni E. Inventory and social interest of medicinal, aromatic and honey-plants from Mokrisset region (NW of Morocco) Stud. Bot. . 2000;19:57–74. [Google Scholar]
- 114.Eddouks M, Maghrani M, Lemhadri A, Ouahidi ML, Jouad H. Ethnopharmacological survey of medicinal plants used for the treatment of diabetes mellitus, hypertension and cardiac diseases in the south-east region of Morocco (Tafilalet) J. Ethnopharmacol. . 2002;82:97–103. doi: 10.1016/s0378-8741(02)00164-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.González-Tejero M, Casares-Porcel M, Sánchez-Rojas C, Ramiro-Gutiérrez J, Molero-Mesa J, Pieroni A, Giusti ME, Censorii E, De Pasquale C, Della A, Paraskeva-Hadijchambi D. Medicinal plants in the Mediterranean area: synthesis of the results of the project Rubia. J. Ethnopharmacol. . 2008;116:341–57. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2007.11.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Leporatti ML, Ivancheva S. Preliminary comparative analysis of medicinal plants used in the traditional medicine of Bulgaria and Italy. J. Ethnopharmacol. . 2003;87:123–42. doi: 10.1016/s0378-8741(03)00047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Mamedov N, Gardner Z, Craker LE. Medicinal plants used in Russia and Central Asia for the treatment of selected skin conditions. J. Herbs Spices Med. Plants . 2005;11:191–222. [Google Scholar]
- 118.Ghorbani A. Studies on pharmaceutical ethnobotany in the region of Turkmen Sahra, north of Iran:(Part 1): General results. J. Ethnopharmacol. . 2005;102:58–68. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2005.05.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.de Santayana MP, Blanco E, Morales R. Plants known as té in Spain: an ethno-pharmaco-botanical review. J. Ethnopharmacol. . 2005;98:1–19. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2004.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Boudjelal A, Henchiri C, Sari M, Sarri D, Hendel N, Benkhaled A, Ruberto G. Herbalists and wild medicinal plants in M’Sila (North Algeria): An ethnopharmacology survey. J. Ethnopharmacol. . 2013;148:395–402. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.03.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Ruberto G, Baratta MT, Sari M, Kaâbeche M. Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of essential oils from Algerian Origanum glandulosum Desf. Flavour Frag. J. . 2002;17:251–4. [Google Scholar]
- 122.Sezik E, Zor M, Yesilada E. Traditional medicine in Turkey II Folk medicine in Kastamonu. Int. J. Pharmacogn. . 1992;30:233–9. [Google Scholar]
- 123.Ozturk M, Altundag E, Ibadullayeva SJ, Altay V, Aslanipour B. A comparative analysis of medicinal and aromatic plants used in the traditional medicine of Igdir (Turkey), Nachchivan (Azerbaijan), and tabriz (Iran) Pak. J. Bot. . 2018;50:337–43. [Google Scholar]
- 124.Altundag E, Ozturk M. Ethnomedicinal studies on the plant resources of east Anatolia, Turkey. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. . 2011;19:756–77. [Google Scholar]
- 125.Hanlidou E, Karousou R, Kleftoyanni V, Kokkini S. The herbal market of Thessaloniki (N Greece) and its relation to the ethnobotanical tradition. J. Ethnopharmacol. . 2004;91:281–99. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2004.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Duarte MCT, Figueira GM, Sartoratto A, Rehder VLG, Delarmelina C. Anti-Candida activity of Brazilian medicinal plants. J. Ethnopharmacol. . 2005;97:305–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2004.11.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Blanco E, Macıa M, Morales R. Medicinal and veterinary plants of El Caurel (Galicia, northwest Spain) J. Ethnopharmacol. . 1999;65:113–24. doi: 10.1016/s0378-8741(98)00178-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Benítez G, González-Tejero M, Molero-Mesa J. Pharmaceutical ethnobotany in the western part of Granada province (southern Spain): Ethnopharmacological synthesis. J J. Ethnopharmacol. . 2010;129:87–105. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.02.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Scherrer AM, Motti R, Weckerle CS. Traditional plant use in the areas of Monte Vesole and Ascea, Cilento National Park (Campania, Southern Italy) J. Ethnopharmacol. . 2005;97:129–43. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2004.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Kültür Ş. Medicinal plants used in Kırklareli province (Turkey) J. Ethnopharmacol. . 2007;111:341–64. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2006.11.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Chorianopoulos N, Kalpoutzakis E, Aligiannis N, Mitaku S, Nychas G-J, Haroutounian SA. Essential oils of Satureja, Origanum, and Thymus species: chemical composition and antibacterial activities against foodborne pathogens. J. Agric. Food Chem. . 2004;52:8261–7. doi: 10.1021/jf049113i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Mancini E, Camele I, Elshafie HS, De Martino L, Pellegrino C, Grulova D, De Feo V. Chemical composition and biological activity of the essential oil of Origanum vulgare ssp hirtum from different areas in the Southern Apennines (Italy) Chem. Biodivers. . 2014;11:639–51. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201300326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Gonceariuc M, a Moldovei AdS, Balmus Z. Promising Origanum vulgare ssp. vulgare l. and Origanum vulgare ssp hirtum (link) Ietswaart genotypes. Buletinul Academiei de Stiinte a Moldovei Stiintele vietii (Republic of Moldova) 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 134.Esen G, Azaz AD, Kurkcuoglu M, Baser KHC, Tinmaz A. Essential oil and antimicrobial activity of wild and cultivated Origanum vulgare L subsp hirtum (Link) letswaart from the Marmara region, Turkey. Flavour Frag. J. . 2007;22:371–6. [Google Scholar]
- 135.Konakchiev A, Genova E, Couladis M. Chemical composition of the essential oil of Origanum vulgare ssp hirtum (Link) Ietswaart in Bulgaria. Comptes Rendus de l ‘Academie Bulg. des Sci. . 2004;57:11–49. [Google Scholar]
- 136.Garcıa M, Sanz J. Analysis of Origanum vulgare volatiles by direct thermal desorption coupled to gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A . 2001;918:189–94. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)00750-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Hashemi SMB, Khaneghah AM, Ghahfarrokhi MG, Eş I. Basil-seed gum containing Origanum vulgare subsp viride essential oil as edible coating for fresh cut apricots. Postharvest Biol. Technol. . 2017;125:26–34. [Google Scholar]
- 138.Nostro A, Blanco AR, Cannatelli MA, Enea V, Flamini G, Morelli I, Sudano Roccaro A, Alonzo V. Susceptibility of methicillin-resistant staphylococci to oregano essential oil, carvacrol and thymol. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. . 2004;230:191–5. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1097(03)00890-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Raina AP, Negi K. Chemical diversity among different accessions of Origanum vulgare L ssp vulgare collected from Central Himalayan region of Uttarakhand, India. J. Essent. Oil Res. . 2014;26:420–6. [Google Scholar]
- 140.Kula J, Majda T, Stoyanova A, Georgiev E. Chemical composition of Origanum vulgare L essential oil from Bulgaria. J. Essent. Oil-Bear. Plants . 2007;10:215–20. [Google Scholar]
- 141.Vazirian M, Mohammadi M, Farzaei M, Amin G, Amanzadeh Y. Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of Origanum vulgare subs vulgare essential oil from Iran. Res. J. Pharmacogn . 2015;2:41–6. [Google Scholar]
- 142.Giuliani C, Maggi F, Papa F, Maleci Bini L. Congruence of phytochemical and morphological profiles along an altitudinal gradient in Origanum vulgare ssp vulgare from Venetian Region (NE Italy) Chem. Biodiver. . 2013;10:569–83. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201300019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Mockute D, Bernotiene G, Judzentiene A. The β-ocimene chemotype of essential oils of the inflorescences and the leaves with stems from Origanum vulgare ss vulgare growing wild in Lithuania. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. . 2003;31:269–78. [Google Scholar]
- 144.Vujicic M, Nikolic I, Kontogianni VG, Saksida T, Charisiadis P, Orescanin-Dusic Z, Blagojevic D, Stosic-Grujicic S, Tzakos AG, Stojanovic I. Methanolic extract of Origanum vulgare ameliorates type 1 diabetes through antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic activity. Br. J. Nutr. . 2015;113:770–82. doi: 10.1017/S0007114514004048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Koukoulitsa C, Karioti A, Bergonzi MC, Pescitelli G, Di Bari L, Skaltsa H. Polar constituents from the aerial parts of Origanum vulgare L ssp hirtum growing wild in Greece. J. Agric. Food Chem. . 2006;54:5388–92. doi: 10.1021/jf061477i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Agiomyrgianaki A, Dais P. Simultaneous determination of phenolic compounds and triterpenic acids in oregano growing wild in Greece by 31P NMR spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Chem. . 2012;50:739–48. doi: 10.1002/mrc.3877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Grevsen K, Frette X, Christensen LP. Content and composition of volatile terpenes, flavonoids and phenolic acids in Greek oregano (Origanum vulgare L ssp hirtum) at different development stages during cultivation in cool temperate climate. Eur. J. Hortic. Sci. . 2009;74:193. [Google Scholar]
- 148.González M, Luis C, Lanzelotti P. Perfil de polifenoles de Origanum vulgare L ssp viridulum de Argentina. Phyton (Buenos Aires) 2014; 83:179–184. [Google Scholar]
- 149.Oniga I, Pușcaș C, Silaghi-Dumitrescu R, Olah N-K, Sevastre B, Marica R, Marcus I, Sevastre-Berghian AC, Benedec D, Pop CE, Hanganu D. Origanum vulgare ss vulgare: Chemical composition and biological studies. Molecules . 2018;23:2077. doi: 10.3390/molecules23082077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Hossain MB, Rai DK, Brunton NP, Martin-Diana AB, Barry-Ryan C. Characterization of phenolic composition in Lamiaceae spices by LC-ESI-MS/MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. . 2010;58:10576–81. doi: 10.1021/jf102042g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Goun E, Cunningham G, Solodnikov S, Krasnykch O, Miles H. Antithrombin activity of some constituents from Origanum vulgare. Fitoterapia . 2002;73:692–4. doi: 10.1016/s0367-326x(02)00245-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Wojdyło A, Oszmiański J, Czemerys R. Antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds in 32 selected herbs. Food chemistry . 2007;105:940–9. [Google Scholar]
- 153.Matsuura H, Chiji H, Asakawa C, Amano M, Yoshihara T, Mizutani J. DPPH radical scavengers from dried leaves of oregano (Origanum vulgare) Biosci. Biotech. Bioch. . 2003;67:2311–6. doi: 10.1271/bbb.67.2311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Tang Z, Zeng Y, Zhou Y, He P, Fang Y, Zang S. Determination of active ingredients of Origanum vulgare L and its medicinal preparations by capillary electrophoresis with electrochemical detection. Anal. Lett. . 2006;39:2861–75. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2005.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.De Martino L, De Feo V, Formisano C, Mignola E, Senatore F. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of the essential oils from three chemotypes of Origanum vulgare L ssp hirtum (Link) Ietswaart growing wild in Campania (Southern Italy) Molecules . 2009;14:2735–46. doi: 10.3390/molecules14082735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Sarac N, Ugur A. Antimicrobial activities of the essential oils of Origanum onites Origanum vulgare L subspecies hirtum (Link) Ietswaart, Satureja thymbra L and Thymus cilicicus Boiss & Bal growing wild in Turkey. J. Med. Food . 2008;11:568–73. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2007.0520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Fournomiti M, Kimbaris A, Mantzourani I, Plessas S, Theodoridou I, Papaemmanouil V, Kapsiotis I, Panopoulou M, Stavropoulou E, Bezirtzoglou EE, Alexopoulos A. Antimicrobial activity of essential oils of cultivated oregano (Origanum vulgare), sage (Salvia officinalis), and thyme (Thymus vulgaris) against clinical isolates of Escherichia coli, Klebsiella oxytoca, and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. . 2015;26 doi: 10.3402/mehd.v26.23289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Stefanakis MK, Touloupakis E, Anastasopoulos E, Ghanotakis D, Katerinopoulos HE, Makridis P. Antibacterial activity of essential oils from plants of the genus Origanum. Food control . 2013;34:539–46. [Google Scholar]
- 159.De Falco E, Roscigno G, Landolfi S, Scandolera E, Senatore F. Growth, essential oil characterization, and antimicrobial activity of three wild biotypes of oregano under cultivation condition in Southern Italy. Ind. Crops Prod. . 2014;62:242–9. [Google Scholar]
- 160.Busatta C, Mossi AJ, Rodrigues MRA, Cansian RL, Oliveira JVd. Evaluation of Origanum vulgare essential oil as antimicrobial agent in sausage. Braz. J. Microbiol. . 2007;38:610–6. [Google Scholar]
- 161.Sakkas H, Gousia P, Economou V, Sakkas V, Petsios S, Papadopoulou C. In-vitro antimicrobial activity of five essential oils on multidrug resistant Gram-negative clinical isolates. J. Intercult. Ethnopharmacol. . 2016;5:212. doi: 10.5455/jice.20160331064446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Santoyo S, Cavero S, Jaime L, Ibanez E, Senorans F, Reglero G. Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of compounds with antimicrobial activity from Origanum vulgare determination of optimal extraction parameters. J. Food Prot. . 2006;69:369–75. doi: 10.4315/0362-028x-69.2.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Teixeira B, Marques A, Ramos C, Serrano C, Matos O, Neng NR, Nogueira JM, Saraiva JA, Nunes ML. Chemical composition and bioactivity of different oregano (Origanum vulgare) extracts and essential oil. J. Sci. Food Agr. . 2013;93:2707–14. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.6089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Hussain AI, Anwar F, Rasheed S, Nigam PS, Janneh O, Sarker SD. Composition, antioxidant and chemotherapeutic properties of the essential oils from two Origanum species growing in Pakistan. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. . 2011;21:943–52. [Google Scholar]
- 165.Bahmani M, Taherikalani M, Khaksarian M, Soroush S, Ashrafi B, Heydari R. Phytochemical profiles and antibacterial activities of Origanum vulgare and Hypericum perforatum and carvacrol and hypericin as a promising anti-Staphylococcus aureus. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. . 2019;19:923–32. doi: 10.2174/1389557519666190121124317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Mazzarrino G, Paparella A, Chaves-López C, Faberi A, Sergi M, Sigismondi C, Compagnone D, Serio A. Salmonella enterica and Listeria monocytogenes inactivation dynamics after treatment with selected essential oils. Food Control . 2015;50:794–803. [Google Scholar]
- 167.Elshafie H, Armentano M, Carmosino M, Bufo S, De Feo V, Camele I. Cytotoxic activity of Origanum vulgare L on hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2 and evaluation of its biological activity. Molecules . 2017;22:1435. doi: 10.3390/molecules22091435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Pesavento G, Maggini V, Maida I, Nostro AL, Calonico C, Sassoli C, Perrin E, Fondi M, Mengoni A, Chiellini C, Vannacci A. Essential oil from Origanum vulgare completely inhibits the growth of multidrug-resistant cystic fibrosis pathogens. Nat. Prod. Commun. . 2016;11 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Grondona E, Gatti G, López AG, Sánchez LR, Rivero V, Pessah O, Zunino MP, Ponce AA. Bio-efficacy of the essential oil of oregano (Origanum vulgare Lamiaceae ssp Hirtum) Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. . 2014;69:351–7. doi: 10.1007/s11130-014-0441-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Ebani V, Nardoni S, Bertelloni F, Pistelli L, Mancianti F. Antimicrobial Activity of Five Essential Oils against Bacteria and Fungi Responsible for Urinary Tract Infections. Molecules . 2018;23:1668. doi: 10.3390/molecules23071668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Boskovic M, Zdravkovic N, Ivanovic J, Janjic J, Djordjevic J, Starcevic M, Baltic MZ. Antimicrobial activity of Thyme (Tymus vulgaris) and Oregano (Origanum vulgare) essential oils against some food-borne microorganisms. Procedia Food Sci. . 2015;5:18–21. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.