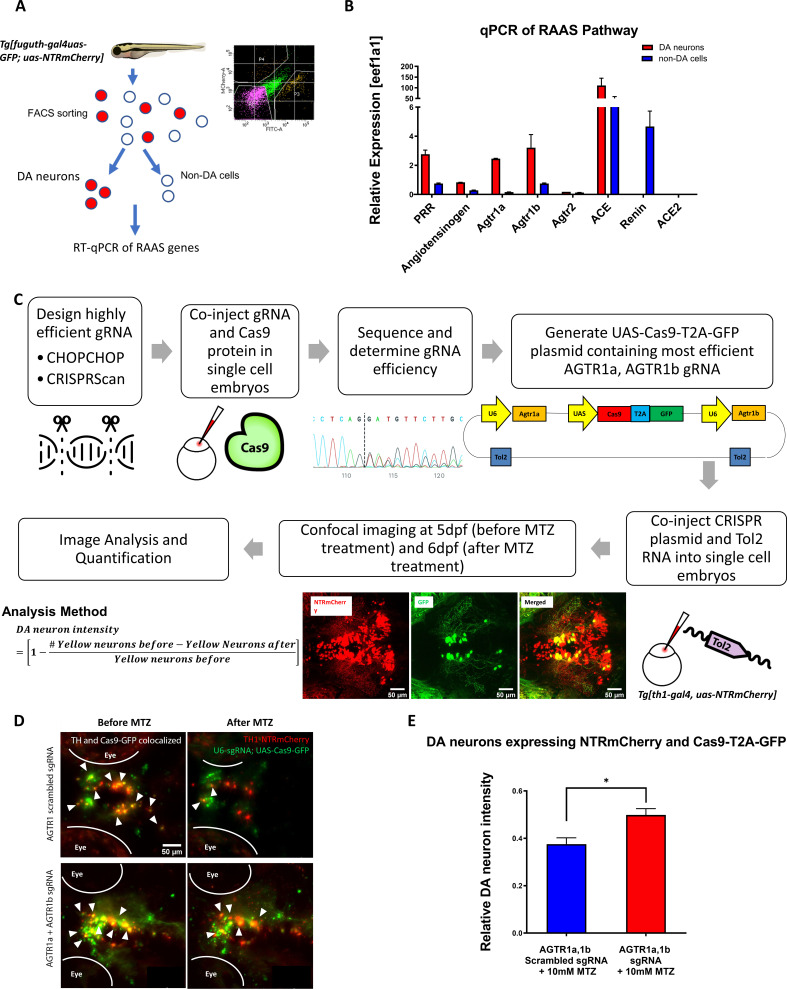
Figure 3. Genetic inactivation of agtr1a and agtr1b in DA neurons is neuroprotective.
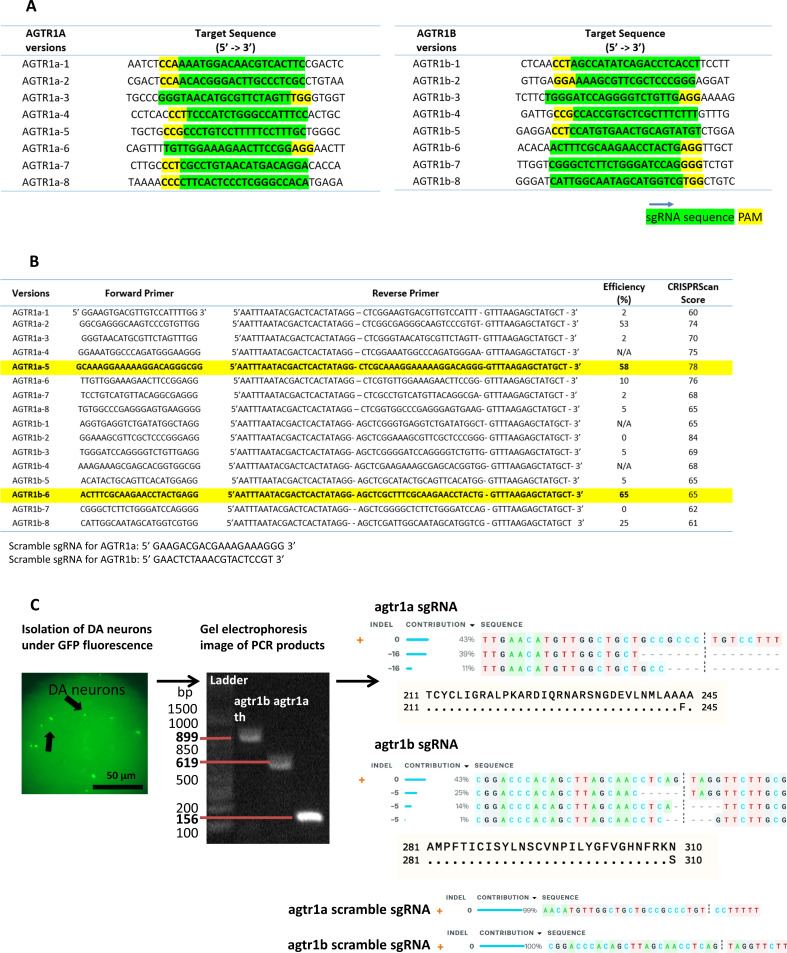
(A) Schematic showing the procedure of FACs to isolate DA neurons for qPCR analysis of RAAS pathway gene expression. (B) qPCR data of 5 dpf larval samples show the relative expression of RAAS pathway genes normalized to the house-keeping gene eef1a1, in DA neurons (red bars) versus non-DA cells (blue bars). PRR (prorenin receptor), agtr1a (Angiotensin II receptor, type 1a), agtr1b (Angiotensin II receptor, type 1b), agtr2 (Angiotensin II receptor, type 2), ace (Angiotensin I converting enzyme), ace2 (Angiotensin I converting enzyme 2) (n = 2 biological replicates, 6 technical replicates). (C) A schematic showing the conditional CRISPR design, imaging, and analysis procedure to inactivate agtr1a and agtr1b in DA neurons. (D) Confocal images of DA neurons in 5 dpf (before MTZ treatment) and 6 dpf (24 hr after 10 mM MTZ treatment) larvae injected with either the scrambled control sgRNA construct (top) or the effective agtr1a and agtr1b sgRNA construct (bottom). Yellow cells express both NTR-mCherry and Cas9. (E) Quantification shows a significant preservation of DA neuron intensity in the agtr1a and agtr1b sgRNA construct-injected animals compared to the scrambled sgRNA control upon 10 mM MTZ treatment. (n = 15, p < 0.01, unpaired t-test).