Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a global pandemic with over 120 million cases and 2.6 million deaths as of March 2021.1 It has had a significant impact on the healthcare system with drastic reductions in elective and nonessential procedures. Previous surveys have shown a significant reduction in procedure volumes at the height of the pandemic.2 Since then, readily available testing for COVID-19 and use of personal protective equipment (PPE) have enabled routine preprocedure testing and the safe conduct of endoscopy in many countries.3
Gastrointestinal (GI) societies have put forth recommendations to help guide endoscopy centers to resume services in a safe manner.4, 5, 6, 7 However, each country has unique challenges, such as rates of infection, local policy, and availability of testing and PPE, that pose as barriers to resumption of services. We conducted this survey-based study to understand the ongoing impact of COVID-19 on endoscopy units and trainees worldwide.
A web-based survey was developed by the World Endoscopy Organization comprising 21 questions focused on endoscopy units’ baseline information, volumes, COVID-19 testing practices and outcomes, pandemic’s impact on volumes, and barriers to resumption of services. The survey was sent on October 15, 2020, and responses were collected through December 15, 2020 (Supplementary Table 1). All participants provided informed consent, and Institutional Review Board exemption was obtained.
One hundred twenty-one endoscopy units including 3618 personnel (36% endoscopists, 47% nurses, and 17% technicians) from 35 countries across 6 continents completed the survey (Figure 1 ). These units reported 1,029,000 endoscopic procedures performed in the year before COVID-19, 45% lower and 55% upper endoscopic procedures (median, 5000; interquartile range [IQR], 1950–10,000). A median number of 8 endoscopists (IQR, 4–15), 6 nurses (IQR, 3-15), and 3 technicians (IQR, 1-8) participated.
Figure 1.
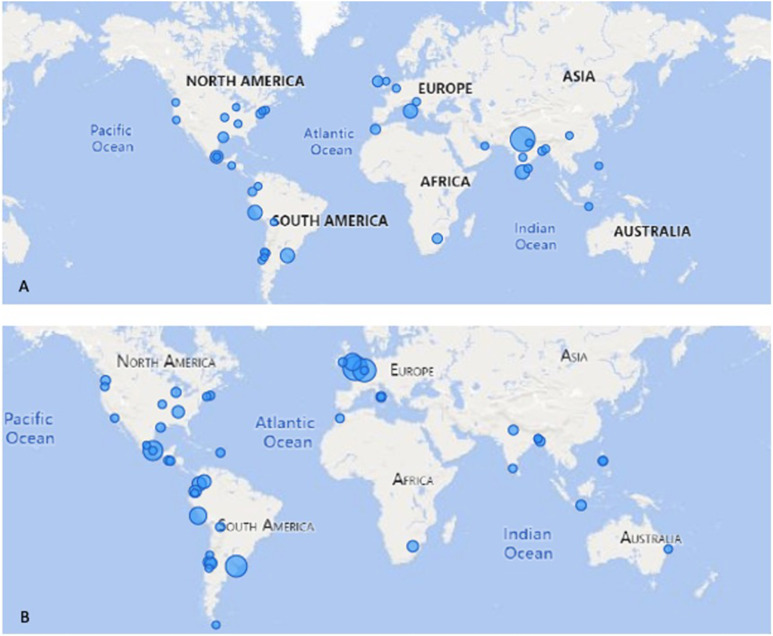
Geographic distribution of positive for COVID-19 in (A) patients and (B) personnel (size of bubble represents relative percent positive).
Of the 121 endoscopy units, 43% reported testing for COVID-19 on all patients before endoscopy, 43% reported no testing, and 14% reported only testing occasionally. Ninety-percent of units used polymerase chain reaction–based or other antigen tests and 10% used antibody-based (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay/fingerstick rapid antibody) tests. An average of 1396 tests (standard deviation, 4402) were completed by each endoscopy unit (median, 275; IQR, 50, 1000): 1.3% of patients tested were positive for COVID-19 (Figure 1 A), 32% of endoscopy units required a negative test before performing an endoscopy, 10% required the patient to be asymptomatic for 72 hours, 31% required both, and 27% reported no further testing or waiting requirements.
Only 19% of participating units tested all endoscopy personnel, whereas 55% tested symptomatic personnel. Of the remaining, 22% performed only symptomatic screenings and 4% neither tested nor screened personnel. Cumulatively, 10% of endoscopy personnel tested positive for COVID-19 since the start of the pandemic, 0.9% were hospitalized, and 0.25% died from COVID-19 (geographic distribution in Figure 1 B).
The surveyed endoscopy units reported a mean reduction of procedure volumes by 58% initially and 54% at the time of this survey. At each respective first peak, Africa (72%) reported the highest reduction followed by Europe (68%), Asia (62%), North America (59%), South America (59%), and Oceania (42%). At the time of this survey, North America reported the highest mean reduction in endoscopy volumes (60%), whereas all other continents had shown some evidence of recovery.
Of the 73 units with training programs, trainee endoscopy volumes reduced on average by 64% at the start of the pandemic and 54% at the time of survey. At the pandemic’s onset, average reduction in trainee volumes were highest in Africa (90%) followed by Europe (76%), North America (75%), Asia (67%), South America (63%), and Oceania (53%). All continents showed improvements by December 2020.
Only 14% of the units reported no barriers to resuming endoscopy. Barriers cited by these units included safety concerns (52%), institutional policy (40%), limited COVID-19 testing (32%), limited endoscopy staff (30%), and limited PPE (23%). Regarding PPE practices, 71% of units reported using N95/powered air-purifying respirator s for all endoscopic procedures, 9% used them only for upper endoscopic procedures, 12% used PPE only if a patient tested positive, and 9% used them if a patient was not tested for COVID-19.
The current survey includes data from 121 endoscopy units from 35 countries after COVID-19 testing became more available and various GI societies have published guidelines to help endoscopy centers resume services safely.4, 5, 6, 7 Although most GI societies recommend patient testing, 57% reported not testing or only testing occasionally. In tested patients, only 1.3% were positive. Recognizing that it may be difficult to test all patients in resource-limited settings, these results rationalize an argument to scale down testing to high-risk groups only (screen-positive patients). Only 10% of the endoscopy personnel tested positive, and <1% were hospitalized or died from COVID-19, which was lower than that reported in our earlier report in which 13.5% of personnel tested positive and 7.9% were hospitalized.2 These results along with other published studies suggest that the risk of transmission from endoscopy itself is relatively low when using appropriate PPE.
All continents, except Oceania, reported over 50% reduction in endoscopy volumes at their first peak of the pandemic. This could be attributed to the relatively low prevalence of the COVID-19 cases in Oceania. At the time of this survey, most continents had also shown improvement. Reduction of endoscopy volumes were noted for trainees. We did not explore specific reasons for reduced trainee volumes, but, conceivably, the safety of trainees and local policy would have mandated this.8
In this large international survey, we reported an ongoing impact of COVID-19 on outpatient endoscopy worldwide. A summary of key findings and suggested next steps are outlined in Supplementary Table 2. The improving trend with signs of recovery of endoscopy volume necessitate continued guidance from GI societies on safe reopening and addressing the backlog of cases. COVID-19 testing is readily available in most places, but outcomes are similar in places where there is limited testing as well, suggesting that following local guidelines is key. The low positive rate in asymptomatic individuals raises the question of whether continued testing of all patients is cost-effective. In addition, the percentage of personnel reporting infection has remained relatively low. With vaccines now available, further recovery of endoscopy services is expected.
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge Kevin F. Kennedy, MS, who helped with the analysis.
CRediT Authorship Contributions
Sachin Srinivasan, MD (Conceptualization: Equal; Formal analysis: Equal; Writing – original draft: Equal; Writing – review & editing: Equal).
Suneha Sundaram, MD (Formal analysis: Equal; Writing – original draft: Equal; Writing – review & editing: Equal).
Fabian Emura, MD (Data curation: Equal; Writing – review & editing: Equal).
Nageshwar Reddy, MD (Data curation: Equal; Writing – review & editing: Equal).
Douglas O. Faigel, MD (Data curation: Equal; Writing – review & editing: Equal).
Alessandro Repici, MD, PhD (Data curation: Equal; Writing – review & editing: Equal).
Sravathi Parasa, MD (Conceptualization: Equal; Data curation: Equal; Writing – review & editing: Equal).
Prateek Sharma, MD (Conceptualization: Equal; Data curation: Equal; Writing – review & editing: Equal).
Footnotes
Conflicts of interest These authors disclose the following: Alessandro Repici is a consultant for Boston Scientific and Medtronic and receives grant support from Fujifilm. Fabian Emura receives research support from Fujifilm. Prateek Sharma is a consultant for Bausch, Covidien LP, Fujifilm, Lumendi, Olympus, and Salix Pharmaceuticals and receives grant support from Cosmo Pharmaceuticals, Erbe, US Endoscopy, and Docbot Inc. The remaining authors disclose no conflicts.
Note: To access the supplementary material accompanying this article, visit the online version of Gastroenterology at www.gastrojournal.org, and at https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.042.
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Table 1.
Survey Form Used for Collection of Data for the Study
| Record ID ____________________________________ Baseline
|
|
EGD, esophagogastroduodenoscopy; ERCP, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; PAPR, powered air purifying respirators; PCR, polymerase chain reaction.
Supplementary Table 2.
Summary of Key Findings and Necessary Next Steps
| Key findings | Necessary action |
|---|---|
| Continued impact on endoscopy volumes with slow ongoing recovery | Endoscopy centers to continue safe practices and GI societies to stay engaged in continued reopening of endoscopy safely, now with availability of vaccines. |
| Outcomes with testing vs no testing is similar globally | Endoscopy centers should seek and follow local guidelines. |
| Trainee volumes have been impacted | Graduate medical education to ease some requirements to reduce fear of graduation; programs to continue ensuring safety of trainees. |
| Infection rates low in endoscopy personnel | Continue safe practices and local guidelines; vaccines would be recommended given current knowledge. |
| Low rates of positivity in asymptomatic patients before procedures | GI societies will need to revisit to address if this cost-effective. However, local guidelines are key as well due to wide variability in the geographic burden of the infection. |
References
- 1.Johns Hopkins University of Medicine. Coronavirus Resource Center. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html.
- 2.Parasa S., et al. Gastroenterology. 2020;159:1579–1581. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.06.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ebigbo A., et al. Endoscopy. 2021;53:156–161. doi: 10.1055/a-1294-0427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gralnek I., et al. Endoscopy. 2020;52:483–490. doi: 10.1055/a-1155-6229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bhandari P., et al. Gut. 2020;69:1915–1924. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.AGA News (2020). https://gastro.org/news/aga-dhpa-release-guidance-for-resuming-elective-endoscopy/.
- 7.Guda N.M., et al. Dig Endosc. 2020;32:844–850. doi: 10.1111/den.13777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pawlak K.M., et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;92:925–935. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2020.06.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]