Abstract
Hyperglycaemia damages the microvasculature in part through the reduced recruitment of immune cells and interference with platelet signalling, leading to poor wound healing and accelerated lipid deposition in mammals. We investigated the utility of zebrafish larvae to model the effect of exogenous glucose on neutrophil and macrophage recruitment to a tail wound, wound-induced haemostasis, and chicken egg yolk feed challenge-induced hyperlipidaemia by supplementing larvae with exogenous glucose by immersion or injection. Neither method of glucose supplementation affected the recruitment of neutrophils and macrophages following tail transection. Glucose injection reduced thrombocyte retention and fibrin plug formation while only thrombocyte retention was reduced by glucose immersion following tail transection. We observed accelerated lipid accumulation in glucose-injected larvae challenged with high fat chicken egg yolk feeding. Our study identifies conserved and divergent effects of high glucose on inflammation, haemostasis, and hyperlipidaemia in zebrafish larvae compared to mammals.
Subject terms: Ichthyology, Coagulation system, Imaging the immune system, Inflammation, Innate immune cells, Innate immunity
Introduction
Hyperglycaemic damage to the microvasculature is hypothesised to underpin much of the pathology associated with diabetes in mammals, including perturbations to leukocyte biology, haemostasis, and the accumulation of lipid laden macrophages in the vessel wall1–4. Previous mammalian research has demonstrated that hyperglycaemia damages the microvasculature resulting in reduced expression of endothelial adhesion molecules for immune cell recruitment2,4. As a result, fewer neutrophils and macrophages are recruited to diabetic wounds1,2,5. Of the macrophages and neutrophils that eventually arrive, there is a skewing of differentiation towards an inflammatory phenotype owing to the inflammatory nature of the diabetic wound microenvironment6,7.
Mammals with hyperglycaemia demonstrate perturbed coagulation and platelet signalling, causing disruption of haemostasis3,8. Reduced efficiency of haemostasis results in unstable and ineffective clots within diabetic foot ulcers3,9. Treatments for diabetic foot ulcers can involve platelet and fibrin therapy, indicating an important role for inadequate fibrin clot production in the ulceration process10,11.
Hyperglycaemia-induced damage to the microvasculature also increases vascular lipid accumulation in conjunction with hyperlipidaemia12. Hyperlipidaemia and hyperglycaemia are compounding risk factors for the development of Type 2 diabetes, associated with the ‘Western Diet’ consisting of fat and sugar alongside limited exercise13,14. There are multiple mechanisms by which hyperglycaemia damages the microvasculature: through the formation of advanced glycation products3, the induction of oxidative stress15, interfering with nitric oxide production16, and inducing macrophages to form lipid-laden foam cells17. The degradation of the endothelial structural integrity increases the rate of lipid deposition by providing a physical niche for lipid infiltration12. This can ultimately lead to the development of atheroma, which are common in diabetic patients17.
These phenotypes have not been previously investigated in fish. Our study investigates the effect of exogenous glucose supplementation on inflammation, thrombosis and hyperlipidaemia using a zebrafish model. Zebrafish are established models for investigating each of these processes in isolation18–22. Pertinent to this study, there have been several zebrafish hyperglycaemia models reported in the literature including technically simple models based on the application of exogenous glucose by immersion or injection, environmental models of toxin or high calorie diet challenge, pancreatic ablation, and genetic models of hyperglycaemia (as covered in a recent meta-analysis by Salehpour and Rezaei et al.22). Additionally, zebrafish have similar clotting, metabolic, and immune systems to mammals, and these have been used to provide insight into the shared function of these systems across vertebrates19,20,23. Here we have combined these models to investigate the role of exogenous glucose supplementation in disrupting thrombosis and lipid accumulation, but not immune cell recruitment to a wound, in zebrafish larvae.
Results
Exogenous glucose exposure increases glucose in zebrafish larvae
To establish the efficacy of the injection and immersion techniques to increase glucose concentrations in 5 dpf zebrafish larvae, we conducted a glucose oxidase assay on homogenised whole zebrafish larvae using the Sigma Amplex Red Glucose oxidase kit. Consistent with past literature, we observed an increase in the glucose concentration contained within the glucose-injected and -immersed larvae compared to controls (Fig. 1A, B)24,25.
Figure 1.
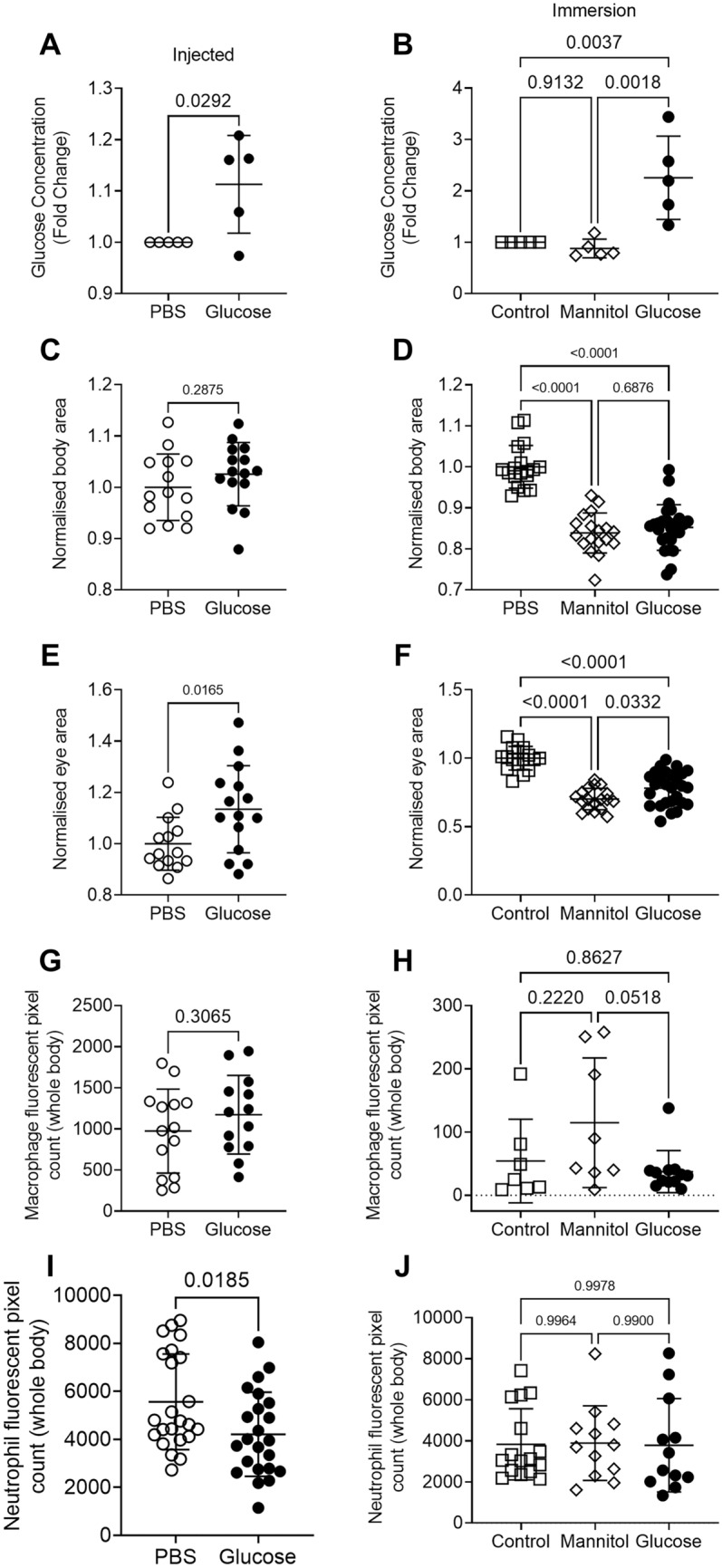
Injection and immersion methods increase glucose levels in zebrafish larvae. (A) Relative concentration of glucose in 5 dpf larvae that had been injected with 15 nmol glucose as eggs. Statistical testing by t test, each data point is representative of a group of n = 10–30 larvae. (B) Relative concentration of glucose in 5 dpf larvae immersed in 5% solutions of glucose or mannitol from 2 dpf. Statistical testing by ANOVA, each data point is representative of a group of n = 10–30 larvae. (C) Total body area calculated from lateral images of 5 dpf glucose-injected larvae. Statistical testing by t test. Data are representative of 2 biological replicates. (D) Total body area calculated from lateral images of 5 dpf larvae immersed in 5% solutions of glucose or mannitol from 2 dpf. Statistical testing by ANOVA. Data are representative of 2 biological replicates. (E) Eye area calculated from lateral images of 5 dpf glucose-injected larvae. Statistical testing by t test. Data are representative of 2 biological replicates. (F) Eye area calculated from lateral images of 5 dpf larvae immersed in 5% solutions of glucose or mannitol from 2 dpf. Statistical testing by ANOVA. Data are representative of 2 biological replicates. (G) Quantification of total macrophage number from lateral images of 5 dpf glucose-injected larvae. Statistical testing by t test. Data are representative of 2 biological replicates. (H) Quantification of total macrophage number from lateral images of 5 dpf larvae immersed in 5% solutions of glucose or mannitol from 2 dpf. Statistical testing by ANOVA. Data are representative of 2 biological replicates. (I) Quantification of total neutrophil number from lateral images of glucose-injected 5 dpf larvae. Statistical testing by t test. Data are representative of 2 biological replicates. (J) Quantification of total neutrophil number from lateral images of 5 dpf larvae immersed in 5% solutions of glucose or mannitol from 2 dpf. Statistical testing by ANOVA. Data are representative of 2 biological replicates.
Glucose immersion caused sporadic microbial overgrowth and we observed reduced growth of larvae immersed in either glucose or mannitol, but not in glucose-injected larvae, as measured by total body area (Fig. 1C, D) or eye area (Fig. 1E, F).
We next analysed the effect of glucose supplementation on the development of key innate immune cells. We estimated the quantity of macrophages in transgenic Tg(mfap4:turquoise)xt27 larvae, where macrophages are marked by turquoise fluorescent protein, and found similar numbers of macrophages in larvae that were injected with or immersed in glucose (Fig. 1G, H). We estimated the quantity of neutrophils in Tg(lyzC:DsRed)nz50 larvae, where neutrophils are marked by DsRed fluorescent protein, and found reduced numbers of neutrophils in glucose-injected larvae but similar numbers of neutrophils in glucose-immersed larvae (Fig. 1I, J).
Glucose does not affect neutrophil and macrophage recruitment to wounds in zebrafish larvae
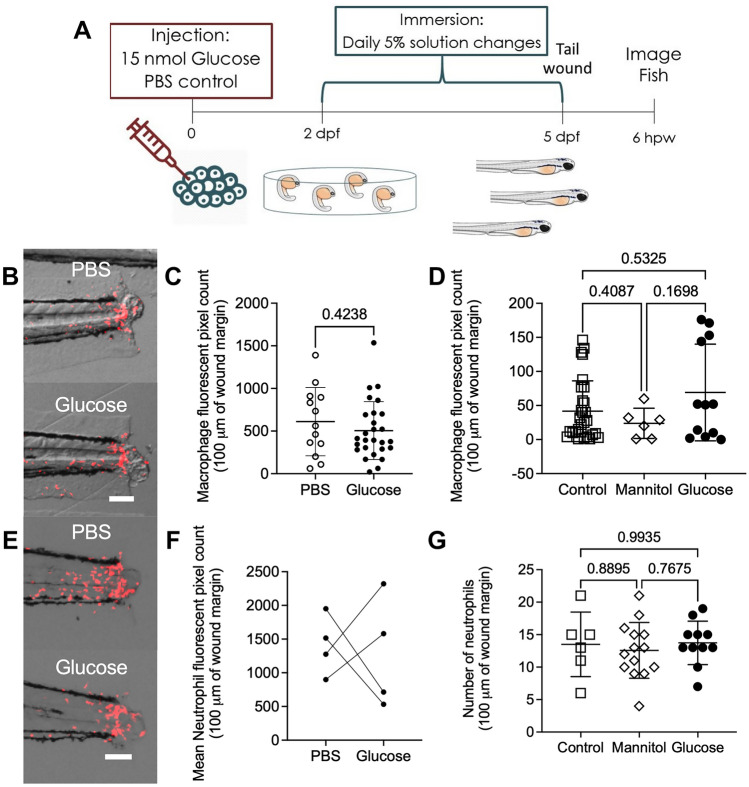
Altered innate immune cell recruitment to wounds is a conserved feature of hyperglycaemia in mammals4,5,26–28. To determine if this phenomenon was conserved in zebrafish larvae, we utilised the tail transection wound model which causes reproducible leukocyte recruitment29 (Fig. 2A). We first performed this assay using transgenic Tg(mfap4:turquoise)xt27 larvae to quantify macrophage recruitment to the tail wound (Fig. 2B). Surprisingly, we observed no difference in macrophage recruitment between the glucose-injected and control larvae at 6 h post wounding (hpw) (Fig. 2C). We also observed no difference in macrophage recruitment in the glucose immersion model (Fig. 2D).
Figure 2.
Exogenous glucose does not affect neutrophil and macrophage recruitment to a tail wound. (A) Schematic of experiment to measure immune cell recruitment to a tail wound. (B) Representative images of macrophage (red) recruitment to a tail wound in glucose-injected larvae. (C) Quantification of macrophage recruitment following tail transection in the glucose injection model. (D) Quantification of macrophage recruitment following tail transection in the glucose immersion model. (E) Representative images of neutrophil (red) recruitment to a tail wound in glucose-injected larvae. (F) Quantification of neutrophil recruitment following tail transection in the glucose injection model. Each paired data point represents the average of an biological replicate with n > 10 embryos per condition. (G) Quantification of neutrophil recruitment following tail transection in the glucose immersion model. Scale bars represent 100 μm. Statistical testing by t test. Data are representative of 3 biological replicates.
We then used Tg(lyzC:DsRed)nz50 larvae to quantify the recruitment of neutrophils to the tail wound (Fig. 2E). We observed great variability between experiments with two out of four experiments finding significantly reduced neutrophil recruitment between the control and glucose-injected larvae at 6 hpw and two out of four experiments finding significantly increased neutrophil recruitment (Fig. 2F). Consistently, we did not observe any difference in neutrophil recruitment in the glucose immersion model (Fig. 2G).
Together, these results indicate that zebrafish neutrophil and macrophage recruitment is not affected by exogenous glucose supplementation in zebrafish larvae.
Glucose impedes haemostasis in zebrafish larvae
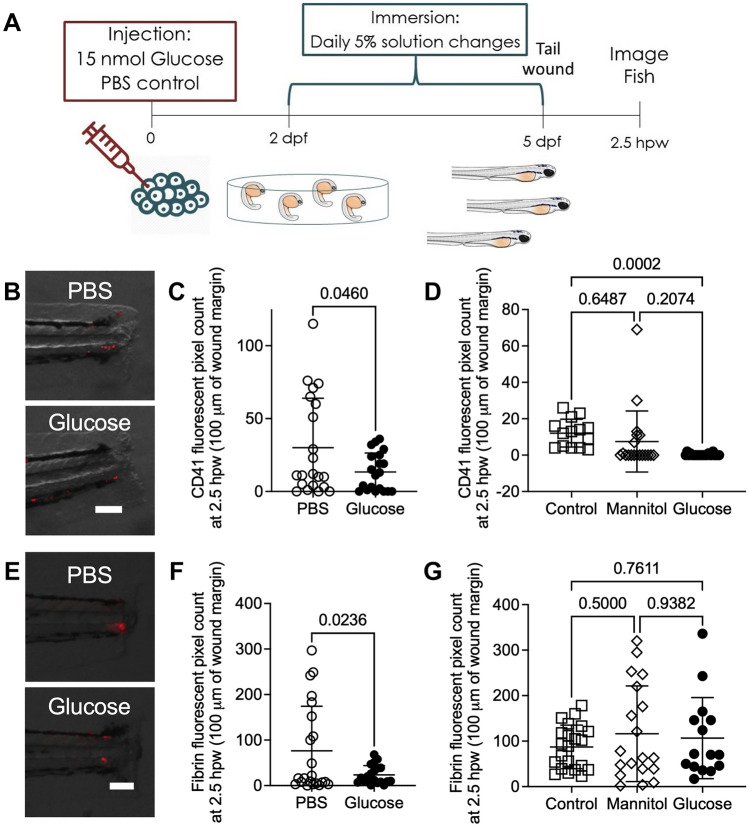
Hyperglycaemia perturbs coagulation and platelet activation in mammals, resulting in ineffective haemostasis3,8. To visualise the effects of exogenous glucose supplementation on haemostasis in zebrafish larvae, we first used the Tg(itga2b:gfp)la2 line to visualise thrombocyte plug formation in the severed blood vessel30,31. Following tail transection (Fig. 3A), glucose-injected Tg(itga2b:gfp)la2 larvae demonstrated reduced thrombocyte accumulation (Fig. 3B, C). This effect was replicated in glucose-immersed embryos compared to control embryos (Fig. 3D).
Figure 3.
Exogenous glucose supplementation reduced thrombocyte and fibrin accumulation at a tail wound. (A) Schematic of experiment to visualise haemostasis following tail transection. (B) Representative overlay of thrombocytes (red) at 2.5 h after tail transection in glucose-injected larvae. (C) Quantification of thrombocyte plug size following tail transection in the glucose injection model. (D) Quantification of thrombocyte plug size following tail transection in the glucose immersion model. (E) Representative images of fibrinogen deposition (red) at 2.5 h after tail transection in glucose-injected larvae. (F) Quantification of fibrin clot size following tail transection in the glucose injection model. (G) Quantification of fibrin clot size following tail transection in the glucose immersion model. Scale bars represent 100 μm. Statistical testing by t test. Data are representative of 3 biological replicates.
To determine if the reduction in thrombocyte recruitment was mirrored by perturbed clotting, we conducted tail transections on Tg(fabp10a:fgb-gfp)mi4001 larvae (Fig. 3E), which express fluorescently tagged fibrinogen and allow visualisation of clots32. Glucose-injected Tg(fabp10a:fgb-gfp)mi4001 larvae had reduced fibrin accumulation following tail transection compared to PBS-injected larvae (Fig. 3F). We did not observe any effect of glucose immersion on the deposition of fluorescently tagged fibrinogen (Fig. 3G).
Together, these results demonstrate that a exogenous glucose supplementation inhibits the thrombocyte component of haemostasis in zebrafish larvae.
Injection of glucose accelerated hyperlipidaemia in zebrafish larvae challenged with a high fat diet
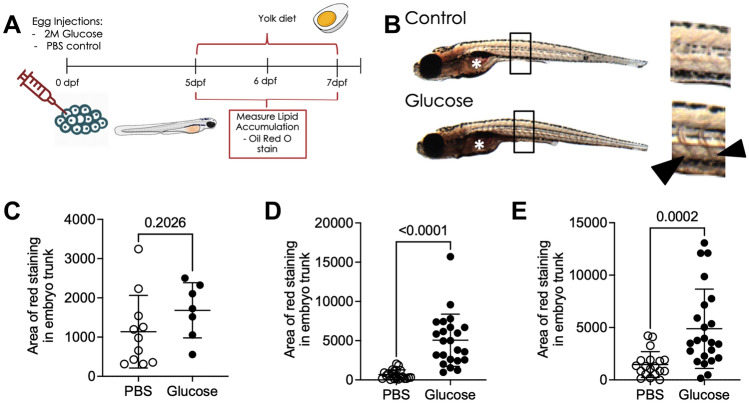
Hyperglycaemia and hyperlipidaemia are intimately associated in mammals33. To determine if this interaction is conserved in zebrafish larvae, we fed glucose-injected larvae a high fat diet consisting of emulsified chicken egg yolk from 5 to 7 dpf (Fig. 4A). Glucose- and PBS-injected larvae had similar Oil Red O vascular staining prior to the initiation of chicken egg yolk feeding at 5 dpf (Fig. 4B, C). Quantification of Oil Red O staining revealed glucose-injected larvae had increased vascular lipid content at one and two days post feeding (Fig. 4D, E).
Figure 4.
Glucose-injected larvae have increased lipid accumulation following a high fat diet. (A) Schematic of the high fat feeding challenge assay to measure lipid accumulation in glucose-injected larvae. (B) Bright field images of 6 dpf Oil Red O-stained larvae, demonstrating darker vascular staining in glucose-injected larvae. Box indicates location of inset, arrowheads indicate stained intersegmental vessels in inset, asterisk indicates intestinal lumen which was excluded from analysis. (C) Quantification of lipid accumulation in 5 dpf glucose-injected larvae. (D) Quantification of lipid accumulation in 6 dpf glucose-injected larvae challenged with a high fat diet from 5 dpf. (E) Quantification of lipid accumulation in 7 dpf glucose-injected larvae challenged with a high fat diet from 5 dpf. Statistical testing by t test. Data are representative of 2 biological replicates.
These results recapitulate the interaction between hyperglycaemia and hyperlipidaemia seen in mammals15, demonstrating that zebrafish larvae are a robust model to study this conserved interaction.
Discussion
In this study, we explored the effect of exogenous glucose supplementation on inflammation, thrombosis, and lipid accumulation in the zebrafish embryo model. We found that exogenous glucose reduces haemostasis around wound sites. In addition, we determined that injection of glucose accelerates lipid accumulation when larvae are challenged with a high fat diet.
The reduced size of glucose and mannitol immersed larvae compared to control larvae is a major caveat when interpreting datasets generated with the glucose immersion model. We thus preferred the injection method for the chicken egg yolk challenge experiments and for the interpretation of the effects of glucose on larval zebrafish immunity and haemostasis. Despite daily changes of media, we experienced further difficulty rearing zebrafish larvae from 2 to 5 dpf in 5% glucose solutions due to microbial overgrowth which may have slowed larval development by consuming oxygen or damaging larval mucosal surfaces. Although the glucose injection model did not achieve as high a fold change in glucose at 5 dpf, we did not observe developmental delays and haematopoiesis was largely comparable to PBS-injected control larvae.
Hyperglycaemia in mammals causes vascular dysfunction that restricts the recruitment of a broad range of immune cells to wounds16. It was therefore surprising that exogenous glucose appeared to have no effect on the recruitment of leukocytes to the tail wound in this study. It is possible that exogenous glucose supplementation to zebrafish larvae does not affect abluminal crawling of leukocytes along blood vessels, since wound-responsive leukocytes have been demonstrated to move predominantly through interstitial tissue in zebrafish larvae5,34. Overall our findings suggest exogenous supply of glucose to zebrafish larvae may not be a suitable platform for studying the impact of hyperglycaemia on leukocyte biology.
The relationship between hyperglycaemia and hyperlipidaemia has been previously reported in various mammalian species15,25,35, and a recent study by Wang et al. has demonstrated a similar the interaction of a high cholesterol diet with glucose immersion on vascular lipid accumulation in zebrafish after 10 days of feeding25. Our study using chicken egg yolk as a high fat diet challenge demonstrates a dramatically accelerated accumulation of lipid after just one day of feeding. This chicken egg yolk feeding-based model, therefore provides a more rapid model to investigate lipid accumulation.
In summary, we report glucose-supplemented zebrafish larvae as a tractable platform to investigate the conserved interactions between glucose and haemostasis, and glucose and diet-induced hyperlipidaemia.
Methods
Zebrafish husbandry
Zebrafish embryos were produced through natural spawning (Sydney Local Health District Animal Welfare Committee Approval 17-036). The strains used were Tg(lyzC:DsRed)nz50 to visualise neutrophils36, Tg(mfap4:turquoise)xt27 to visualise macrophages37, Tg(itga2b:gfp)la2 to visualise thrombocytes31, and Tg(fabp10a:fgb-gfp)mi4001 to visualise fibrin deposition32. From 1 to 5 days post fertilisation (dpf) embryos were kept in a dark incubator at 28 °C.
Induction of high glucose concentrations in the zebrafish
Injection method: Eggs were injected with approximately 15 nmol of glucose from a filter-sterilised 2 M solution dissolved in PBS, or an equal volume of PBS as a control within four hours of fertilisation.
Immersion method: Dechorionated 2 dpf embryos were immersed in 5% mannitol (osmolarity control) or 5% glucose dissolved in E3 media, media was changed daily to reduce microbial growth.
Glucose oxidase assay
Whole larvae were snap frozen and stored at − 20 °C for quantification of glucose content. Larvae were lysed in the buffer solution from the Amplex Red Oxidase kit (Sigma: A22188), lysates were then sedimented by centrifugation, and the Amplex Red Glucose oxidase kit was used to measure the glucose content of the supernatant with a microplate reader in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
Tail transection assays
Caudal fin amputations were performed on larvae at 5 dpf. Larvae were anesthetised with 2.5% (v/v) ethyl-3-aminobenzoate methanesulfonate (tricaine) (Sigma, E10521), wounded posterior to the notochord using a sterile scalpel and kept in a 28 °C incubator to recover as previously described29. Wounded larvae were imaged at 6 h (neutrophil and macrophages) or 2.5 h (fibrin and thrombocytes).
Hyperlipidaemia assay
Post 5 dpf, larvae were transferred to a 28 °C incubator with a 14/10 h light/dark cycle. Larvae were placed in an E3 solution containing 0.05% of emulsified chicken egg yolk from 5 dpf. Each day, a random sample of larvae were removed, euthanised, and fixed in paraformaldehyde. Larvae were stained with Oil Red O to quantitate lipid accumulation, as previously described21,38,39.
Imaging and image analysis
Larvae were imaged using a Leica M205FA fluorescent microscope. ImageJ software was used to quantify fluorescent pixel count within 100 µm of the wound site for transgenic wound assays as previously described29,40.
Oil Red O staining was quantified in ImageJ by adjusting the colour threshold to eliminate non-red signal. The image was then converted to a binary mask, and the tail region posterior to the swim bladder was selected to measure the number and area of particles39.
Statistical analysis
Outliers were excluded using a 1% ROUT test. Statistical testing was carried out by ANOVA with correction for multiple comparisons or Student’s t tests as appropriate using GraphPad Prism. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. Every datapoint represents a single embryo unless otherwise noted.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experimental protocols were approved by Sydney Local Health District Animal Welfare Committee Approval 17-036. All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations as approved under Approval 17-036. All methods are reported in accordance with ARRIVE guidelines.
Data availability statement
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgements
We thank other members of the Oehlers lab at the Centenary Institute for their input into this work and maintenance of the zebrafish aquarium; Dr. Angela Kurz and Sydney Cytometry for assistance with imaging; and A/Prof Jordan Shavit for supplying the Tg(fabp10a:fgb-gfp)mi4001 line.
Author contributions
S.M. and P.M.C. performed experiments, S.M. and S.O. drafted the manuscript, all authors reviewed the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a Centenary Institute Summer Scholarship to S.M.; University of Sydney Fellowship [Grant No. G197581] and NSW Ministry of Health under the NSW Health Early-Mid Career Fellowships Scheme [Grant No. H18/31086] to S.H.O.; and the NHMRC Centre of Research Excellence in Tuberculosis Control (APP1153493) to W.J.B.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Pradeep Manuneedhi Cholan, Email: pradeep.manuneedhicholan@mq.edu.au.
Stefan H. Oehlers, Email: s.oehlers@centenary.org.au
References
- 1.Salazar JJ, Ennis WJ, Koh TJ. Diabetes medications: Impact on inflammation and wound healing. J. Diabetes Compl. 2016;30:746–752. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.12.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Galkowska H, Wojewodzka U, Olszewski WL. Low recruitment of immune cells with increased expression of endothelial adhesion molecules in margins of the chronic diabetic foot ulcers. Wound Repair Regener. 2005;13:248–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1067-1927.2005.130306.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vazzana N, Ranalli P, Cuccurullo C, Davì G. Diabetes mellitus and thrombosis. Thromb. Res. 2012;129:371–377. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2011.11.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sawaya AP, et al. Deregulated immune cell recruitment orchestrated by FOXM1 impairs human diabetic wound healing. Nat. Commun. 2020;11:1–14. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18276-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Son SM, Kim IJ, Kim Y. K. Diabetes. 2000;49:A147. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lucas, T. et al. Differential roles of macrophages in diverse phases of skin repair. J. Immunol. (Baltimore, Md. : 1950)184, 3964–3977. 10.4049/jimmunol.0903356 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 7.Miriam AML, et al. Differences in cellular infiltrate and extracellular matrix of chronic diabetic and venous ulcers versus acute wounds. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1998;111:850. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.1998.00381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Rao AK, et al. Alterations in insulin-signaling and coagulation pathways in platelets during hyperglycemia–hyperinsulinemia in healthy non-diabetic subject. Thromb. Res. 2014;134:704–710. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2014.06.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tsimerman G, et al. Involvement of microparticles in diabetic vascular complications. Thromb. Haemost. 2011;106:310–321. doi: 10.1160/th10-11-0712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ding Y, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin accelerates skin wound healing in diabetic mice. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2017;79:e15–e19. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000001091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Babaei V, et al. Management of chronic diabetic foot ulcers using platelet-rich plasma. J. Wound Care. 2017;26:784–787. doi: 10.12968/jowc.2017.26.12.784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Okon EB, Chung AWY, Zhang H, Laher I, van Breemen C. Hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia are associated with endothelial dysfunction during the development of type 2 diabetes. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2007;85:562–567. doi: 10.1139/Y07-026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Andreadou I, et al. Hyperlipidaemia and cardioprotection: Animal models for translational studies. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019 doi: 10.1111/bph.14931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Crawford-Faucher A. Preventing or delaying type 2 diabetes mellitus with diet and exercise. Am. Fam. Physician. 2018;98:643–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pulakazhi Venu, V. K. et al. Minimizing hyperglycemia-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction by inhibiting endothelial sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 and attenuating oxidative stress: Implications for treating individuals with type 2 diabetes. Can. J. Diabetes43, 510–514. 10.1016/j.jcjd.2019.01.005 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 16.Williams SB, et al. Acute hyperglycemia attenuates endothelium-dependent vasodilation in humans in vivo. Circulation. 1998;97:1695–1701. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.97.17.1695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lamharzi N, et al. Hyperlipidemia in concert with hyperglycemia stimulates the proliferation of macrophages in atherosclerotic lesions. Diabetes. 2004;53:3217. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.53.12.3217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Oyelaja-Akinsipo, O. B., Dare, E. O. & Katare, D. P. Protective role of diosgenin against hyperglycaemia-mediated cerebral ischemic brain injury in zebrafish model of type II diabetes mellitus. Heliyon. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03296 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 19.Richardson R, et al. Adult zebrafish as a model system for cutaneous wound-healing research. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013;133:1655–1665. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Martin P, Feng Y. Wound healing in zebrafish. Nature. 2009;459:921–923. doi: 10.1038/459921a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fang L, Liu C, Miller YI. Zebrafish models of dyslipidemia: Relevance to atherosclerosis and angiogenesis. Transl. Res. 2014;163:99–108. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2013.09.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Salehpour A, Rezaei M, Khoradmehr A, Tahamtani Y, Tamadon A. Which hyperglycemic model of zebrafish (Danio rerio) suites my type 2 diabetes mellitus research? A scoring system for available methods. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021;9:652061. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.652061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kinkel, M. D. & Prince, V. 139–152 (Wiley‐VCH Verlag, Weinheim, 2009).
- 24.Rocha F, et al. Glucose overload in yolk has little effect on the long-term modulation of carbohydrate metabolic genes in zebrafish (Danio rerio) J. Exp. Biol. 2014;217:1139–1149. doi: 10.1242/jeb.095463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wang Z, Mao Y, Cui T, Tang D, Wang XL. Impact of a combined high cholesterol diet and high glucose environment on vasculature. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e81485. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Delamaire M, et al. Impaired leucocyte functions in diabetic patients. Diabet. Med. 1997;14:29–34. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9136(199701)14:1<29::AID-DIA300>3.0.CO;2-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wong SL, et al. Diabetes primes neutrophils to undergo NETosis, which impairs wound healing. Nat. Med. 2015;21:815–819. doi: 10.1038/nm.3887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zykova SN, et al. Altered cytokine and nitric oxide secretion in vitro by macrophages from diabetic type II-like db/db mice. Diabetes. 2000;49:1451. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.49.9.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cholan PM, et al. Conserved anti-inflammatory effects and sensing of butyrate in zebrafish. Gut Microbes. 2020;12:1–11. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1824563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Huarng MC, Shavit JA. Simple and rapid quantification of thrombocytes in zebrafish larvae. Zebrafish. 2015;12:238–242. doi: 10.1089/zeb.2014.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lin HF, et al. Analysis of thrombocyte development in CD41-GFP transgenic zebrafish. Blood. 2005;106:3803–3810. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-01-0179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Vo AH, Swaroop A, Liu Y, Norris ZG, Shavit JA. Loss of fibrinogen in zebrafish results in symptoms consistent with human hypofibrinogenemia. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e74682. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Goldberg IJ. Diabetic dyslipidemia: Causes and consequences. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001;86:965–971. doi: 10.1210/jcem.86.3.7304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Barros-Becker F, Lam P-Y, Fisher R, Huttenlocher A. Live imaging reveals distinct modes of neutrophil and macrophage migration within interstitial tissues. J. Cell Sci. 2017;130:3801. doi: 10.1242/jcs.206128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Chait A, Bornfeldt KE. Diabetes and atherosclerosis: Is there a role for hyperglycemia? J. Lipid Res. 2009;50(Suppl):S335–S339. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R800059-JLR200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hall C, Flores MV, Storm T, Crosier K, Crosier P. The zebrafish lysozyme C promoter drives myeloid-specific expression in transgenic fish. BMC Dev. Biol. 2007;7:42. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-7-42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Walton EM, Cronan MR, Beerman RW, Tobin DM. The macrophage-specific promoter mfap4 allows live, long-term analysis of macrophage behavior during mycobacterial infection in zebrafish. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0138949. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Passeri MJ, Cinaroglu A, Gao C, Sadler KC. Hepatic steatosis in response to acute alcohol exposure in zebrafish requires sterol regulatory element binding protein activation. Hepatology. 2009;49:443–452. doi: 10.1002/hep.22667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Johansen MD, et al. Mycobacterium marinum infection drives foam cell differentiation in zebrafish infection models. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018;88:169–172. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2018.07.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Matty MA, Oehlers SH, Tobin DM. Live imaging of host–pathogen interactions in zebrafish larvae. Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1451:207–223. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3771-4_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.