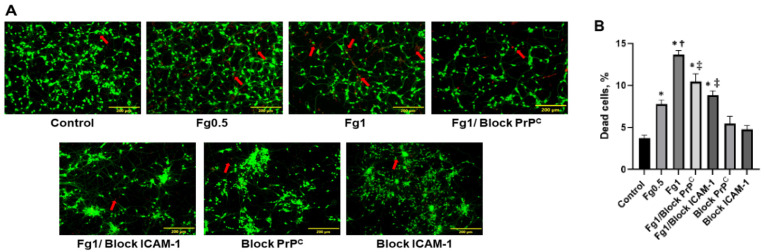
Figure 1.
Neuronal cell death induced by fibrinogen (Fg). (A) Representative images show staining of live/dead neurons that were treated with medium alone (control), 0.5 mg/mL of Fg (Fg0.5), 1 mg/mL of Fg (Fg1), 1 mg/mL of Fg (Fg1) in the presence of a cellular prion protein (PrPC)-blocking peptide (Fg1/block PrPC), 1 mg/mL of Fg in the presence of a function-blocking antibody against intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) (Fg1/block ICAM-1), the prion protein-blocking peptide alone, or the ICAM function-blocking antibody alone. Hirudin was present in all experimental groups to prevent the conversion of Fg to fibrin. (B) The summary of the image analyses for the detection of live neurons using a live/dead assay. An automatic cell count was performed based on the fluorescence signal threshold of the images provided by the OLYMPUS CellSens Dimension Desktop 2.3. Arrows indicate exemplary dead cells shown in red. Data are presented as the average of number of dead cells as a percent of the total number of cells in a selected constant area of interest in each experimental group. p < 0.05; ∗—vs. Control, †—vs. Fg0.5, ‡—vs. Fg1; n = 4.