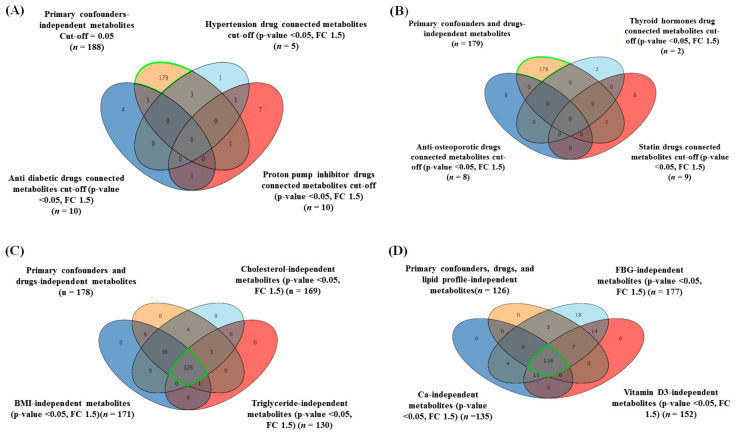
Figure 2.
A sequential exclusion of drug- (A,B) and secondary confounder-related metabolites (C,D) from the panel of primary confounder-independent metabolites. (A,B) Venn diagrams illustrating the overlap between the drug-related metabolites and primary confounder-independent metabolites (n = 188), using a moderated t-test considering fold-change (FC) = 1.5 and cutoff p-value < 0.05. A total of 178 metabolites were identified as both drug- and primary confounder-independent metabolites after the exclusion of 10 metabolites. (C) Venn diagram illustrating the overlap between metabolites independent of secondary confounders (cholesterol, BMI, and triglycerides (TG)) (n = 169, 171, and 130, respectively) and the primary confounder- and drug-independent metabolites identified in (B) (n = 178), using a moderated t-test considering fold-change (FC) = 1.5 and cutoff p-value < 0.05. A total of 126 metabolites were identified as metabolites independent from the effects of the primary confounders, drugs, lipid profile, and weight. (D) Venn diagram demonstrating further overlap between secondary confounder (FBG, vitamin-D3, and calcium)-independent metabolites (n = 177, 152, and 135, respectively) with the primary confounder, drug, lipid profile, and independent weight metabolites identified in (C) (n = 126), using a moderated t-test considering fold-change (FC) = 1.5 and cutoff p-value < 0.05. A total of 116 metabolites were identified as significantly associated with LBMD independent of the effect of primary and secondary confounders and drugs.