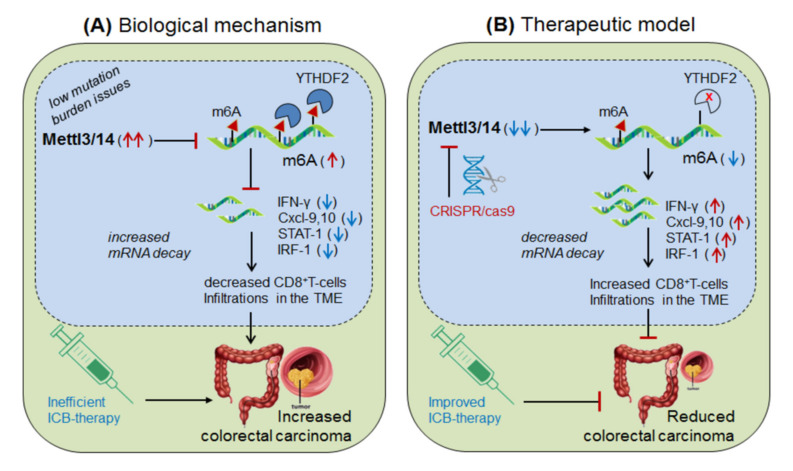
Figure 3.
Therapeutic model targeting ‘Mettl-3/14’ in colorectal cancer. (A) Biological mechanism: Mettl-3/14 is up-regulated in colorectal cancer and melanoma, and inhibits the expression of IFNγ-STAT1-IRF1 signaling via YTHDF2-mediated (decreased mRNA decay) mechanism and thereby decreases the efficacy of anti-PD-1 effect by lowering CD8+T-cell infiltrations in the TME, and thus facilitated disease progression. (B) Therapeutic model: Anti-Mettl-3/14 therapy: CRISPR/cas9-silencing of Mettl-3/14 increases the expression of its target IFNγ-STAT1-IRF1 genes/signaling by reducing the recruitment of YTHDF2-mediated decay mechanism, and thus enhances the efficacy of anti-PD-1 antibody by increasing infiltrations of CD8+T-cell in the TME. Moreover, FTO overexpression might decrease Mettl-3/14 level via balancing mechanisms, and ‘anti-YTHDF2 therapy’ by directly augmenting target gene expressions, via its mRNA stability mechanisms, might have therapeutic benefits.