Abstract
The aim of the study was to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) techniques in oropharyngeal cancer. PubMed, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library and clinicaltrials.org were systematically searched for studies reporting methods of HPV detection. Primary outcomes were sensitivity and specificity of HPV detection. In this case, 27 studies were included (n = 5488, 41.6% HPV+). In this case, 13 studies evaluated HPV detection in tumour tissue, nine studies examined HPV detection in blood samples and five studies evaluated HPV detection in oral samples. Accuracy of HPV detection in tumour tissue was high for all detection methods, with pooled sensitivity ranging from 81.1% (95% CI 71.9–87.8) to 93.1% (95% CI 87.4–96.4) and specificity ranging from 81.1% (95% CI 71.9–87.8) to 94.9% (95% CI 79.1–98.9) depending on detection methods. Overall accuracy of HPV detection in blood samples revealed a sensitivity of 81.4% (95% CI 62.9–91.9) and a specificity of 94.8% (95% CI 91.4–96.9). In oral samples pooled sensitivity and specificity were lower (77.0% (95% CI 68.8–83.6) and 74.0% (95% CI 58.0–85.4)). In conclusion, we found an overall high accuracy for HPV detection in tumour tissue regardless of the HPV detection method used. HPV detection in blood samples may provide a promising new way of HPV detection.
Keywords: human papillomavirus, HPV, oropharyngeal cancer, diagnostic
1. Introduction
The incidence of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas (OPSCCs) caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) is increasing worldwide [1,2]. Previously, the main causes of OPSCCs were smoking and alcohol consumption but today up to 70% of cases in most parts of the Western world are associated with HPV-driven carcinogenesis [3,4,5,6,7]. HPV+ OPSCC has a unique epidemiologic profile, molecular composition and histopathological features compared to the tobacco and alcohol associated OPSCC [3,8,9,10]. Patients are commonly younger, with fewer co-morbidities and have a better prognosis [11,12,13]. A surrogate marker for HPV infection is tumour suppressor protein p16 positivity (p16+). p16+ OPSCC has shown better prognosis compared to p16 negative (p16−) tumours. However, double positivity, i.e., tumours being positive for both HPV and p16 have shown better prognostication compared to a single marker of positivity [14].
Several techniques to evaluate HPV positivity exist. These includes p16 evaluation by immunohistochemistry (IHC), detection of HPV DNA by in situ hybridisation (ISH) or by polymerase chain reaction (PCR), E6/E7 HPV mRNA evaluation by ISH and reverse transcriptase-PCR (RT-PCR), or a combination of the above-mentioned methods. E6/E7 HPV mRNA evaluation is considered the golden standard to assess HPV positivity, as this technique detects oncogenic transcriptional active HPVs, but the test is expensive and technically challenging to perform [15]. On the other hand, p16 assessment is the most used technique in clinical settings as it is easy to conduct and to interpret, is less expensive and widely available [15,16]. This has led to p16 being included in the 8th edition of American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) and the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) tumour, node, metastasis (TNM) staging system of OPSCC, where p16+ tumours now have a novel staging system distinct from the staging of p16− tumours [17]. The recommendation from The American Society of Oncology (ASCO) for defining a tumour as p16+ is by a cut-off of 70% nuclear and cytoplasmic staining [15]. However, several studies have shown disparities in the cut-off level defining a tumour as p16 positivity [15,18].
The definition of HPV+ OPSCC is a critical issue as treatment de-escalation in patients with HPV+ tumours is currently being investigated in clinical trials to avoid unneeded treatment-related side effects, overtreatment, and to minimize the risk of treatment-related acute and long-term morbidity in this patient group. However, this should be performed without misallocating patients with less favourable prognosis to less treatment.
In addition, several new techniques for assessing HPV positivity without the need of an invasive biopsy of tumour tissue, e.g., by liquid biopsy using saliva or blood are advancing which would be a readily available way of detecting HPV. Circulating tumur DNA (ctDNA) from virus-induced cancers has previously been shown to be clinically useful as a diagnostic test for oncovirus-driven cancers, such as Hepatitis B virus (HBV)-induced hepatocellular carcinoma [17] and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-induced nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) [18,19]. HPV DNA has also been shown to be present in plasma in patients with HPV-induced cervical cancer but absent in patients with cervical dysplasia [20,21].
Evolution in laboratory techniques is rapidly evolving, experience with p16 detection is increasing and new detection standards are continuously being presented. An update on the recent knowledge in HPV detection is a timely needed study. Furthermore, a comparison of the diagnostic accuracy in different specimens and a ranking of these are warranted.
The aim of this study was to systematic review the literature on methods of HPV detection and to assess the diagnostic accuracy for HPV detection in patients with OPSCC based on detection methods and in different sample types.
2. Materials and Methods
This systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted with reference to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement [19].
One author (KKJ) systematically searched the PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane databases and clinical trials.org for articles in English and Scandinavian language. The search was last updated on the 28 May 2021. We included original studies comprising OPSCC patients investigating diagnostic methods of HPV detection published within the last five years. Studies comprising patients with OPSCC along with other head and neck cancer subsites were included, if they provided information specifying the results of the diagnostic accuracy of HPV detection for the OPSCC patients. Studies were excluded if they included less than 10 OPSCC cases and if the HPV detection method, including the definition of HPV positivity and p16 positivity, was not defined.
The search term was phrased broadly to identify relevant references. The following keywords were used to build the search: (Oropharyn* cancer or oropharyn* neoplasm or oropharyn* carcinoma or oropharyn* malignancy or oropharyn* tumour or oropharyn* tumour) AND (HPV or human papillomavirus or human papilloma virus or p16 or papillomavirus or p16 or cdkn2a or cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16 or p16 genes) AND (diagnosis or diagnostic)). The search strategy in PubMed included MeSH terms.
We collected information on study type, diagnostic methods, reference methods, sample type, HPV type and the sensitivity and specificity of the diagnostic methods.
Statistical analyses were performed using R studio, version 1.2.5. We generated paired forest plots depicting sensitivity and specificity estimates across studies. We conducted a meta-analysis using the bivariate model in R studio by using the mada package function reitsma [20]. The model is a linear mixed model with known variance of the random effects. In the bivariate model, the logit transformed sensitivities and specificities and the correlation are modeled directly. The model accounts for sampling variability within studies and also account for between-study variability through the inclusion of random effects. The bivariate approach incorporates any correlation that might exist between two measures using a random effects approach.
3. Results
The literature search generated 1513 articles, of which 24 were enrolled. Three additional articles were identified through reference lists (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Prisma flow diagram. Abbreviation: Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC). * Studies focused on the epidemiological aspects of OPSCC (e.g., survival and incidence in patients with HPV+ and HPV- OPSCC) (n = 385), treatment of HPV+ OPSCC (n = 230), biomarkers, molecular characterization and gene expression in HPV+ tumours (n = 218), imaging of OPSCC tumours (n = 53), quality of life in OPSCC patients (n = 26), HPV vaccines (n = 14), validation of assays for HPV detection (n = 11), costs of HPV detection (n = 9), concerning oral health (n = 4), others (n = 25), e.g., HPV clearance profile, HPV load in relation to tumour size and HPV genotypes.
A total of 1389 articles were excluded based on screening of the title and abstract. Of these, we excluded studies that did not focus on the diagnostic accuracy of HPV detection (n = 975), other reviews, case reports and editorials (n = 218) and lastly, studies regarding HPV diagnostics in other patient groups than OPSCC (n = 196). Thus, 119 articles were assessed by full-text. In this case, 92 studies were not included as they did not concern diagnostic methods (n = 50), did not report diagnostic accuracy (15), did not specify results for OPSCC patients (n = 11), did not define HPV or p16 positivity (n = 9) or included less than 10 patients (n = 7).
Finally, 27 studies were included comprising a total of 5488 patients diagnosed with OPSCC (41.6% HPV+). Three studies included a non-OPSCC control group (n = 229) consisting of head and neck cancer patients with a cancer located at another subsite than the oropharynx (n = 74), healthy controls (n = 75), patients with Warthin’s tumour (n = 20) or branchial cleft cyst (n = 10). The studies including non-OPSCC patients were excluded in the meta-analysis. In this case, 14 studies were European, 10 were US and Canada based and three studies were Asian (Table 1).
Table 1.
Overview of included studies.
| Author (Year of Publication) Country [Study] | Study Period | OPSCC Patients. Total/HPV+ | Sample | Method of Testing | Reference | True Positive | False Positive | False Negative | True Negative | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henley-Smith et al. (2020) London [21] | 2005–2016 | 100/38 | FFPE | RNA ISH | p16 IHC, staining >70% and DNA ISH | 38 | 18 | 0 | 44 | NR. The 18 false positive cases were p16+/HPV- |
| Shengming et al. (2020) China [22] | 2014–2019 | 257/47 | FFPE | p16 IHC staining >70% DNA PCR |
RNA ISH | p16: 44 DNA PCR: 47 p16/DNA PCR: 44 |
p16: 22 DNA PCR: 4 p16/DNA PCR: 4 |
p16: 3 DNA PCR: 0 p16/DNA PCR: 3 |
p16: 188 DNA PCR: 206 p16/DNA PCR: 206 |
p16 ISH: Sen: 93.6%; Spe: 89.10% DNA PCR: Sen: 97.9%; Spe: 97.6% p16 and DNA PCR: Sen: 91.7%; Spe: 98.1% |
| Mes et al. (2019) Netherlands [23] | 2008–2011 | 80/20 | FFPE | DNA RT-PCR | HPV16 E6 mRNA RT-PCR | 19 | 0 | 1 | 55 | NR |
| Randén-Brady et al. (2019) Finland [24] | Study I: 2000–2009 Study 2: 2012–2016 |
Study 1: 202/NR Study 2: 155/NR Study 1 + 2: HPV positive: 226 |
FFPE | Study 1: DNA ISH Study 2: DNA PCR Study 1 + 2: results combined: E6/E7 mRNA ISH |
p16 IHC, staining >70% | mRNA: 211 DNA ISH: 101 DNA PCR: 91 |
mRNA: 10 DNA ISH: 4 HPV PCR: 5 |
mRNA: 15 DNA ISH: 16 HPV PCR: 18 |
mRNA: 121 DNA ISH: 81 HPV PCR: 41 |
mRNA ISH: Sen: 93.4%; Spe: 92.4% DNA ISH: Sen: 86.3%; Spe: 95.3% DNA PCR: Sen: 83.5%; Spe: 89.1% |
| Craig et al. (2019) Ireland [25] | 2000–2011 | 221/90 | FFPE | RNA-ISH DNA-ISH DNA-PCR |
p16 IHC, staining >70% | DNA PCR: 71 DNA ISH: 67 RNA ISH:80 |
DNA PCR: 43 DNA ISH: 0 RNA ISH: 0 |
DNA PCR: 19 DNA ISH: 23 RNA ISH:10 |
DNA PCR: 88 DNA ISH: 131 RNA ISH: 131 |
DNA PCR: Sen: 79% (95% CI: 69–87); Spe: 67% (95% CI: 58–75) DNA ISH: Sen: 74% (95% CI: 64–83); Spe: 100% (95% CI: 87–100) RNA ISH: Sen: 88% (95% CI: 80–94); Spe: 100% (95% CI: 96–100) |
| Mena et al. (2018) Spain [26] | 1990–2013 | 788/80 | FFPE | DNA PCR p16 IHC, staining >70% |
E6 mRNA RT-PCR | DNA PCR/p16: 58 p16: 58 |
DNA PCR/p16: 0 p16: 28 |
DNA PCR/p16: 9 p16: 9 |
DNA PCR/p16: 721 p16: 691 |
DNA PCR/p16: Sen: 86.6% (95% CI 76.0–93.7); Spe: 100.0% (95% CI 99.5–100.0). p16: Sen: 86.6% (95% CI 76.0–93.7); Spe: 96.1% (95% CI 94.4–97.4) |
| Meng et al. (2018) China [27] | 2000–2016 | 1470/81 | FFPE | DNA PCR | p16 IHC, staining >80% | 78 | 0 | 3 | 1389 | Sen: 100% Spe: 96% |
| Augustin et al. (2018) France [28] | 2011–2013 | 126/56 | FFPE | p16 IHC, staining >70% DNA-ISH RNA-ISH |
DNA PCR | p16: 46 DNA ISH: 41 RNA ISH:49 |
p16: 7 DNA ISH: 2 RNA ISH: 2 |
p16: 10 DNA ISH: 15 RNA ISH: 7 |
p16: 68 DNA ISH: 63 RNA ISH: 68 |
p16: Sen: 82% (95% CI 70–91); Spe: 90% (95% CI 80–96) DNA ISH: Sen: 73% (95% CI 60–84); Spe: 97% (95% CI 90–100) RNA ISH: Sen: 88% (95% CI 76–95); Spe: 97% (95% CI 90–100) p16 and DNA ISH: Sen: 88% (95% CI 76–95); Spe: 97% (95% CI 90–100) p16 and RNA ISH: Sen: 95% (95% CI 85–99); Spe: 100% (95% CI 92–100) |
| Mendez-Pena et al. (2017) Boston, USA [29] | 2015–2016 | 57/26 | FFPE | RNA ISH DNA ISH p16 IHC, staining >50% |
DNA PCR | RNA ISH: 26 DNA ISH: 23 p16: 24 |
RNA ISH: 4 DNA ISH: 8 p16: 13 |
RNA ISH: 0 DNA ISH: 3 p16: 1 |
RNA ISH: 27 DNA ISH: 23 p16: 16 |
RNA ISH: Sen: 100%; Spe: 87% DNA ISH: Sen: 88%; Spe: 74% p16: Sen: 96%; Spe: 55% |
| Wright et al. (2020) Tennessee, USA [30] | NR | 20/19 | FNA | DNA RT-PCR | p16 IHC, staining >70% | 19 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Sen: 100%; Spe: 100% |
| Menegaldo et al. (2020) Italy [31] | 2016–2019 | 29/16 | FNA | HPV16 and HPV18 E6 oncoproteins, lateral flow immunochromatographic strip test | p16 IHC, staining >70% combined with DNA PCR and/or E6 seropositivity | 15 | 0 | 1 | 11 | Sen: 94% (95% CI: 70–100); Spe: 100% (95% CI: 72–100) |
| Channir (2016) Denmark [32] | 2002–2016 | 71/71 (HPV- group: 47/7 with OSCC, 20 Warthin’s tumour, 20 branchial cleft cyst) |
FNA | DNA PCR p16 IHC, staining <75% |
DNA PCR | 68 | 0 | 3 | 47 | Sen: NR. Spe: 100% (95% CI 92.5–100.0) |
| Sivars et al. (2016) Sweden [33] | 2013–2016 | 16/13 | FNA | DNA multiplex assay | p16 IHC, staining >70% | 13 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Sen: 100%; Spe: 100% |
| Chernesky et al. (2018) Canada [34] | NR | 59/48 | Saliva and oral swabs (BOT and tonsillar area) pooled and FNA | (1) OncoE6 proteins–lateral flow strip (2) HPV E6/E7 mRNA assay (3) DNA PCR |
p16 IHC, staining >70% | Oral sample: (1) 3 (2) 22 (3) 35 FNA: (1) 38 (2) 46 (3) 42 |
Oral sample: (1) 0 (2) 0 (3) 1 FNA: (1) 1 (2) 1 (3) 2 |
Oral sample: (1) 45 (2) 26 (3) 11 FNA: (1) 10 (2) 2 (3) 2 |
Oral sample: (1) 11 (2) 11 (3) 10 FNA: (1) 10 (2) 10 (3) 9 |
NR |
| Borena et al. (2020) Austria [35] | 2018–2020 | 50/23 | Cytology brush tests of tumour surface | E7 antigen test, ELISA | p16 IHC, staining >66% and DNA PCR | 14 | 9 | 9 | 18 | Sen: 60.9% (95% CI 38.5–80.3); Spe: 66.7% (95% CI 46–83.5) |
| Martin-Gomez et al. (2019) Florida, USA [36] | 2014–2017 | 171/157 | Oral rinse | DNA PCR | p16 IHC, staining >70% and DNA PCR | 119 | 7 | 38 | 7 | Sen: 75.8%; Spe: 50.0% |
| Fakhry et al. (2019) Ohio and Baltimore USA [37] | 2011–2016 | 217/187 | Oral rinse | DNA PCR | mRNA E6 or E7 or p16 IHC/combined with DNA ISH | 161 | 5 | 26 | 25 | NR |
| Qureishi et al. (2018) United Kingdom [38] | 2015–2016 | 46/36 | Oral rinse | DNA PCR | p16 IHC, staining >70% and DNA ISH. Positive if: p16+/no HPV DNA test, p16+/HPV DNA+ or p16- and HPV DNA+. |
p16/HPV: 26 | p16/HPV: 1 | p16/HPV: 10 | p16/HPV: 9 | Oral rinse vs. p16: Sen: 73.5% (95% CI 55.6–87.1); Spe: 83.3% (95% CI 51.6–97.9). Oral rinse vs. DNA ISH: Sen: 66.7% (95% CI 43–85.4); Spe: 87.5% (95% CI 47.4–99.7). Oral rinse vs. p16/HPV: Sen: 72.2 (95% CI 54.8–85.8); Spe: 90 (95% CI 55.5–99.8) |
| Reder et al. (2020) Germany [39] | 2014–2017 | 48/28 | Plasma | E6 and E7 oncogenes RT-PCR | HPV16-DNA RT-PCR | 23 | 0 | 7 | 20 | Sen: 77%; Spe: 100% |
| Economopoulou et al. (2019) Ohio, USA [40] | NR | 22/14 | Blood (CtC) | HPV16 E6/E7 mRNA qPCR | p16 IHC, staining > 70% and HPV DNA qPCR | 3 | 0 | 11 (7 HPV16) | 8 | NR |
| Chera et al. (2019) North Carolina, USA [41] | 2016 –2018 | 103/103. 155 controls (55 healty controls and 60 non-HPV malignancies (not OPSCC)) |
Plasma | DNA, ddPCR | p16 IHC, staining > 70% | 84 | Control: 3 | 19 | Control: 112 | Sen: 89%; Spe: 97% |
| Ren et al. (2019) China [42] | 2007–2017 | 783/611 | Plasma | HPV16 E6 antibody advanced multiplex analysis/ELISA | p16 IHC, staining >70% | 545 | 8 | 66 | 164 | Sen: 89% (95%CI 86–92); Spe: 95% (95%CI 91–98) |
| Damerla et al. New York, USA (2019) [43] | NR | 97/97. (HPV- group: 7 HPV- HNC and 20 healthy controls) |
Plasma | HPV16 and HPV33 ddPCR | p16 IHC, staining >70% or DNA ISH, or RNA ISH | 90 | 0 | 7 | 27 | Sen: 92.8%; Spe: 100% |
| Hanna et al. (2018) Boston, USA [44] | 2017–2018 | 17/15 | Blood (Obtained at any time during treatment) | DNA ddPCR | p16 IHC, staining >70% and DNA ISH or PCR | 14 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Sen: 93.3% (95%CI 68.0–99.8); Spe: 50% (95%CI 1.3–98.7) |
| Kuhs et al. (2017) Pittsburgh, USA [45] | 2003–2013 | 112/87 | Serum | HPV16 E6 multiplex serology | p16 IHC, staining >70% and DNA ISH | 78 | 1 | 9 | 24 | Sen: 89.7% (95%CI, 81.3–95.2); Spe: 96.0% (95% CI, 79.6–99.9) |
| Holzinger et al. (2017) Germany and Italy [46] | NR | 120/66 | Serum | HPV16 E6 antibody ELISA | HPV16 DNA, RT-PCR | 63 | 1 | 3 | 53 | Sen: 96% (95%CI 88–98); Spe: 98% (95%CI 90–100) |
| Mazurek et al. (2016) Poland [47] | 2011–2013 | 51/29 | Plasma | HPV16 DNA, RT-PCR | HPV16 DNA qPCR | 21 | 0 | 8 | 22 | Sen: 72%; Spe: 100%. |
Abbreviation: Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC); Human Papillomavirus (HPV); 95% confidence intervals (95% CI); Immunohistochemistry (IHC); In situ hybridization (ISH); Droplet-based digital PCR (ddPCR); Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR); Not reported (NR); Sensitivity (sen); Specificity (SPE); Unstimulated whole mouth saliva (UWMS); Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE); Fine needle aspiration (FNA); Base of tongue (BOT); Circulating tumour cells (CtC).
3.1. Diagnostic Accuracy of HPV in Tissue Samples
Nine studies evaluated HPV testing in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue [21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29], and five studies evaluated HPV detection in fine needle aspiration (FNA) [30,31,32,33,34]. Reference methods varied between studies; seven studies used p16 IHC as reference [24,25,27,30,33,34], three studies used HPV RNA as reference, where one study detected HPV RNA by ISH [22] and the other two studies detected HPV RNA by PCR [23,26]. Another three studies used HPV DNA by PCR [28,29,32] as reference and finally, two studies combined two detection methods for reference; p16 IHC combined with HPV DNA PCR [21] and p16 IHC combined with HPV DNA PCR and/or HPV E6 seropositivity [31], respectively (Table 1).
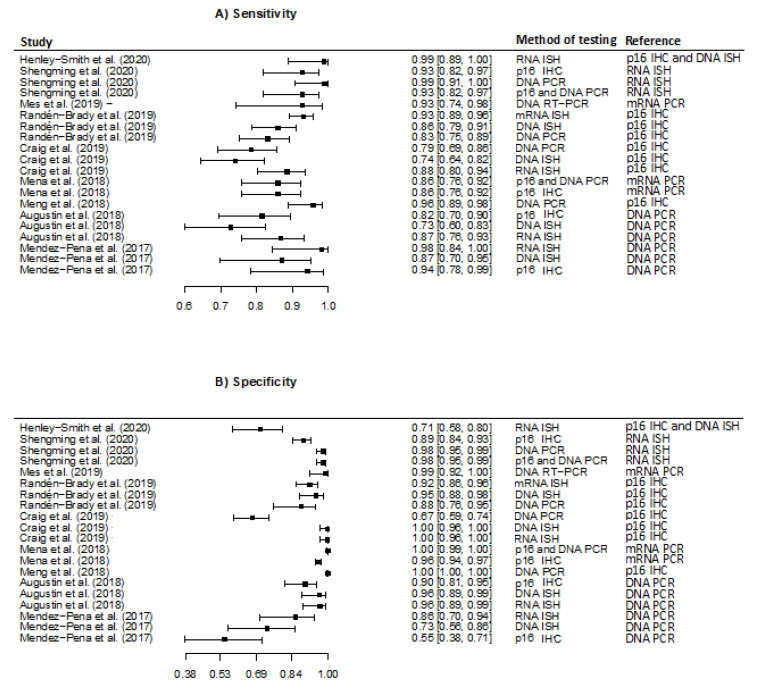
Of the nine studies evaluating HPV detection in FFPE, six studies evaluated more than one detection method [22,24,25,26,28,29]. Five studies investigated accuracy of HPV RNA ISH, four studies investigated accuracy of p16 IHC, five studies investigated accuracy of HPV DNA PCR and four studies investigated the accuracy of HPV DNA ISH. Sensitivity was overall high and ranged from 74% (95% CI 64–82%) [25] to 99% (95% CI 89–100) [21] (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Forest plots of the meta-analysis estimating (A) Sensitivity with 95% confidence intervals, (B) Specificity with 95% confidence intervals in studies evaluating detection of Human Papillomavirus in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. Abbreviation: Immunohistochemistry (IHC); in situ hybridization (ISH); polymerase chain reaction (PCR); droplet-based digital PCR (ddPCR).
Specificity ranged considerably, with the lowest specificity reported as 55% (95% CI 38–71) [29], and three studies reported specificity as high as 100% [25,26,27]. Stratified by detection method, the meta-analysis revealed that the pooled sensitivity was highest for HPV RNA ISH, 93.1 (95% CI 87.4–96.4) and lowest for HPV DNA ISH, 81.1% (95% CI 71.9–87.8). Regarding the pooled specificity the method with the highest specificity was the HPV DNA ISH detection method (94.9% (95% CI 79.1–98.9)) and the lowest was found for HPV DNA PCR (81.1 (95% CI 71.9–87.8)). The reference detection method varied between studies (Table 2).
Table 2.
Pooled sensitivity and specificity for different Human Papillomavirus (HPV) detection methods in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded oropharyngeal cancer tissue.
| Number of Studies Included in Meta-Analysis | References: | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RNA ISH | 5 | p16 IHC: 3 studies DNA PCR: 2 studies |
93.1 (87.4–96.4) | 91.9 (78.8–97.2) |
| DNA ISH | 4 | p16 IHC: 2 studies DNA PCR: 3 studies |
81.1 (71.9–87.8) | 94.9 (79.1–98.9) |
| DNA PCR | 5 | p16 IHC: 3 studies RNA: 2 studies |
90.4 (81.4–95.3) | 81.1 (71.9–87.8) |
| p16 IHC | 4 | RNA: 2 studies DNA PCR: 2 studies |
83.3 (69.0–91.8) | 93.5 (88.4–96.5) |
Abbreviation: Immunohistochemistry (IHC); In situ hybridization (ISH); Polymerase chain reaction (PCR); 95% confidence intervals (95% CI).
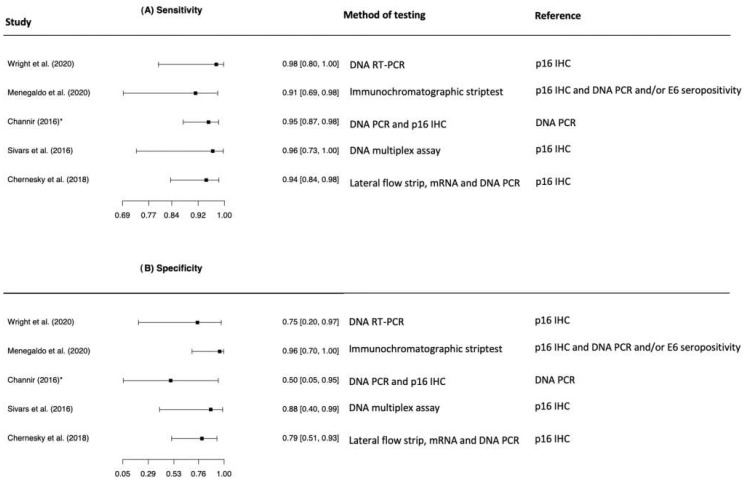
The five studies evaluating the diagnostic accuracy in FNA comprised few patients (n = 195) with the majority of patients being HPV+ OPSCC (85.6%). Four of the five included studies reported a specificity of 100% [30,31,32,33] calculated on the basis of a total of 15 patients with HPV- OPSCC. One study did not include HPV- OPSCC patients and specificity was calculated on the basis of seven patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), 20 Warthin´s tumours and 20 branchial cleft cysts [32]. The studies all reported sensitivity above 94% (Figure 3). The five studies evaluating diagnostic accuracy in FNA were not included in the meta-analysis, as the study numbers were too few to conduct a valid meta-analysis.
Figure 3.
Forest plots of the meta-analysis estimating (A) Sensitivity with 95% confidence intervals, (B) Specificity with 95% confidence intervals in studies evaluating detection of Human Papillomavirus in fine needle aspiration.
3.2. Diagnostic Accuracy of Detecting HPV in Blood Samples
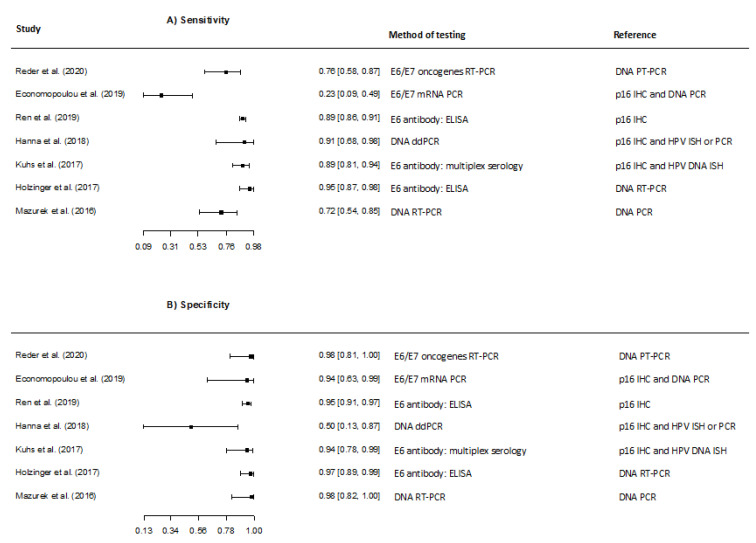
Nine studies (n = 1353, 77.6% HPV+) examined the diagnostic accuracy of HPV detection by liquid biopsy using blood samples. One study collected the blood samples both at time of diagnosis and during treatment and evaluated the accuracy of the test regardless of the time of blood collection [35], the other eight studies collected blood samples before treatment initiation [36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43]. Five studies tested HPV in plasma [36,37,38,39,40], two studies reported detection in blood [35,41] and two studies investigated HPV in serum [42,43].
Studies predominantly evaluated detection of circulating HPV DNA in the blood. However, one study examined the accuracy of detecting HPV16 E6/E7 expression in circulating tumour cells (CtCs) [41]. The study addressing diagnostic accuracy of HPV expression in CtCs had a significantly lower sensitivity compared to the remaining studies (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
Forest plots of the meta-analysis estimating (A) Sensitivity with 95% confidence intervals, (B) Specificity with 95% confidence intervals in studies evaluating detection of Human Papillomavirus DNA in blood.
In the pooled analysis of sensitivity and specificity, the overall sensitivity was 81.4% (95% CI 62.9–91.9), and the overall specificity was 94.8% (95% CI 91.4–96.9) covering all studies regardless of detection method and reference [35,36,38,40,41,42,43] (excluding the two studies with non-OPSCC patients [37,39]).
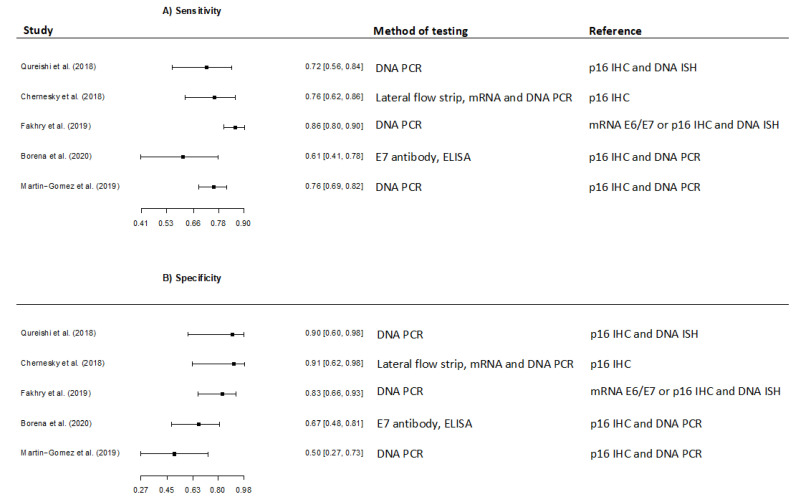
3.3. Diagnostic Accuracy of Detecting HPV in Oral Samples
Five studies evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of HPV detection in oral samples (Table 1) corresponding to a total of 543 patients with OPSCC. Three studies collected oral samples by oral rinse [44,45,46], one study used cytologic brush of the tumour area [47] and one study combined saliva collection with oral swabs [34]. Three studies used p16 IHC combined with HPV DNA as reference [44,46,47], one study only used p16 IHC as reference [34] and one study used mRNA E6 and E7 as reference [45].
A considerable variability in sensitivity and specificity estimates were observed among the studies ranging from 60.9% (95% CI 40.8–77.8) [47] to 86.1% (95% CI 80.4–90.3) [45] in sensitivity, and from 50% (95% CI 27–73) [46] to 91% (95% CI 62–98) [34] in specificity (Figure 5).
Figure 5.
Forest plots of the meta-analysis estimating (A) Sensitivity with 95% confidence intervals, (B) Specificity with 95% confidence intervals in studies evaluating detection of Human Papillomavirus in oral samples.
Regardless of oral sample collection method and reference, method the meta-analysis revealed a pooled sensitivity and specificity of 77.0% (95% CI 68.8–83.6) and 74.0% (95% CI 58.0–85.4), respectively. When restricted to the four studies using p16 IHC as a reference, the pooled sensitivity and specificity was 77.6% (95% CI 67.8–78.7) and 72.1% (95% CI 49.1–87.4).
4. Discussion
This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of HPV detection in patients with OPSCC. As laboratory techniques are evolving rapidly and new detection methods continuously are being introduced, this is an area in need of an update in the current literature. A ranking and comparison of the diagnostic accuracy in different specimens are furthermore needed.
As p16-status is an important factor in staging OPSCC [17], and as clinical trials on treatment de-escalation for HPV+ OPSCC are continuously being introduced, precise detection methods of HPV is of immense importance.
We included a total of 27 studies with varying specimens, methods of HPV detection and references for the latter. We first looked at studies evaluating the diagnostic accuracy of HPV detection in tumour tissue. Two studies evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of combining two detection methods, i.e., p16 IHC combined with HPV DNA PCR. Both studies reported high sensitivity of 93% (95% CI 74–98%) and 86% (95% CI 76–92%), respectively. A similar systematic review [48] also found that combination of diagnostic tests represented the most attractive testing strategy in HPV-related OPSCC. However, it should be noted that only two of the included studies on diagnostic accuracy in FFPE used combined detection methods. We did also find a high diagnostic accuracy in studies where only one diagnostic test was used.
Of importance, we excluded nine studies where the definition of p16 positivity was not specified. The exclusion may have had an impact on the results of our review. It is incredibly important to specify the p16 positivity, since it has been shown that to achieve the highest correlation between p16 and HPV results, a staining of >70% of tumour cells to classify the tumour as p16 positive is advised [49]. The enrolled studies evaluating p16 in tumour cells used a limit >70% staining, except two studies using a cut-off value of 66% and 50%.
Recently, the ability to detect HPV in liquid biopsies was introduced as a novel, non-invasive method of HPV detection. The use of a liquid biopsy for cancer detection has shown encouraging results in both colorectal cancer and bladder cancer [50,51,52]. In contrast to HPV-related cervical cancer, precancerous lesions are lacking in OPSCC and reliable screening methods are thus needed. At present, only a few studies on the use of liquid biopsies in OPSCC exists. Our review indicates that the diagnostic accuracy of HPV detection in blood samples constitutes a promising tool in HPV detection with an overall sensitivity of 81.4% (95% CI 62.9–91.9) and an overall specificity of 94.8% (95% CI 91.4–96.9). Methods used for estimating HPV positivity in primary OPSCC patients varied which could partly explain some of the heterogeneity in sensitivity and specificity. The conclusion that HPV detection in liquid biopsy obtained from OPSCC patients may have a promising role correlates well with a closely related meta-analysis [53]. It is worth noticing that despite of the high sensitivity and specificity, the low prevalence of OPSCC in the general population will result in a low positive predictive value leading to a low current value of HPV as a population-wide cancer screening biomarker as described by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and the US National Cancer Institute (NCI) [54].
When looking at the diagnostic accuracy in oral samples obtained from OPSCC patients, our study revealed a lower diagnostic accuracy than the other specimen types with a sensitivity and specificity of 77.6% (95% CI 67.8–78.7) and 72.1% (95% CI 49.1–87.4), respectively. Variability amongst the studies detecting HPV in oral samples varied considerably. A similar meta-analysis [55] investigating the diagnostic accuracy of HPV detection in oral samples from OPSCC patients found a lower sensitivity 55% (95% CI 25–82%), but with a higher specificity 94% (95% CI 85–98%). The difference could be explained by the fact that their study differed from ours as they enrolled non-OPSCC head and neck cancer patients in their cohort. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and the US National Cancer Institute (NCI) reported similar findings with ranging sensitivity and specificity [54].
In general, the included studies varied in regards to reference method as well as method of detecting HPV, which comprises a significant limitation when comparing the diagnostic accuracy between studies. This might be one possible explanation for the variation in accuracy across the included studies. The pooled sensitivity and specificity should thus be interpreted with caution as accuracy can vary depending on testing method and reference method. To investigate the accuracy of the specific detection methods in order to circumvent the variability and uncertainty different detection methods might bring to the meta-analyses, we performed a sub-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy stratified on detection method for the studies assessing accuracy in FFPE. We found that sensitivity and specificity in general were high for all detection methods with sensitivity ranging from 81.1 (95% CI 71.9–87.8) to 93.1 (95% CI 87.4–96.4), and specificity ranging from 81.1 (95% CI 71.9–87.8) to 94.9 (95% CI 79.1–98.9). It was not possible to conduct sub-analysis for accuracy in liquid biopsy and FNA due to the lower study numbers. We did not account for the different reference methods in the meta-analysis, as it would have resulted in too few studies to perform a valid meta-analysis. In general, grouping studies regardless of the reference methods when comparing sensitivity and specificity of diagnostic testing in meta-analyses [53,55] is a limitation and an ongoing challenge. It is difficult to circumvent, as further stratification according to reference method would lead to very few studies resulting in new limitations and limiting the number of eligible studies so considerable that a meta-analysis could not be performed. Further studies on diagnostic accuracy of HPV detection with similar reference methods are thus warranted.
We included studies published within the last five years to avoid excessive variation in the detection methods between studies as p16 positivity previously ranged considerably and a large part of studies used a minimum of 5–69% staining [49] before ASCO published guidelines for defining a tumours as p16+ by a cut-off of 70% nuclear and cytoplasmic staining [15]. This is however also a limitation to the study that should be noted.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our systematic review evaluating HPV detection methods in patients with OPSCC showed an overall high sensitivity and specificity of HPV detection in FFPE for both RNA ISH, DNA ISH, DNA PCR and p16 IHC. HPV detection by liquid biopsy and blood samples provides a promising, less invasive method of HPV detection and both sensitivity and specificity were high, thus highlighting HPV detection in blood samples as a promising novel tool of HPV detection. HPV detection in blood samples showed an overall sensitivity of 81.4% (95% CI 62.9–91.9), and an overall specificity of 94.8% (95% CI 91.4–96.9) which is thus comparable to the sensitivity and specificity of HPV detection in FFPE where the sensitivity was ranging from 81.1% (95% CI 71.9–87.8) to 93.1 (95% CI 87.4–96.4) and the specificity was ranging from 81.1 (95% CI 71.9–87.8) to 94.9% (95% CI 79.1–98.9.
Lastly, results on the accuracy of HPV detection in FNA and in oral samples were scarce and varied considerably, and evidence on the use of oral samples in HPV detection is currently not substantial enough to highlight it as an acceptable diagnostic tool. In summary, larger studies with homogenous study designs are required to further explore the diagnostic applicability of various HPV detection methods in patients with HPV+ OPSCC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.K.J. and C.v.B.; writing—original draft preparation, K.K.J.; validation, all authors; formal analysis, K.K.J.; writing—review and editing, all authors; supervision, C.v.B.; funding acquisition, K.K.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
K.K.J. was funded by Rigshospitalet. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Garnaes E., Kiss K., Andersen L., Therkildsen M.H., Franzmann M.B., Filtenborg-Barnkob B., Hoegdall E., Krenk L., Josiassen M., Lajer C.B., et al. A high and increasing HPV prevalence in tonsillar cancers in Eastern Denmark, 2000–2010: The largest registry-based study to date. Int. J. Cancer. 2015;136:2196–2203. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Carlander A.-L.F., Grønhøj Larsen C., Jensen D.H., Garnæs E., Kiss K., Andersen L., Olsen C.H., Franzmann M., Høgdall E., Kjær S.K., et al. Continuing rise in oropharyngeal cancer in a high HPV prevalence area: A Danish population-based study from 2011 to 2014. Eur. J. Cancer. 2017;70:75–82. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2016.10.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ang K.K., Harris J., Wheeler R., Weber R., Rosenthal D.I., Nguyen-Tan P.F., Westra W.H., Chung C.H., Jordan R.C., Lu C., et al. Human papillomavirus and survival of patients with oropharyngeal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010;363:24–35. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0912217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chaturvedi A.K., Engels E.A., Pfeiffer R.M., Hernandez B.Y., Xiao W., Kim E., Jiang B., Goodman M.T., Sibug-Saber M., Cozen W., et al. Human papillomavirus and rising oropharyngeal cancer incidence in the United States. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011;29:4294–4301. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.36.4596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lai S., Wenaas A.E., Sandulache V.C., Hartman C., Chiao E., Kramer J., Zevallos J.P. Prognostic significance of p16 cellular localization in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2016;46:132–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tomaic V. Functional roles of E6 and E7 oncoproteins in HPV-induced malignancies at diverse anatomical sites. Cancers. 2016;8:95. doi: 10.3390/cancers8100095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zamani M., Grønhøj C., Jensen D.H., Carlander A.F., Agander T., Kiss K., Olsen C., Baandrup L., Nielsen F.C., Andersen E., et al. The current epidemic of HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer: An 18-year Danish population-based study with 2,169 patients. Eur. J. Cancer. 2020;134:52–59. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.04.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gillison M.L., Zhang Q., Jordan R., Xiao W., Westra W.H., Trotti A., Spencer S., Harris J., Chung C.H., Ang K.K. Tobacco smoking and increased risk of death and progression for patients with p16-positive and p16-negative oropharyngeal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012;30:2102–2111. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.38.4099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gillison M.L., Koch W.M., Capone R.B., Spafford M., Westra W.H., Wu L., Zahurak M.L., Daniel R.W., Viglione M., Symer D.E., et al. Evidence for a causal association between human papillomavirus and a subset of head and neck cancers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000;92:709–720. doi: 10.1093/jnci/92.9.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ragin C.C.R., Taioli E. Survival of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck in relation to human papillomavirus infection: Review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer. 2007;121:1813–1820. doi: 10.1002/ijc.22851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Grønhøj Larsen C., Jensen D.H., Fenger Carlander A.-L., Kiss K., Andersen L., Holkmann Olsen C., Andersen E., Garnæs E., Cilius F., Specht L., et al. Novel nomograms for survival and progression in HPV+ and HPV- oropharyngeal cancer: A population-based study of 1,542 consecutive patients. Oncotarget. 2016;7:71761. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fakhry C., Zhang Q., Nguyen-Tan P.F., Rosenthal D., El-Naggar A., Garden A.S., Soulieres D., Trotti A., Avizonis V., Ridge J.A., et al. Human papillomavirus and overall survival after progression of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014;32:3365. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.55.1937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Argiris A., Li S., Ghebremichael M., Egloff A.M., Wang L., Forastiere A.A., Burtness B., Mehra R. Prognostic significance of human papillomavirus in recurrent or metastatic head and neck cancer: An analysis of Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group trials. Ann. Oncol. 2014;25:1410–1416. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Garnaes E., Frederiksen K., Kiss K., Andersen L., Therkildsen M.H., Franzmann M.B., Specht L., Andersen E., Norrild B., Kjaer S.K., et al. Double positivity for HPV DNA/p16 in tonsillar and base of tongue cancer improves prognostication: Insights from a large population-based study. Int. J. Cancer. 2016;139:2598–2605. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lewis J.S., Beadle B., Bishop J.A., Chernock R.D., Colasacco C., Lacchetti C., Moncur J.T., Rocco J.W., Schwartz M.R., Seethala R.R., et al. Human papillomavirus testing in head and neck carcinomas guideline from the college of American pathologists. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018;142:559–597. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2017-0286-CP. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lewis J.S. p16 Immunohistochemistry As a Standalone Test for Risk Stratification in Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Head Neck Pathol. 2012;6:75–82. doi: 10.1007/s12105-012-0369-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Emergence of a Novel Staging System for Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Based on HPV Status. [(accessed on 7 May 2021)]. Available online: https://www.cancernetwork.com/view/emergence-novel-staging-system-oropharyngeal-squamous-cell-carcinoma-based-hpv-status. [PubMed]
- 18.Schache A., Liloglou T., Risk J.M., Filia A., Jones T.M., Sheard J., Woolgar J.A., Helliwell T.R., Triantafyllou A., Robinson M., et al. Evaluation of human papilloma virus diagnostic testing in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma: Sensitivity, specificity and prognostic discrimination Conclusions—Caution must be exercised in applying HPV16 diagnostic tests due to significant disparities. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011;17:6262–6271. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Moher D., Liberati A., Tetzlaff J., Altman D.J. PRISMA 2009 Flow Diagram. Prism. Statement. 2009;6:e1000097. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Reitsma J.B., Glas A.S., Rutjes A.W.S., Scholten R.J., Bossuyt P.M., Zwinderman A.H. Bivariate analysis of sensitivity and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic reviews. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2005;58:982–990. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2005.02.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Henley-Smith R., Santambrogio A., Andoniadou C.L., Odell E., Thavaraj S. RNA in situ hybridization for human papillomavirus testing in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma on a routine clinical diagnostic platform. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2021;50:68–75. doi: 10.1111/jop.13103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Xu S., Sun B., Zhou R., Shi C., Han Y., Li J., Sun J., Tian Z., Zhang Z., Li J. Evaluation of p16 as a surrogate marker for transcriptionally active human papillomavirus status of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma in an eastern Chinese population. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2020;129:236–245.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2019.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mes S.W., Heideman D.A.M., Bloemena E., Brink A., Bogaarts M., Leemans C.R., Brakenhoff R.H. Development and Validation of a Novel and Rapid Molecular Detection Method for High-Risk Human Papillomavirus in Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Tumor Tissue. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020;22:262–271. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2019.10.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Randén-Brady R., Carpén T., Jouhi L., Syrjänen S., Haglund C., Tarkkanen J., Remes S., Mäkitie A., Mattila P.S., Silén S., et al. In situ hybridization for high-risk HPV E6/E7 mRNA is a superior method for detecting transcriptionally active HPV in oropharyngeal cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2019;90:97–105. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2019.05.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Craig S.G., Anderson L.A., Moran M., Graham L., Currie K., Rooney K., Robinson M., Bingham V., Cuschieri K.S., McQuaid S., et al. Comparison of molecular assays for HPV testing in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas: A population-based study in Northern Ireland. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2020;29:31–38. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-19-0538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Mena M., Taberna M., Tous S., Marquez S., Clavero O., Quiros B., Lloveras B., Alejo M., Leon X., Quer M., et al. Double positivity for HPV-DNA/p16ink4a is the biomarker with strongest diagnostic accuracy and prognostic value for human papillomavirus related oropharyngeal cancer patients. Oral Oncol. 2018;78:137–144. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2018.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Meng H.X., Miao S.S., Chen K., Li H.N., Yao G., Geng J., Wang H., Shi Q.T., He J., Mao X., et al. Association of p16 as prognostic factors for oropharyngeal cancer: Evaluation of p16 in 1470 patients for a 16 year study in Northeast China. Biomed Res. Int. 2018;2018:9594568. doi: 10.1155/2018/9594568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Augustin J., Outh-Gauer S., Mandavit M., Gasne C., Grard O., Denize T., Nervo M., Mirghani H., Laccourreye O., Bonfils P., et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of the 4 tests (p16 immunochemistry, polymerase chain reaction, DNA, and RNA in situ hybridization) to evaluate a human papillomavirus infection in head and neck cancers: A cohort of 348 French squamous cell carcinomas. Hum. Pathol. 2018;78:63–71. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2018.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mendez-Pena J.E., Sadow P.M., Nose V., Hoang M.P. RNA chromogenic in situ hybridization assay with clinical automated platform is a sensitive method in detecting high-risk human papillomavirus in squamous cell carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2017;63:184–189. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2017.02.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wright M.F., Weiss V.L., Lewis J.S., Schmitz J.E., Ely K.A. Determination of high-risk HPV status of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma using the Roche cobas HPV test on cytologic specimens and acellular supernatant fluid. Cancer Cytopathol. 2020;128:482–490. doi: 10.1002/cncy.22258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Menegaldo A., Schroeder L., Holzinger D., Tirelli G., Dal Cin E., Tofanelli M., Rigo S., Mantovani M., Stellin M., Del Mistro A., et al. Detection of HPV16/18 E6 Oncoproteins in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Using a Protein Immunochromatographic Assay. Laryngoscope. 2021;131:1042–1048. doi: 10.1002/lary.29184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Channir H.I., Grønhøj Larsen C., Ahlborn L.B., van Overeem Hansen T., Gerds T.A., Charabi B.W., Vainer B., von Buchwald C., Lajer C.B., Kiss K. Validation study of HPV DNA detection from stained FNA smears by polymerase chain reaction: Improving the diagnostic workup of patients with a tumor on the neck. Cancer Cytopathol. 2016;124:820–827. doi: 10.1002/cncy.21753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sivars L., Landin D., Haeggblom L., Tertipis N., Grün N., Bersani C., Marklund L., Ghaderi M., Näsman A., Ramqvist T., et al. Human papillomavirus DNA detection in fine-needle aspirates as indicator of human papillomavirus–positive oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma: A prospective study. Head Neck. 2017;39:419–426. doi: 10.1002/hed.24641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Chernesky M., Jang D., Schweizer J., Arias M., Doerwald-Munoz L., Gupta M., Jackson B., Archibald S., Young J., Lytwyn A., et al. HPV E6 oncoproteins and nucleic acids in neck lymph node fine needle aspirates and oral samples from patients with oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Papillomavirus Res. 2018;6:1–5. doi: 10.1016/j.pvr.2018.05.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hanna G.J., Supplee J.G., Kuang Y., Mahmood U., Lau C.J., Haddad R.I., Jänne P.A., Paweletz C.P. Plasma HPV cell-free DNA monitoring in advanced HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2018;29:1980–1986. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Reder H., Taferner V.F., Wittekindt C., Bräuninger A., Speel E.J.M., Gattenlöhner S., Wolf G., Klussmann J.P., Wuerdemann N., Wagner S. Plasma Cell-Free Human Papillomavirus Oncogene E6 and E7 DNA Predicts Outcome in Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020;22:1333–1343. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2020.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Chera B.S., Kumar S., Beaty B.T., Marron D., Jefferys S., Green R., Goldman E.C., Amdur R., Sheets N., Dagan R., et al. Rapid clearance profile of plasma circulating tumor HPV type 16 DNA during chemoradiotherapy correlates with disease control in HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019;25:4682–4690. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ren J., Xu W., Su J., Ren X., Cheng D., Chen Z., Bender N., Mirshams M., Habbous S., de Almeida J.R., et al. Multiple imputation and clinico-serological models to predict human papillomavirus status in oropharyngeal carcinoma: An alternative when tissue is unavailable. Int. J. Cancer. 2020;146:2166–2174. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Damerla R.R., Lee N.Y., You D., Soni R., Shah R., Reyngold M. Detection of Early Human Papillomavirus—Associated Cancers by Liquid Biopsy. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019;3:1–17. doi: 10.1200/PO.18.00276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Mazurek A.M., Rutkowski T., Śnietura M., Pigłowski W., Suwiński R., Składowski K. Detection of circulating HPV16 DNA as a biomarker in the blood of patients with human papillomavirus-positive oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 2019;41:632–641. doi: 10.1002/hed.25368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Economopoulou P., Koutsodontis G., Avgeris M., Strati A., Kroupis C., Pateras I., Kirodimos E., Giotakis E., Kotsantis I., Maragoudakis P., et al. HPV16 E6/E7 expression in circulating tumor cells in oropharyngeal squamous cell cancers: A pilot study. PLoS ONE. 2019;14:e0215984. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lang Kuhs K.A., Kreimer A.R., Trivedi S., Holzinger D., Pawlita M., Pfeiffer R.M., Gibson S.P., Schmitt N.C., Hildesheim A., Waterboer T., et al. Human papillomavirus 16 E6 antibodies are sensitive for human papillomavirus–driven oropharyngeal cancer and are associated with recurrence. Cancer. 2017;123:4382–4390. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Holzinger D., Wichmann G., Baboci L., Michel A., Höfler D., Wiesenfarth M., Schroeder L., Boscolo-Rizzo P., Herold-Mende C., Dyckhoff G., et al. Sensitivity and specificity of antibodies against HPV16 E6 and other early proteins for the detection of HPV16-driven oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer. 2017;140:2748–2757. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Qureishi A., Ali M., Fraser L., Shah K.A., Møller H., Winter S. Saliva testing for human papilloma virus in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma: A diagnostic accuracy study. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2018;43:151–157. doi: 10.1111/coa.12917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Fakhry C., Blackford A.L., Neuner G., Xiao W., Jiang B., Agrawal A., Gillison M.L. Association of Oral Human Papillomavirus DNA Persistence with Cancer Progression after Primary Treatment for Oral Cavity and Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 2019;5:985–992. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.0439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Martin-Gomez L., Fulp J., Schell M.J., Sirak B., Abrahamsen M., Isaacs-Soriano K.A., Lorincz A., Wenig B., Chung C.H., Caudell J., et al. Oral Gargle-Tumor Biopsy Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Agreement and Associated Factors Among Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OPSCC) Cases. Oral Oncol. 2019;92:85–91. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2019.03.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Borena W., Schartinger V.H., Dudas J., Ingruber J., Greier M.C., Steinbichler T.B., Laimer J., Stoiber H., Riechelmann H., Kofler B. HPV-induced oropharyngeal cancer and the role of the E7 oncoprotein detection via brush test. Cancers. 2020;12:2388. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Prigge E.S., Arbyn M., von Knebel Doeberitz M., Reuschenbach M. Diagnostic accuracy of p16INK4a immunohistochemistry in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer. 2017;140:1186–1198. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Larsen C.G., Gyldenløve M., Jensen D.H., Therkildsen M.H., Kiss K., Norrild B., Konge L., Von Buchwald C. Correlation between human papillomavirus and p16 overexpression in oropharyngeal tumours: A systematic review. Br. J. Cancer. 2014;110:1587–1594. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Christensen E., Birkenkamp-Demtröder K., Sethi H., Shchegrova S., Salari R., Nordentoft I., Wu H.T., Knudsen M., Lamy P., Lindskrog S.V., et al. Early detection of metastatic relapse and monitoring of therapeutic efficacy by ultra-deep sequencing of plasma cell-free DNA in patients with urothelial bladder carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019;37:1547–1557. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.02052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Reinert T., Henriksen T.V., Christensen E., Sharma S., Salari R., Sethi H., Knudsen M., Nordentoft I., Wu H.T., Tin A.S., et al. Analysis of Plasma Cell-Free DNA by Ultradeep Sequencing in Patients with Stages i to III Colorectal Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019;5:1124–1131. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.0528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Schøler L.V., Reinert T., Ørntoft M.B.W., Kassentoft C.G., Arnadøttir S.S., Vang S., Nordentoft I., Knudsen M., Lamy P., Andreasen D., et al. Clinical implications of monitoring circulating Tumor DNA in patients with colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017;23:5437–5445. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-0510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Wuerdemann N., Jain R., Adams A., Speel E.J.M., Wagner S., Joosse S.A., Klussmann J.P. Cell-free hpv-dna as a biomarker for oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma—A step towards personalized medicine? Cancers. 2020;12:2997. doi: 10.3390/cancers12102997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kreimer A.R., Chaturvedi A.K., Alemany L., Anantharaman D., Bray F., Carrington M., Doorbar J., D’Souza G., Fakhry C., Ferris R.L., et al. Summary from an international cancer seminar focused on human papillomavirus (HPV)-positive oropharynx cancer, convened by scientists at IARC and NCI. Oral Oncol. 2020;108:104736. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.104736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Gipson B.J., Robbins H.A., Fakhry C., D’Souza G. Sensitivity and specificity of oral HPV detection for HPV-positive head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol. 2018;77:52–56. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2017.12.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.