Abstract
Biomaterials that can harness the intrinsic osteogenic potential of stem cells offer a promising strategy to accelerate bone regeneration and repair. Previously, we had used methacrylated gelatin (GelMA)-based scaffolds to achieve bone formation from human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs). In this study, we aimed to further enhance hMSC osteogenesis by incorporating graphene oxide (GO)-based nanosheets into GelMA. In vitro results showed high viability and metabolic activities in hMSCs encapsulated in the newly developed nanocomposite. Incorporation of GO markedly increased mineralization within hMSC-laden constructs, which was further increased by replacing GO with silica-coated graphene oxide (SiGO). Mechanistic analysis revealed that the nanosheet enhanced the production, retention, and biological activity of endogenous bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), resulting in robust osteogenesis in the absence of exogenous osteoinductive growth factors. Specifically, the osteoinductive effect of the nanosheets was abolished by inhibiting the BMP signaling pathway with LDN-193189 treatment. The bone formation potential of the technology was further tested in vivo using a mouse subcutaneous implantation model, where hMSCs-laden GO/GelMA and SiGO/GelMA samples resulted in bone volumes 108 and 385 times larger, respectively, than the GelMA control group. Taken together, these results demonstrate the biological activity and mechanism of action of GO-based nanosheets in augmenting the osteogenic capability of hMSCs, and highlights the potential of leveraging nanomaterials such as GO and SiGO for bone tissue engineering applications. This study demonstrates the mechanism of action of graphene oxide nanosheets in augmenting bone regeneration.
Keywords: methacrylated gelatin, graphene oxide, silicon oxide, mesenchymal stem cells, bone morphogenetic protein, bone tissue engineering
1. Introduction
As the median age of the world’s population increases, the need for bone repair and regeneration is trending steeply upward [1]. Conventional bone defect management includes bone transplants, with autografts being the “gold standard” [2]. Although these natural grafts usually lead to increased osteoinduction and osteoconduction, they have a number of drawbacks, such as limited availability and donor site morbidity, as well as risks of infection and disease transmission [3]. As an alternative, stem cell-based tissue engineering offers a promising approach to treating bone damage. In particular, human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs), which are multipotent cells present in a number of tissues throughout the body, are among the most widely studied cell sources for bone tissue engineering [4]. For example, we recently seeded hMSCs in a gene-activated, methacrylated gelatin (GelMA)-based scaffold and achieved robust reparative capacity in cranial bone defects in mice [5].
To induce osteogenic differentiation of hMSCs, growth factors such as bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are usually required. Among the different BMPs, BMP2 and BMP7 are both highly osteoinductive and have been used in commercially available medical products [6]. However, as is the case with other growth factors, BMP application in tissue engineering is generally hindered by its low stability, short half-life, high cost of production, and undesirable potential side effects, including carcinogenesis [7]. Therefore, growth factor-free approaches to bone tissue engineering are attracting increasing attention [8, 9]. Previous studies by our group and others have shown that delivery of osteogenic genes to hMSCs could lead to sustained production of osteogenic growth factors such as BMPs at physiologically relevant concentrations, resulting in enhanced osteogenic differentiation and mineralization of hMSCs in vitro and in vivo [5, 10, 11]. However, the safety of such gene delivery strategies warrants further investigation to reach clinical trials.
Discoveries and advances in nanomaterials and nanocomposites in recent decades have greatly advanced technological developments in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [12, 13]. The importance of the nano-dimension and -topography of the components of the native cellular niche provides the conceptual rationale driving these developments. For example, Reznikov et al. [14] identified the hierarchical assembly of bone minerals and collagen at the nanoscale. Recently, the application of graphene and graphene derivatives in tissue engineering has been enthusiastically pursued [15]. These two-dimensional (2D) nanomaterials possess remarkable electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties [16, 17]; in addition, the large specific surface area makes graphene nanomaterials effective drug delivery carriers [18, 19]. Nayak et al. [20] reported that hMSCs seeded on graphene-coated surfaces had accelerated osteogenic differentiation. Similar results were reported in another study, which demonstrated graphene’s ability to preconcentrate β-glycerolphosphate and dexamethasone, two important osteogenic inducers [21]. Lu et al. fabricated free-standing, multi-layered graphene membranes, which facilitated in vivo bone formation via enhanced protein adsorption [22, 23]. These studies suggest that graphene nanosheets can independently induce robust osteogenesis, thus overcoming the limitation of using osteogenic growth factors in bone tissue engineering. However, the mechanism governing the responses of cells/tissues to nano-dimensional materials such as graphene are incompletely understood. Future success in clinical applications of nanomaterials requires a more in-depth understanding of how nanomaterials influence cell behavior. In this study, we have characterized BMP signaling in hMSCs encapsulated in 3D nanocomposite scaffolds, in order to gain insights into the nature of biomolecular interactions between hMSCs and 2D nanomaterials.
Hydrogels, such as GelMA, represent an important type of scaffold for bone regeneration. With their high water content, hydrogels provide a tissue-like, biocompatible, 3D environment for cell culture. In particular, injectable and degradable hydrogels can conform to the shape of irregular bone defects and be gradually replaced via natural biodegradation by the new, growing tissue. However, compared with commonly used biometals (e.g., Ti and Mg alloys) and bioceramics (e.g., tricalcium phosphate, hydroxyapatite), hydrogels usually have reduced osteoinductivity and substantially lower mechanical strengths [24, 25]. With the incorporation of nanomaterials such as graphene, hydrogel-based nanocomposites can serve as a versatile bone tissue engineering platform that allows for the generation of 3D cell-laden constructs with tunable mechanical, structural, and biological characteristics [26]. For example, our previous study reported that graphene oxide (GO), a graphene derivative with high aqueous dispersity, increased the Young’s modulus of a hydrogel-based cartilage scaffold [27]. GO incorporation in hydrogel scaffolds was also reported to enhance osteogenic differentiation of the encapsulated hMSCs [28, 29]. However, the underlying mechanisms need to be further explored to pave the road for their future clinical applications.
In this study, we aimed to incorporate GO-based nanosheets to enhance hMSC osteogenesis within GelMA. We hypothesized that the nanosheet-functionalized hydrogels could induce robust osteogenesis of hMSCs without the supplementation of osteoinductive growth factors. To test this hypothesis, we first prepared 3D constructs consisting of GO-encapsulated, hMSC-laden hydrogel scaffolds, and osteogenesis was assessed after 28 days of culture in growth factor-free osteogenic medium (OM). Moreover, in light of the reported benefits of silicon in bone metabolism [30], we tested the potential of a novel GO derivative—silica-coated GO (SiGO)—in supporting hMSC osteogenesis, which has not been investigated previously. To explore the mechanism responsible for nanosheet-induced osteogenesis, we first assessed the presence of endogenous osteogenic growth factors, such as BMP2 and BMP7, and examined their interactions with the carbonaceous nanosheets. Next, the BMP antagonist, LDN-193189, was used to test the involvement of the BMP signaling pathway in the pro-osteogenesis effect of the nanosheets. Finally, a mouse subcutaneous implantation model was employed to assess the ability of constructs of hMSC-laden, GO- or SiGO-functionalized GelMA scaffolds for in vivo bone formation.
2. Materials & Methods
2.1. hMSC isolation and characterization
Bone marrow was obtained by flushing the femoral heads and trabecular bone collected from patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty (approved by Institutional Review Board, University of Washington and University of Pittsburgh). After several rounds of rinsing, the hMSCs were plated in T150 flasks (Corning Inc., corning, NY) and cultured in growth medium [GM, Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM; Gibco, Grand Island, NY) supplemented with 10 % (v/v) fetal bovine serum (FBS; Gemini Bio-Products, West Sacramento, CA) and 1X antibiotic-antimycotic (anti-anti; Gibco)] supplemented with 1.5 ng/mL fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2; RayBiotech, Norcross, GA). When the cultures reached 70%–80% confluence, the hMSCs were detached with trypsin-0.25% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (ThermoFisher, Waltham, MA) and passaged at 1:3 dilution.
The colony formation ability of the hMSCs was evaluated using the colony forming unit (CFU) assay using a standard protocol [31]. Trilineage (osteogenic, chondrogenic, and adipogenic) cell differentiation was routinely performed in 2D culture to validate the stemness of the pooled hMSCs [32]. hMSCs isolated from 10 male (average age: 51 years old) and 10 female (average age: 53 years old) donors were pooled before use. All experiments were performed with passage 5 hMSCs.
2.2. Synthesis and characterization of nanomaterials and hydrogel
Graphene oxide (GO) nanosheets were prepared from graphite flakes (Superior Graphite, Chicago, IL) via a modified Hummers’ method [33, 34]. Silica-coated graphene oxide (SiGO) nanoplatelets were prepared through a sol-gel process reported previously [35]. The morphology of the nanoplatelets was observed using transmission electron microscopy (TEM; JEOL JEM 2100F, Japan). The thickness of the as-synthesized GO and SiGO nanosheets was characterized by atomic force microscopy (AFM; Veeco™ Dimension V with Nanoscope V controller); Bruker DNP probes were used to collect contact-mode micrographs with a nominal cantilever spring constant of 0.35 N/m. Bruker NanoScope Analysis software version 2.0 was used for post-processing and analysis of AFM micrographs. Samples were prepared for AFM analysis by drop-casting diluted stock solutions, with approximate concentrations of 0.03 mg/ml, onto freshly cleaved mica substrates. The solvent was evaporated at ambient laboratory conditions prior to imaging. Thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) (TA instrument, New Castle, DE) was performed with N2 used as the purge gas to assess the thermal stability of the nanomaterials. Raman spectroscopy (Renishaw Invia, UK) and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) (Kratos, Axis- ULTRA, UK) were employed to study the chemical compositions of GO and SiGO.
GelMA was synthesized following a protocol described in our previous study [36]. Briefly, bovine skin-derived gelatin (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) dissolved in deionized (DI) water was reacted with excessive methacrylic anhydride (Sigma-Aldrich) overnight at 37 °C under continuous agitation. The solution was then dialyzed against DI water using a 3.5K molecular weight cut-off membrane (ThermoFisher) for 5 days to remove impurities. The lyophilized GelMA was dissolved at 15% (w/v) in Hanks’ Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS, with Ca2+, Mg2+; ThermoFisher), into which 0.15% (w/v) lithium phenyl-2,4,6-trimethylbenzoylphosphinate as the photo-initiator and 1X antibiotic-antimycotic were added.
Hydrogels with 5 mm diameter and 2 mm thickness were prepared for equilibration, swelling, and degradation tests. Dried hydrogels were obtained by lyophilizing gels that had been equilibrated in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, Gibco) overnight. The equilibrium water content (EWC) was calculated according to the following equation:
| (1) |
where Me and Md are the weight of equilibrated gel and pre-equilibrated, dried gel, respectively. The swelling behaviors of the hydrogels were also studied by incubating each crosslinked gel in 1 mL DMEM supplemented with 1X anti-anti at 37 °C on a shaker (100 rpm), with weekly medium change.
2.3. Preparation of cell-laden hydrogel scaffolds
The cell-laden hydrogel scaffolds were prepared by resuspending hMSCs in the pre-gel solution, transferring the cell suspension to silicone molds (2 mm height, 5 mm diameter), and photocrosslinking the gel via photo-illumination at a wavelength of 395 nm [31]. To fabricate nanomaterial-reinforced scaffolds, UV-sterilized GO and SiGO powders were first dissolved in HBSS by ultrasonication, and the solutions were then used to reconstitute the lyophilized GelMA. The GO concentration in the pre-gel solution was 167 μg/mL, a value within the range of GO concentrations found to cause no cytotoxicity in cell-laden GelMA scaffolds previously [26, 37]. TGA results revealed that the silica coating took up ~88 wt % of the SiGO nanomaterial; we therefore used 1.42 mg/mL SiGO in the pre-gel solution so that the amount of GO in the SiGO-reinforced scaffolds remained the same. After gelation, the cell-laden scaffolds were rinsed twice with HBSS and transferred to polystyrene plates with a non-treated surface (ThermoFisher). We also prepared cell-free scaffolds using the aforementioned method.
2.4. Evaluation of biocompatibility
LIVE/DEAD cell viability assay (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA) was used to evaluate the viability of cells encapsulated in the 3D hydrogel scaffolds as well as those seeded on the top of scaffolds (2D culture) (Fig. 2A). The 3D cultures used the same method described above. For 2D cultures, the hydrogels were fabricated as thin disks with a diameter of 22 mm and thickness of 0.8 mm, on which 10,000 cells were plated and grown in either GM or osteogenic medium [OM, DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS (v/v), 1X anti-anti, 10 mM β-glycerophosphate (Sigma-Aldrich), 0.1 μM dexamethasone (Sigma-Aldrich), 50 μg/mL ascorbate 2-phosphate(Sigma-Aldrich), and 10 nM 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (Sigma-Aldrich)] [27] for 4—5 days before the LIVE/DEAD assay. For LIVE/DEAD staining, the culture medium was switched to Phenol Red-free DMEM (Gibco) containing 10% (v/v) FBS, into which calcein AM and ethidium homodimer-1 were added following the manufacturer’s protocol. After 30 min of incubation at 37 °C, the cells were imaged using an Olympus IX81 inverted microscope (Olympus, Waltham, MA).
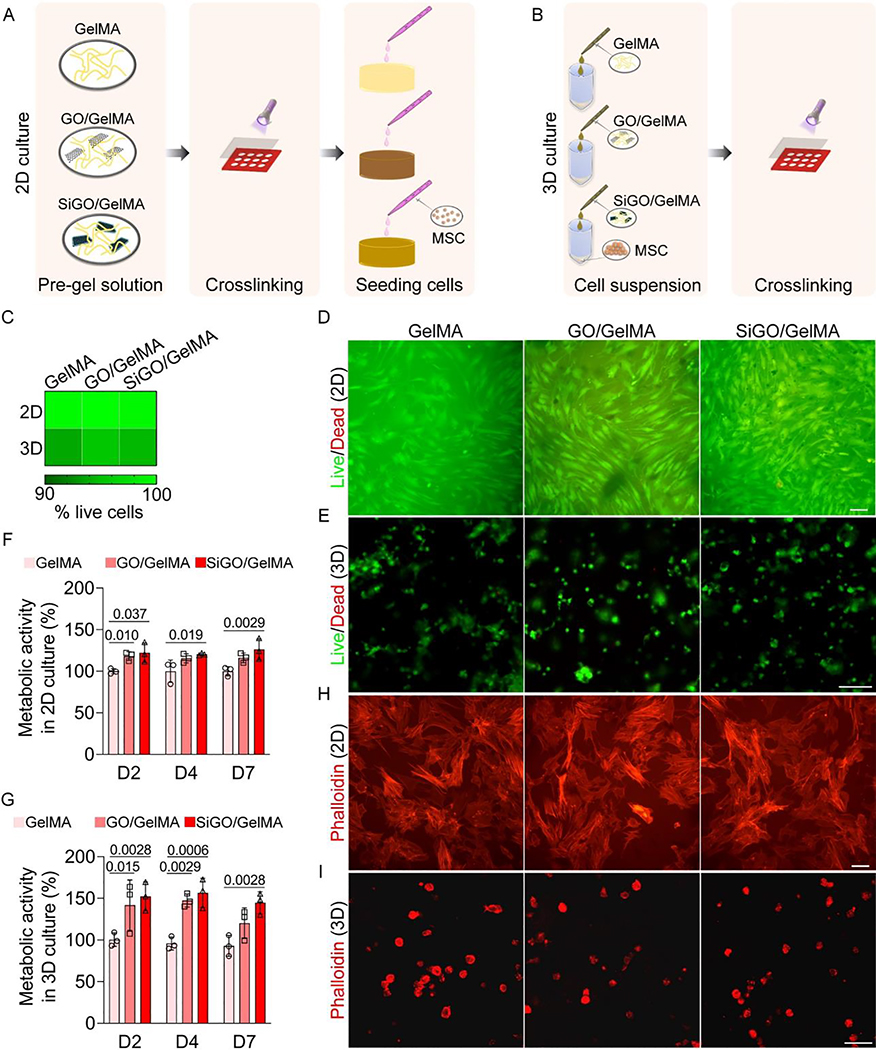
Fig. 2. Cytocompatibility assessment of GO- and SiGO-functionalized hydrogels.
(A, B) Schematics of the establishment of (A) 2D and (3) 3D cultures. (C) Heatmap showing the percentage of live cells in 2D and 3D cultures. N = 3. (D) Representative LIVE/DEAD assay images. hMSCs were cultured on three types of hydrogels for 4 days. Scale bar = 100 μm. (E) Representative LIVE/DEAD images of hMSCs after 4 days of culture within 3D scaffolds. Scale bar = 100 μm. (F) hMSCs were seeded on TCP and cultured in the scaffold-conditioned medium. Metabolic activities were measured by the alamarBlue assay on day 2 (D2), D4, and D7, and normalized to the GelMA group. N = 3, one-way ANOVA was carried out. P values were labeled. (G) Metabolic activity of cells encapsulated in the hydrogel scaffolds normalized to the GelMA group. N = 3, one-way ANOVA was carried out. P values were labeled. (H) Phalloidin staining of hMSCs after 4 days of 2D culture on the scaffolds in OM. Scale bar = 100 μm. (I) Phalloidin staining of hMSCs after 4 days of culture in hydrogels. Scale bar = 50 μm.
To compare the morphology of cells grown on different hydrogel surfaces, Alexa Fluor 568 phalloidin (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) was used to stain cytoskeletal actin filaments. Prior to dye application, cells were fixed in 10% formalin (Fisher Scientific, Hampton, NH) for 15 min and permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich). The 2D cultured cells were imaged using an Olympus IX81 inverted microscope (Olympus), and the morphology of 3D cultured cells was observed using an Olympus Fluoview 1000 I confocal microscope (Center Valley, PA; excitation/emission, 568 nm/603 nm).
Scaffold biocompatibility was further assessed using the alamarBlue cell viability reagent (Invitrogen). hMSCs were encapsulated in different hydrogels and cultured in GM. At pre-set time points, the alamarBlue reagent was added at 1:10 (v/v) to the cell culture medium. After ~4 h of incubation in tissue culture incubator, the fluorescent intensity of the medium was recorded at an excitation/emission wavelength of 560 nm/590 nm. To examine the effect of substances released from hydrogel on hMSCs, the cell-free scaffold was maintained in 1 mL GM overnight at 37 °C. Scaffold-conditioned GM was then used for the culture of hMSCs seeded on 96-well plates (8,000 cells/well). A similar assay was performed as described above.
2.5. BMP2 release study
To test the ability of GelMA and the nanocomposites to retain BMPs, BMP2 was used as a representative. Briefly, 60 ng recombinant human BMP2 (PeproTech, Rocky Hill, NJ) was loaded into cell-free scaffolds before photocrosslinking. After polymerization, the hydrogels were maintained in 0.5 mL of 0.5% solution of bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Sigma-Aldrich) at 37 °C in a tissue culture incubator, with daily change of BSA solution. The solution was collected at different time points for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) of BMP2 over 5 days and replaced with fresh BSA solution. ELISA was carried out following the manufacturer’s protocol (Human/Murine/Rat BMP2 Standard ABTS ELISA Development Kit, PeproTech).
2.6. In vitro osteogenesis of hMSCs within hydrogels
The hMSCs were differentiated in 3D scaffolds over 28 days in growth factor-free OM. The culture medium was changed every other day. Osteogenesis was assessed with real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), histological staining, and immunostaining.
BMP2 and BMP7 both possess well-recognized ability to induce osteogenic differentiation of hMSCs [38], and supplementing basic OM with these osteogenic growth factors represent the current optimal osteoinduction condition. Therefore, MSC-laden GelMA scaffolds were also cultured in BMP2- or BMP7-supplemented (100 ng/mL; both supplied by PeproTech) OM for 28 days, and the mineralization level in these scaffolds was compared side-by-side to that in cell-laden GO/GelMA and SiGO/GelMA scaffolds cultured in BMP2/BMP7-free OM by histological staining.
To examine the role of BMP-SMAD1/5 axis in the osteogenic differentiation of encapsulated hMSCs, LDN-193189 (LDN; Selleck Chemicals, Houston, TX), a small molecule BMP inhibitor that acts as a highly selective antagonist of BMP receptor isotypes ALK2 and ALK3 [39, 40], was added at 0.5 μM to the OM. Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was used as vehicle control. After 7 days of treatment, phosphorylated SMAD1/5 (pSMAD1/5) expression level was assessed by western blot. The extent of osteogenesis quality was evaluated following 4 weeks of treatment.
2.7. Gene expression analysis
The cell-laden constructs were pulverized, and cells lysed in QIAzol reagent, followed by RNA extraction using an RNeasy Plus Universal Kit (Qiagen, Germantown, MD). Reverse transcription was then carried out to obtain cDNA for RT-qPCR using the SYBR green chemistry and the QuantStudio 3 RT-qPCR system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). The primer sequences (IDT, Newark, NJ) used for RT-qPCR are given in Supplementary Table S1.
2.8. Histology and immunostaining
The scaffolds were fixed overnight in buffered formalin at 4 °C. Dehydrated samples were embedded in paraffin and sectioned at 6 μm thickness. To detect matrix mineralization, sections were stained with Alizarin Red S (Alfa Aesar, Haverhill, MA) and Von Kossa (silver nitrate and sodium thiosulfate; ThermoFisher) stains for the presence of calcium and phosphate, respectively, in the sections. For hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, the rehydrated tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin (Sigma-Aldrich) for 5 min and alcoholic eosin (Leica Biosystems, Buffalo Grove, IL) for 30s. The stained sections were observed using a Nikon Eclipse E800 upright microscope (Nikon, Melville, NY).
For immunohistochemistry (IHC) and immunofluorescence (IF), the histological sections were first processed for antigen retrieval by heating in sodium citrate solution (eBioscience, San Diego, CA) at 90°C for 20 min. The sample sections were incubated at 4 °C overnight in solutions of primary antibodies against osteocalcin (OCN; ab93876, Abcam, Cambridge, MA; 1:250 dilution), alkaline phosphatase (ALP; ab108337, Abcam; 1:250 dilution), collagen type I (COL1; ab34710, Abcam; 1:100 dilution), BMP2 (ab6285, Abcam; 1:500 dilution), BMP7 (sc-517294, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX; 1:100 dilution), and pSMAD1/5 (9516S, Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA; 1:500 dilution). For IHC, a biotinylated anti-mouse/rabbit immunoglobulin G (IgG) secondary antibody was utilized, with signal amplification via the avidin-biotin complex (ABC) method (VECTASTAIN Elite ABC-HRP Kit); a 3,3’-Diaminobenzidine (DAB) substrate kit or Vector NovaRED substrate kit (Vector Laboratories; Burlingame, CA) was employed for signal visualization. Hematoxylin was used for counterstaining (Vector Laboratories). For IF, either a goat anti-mouse IgG (Alexa Fluor 488, Abcam; 1:500 dilution) secondary antibody or a goat anti-rabbit IgG (heavy & light chain; Alexa Fluor 594, Invitrogen; 1:500 dilution) secondary antibody was utilized. The IF samples were mounted with a 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI)-containing antifade medium (Vector Laboratories). An Olympus IX81 inverted microscope (Olympus) and an Olympus Fluoview 1000 II confocal microscope (Center Valley, PA) were used to image the stained sections.
2.9. Image analysis
NIH ImageJ was used to process the positive staining signals in histology, IF, and IHC images [41]. To quantify the positively stained areas in Von Kossa- and Alizarin Red-stained sections, the images were converted into greyscale duplicates, transformed into binary images, and analyzed using the Analyze tool in ImageJ. After measuring the total area of the section, the percentage of stained area in each section was then calculated. For IF images, the original colored images were converted into grayscale duplicates and transformed to binary images after denoising. The mean gray value (MGV) of fluorescence was obtained by comparing the original colored images to the binary duplicates using ImageJ’s Analyze tool. The MGV values were normalized to the number of cells (indicated by DAPI staining) present in the field to obtain the MGV per cell.
For IHC images, image deconvolution was conducted to separate the substrate and hematoxylin staining. The isolated substrate staining was then transformed to binary images, and the MGV of each image was obtained and normalized to the cell number.
2.10. Western blot
At pre-set time points, the cell-laden constructs were washed twice with ice-cold PBS, followed by pulverization and lysis in ice-cold radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) buffer (Sigma-Aldrich) containing 1% (v/v) protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (ThermoFisher). The sample solutions were then centrifuged at 14,000 g for 15 min at 4 °C to collect the supernatant. Protein concentration was measured using a bicinchoninic acid (BCA) protein assay kit (ThermoFisher). The protein samples were heated in Laemmli buffer containing 10% (v/v) β-mercaptoethanol (Biorad; Hercules, California) at 90 °C for 5 min and stored at −20 °C.
Samples containing equal amounts of protein were subjected to SDS PAGE in a 4–12% bis-Tris polyacrylamide gel (200 V, 50 min). The separated proteins were then transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane (0.2 μm) in a semi-dry manner using an iBlot 2 Dry Blotting System (Invitrogen). After blocking in 3% non-fat milk (Biorad) for 1.5 h at room temperature, the membrane was incubated overnight in 1% milk containing a primary antibody against the target protein at 4 °C with gentle agitation. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH; Cell Signaling; 1:1,000 dilution) was used as the protein loading control. The primary antibodies used were the same as those used for immunostaining, except for ALP (ab126820, Abcam; 1:1000 dilution) and OCN (ab133612, Abcam; 1:1000 dilution) antibodies. The peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies were purchased from Abcam (anti-mouse IgG; 1:1,000 dilution) or Cell Signaling (anti-rabbit IgG; 1:1,000 dilution). The blots were imaged using a ChemiDoc™ Touch Imaging System (Bio-Rad) after incubating the membrane in the SuperSignal West Femto Maximum Sensitivity Substrate solution (ThermoFisher). Quantification of the blot images was conducted using ImageJ [41].
2.11. Calcein green staining
Real-time mineralization in bone scaffolds was monitored by calcein green staining using a previously reported method [42, 43]. In brief, calcein powder (Sigma-Aldrich) was first dissolved in a 0.1 M NaOH solution and then diluted with double-distilled water to obtain the 1 mM working solution, which was sterilized by 0.22 μm membrane filtration before use. Starting from day 4 of osteogenic culture, calcein solution was added to the cell culture medium to reach a final concentration of 2 μM. Green fluorescence was visualized with an excitation laser wavelength of 488 nm on an Olympus Fluoview 1000 I confocal microscope (Center Valley, PA).
2.12. Mechanical testing
Compression tests were carried out on a mechanical tester (Bose ElectroForce 3230 Series II, TA Instruments, New Castle, DE) to assess the mechanical properties of the constructs. The cylindrical samples were placed between two circular plates attached to the load cell and compressive motor, respectively, and compressed at 0.01 mm/s until 10 % strain (0.2 mm) was achieved. The linear portion of the stress-strain curve was used to calculate the compressive modulus.
2.13. Subcutaneous implantation in mice
All the animal experiments were performed with the approval of the University of Pittsburgh Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC). Male Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) mice (B6.CB17-Prkdcscid/SzJ, 8–12 weeks old) were purchased from the Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME). The mice were anesthetized in 2% isoflurane carried by oxygen, and a ~6 mm skin incision was created on the back. Cell-laden scaffolds that had been cultured in OM for 21 days were subcutaneously implanted in the mice (3 mice per group), and the incisions were closed with suture. The animals were provided ad libitum with water and food and had unrestricted mobility. For 3 days after surgery, the animals were administered carprofen through Rimadyl tablets (Rimadyl MD’s; Bio-Serv, Flemington, NJ).
2.14. Micro-computed tomography (μCT) analysis
After 4 weeks of in vivo implantation, the mice were euthanized by exposure to carbon dioxide in an enclosed container. Cervical dislocation was subsequently applied to ensure death. The implants were carefully harvested, fixed with buffered formalin, dehydrated, and kept in 70% ethanol for μCT examination (vivaCT 40, Scanco Medical, Switzerland). The μCT scans were acquired using 45 kVp energy, 88 μA intensity, 300 ms integration time, and 35 μm resolution. The raw μCT images were used to reconstruct the 3D specimens.
After μCT, the samples were subjected to histological and immunofluoresence staining using the methods described above.
2.15. Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was carried out with Prism 9 (GraphPad, San Diego, CA). The data are presented as mean ± standard deviation, with N ⩾ 3. The type of analysis conducted is specified in figure captions, and P values are given in the figure wherever applicable.
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of GO and SiGO nanosheets
Fig. 1A shows the schematic of converting GO nanosheets to SiGO. While GO displayed smooth, fabric-like morphology under TEM, SiGO appeared wavy and thicker (Fig 1B, C). The topographical difference between GO and SiGO was clearly seen in the AFM micrographs (Fig. 1D, E). The height profile recorded from AFM imaging revealed a sheet thickness of ~1.3 nm for GO and ~46 nm for SiGO (Fig. 1D, E). Both D and G bands, characteristic of graphitic materials and indicative of structural defects, respectively, were observed for GO and SiGO nanosheets (Fig. 1F). In the XPS survey scan spectra, additional Si 2p and Si 2s peaks were seen for SiGO, implying successful preparation of a silica coating (Fig. 1G). TGA curves showed a much larger weight reduction in GO than SiGO when heated from RT to 750 °C (Fig. 1H).
Fig. 1. Preparation and characterization of GO and SiGO nanosheets.
(A) Schematic showing the conversion of GO to SiGO. (B, C) TEM images showing (B) smooth, few-layered GO sheets and (C) thicker SiGO platelets. Scale bar =100nm. (D, E) AFM contact mode micrographs (left) and corresponding height profiles (right, recorded along the dashed lines in the micrographs) of (D) GO and (E) SiGO nanosheets. Scale bar = 1 μm. (F) Raman spectra, (G) XPS spectra, and (H) TGA curves of GO and SiGO.
3.2. GO- and SiGO-functionalized GelMA hydrogels are biocompatible
The addition of GO or SiGO nanosheets did not alter the EWC or swelling behavior of the scaffolds (Figure S1). To evaluate the biocompatibility of the nanocomposite hydrogels, LIVE/DEAD cell viability assays were carried out for co-cultured hMSCs. Fig. 2A and B show the schematics of scaffold preparation for testing cell viability in 2D and 3D culture, respectively. In 2D cultures, only a few dead cells were found in hMSCs cultured on all three types of hydrogels (Fig. 2C, D). An equivalent or higher percentage of live cells were seen in the GO/GelMA and SiGO/GelMA groups compared to the GelMA group. Similarly, the majority of the cells remained viable after 4 and 21 days of culture in hydrogels (Fig. 2E & Figure S2). Specifically, the percentage of viable cells in the GO/GelMA and SiGO/GelMA groups was 95.5% and 94.6%, respectively, compared to 93.8% in the GelMA group (Fig. 2C). In addition, we used the alamarBlue assay to quantify cell metabolic activity. Generally, 2D hMSC cultures maintained in the nanocomposite-conditioned medium had higher metabolic activities than those grown in GelMA-conditioned medium (Fig. 2F). Cells encapsulated in the nanocomposite hydrogels also displayed higher or equivalent metabolic activities to those in GelMA at the same time points (Fig. 2G). These results collectively suggested the absence of cytotoxicity of the scaffolds themselves or their leachates. In addition, the encapsulation of nanosheets led to higher metabolic activities of hMSCs.
We then examined cell morphology by means of phalloidin staining of cytoskeletal actin filaments. Attachment and spreading of cells were observed when hMSCs were grown on all three hydrogels (Fig. 2H). In comparison, all cells encapsulated within scaffolds displayed round morphology (Fig. 2I).
3.3. GO or SiGO Encapsulation significantly promotes mineral deposition by hMSCs
The nature of hMSCs was confirmed with trilineage differentiation and CFU assays (Figure S3). To induce bone formation, hMSCs were encapsulated within GelMA, GO/GelMA or SiGO/GelMA, and then subjected to 28 days of osteogenic culture. As shown in Fig. 3A, the encapsulation of SiGO nanosheets increased the compressive modulus of GelMA on day 0. After 28-day culture, both GO- and SiGO-containing constructs had significantly increased compressive modulus, which remained unchanged in the GelMA group. In addition, both nanosheet-reinforced scaffolds had significantly higher compressive moduli than the GelMA group (Fig. 3A). The representative stress-strain curves given in Fig. 3B showed higher stress for the nanocomposites at the same strain level.
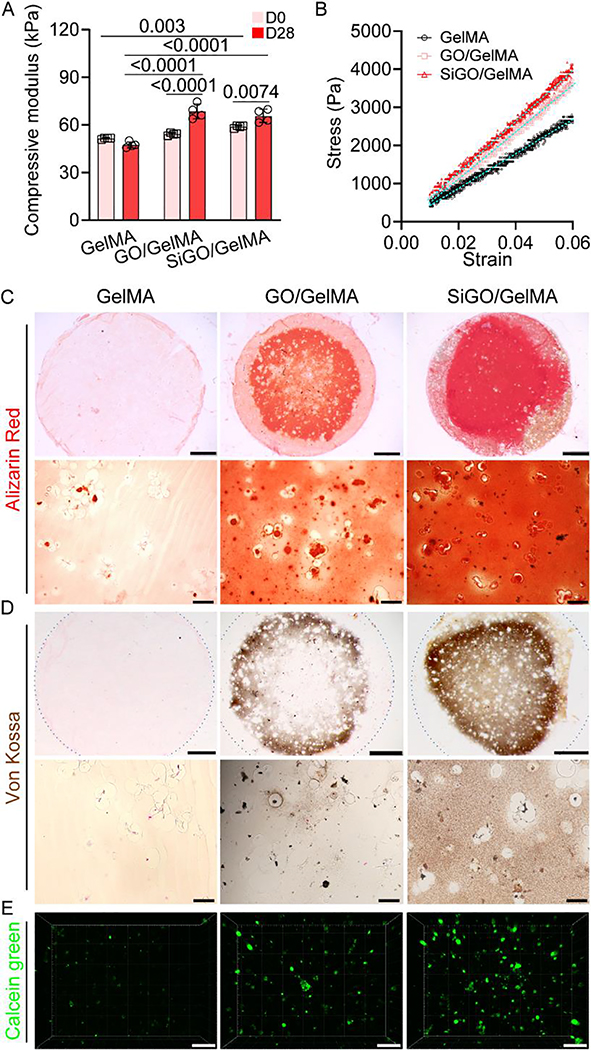
Fig. 3. Assessment of mechanical property and mineralization.
(A) The compressive modulus of cell-laden scaffolds before and after 28 days of culture in OM. N = 4, data analyzed by unpaired t-test. P values were labeled. (B) Representative stress-strain curves of the D28 samples. (C, D) Alizarin Red staining (C) and von Kossa staining (D) images showing mineralization in the constructs after 28 days of culture in OM. The dotted circles in D depicts the outline of the entire section. Scale bars = 1 mm (top row) or 50 μm (bottom row). (E) Confocal images of calcein green-stained calcium minerals in the D28 samples. Scale bar = 100 μm.
Alizarin Red, Von Kossa, and calcein staining showed markedly more mineralization in both nanocomposite scaffolds, while little to no positive staining was seen for the GelMA group (Fig. 3C–E, Supplementary Videos 1–3). Interestingly, the highest calcium phosphate mineral content and most homogeneous mineralization across the construct was observed in the SiGO/GelMA group (Figure S4). Of note, no positive staining was observed in the constructs cultured in GM (Figure S5), or in cell-free constructs cultured in OM (Figure S6). These results indicated that the mineralization observed was produced by the differentiated hMSCs in the construct and not caused by direct absorption by the nanomaterials.
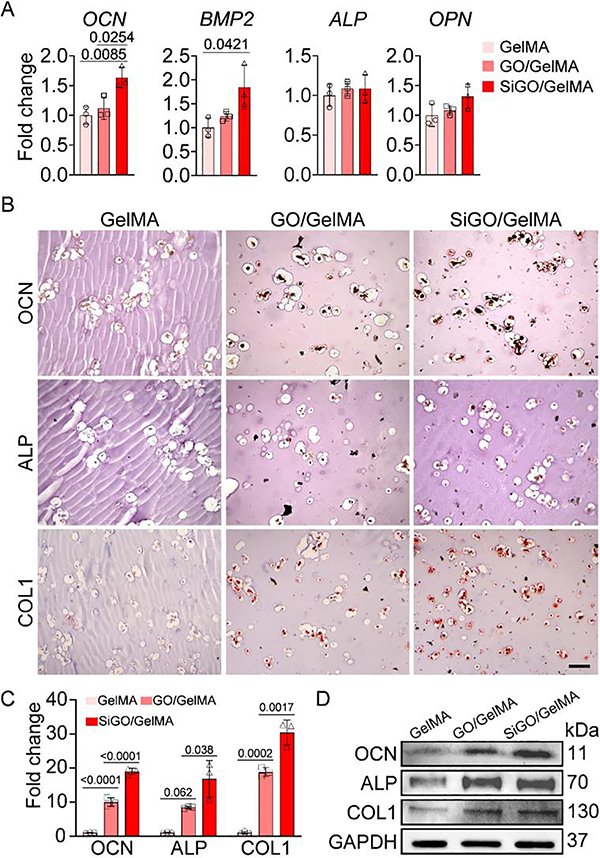
The RT-qPCR results showed that the incorporation of SiGO in GelMA upregulated the expression of OCN and BMP2, two major osteogenic marker genes (Fig. 4A). In the IHC assay, significantly higher levels of OCN, ALP, and collagen type I (COL1) proteins were observed in the two nanocomposites than GelMA. Moreover, these three proteins were present in the largest amount in SiGO/GelMA group (Fig. 4B, C). Western blot was employed to further assess the relative quantities of these osteogenic markers in the samples (Fig. 4D, Figure S7). The results confirmed that the encapsulation of nanosheets significantly promoted the deposition of osteogenesis-relevant proteins.
Fig. 4. Examination osteogenic marker expression after 28 days of osteogenic culture.
(A) Expression of representative osteogenic marker genes analyzed by RT-qPCR. N = 3; analyzed by one-way ANOVA. (B) IHC images showing the presence of OCN, ALP, and COL1 proteins. Scale bar = 100 μm. (C) Quantitation of positive staining in IHC images in (B). The staining intensity was normalized to that of GelMA (set as 1). N = 3; analyzed by one-way ANOVA. P values were labeled. (D) Western blot assessment of OCN, ALP, and COL1 protein levels. GAPDH was used as the loading control.
3.4. GO- and SiGO-functionalized hydrogels enhance production, retention and signaling activity of endogenous BMP2
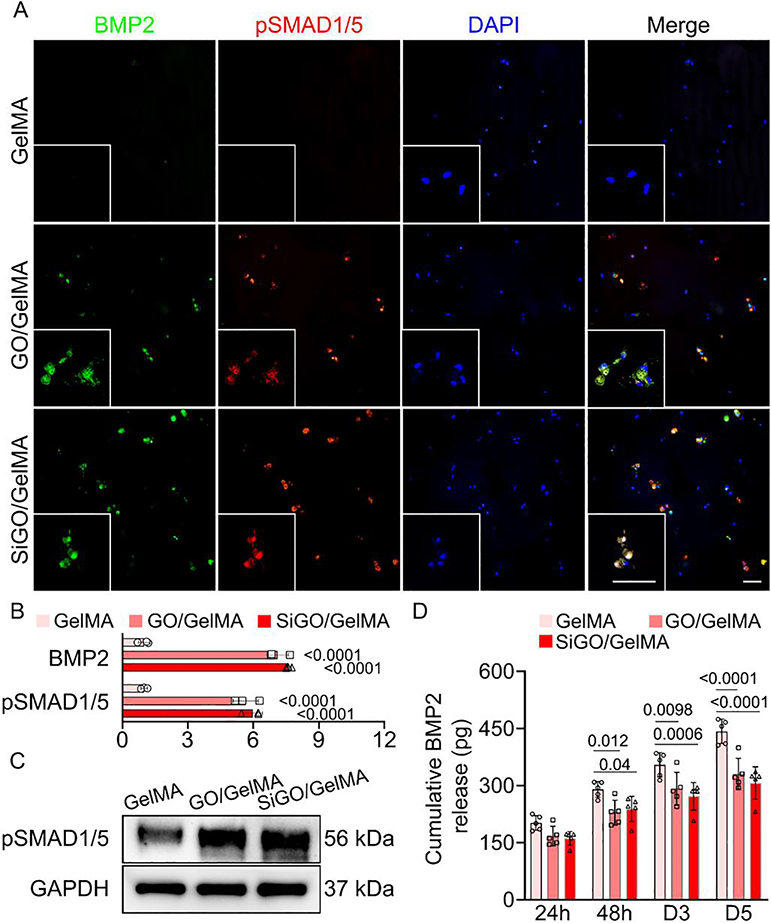
Next, we conducted mechanistic analysis of the osteoinductive potential of GO. Given the proven importance of the BMP-SMAD1/5 axis in osteogenesis [44], we first examined the expression levels of BMP2, an extensively studied osteogenic growth factor. Immunofluorescence images revealed the ubiquitous presence of BMP2 in SiGO- and GO-containing samples, while little positive staining was seen in the GelMA samples (Fig. 5A & B). In addition, a similar trend was observed in terms of expression of pSMAD1/5, downstream mediators in BMP signaling (Fig. 5A–C).
Fig. 5. Influence of GO and SiGO encapsulation on BMP2 production, retention, and signaling activity.
(A) Immunofluorescence (IF) images of sections co-stained with antibodies against BMP2 and pSMAD1/5. Cell nuclei were visualized with DAPI staining. Scale bars = 50 μm. (B) Quantitation of BMP2 and pSMAD1/5 based on IF staining. The fluorescence intensity was normalized to that of GelMA (set as 1). N = 3; analyzed by one-way ANOVA. P values indicate statistical difference when compared to the GelMA group. (C) Western blot analysis of pSMAD1/5 in the samples after 28 days of osteogenic culture. (D) Cumulative release of recombinant human BMP2 preloaded in cell-free scaffolds over 5 days. N = 5; analyzed by one-way ANOVA. P values were labeled.
To examine if the higher levels of BMPs associated with the nanocomposites were due to the capacity of GO and SiGO to bind BMPs, recombinant human BMP2 was loaded as a representative BMP ligand in cell-free GelMA or the two nanocomposites for a release test. At each tested time pointed, more BMP2 was released from GelMA than the two nanocomposites (Fig. 5D), indicating the capacity of nanosheets in retaining BMP2. In addition, we observed enriched BMP2 in areas of SiGO conglomeration in the cell-laden constructs (Figure S8), further supporting the BMP adsorption capability of the nanosheets. It is noteworthy that the nanosheets did not non-specifically adsorb secondary antibodies (Figure S9), confirming that the high staining intensity seen around the nanosheets in BMP2 immunofluorescence was because of the presence of BMP2 protein instead of being caused by non-specifically bound secondary antibodies.
BMP7, another BMP ligand widely known to promote osteogenesis through the BMP-SMAD1/5 axis, was also co-stained with pSMAD1/5 by IF (Figure S10). A similar trend was observed to that seen for the BMP2- pSMAD1/5 IF staining shown in Fig. 5A.
3.5. Inhibition of BMP signaling diminishes the osteoinductive potential of GO and SiGO nanosheets
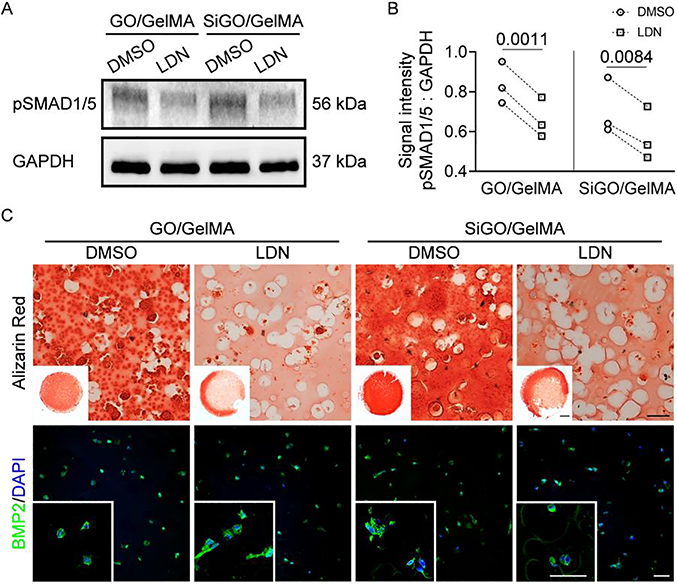
LDN blocks BMP-induced SMAD1/5 phosphorylation through inhibiting type I BMP receptors [39, 40]. After 7 days of LDN treatment, the protein levels of pSMAD1/5 were significantly lower in GO/GelMA and SiGO/GelMA than in the corresponding DMSO-treated controls (Fig. 6A & B). After 28 days of LDN treatment, both GO/GelMA and SiGO/GelMA displayed significantly less mineralization than the corresponding DMSO-treated control samples, as shown by Alizarin Red staining (Fig. 6C). In particular, mineralization was almost abolished at the center of the constructs (Fig. 6C insets). At the same time, BMP2 was ubiquitously detected in all samples and no obvious difference was observed between DMSO- and LDN-treated groups (Fig. 6C), suggesting that treatment with LDN did not impair the nanosheets’ capacity of inducing BMP2 production or retention.
Fig. 6. Effect of inhibiting BMP signaling pathway on bone formation in hMSCs-laden GO/GelMA and SiGO/GelMA hydrogels.
(A) Western blot analysis of pSMAD1/5 levels in samples treated with DMSO vehicle control or LDN for 7 days. (B) Quantitative analysis of Western blots. N = 3; analyzed by paired t-test. P values were labeled. (C) Alizarin Red staining and IF of GO/GelMA and SiGO/GelMA samples after 28 days of culture in osteogenic medium supplemented with 0.5 μM LDN or DMSO vehicle. Scale bar = 50 μm; Insets: scale bar = 1 mm for Alizarin Red and 50 μm for IF.
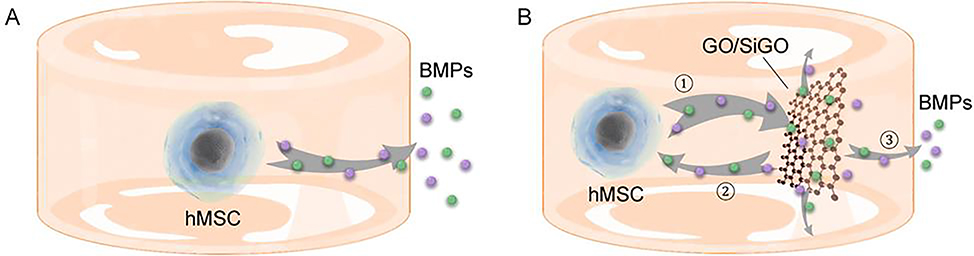
Based on these findings, we proposed a “nano-reservoir” mechanism for the osteogenesis-enhancing activity of the GO-based nanosheets on hMSCs (Fig. 7). The moderate binding affinity of BMPs to the nanosheets enables adsorption and release of cell-produced, endogenous BMPs, establishing a dynamic deposit—release process and reducing the loss of BMPs to the culture medium. The released BMPs could partly bind the BMP ligands of adjacent cells, proving a positive “feedback loop” to enhance osteogenesis.
Fig. 7. GO and SiGO nanosheets act as nanoscale “reservoirs” of endogenous BMPs to promote hMSCs osteogenesis.
(A) Endogenous BMPs produced by the cells diffuse through the hydrogel into the culture medium. (B) The GO or SiGO nanosheets adsorb and sequester BMP molecules, likely with moderate affinity but with high capacity, and act as “nano-reservoirs” of BMPs (process ①). The deposited BMPs can be released, partly to bind BMP ligands on the cell membrane (process ②), establishing a positive “feedback loop”, and partly to diffuse into the culture medium (process ③).
3.6. Incorporation of GO-based nanosheets leads to accelerated bone formation in vivo
The enhanced hMSC osteogenesis activity seen in the nanosheet-containing constructs prompted an examination of the ability of the constructs to form bone in vivo. This was evaluated in a mouse subcutaneous implantation model. The timeline of the in vivo experiment is shown in Fig. 8A. The cell-laden scaffolds were implanted following 21 days of in vitro culture in OM, when no bone formation was detected by μCT (Figure S11A, B). Prior to implantation, Alizarin Red staining showed no positive staining for GelMA, mostly mineral deposition in the immediate surrounding area of the cells in GO/GelMA, and ubiquitous mineralization both surrounding the cells and in acellular areas in SiGO/GelMA (Figure S11C). After 21 days of culture in OM, the calcium minerals in GO/GelMA and SiGO/GelMA, albeit identifiable in Alizarin Red staining, were not sufficiently dense to be recognized as “bone” in μCT. Four weeks after implantation of the cell-laden constructs, μCT revealed significantly more bone formation in the nanocomposite-containing implants than the GelMA control group (Fig. 8B). Specifically, incorporation of GO/GelMA and SiGO/GelMA resulted in a 108±27-fold and 385±65-fold increase in bone volume, respectively (Fig. 8C). In addition, the bone mineral density (BMD) in the nanocomposites was found to be significantly higher than in the GelMA scaffolds (Fig. 8C). Alizarin Red histological staining also confirmed the significantly higher level of mineralization in the nanocomposites than in GelMA (Fig. 8D). Furthermore, H&E staining was carried out to examine the tissue microstructure (Figure S12). While the GelMA sections were characterized by smoothness and uniformity, the extracellular matrix of GO/GelMA and SiGO/GelMA scaffolds appeared to be enriched with newly deposited fibrils and mineral particulates, which better resembles the morphology of developing bone. Comparison of the Alizarin Red staining intensities observed prior to and post-implantation reveals that 4 weeks of subcutaneous implantation induced mineralization around the cells in GelMA scaffolds, caused mineral deposition to also occur in cell-free areas in GO/GelMA, and promoted uniform and robust mineralization in SiGO/GelMA (Fig. 8D, Figure S11). The IF images shown in Fig. 8E indicated higher OCN and ALP levels in the GO- and SiGO-functionalized scaffolds, implying elevated osteogenesis. Notably, a substantially higher level of ALP expression was observed in the SiGO/GelMA group, signifying the robust osteoinductive potential of SiGO.
Fig. 8. Evaluation of bone formation in vivo.
(A) Timeline of the in vivo subcutaneous implantation experiment. (B) Representative μCT images showing bone formation in the implanted constructs on day 28 post-surgery. Scale bar = 1 mm. (C) Quantitative analyses of bone volume and bone mineral density (BMD). N = 3; analyzed by one-way-ANOVA. P values were labeled. (D) Alizarin Red staining and (E) IF analysis of the 28 day implants. Scale bars = 50 μm.
4. Discussion
Leveraging functional nanomaterials and their interactions with hMSCs represents a promising approach to growth factor-free bone tissue engineering. The results of in vitro and in vivo tests in this study show that matrix mineralization of 3D, hMSC-laden GelMA constructs was significantly enhanced with the incorporation of GO and SiGO nanosheets. Mechanistically, the introduction of the GO-based nanosheets increased the production, retention and function of endogenous, cell-secreted BMPs, enabling dynamic deposition and release of BMPs and establishing a “positive feedback loop” that enhances the quality of osteogenesis.
The GO-based nanosheets employed in this study displayed no cytotoxicity on hMSCs (Fig. 2C–E). While GO and silica nanoparticles have both been reported to induce cell death at high concentrations, such adverse effects can be mitigated or even abolished by, among other methods, lowing their concentrations and surface modification with biopolymers such as chitosan [45, 46]. The LIVE/DEAD assay results indeed showed that the GO and SiGO loadings used in this study supported high cell viability (Fig. 2C–E), which agrees well with results from previous studies on GO/GelMA composites [26, 47]. GelMA could also act as a biocompatible surfactant on the nanosheets to enhance their cytocompatibility [26].
The incorporation of the nanosheets in GelMA was found to increase the metabolic activities of the 2D- and 3D-cultured cells (Fig. 2F & G). Previous studies reported that a unique nanotopography was introduced upon the addition of GO and SiGO nanosheets in GelMA, possibly altering cell metabolism and directing stem cell fate toward osteogenesis [48, 49]. Interestingly, osteogenic differentiation of stem cells has been reported to be characterized by lower levels of unsaturated metabolome and increased general metabolism [50].
Compared to unmodified GO, the use of SiGO nanosheets has additional benefits. SiGO incorporation increased the compressive modulus of GelMA hydrogel (Fig. 3A), which possibly promoted osteogenic marker expression via mechanotransduction [51]. Moreover, coating GO with a silica layer introduced silicon, a trace element that has been shown to play key roles in bone development and turnover [52]. Silicon deficiency has been associated with abnormal bone formation in chicks [53], and silicon supplementation resulted in higher water content and biochemical changes in matrix collagen and minerals in bone [54]. These discoveries have motivated biomaterials researchers to incorporate silicon in various bone scaffolds and substitutes. In fact, the discovery of bone-bonding, bioactive silicate bioglasses in the 1960s greatly catalyzed the field of bioactive materials [55]. Silicon substitution in hydroxyapatite, a bioceramic common to the components of bone mineral, has also been actively pursued [56]. Recently, 2D nanosilicate platelets have emerged as an increasingly popular biomaterial for growth factor-free bone tissue engineering [8, 9]. Our findings that GO and the silica coating synergistically promoted osteogenesis both in vitro and in vivo further support the potential of a silicon adjunct for the enhancement of bone formation induced by nanocomposites.
Compared to the application of high amounts of exogenous BMPs, leveraging the endogenous BMPs secreted by seeded cells represents a convenient, less costly, more natural, and safer approach. In our study, the incorporation of GO and SiGO nanoplatelets into 3D GelMA scaffolds enhanced the adsorption and retention of endogenous BMPs, which subsequently was released in a sustained manner to promote hMSC osteogenic differentiation. As the differentiated osteoblasts presumably would produce a higher level of BMPs, a functional “positive feedback loop” would result. The establishment of this “feedback loop” likely depends on two key factors. First, the high specific surface area of the nanosheets [35] led to an increased BMP-loading capacity of the 3D constructs and enabled the deposition of a higher amount of BMPs. Second, the binding affinity of BMPs to the nanosheets was moderate, thus allowing both adsorption and release of BMPs. Such a moderate binding affinity has been observed in previous studies by our group and others [18, 19, 57]. Therefore, the 2D nanosheets acted as nanosized “BMP depots” to enhance hMSC osteogenic differentiation and matrix mineralization (Fig. 7). Although it appears in the IF images (Fig. 5A and Figure S10) that BMP2 showed stronger staining than BMP7, the relative amount of these two proteins needs to be quantified by other methods as IF staining is qualitative. This represents an interesting area to explore in our future studies. In addition, it is worth mentioning that the hMSC-secreted BMPs and other growth factors may be released to the surrounding tissues, possibly resulting in a paracrine effect on the in vivo bone formation. In our previous study, BMP-2-transduced hMSCs was used to engineer bone tissues [58], where the released BMP2 from the hMSCs induced bone formation by host cells in mice.
Compared to the gene expression data from RT-qPCR, osteogenic marker proteins showed more consistent trends in upregulated osteogenesis in the nanocomposites (Fig. 4, Figure S7). For example, ALP expression in GO/GelMA and SiGO/GelMA was significantly higher than in GelMA at the protein level, although ALP gene expression appeared similar for all three groups. It suggests that the transcripts for ALP might have been translated at higher levels in the nanocomposite scaffolds, possibly because of differences in post-transcriptional regulation mechanisms. In addition, considering the wide range of biomolecules that can be adsorbed by GO-based nanosheets, the hMSC-synthesized ALP was likely to be adsorbed by the nanosheets and better retained in the nanocomposites, leading to significantly higher ALP levels detected by IHC and western blot. The IHC and western blot results consistently support the upregulated expression of osteogenic marker proteins in GO/GelMA and SiGO/GelMA scaffolds, confirming the osteoinductive roles of the added nanomaterials.
To estimate the extent to which BMP ligands alone could contribute to the observed osteogenesis, we cultured hMSC-laden GelMA, prepared from the same cells and hydrogel as described above but in the absence of GO-based nanosheets, in OM supplemented with exogenous BMP2 or BMP7 and assessed the level of osteogenesis. Only moderate mineralization was observed in the GelMA constructs (Figure S13), indicating that supplementing exogenous BMPs was much less effective in inducing osteogenic differentiation of hMSCs, in comparison to GelMA containing GO-based nanosheets. These data highlight the functional importance of the “positive feedback loop” of BMP signaling, which was realized only in the nanosheet-incorporated scaffolds, in inducing robust osteogenesis of MSCs.
Considering the protein adsorption capability of negatively charged GO sheets, it was important to assess whether the nanosheets could in fact be sequestering the BMPs that may be present in FBS, a component of the OM used, and thus contribute to the osteogenesis of hMSCs. This possibility was dispelled by the absence of immunopositive staining observed in the acellular constructs cultured in OM (Figure S9), indicating that the positive BMP signals detected in the cell-seeded constructs indeed represented BMPs produced by the encapsulated cells. BMP ligands, including BMP2 and BMP7, signal by binding to cell membrane BMP receptors, leading to the phosphorylation of receptor-activated SMAD1/5 [59]. These activated SMADs then associate with the common mediator, SMAD 4, and form a SMAD complex that translocates to the cell nucleus and regulates osteogenic gene expression. The functional involvement of BMP signaling in hMSC differentiation was demonstrated by the significantly reduced mineralization observed when the cultures were treated with the BMP signaling inhibitor, LDN (Fig. 6C). However, as GO and SiGO nanosheets have strong adsorptive capacity, it remains possible that other growth factors and biomolecules are also sequestered and participate in the hMSC-GO and hMSC-SiGO interactions [21, 60]. It is worth mentioning that during IF staining, the adsorption of secondary antibodies to the nanosheets could only occur in a short period. Considering the moderate binding affinity of the nanosheets with biomolecules, the secondary antibodies were likely to be washed off by PBS during the extensive rinsing steps in immunostaining. Hence, no non-specific binding of the secondary antibody was observed in the IF images (Figure S9).
In terms of in vivo bone formation, the μCT results from this study suggest that SiGO incorporation was especially efficacious (Fig. 8B, C). This can possibly be ascribed to the additional beneficial effects of silicon on cellular and tissue components, which are absent in the in vitro cultures. Previous studies have found that silicon ions stimulate vascular endothelial growth factor expression in fibroblasts and endothelial cells, which in turn enhances osteogenesis [61]. Silicon was also reported to inhibit osteoclast formation [62, 63], and the SiGO-induced upregulation of BMP2 may also modulate macrophage behaviors to favor in vivo bone formation [64].
It is worth mentioning that while the enhanced BMP-SMAD signaling was achieved in the hMSC interactions with GO and SiGO, this effect is expected to be applicable to other cell types as well, such as osteoblast precursors and induced pluripotent stem cells, and other material systems, including GO derivatives with different functionalities and other 2D nanoplatelets [65, 66]. Our findings should shed light on the biomolecular structural mechanisms regulating osteogenesis in the context of a vast array of cell-laden nanocomposites.
In future studies, we will investigate additional BMP ligands, other than BMP2 and BMP7, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the nature of BMP signaling responsible for the robust osteogenesis in the nanocomposites. The involvement of other bioactive factors will also be explored. Finally, although subcutaneous implantation served as a satisfactory initial test of the nanocomposites’ bone forming capability, evaluating the scaffolds in a bone defect can provide a more powerful and clinically relevant assessment of their effectiveness for bone repair applications. Thus, in vivo bone defect animal models will be applied to evaluate the effectiveness of the nanocomposite scaffolds for bone repair [8, 67].
5. Conclusions
The incorporation of GO and SiGO nanosheets in 3D GelMA scaffolds markedly enhanced osteogenesis of encapsulated hMSCs both in vitro and in vivo. These 2D nanomaterials acted as “BMP reservoirs” that enabled effective adsorption and release of endogenous BMP2 and BMP7, which together acted to enhance osteogenesis accompanied by high activation of SMAD1/5. In addition, the beneficial osteoinductive effects of GO was effectively amplified by surface functionalization with a silica coating, leading to the formation of remarkably larger bone volumes in a mouse subcutaneous implantation model. Knowledge gained from studying the interactions between BMP and GO nanomaterials should shed light on the mechanism(s) that underly various cell–nanomaterial interactions at the biomolecular level in 3D, cell-laden nanocomposite scaffolds.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
Dr. Paul Manner (University of Washington) is gratefully acknowledged for providing the human tissue samples. We thank Dr. Jian Tan for isolating the human hMSCs, and Dr. Shuguang Bi for technical assistance with material preparation. This research was supported by funding from the National Institutes of Health (UG3/UH3TR002136) and Department of Orthopaedic Surgery at the University of Pittsburgh (to HL). The Center for Biological Imaging (CBI) at University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine is acknowledged for supporting the confocal imaging (Grants 1S10RR028478-01 & 1S10OD019973-01).
Footnotes
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Declaration of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Data availability
The authors declare that all data supporting the findings of this study are available from the authors upon reasonable request.
References
- [1].Acevedo C, Stadelmann VA, Pioletti DP, Alliston T, Ritchie RO, Fatigue as the missing link between bone fragility and fracture, Nat. Biomed. Eng 2 (2018) 62–71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [2].Laurencin C, Khan Y, El-Amin SF, Bone graft substitutes, Expert Rev. Med. Devices 3 (2006) 49–57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [3].Li JJ, Ebied M, Xu J, Zreiqat H, Current approaches to bone tissue engineering: the interface between biology and engineering, Adv. Healthc. Mater 7 (2018) 1701061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [4].Lin H, Sohn J, Shen H, Langhans MT, Tuan RS, Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: aging and tissue engineering applications to enhance bone healing, Biomaterials 203 (2019) 96–110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [5].Sun K, Lin H, Tang Y, Xiang S, Xue J, et al. , Injectable BMP-2 gene-activated scaffold for the repair of cranial bone defect in mice, Stem Cells Transl. Med. 9 (2020) 1631–1642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [6].Bessa PC, Casal M, Reis RL, Bone morphogenetic proteins in tissue engineering: the road from laboratory to clinic, part II (BMP delivery), J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2 (2008) 81–96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [7].Skovrlj B, Koehler SM, Anderson PA, Qureshi SA, Hecht AC, et al. , Association between BMP-2 and carcinogenicity, Spine 40 (2015) 1862–1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [8].Cui Z-K, Kim S, Baljon JJ, Wu BM, Aghaloo T, et al. , Microporous methacrylated glycol chitosan-montmorillonite nanocomposite hydrogel for bone tissue engineering, Nat. Commun 10 (2019) 3523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [9].Xavier JR, Thakur T, Desai P, Jaiswal MK, Sears N, et al. , Bioactive nanoengineered hydrogels for bone tissue engineering: a growth-factor-free approach, ACS Nano 9 (2015) 3109–3118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [10].Lin H, Tang Y, Lozito TP, Oyster N, Kang RB, et al. , Projection stereolithographic fabrication of BMP-2 gene-activated matrix for bone tissue engineering, Sci. Rep 7 (2017) 11327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [11].Malek-Khatabi A, Javar HA, Dashtimoghadam E, Ansari S, Hasani-Sadrabadi MM, et al. , In situ bone tissue engineering using gene delivery nanocomplexes, Acta Biomater 108 (2020) 326–336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [12].Zhang L, Webster TJ, Nanotechnology and nanomaterials: promises for improved tissue regeneration, Nano Today 4 (2009) 66–80. [Google Scholar]
- [13].Alvarez MM, Aizenberg J, Analoui M, Andrews AM, Bisker G, et al. , Emerging Trends in Micro- and Nanoscale Technologies in Medicine: From Basic Discoveries to Translation, ACS Nano 11 (2017) 5195–5214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [14].Reznikov N, Bilton M, Lari L, Stevens MM, Kröger R, Fractal-like hierarchical organization of bone begins at the nanoscale, Science 360 (2018) eaao2189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [15].Goenka S, Sant V, Sant S, Graphene-based nanomaterials for drug delivery and tissue engineering, J. Control. Release 173 (2014) 75–88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [16].Lee C, Wei X, Kysar JW, Hone J, Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene, Science 321 (2008) 385–388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [17].Novoselov KS, Geim AK, Morozov S, Jiang D, Zhang Y, et al. , Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films, Science 306 (2004) 666–669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [18].Shen H, Lin H, Sun AX, Song S, Wang B, et al. , Acceleration of chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells by sustained growth factor release in 3D graphene oxide incorporated hydrogels, Acta Biomater 105 (2020) 44–55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [19].La W-G, Park S, Yoon H-H, Jeong G-J, Lee T-J, et al. , Delivery of a therapeutic protein for bone regeneration from a substrate coated with graphene oxide, Small 9 (2013) 4051–4060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [20].Nayak TR, Andersen H, Makam VS, Khaw C, Bae S, et al. , Graphene for controlled and accelerated osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells, ACS Nano 5 (2011) 4670–4678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [21].Lee WC, Lim CHYX, Shi H, Tang LAL, Wang Y, et al. , Origin of enhanced stem cell growth and differentiation on graphene and graphene oxide, ACS Nano 5 (2011) 7334–7341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [22].Lu J, Cheng C, He Y-S, Lyu C, Wang Y, et al. , Multilayered graphene hydrogel membranes for guided bone regeneration, Adv. Mater. 28 (2016) 4025–4031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [23].Lu J, He Y-S, Cheng C, Wang Y, Qiu L, et al. , Self-supporting graphene hydrogel film as an experimental platform to evaluate the potential of graphene for bone regeneration, Adv. Funct. Mater. 23 (2013) 3494–3502. [Google Scholar]
- [24].LeGeros RZ, Calcium phosphate-based osteoinductive materials, Chem. Rev. 108 (2008) 4742–4753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [25].Fujibayashi S, Neo M, Kim H-M, Kokubo T, Nakamura T, Osteoinduction of porous bioactive titanium metal, Biomaterials 25 (2004) 443–450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [26].Shin SR, Aghaei-Ghareh-Bolagh B, Dang TT, Topkaya SN, Gao X, et al. , Cell-laden microengineered and mechanically tunable hybrid hydrogels of gelatin and graphene oxide, Adv. Mater. 25 (2013) 6385–6391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [27].Shen H, Lin H, Sun AX, Song S, Zhang Z, et al. , Chondroinductive factor-free chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells in graphene oxide-incorporated hydrogels, J. Mater. Chem. B 6 (2018) 908–917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [28].Choe G, Oh S, Seok JM, Park SA, Lee JY, Graphene oxide/alginate composites as novel bioinks for three-dimensional mesenchymal stem cell printing and bone regeneration applications, Nanoscale 11 (2019) 23275–23285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [29].Noh M, Kim S-H, Kim J, Lee J-R, Jeong G-J, et al. , Graphene oxide reinforced hydrogels for osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells, RSC Adv 7 (2017) 20779–20788. [Google Scholar]
- [30].Thian ES, Huang J, Best SM, Barber ZH, Brooks RA, et al. , The response of osteoblasts to nanocrystalline silicon-substituted hydroxyapatite thin films, Biomaterials 27 (2006) 2692–2698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [31].Lin Z, Li Z, Li EN, Li X, Del Duke CJ, et al. , Osteochondral tissue chip derived from ipscs: modeling OA pathologies and testing drugs, Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 7 (2019) 411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [32].Pittenger MF, Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells, Science 284 (1999) 143–147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [33].Hummers WS, Offeman RE, Preparation of graphitic oxide, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80 (1958) 1339–1339. [Google Scholar]
- [34].Li Z, Tang X-Z, Zhu W, Thompson BC, Huang M, et al. , Single-step process toward achieving superhydrophobic reduced graphene oxide, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8 (2016) 10985–10994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [35].Li Z, Zhu W, Bi S, Li R, Hu H, et al. , Incorporating silica-coated graphene in bioceramic nanocomposites to simultaneously enhance mechanical and biological performance, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 108 (2020) 1016–1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [36].Lin H, Cheng AW-M, Alexander PG, Beck AM, Tuan RS, Cartilage tissue engineering application of injectable gelatin hydrogel with in situ visible-light-activated gelation capability in both air and aqueous solution, Tissue Eng. Part A 20 (2014) 2402–2411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [37].Cha C, Shin SR, Gao X, Annabi N, Dokmeci MR, et al. , Controlling Mechanical Properties of Cell-Laden Hydrogels by Covalent Incorporation of Graphene Oxide, Small 10 (2014) 514–523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [38].Yilgor P, Tuzlakoglu K, Reis RL, Hasirci N, Hasirci V, Incorporation of a sequential BMP-2/BMP-7 delivery system into chitosan-based scaffolds for bone tissue engineering, Biomaterials 30 (2009) 3551–3559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [39].Cuny GD, Yu PB, Laha JK, Xing X, Liu JF, et al. , Structure-activity relationship study of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling inhibitors, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 18 (2008) 4388–4392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [40].Williams E, Bullock AN, Structural basis for the potent and selective binding of LDN-212854 to the BMP receptor kinase ALK2, Bone 109 (2018) 251–258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [41].Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW, NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis, Nat. Methods 9 (2012) 671–675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [42].Serguienko A, Wang MY, Myklebost O, Real-time vital mineralization detection and quantification during in vitro osteoblast differentiation, Biol. Proced. Online 20 (2018) 14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [43].Kihara T, Oshima A, Hirose M, Ohgushi H, Three-dimensional visualization analysis of in vitro cultured bone fabricated by rat marrow mesenchymal stem cells, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 316 (2004) 943–948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [44].Hayrapetyan A, Jansen JA, van den Beucken JJ, Signaling pathways involved in osteogenesis and their application for bone regenerative medicine, Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 21 (2015) 75–87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [45].Liao K-H, Lin Y-S, Macosko CW, Haynes CL, Cytotoxicity of graphene oxide and graphene in human erythrocytes and skin fibroblasts, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 3 (2011) 2607–2615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [46].Chang J-S, Chang KLB, Hwang D-F, Kong Z-L, In vitro cytotoxicitiy of silica nanoparticles at high concentrations strongly depends on the metabolic activity type of the cell line, Environ. Sci. Technol. 41 (2007) 2064–2068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [47].Paul A, Hasan A, Kindi HA, Gaharwar AK, Rao VTS, et al. , Injectable graphene oxide/hydrogel-based angiogenic gene delivery system for vasculogenesis and cardiac repair, ACS Nano 8 (2014) 8050–8062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [48].Tsimbouri PM, McMurray RJ, Burgess KV, Alakpa EV, Reynolds PM, et al. , Using nanotopography and metabolomics to identify biochemical effectors of multipotency, ACS Nano 6 (2012) 10239–10249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [49].Qian W, Gong L, Cui X, Zhang Z, Bajpai A, et al. , Nanotopographic regulation of human mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9 (2017) 41794–41806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [50].Yanes O, Clark J, Wong DM, Patti GJ, Sánchez-Ruiz A, et al. , Metabolic oxidation regulates embryonic stem cell differentiation, Nat. Chem. Biol 6 (2010) 411–417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [51].Mao AS, Shin J-W, Mooney DJ, Effects of substrate stiffness and cell-cell contact on mesenchymal stem cell differentiation, Biomaterials 98 (2016) 184–191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [52].Henstock JR, Canham LT, Anderson SI, Silicon: The evolution of its use in biomaterials, Acta Biomater. 11 (2015) 17–26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [53].Carlisle EM, Silicon: An essential element for the chick, Science 178 (1972) 619–621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [54].Carlisle EM, In vivo requirement for silicon in articular cartilage and connective tissue formation in the chick, J. Nutr. 106 (1976) 478–484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [55].Jones JR, Review of bioactive glass: from Hench to hybrids, Acta Biomater 9 (2013) 4457–4486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [56].Thian ES, Huang J, Best SM, Barber ZH, Bonfield W, Silicon-substituted hydroxyapatite: the next generation of bioactive coatings, Mater. Sci. Eng. C 27 (2007) 251–256. [Google Scholar]
- [57].Lee WC, Lim CH, Kenry, Su C, Loh KP, et al. , Cell-assembled graphene biocomposite for enhanced chondrogenic differentiation, Small 11 (2015) 963–969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [58].Lin H, Tang Y, Lozito TP, Oyster N, Wang B, et al. , Efficient in vivo bone formation by BMP-2 engineered human mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in a projection stereolithographically fabricated hydrogel scaffold, Stem Cell. Res. Ther 10 (2019) 254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [59].Liu A, Niswander LA, Bone morphogenetic protein signalling and vertebrate nervous system development, Nat. Rev. Neurosci 6 (2005) 945–954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [60].Wei X-Q, Hao L-Y, Shao X-R, Zhang Q, Jia X-Q, et al. , Insight into the Interaction of Graphene Oxide with Serum Proteins and the Impact of the Degree of Reduction and Concentration, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7 (2015) 13367–13374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [61].Li H, Xue K, Kong N, Liu K, Chang J, Silicate bioceramics enhanced vascularization and osteogenesis through stimulating interactions between endothelia cells and bone marrow stromal cells, Biomaterials 35 (2014) 3803–3818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [62].Mladenović Ž, Johansson A, Willman B, Shahabi K, Björn E, et al. , Soluble silica inhibits osteoclast formation and bone resorption in vitro, Acta Biomater 10 (2014) 406–418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [63].Henstock J, Ruktanonchai U, Canham L, Anderson S, Porous silicon confers bioactivity to polycaprolactone composites in vitro, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 25 (2014) 1087–1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [64].Wei F, Zhou Y, Wang J, Liu C, Xiao Y, The immunomodulatory role of BMP-2 on macrophages to accelerate osteogenesis, Tissue Eng. Part A 24 (2018) 584–594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [65].Chen Y, Zheng Z, Zhou R, Zhang H, Chen C, et al. , Developing a strontium-releasing graphene oxide-/collagen-based organic–inorganic nanobiocomposite for large bone defect regeneration via MAPK signaling pathway, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11 (2019) 15986–15997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [66].Liu X, Miller AL, Park S, George MN, Waletzki BE, et al. , Two-dimensional black phosphorus and graphene oxide nanosheets synergistically enhance cell proliferation and osteogenesis on 3d printed scaffolds, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11 (2019) 23558–23572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [67].Jiao D, Zheng A, Liu Y, Zhang X, Wang X, et al. , Bidirectional differentiation of BMSCs induced by a biomimetic procallus based on a gelatin-reduced graphene oxide reinforced hydrogel for rapid bone regeneration, Bioactive Materials 6 (2021) 2011–2028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The authors declare that all data supporting the findings of this study are available from the authors upon reasonable request.