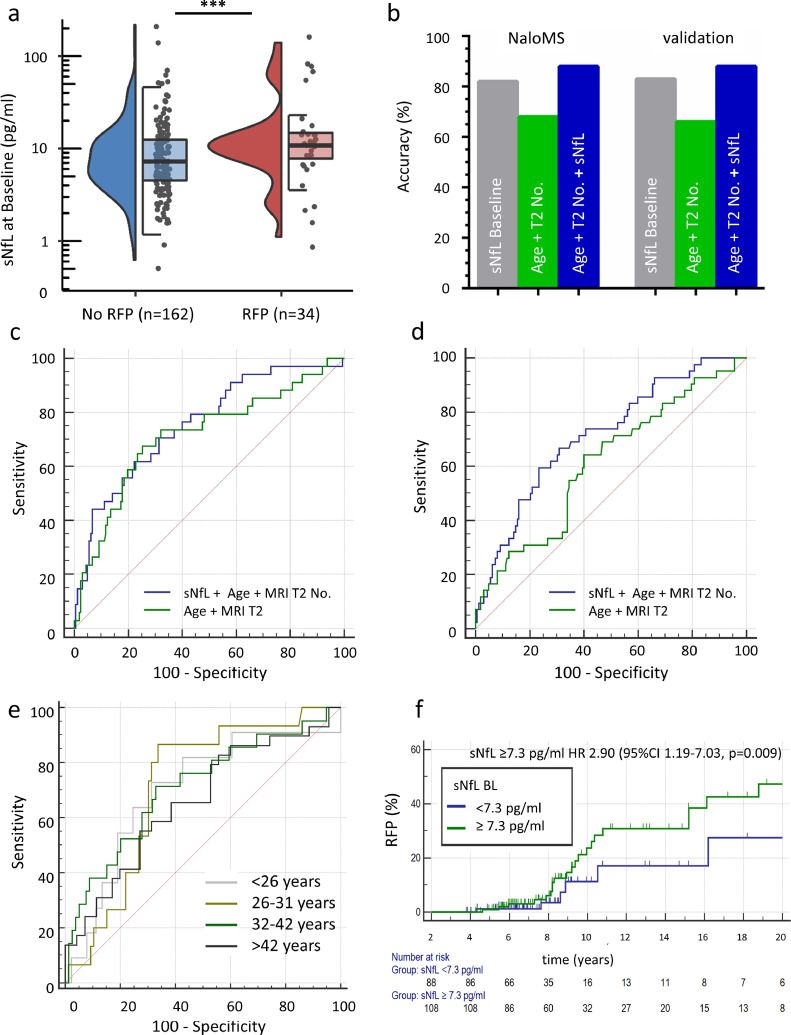
Fig. 2.
sNfL levels at baseline predict relapse-free disability progression in a prospective longitudinal study (NaloMS cohort)
a) Baseline NfL was increased in patients with relapse free EDSS-progression (RFP) (median (IQR) 10.8 (7.7-15.0) vs. 7.2 (4.5-12.5), p=0.017); data is displayed as a violin plot, left side: density of all data points, right side: median and IQR. b) Machine learning by support vector machine assessed the predictive accuracy of sNfL at Baseline for RFP under consideration of covariates (EDSS Baseline, Number of Gadolinium-enhancing lesions at Baseline, T2-hyperintense lesions at Baseline, Age at Baseline, Disease Duration and Relapses within the last 12 months prior to FU; grey bar). In addition, the predictive accuracy for RFP of a combination of Age + T2-hyperintense lesion number (green bar, without covariate adjustment) and a combination of Age + T2-hyperintense lesion number + sNfL at Baseline (blue bar) was similarly analyzed. c,d) Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC-AUC) for a combination of Age+T2-hyperintense lesions and additional inclusion of sNfL at Baseline in NaloMS (development cohort; c) and validation cohort (Düsseldorf, Essen; d). c) AUC increased from 0.714 (95%CI 0.645-0.776, green line) to 0.755 (95%CI 0.688-0.813, blue line) after additional consideration of sNfL within the NaloMS cohort (development). d) This finding could be confirmed within the validation cohort (Düsseldorf, Essen): AUC increased from 0.613 (95%CI 0.543-0.680) to 0.715 (95%CI 0.648-0.776) after inclusion of sNfL. e) Receiver operating characteristic curve in the combined NaloMS and validation cohort (Düsseldorf, Essen) with regard to prediction of RFP by sNfL at Baseline according to quartiles based on patient age at sampling (<26 years (grey line), 26-31 years (light green line), 32-42 years (dark green line), >42 years (black line)). f) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis for occurrence of RFP in patients with sNfL at baseline ≥7.3 pg/ml (green line) or <7.3 pg/ml (blue line), logrank test p=0.0135. Patients with sNfL ≥7.3 pg/ml at baseline suffer a 190% increased risk of experiencing RFP at follow-up (Hazard Ratio 2.90, 95%CI 1.19-7.03, p=0.009).