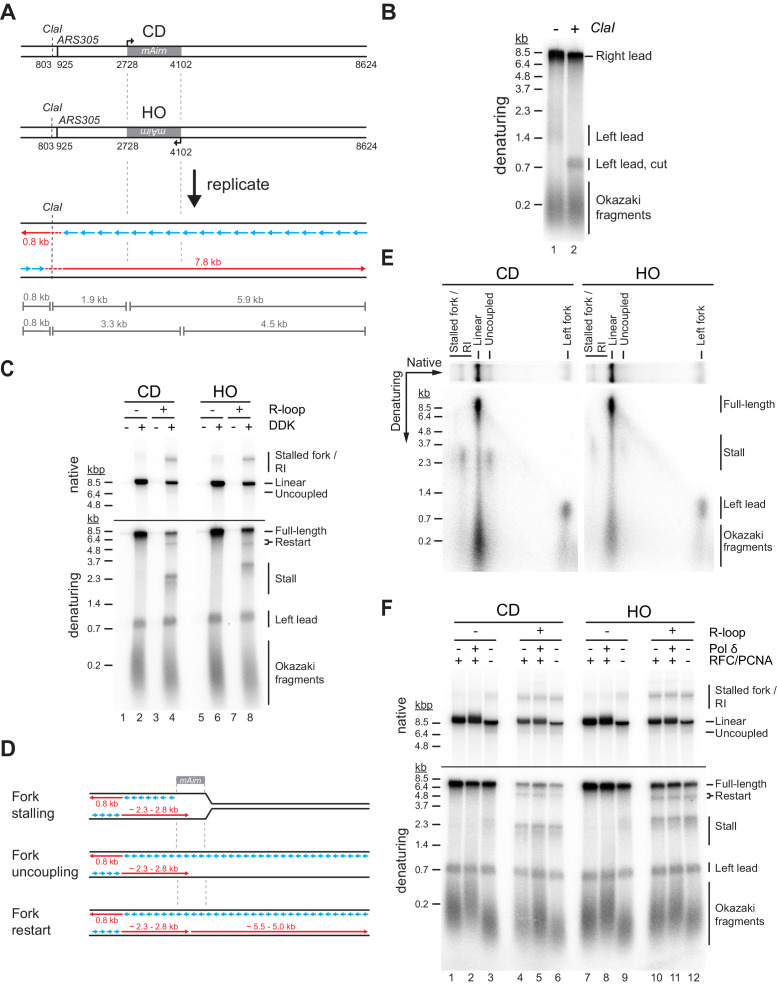
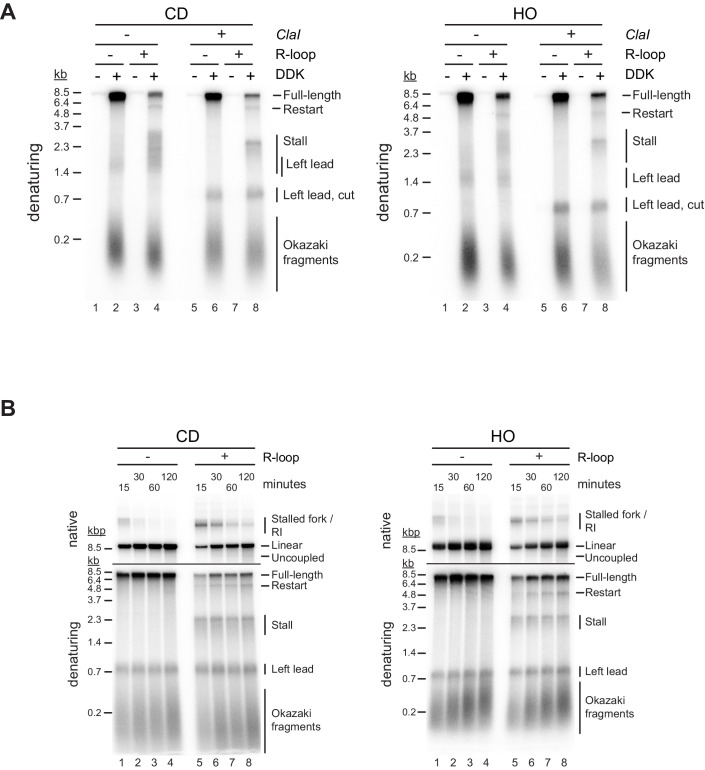
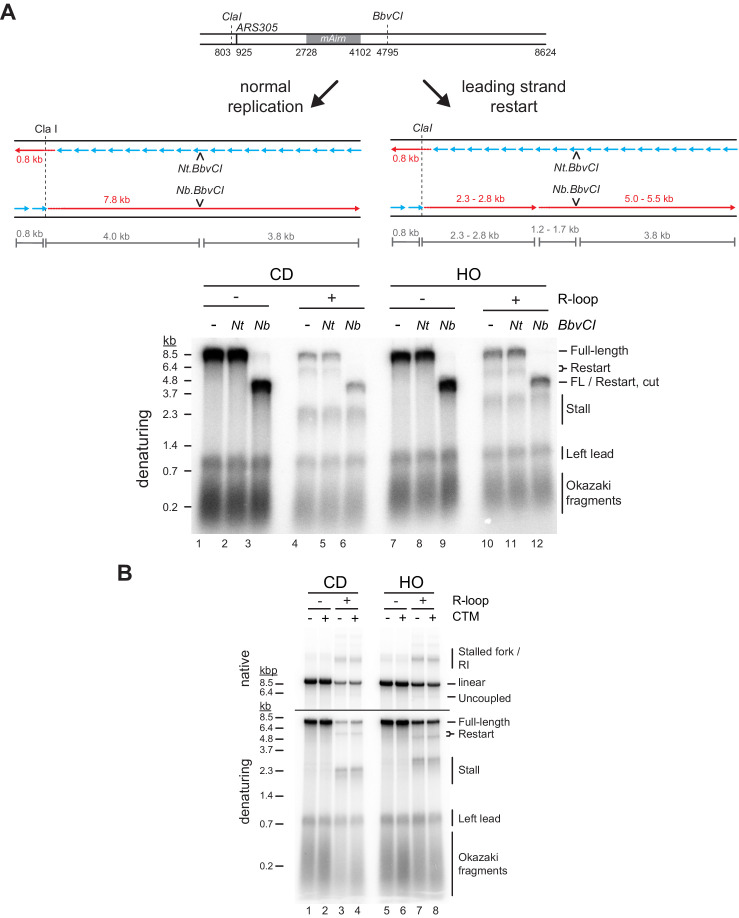
Figure 2. Both co-directional (CD) and head-on (HO) R-loops perturb normal fork progression.
(A) Schematic illustrating expected sizes of replication products. (B) Denaturing agarose gel analysis of replication products obtained on R-loop-free template. Left lead: Leftward leading strands; Right lead: Rightward leading strands. (C) Native (top) and denaturing (bottom) agarose gel analyses of replication products obtained on templates harboring Airn sequence in CD or HO orientation. Stall: Stalled rightward leading strands; Restart: Rightward leading strand restart product; Full-length: full-length rightward leading strand; RI: replication intermediates. (D) Schematic illustrating replication products observed in (C). (E) Two-dimensional gel analysis of replication products obtained in presence of R-loops (corresponding to lanes 4 and 8 in (C)). Products were digested with ClaI. (F) Replication products obtained in the absence or presence of RFC/PCNA or Pol δ.